How to make grounding for a gas boiler: requirements for a ground electrode and installation instructions
Installing a gas boiler will help solve the issue of heating, warm water and optimize the internal microclimate in your home at your discretion. But in order to avoid breakdowns and eliminate the risk of gas fire, the installation and further operation of such a powerful electrical appliance must be carried out in compliance with all rules. Do you agree?
We will tell you how to make grounding for a gas boiler in accordance with building codes and PUE recommendations. In our proposed article, the installation technology is analyzed in detail. Our advice on choosing materials and performing preliminary calculations will allow you to ground your equipment flawlessly.
The content of the article:
Why do you need to ground a gas boiler?
A mandatory element of any gas boiler is a metal casing, on the surface of which static charges are formed when the device is connected to the network.
And if you do not take care of the “escape routes” for electricity, at one unfavorable moment the entire electronic component of the device or its individual elements may fail. For example, a board or control system.
To prevent this from happening, the boiler is “secured” by grounding - a conductor that connects the electrical appliance to the ground electrode, and the latter directly to the ground.The earth has the ability to “absorb” electric current, so its environment will be a guarantee of safety against equipment failure due to voltage surges or short circuits in the network.
Grounding is necessary to:
- Reduce the explosion hazard of the device - static electricity often causes spontaneous combustion of devices powered by gas, and even under pressure.
- Eliminate the possibility of injury - the metal case sometimes “pierces”, and when touched, a person can feel an electric shock from a slight tingling sensation to a powerful charge, followed by death.
- Prevent automation breakdowns - gas boiler boards are sensitive to voltage surges, and replacing them will cost at least a third of the cost of the equipment itself.
In addition, a boiler operating without grounding will have a lot of questions from gas service inspectors, which can result in significant fines and forced shutdown of the device. Therefore, it is worth equipping a grounding loop in any case, because we are talking not only about economic nuances, but also about your safety.
Subtleties of the circuit device
The grounding system can be natural or artificial. The first option includes structures made of metal or reinforced concrete that are in direct contact with the ground.This could be the foundation of a building, a pipeline or other underground utilities.
But for gas boiler natural grounding requires the presence of at least two contacts with individual parts of the housing, and sewerage, heating and gas pipes are excluded in this case. Therefore, during installation, an artificial system is often used, the organization of which we will consider.
What material to choose for grounding conductors?
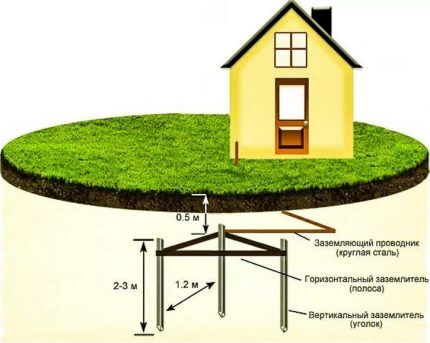
For artificial grounding, rods or pipes become conductor-electrodes, which are connected to each other by metal strips. They are installed vertically in the soil to ensure operation of the system even in winter, when the top layer of the earth freezes.
An important condition is that metal elements should not be protected from corrosion by insulating material.
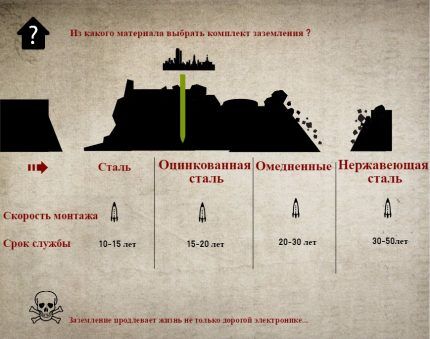
You can also find ready-made kits for a grounding system on sale, which consist of steel rods (usually copper-plated) and special pointed tips for soil of varying densities.
The kit also includes an anti-corrosion agent for treating the system before installation and connecting elements - brass couplings, clamps. The main advantage of this solution is that the circuit can be assembled without welding and lengthy preparation.

To assemble a system from scrap materials, you should consider several important nuances:
- Metal structures intended for installation in the ground can be made from a profile pipe, an I-beam, a channel, or an angle.
- The metal of the grounding conductor must be protected from destruction by galvanizing, copper plating or, as a last resort, anti-corrosion paste.
- The cross-sectional area of the wire connecting the zero phase of the shield to the ground loop depends on the type of metal from which it is made. For copper, the optimal value is 1 cm2, for steel - 7.5 cm2, and for aluminum - 16 cm2.
- The grounding resistance for sandy soil should not exceed 50 Ohms, for clay soil - a maximum of 10 Ohms.
- Electrode materials must be selected taking into account the circuit resistance. The best option is two-inch pipes or corners with a length of 2 m and a cross-sectional area of 5 cm2.
- The grounding bus is made of copper or steel strip (aluminum is prohibited for this case).
Compliance with these requirements and correctly performed installation of a grounding loop will help eliminate claims from gas service inspectors, regardless of whether you used a ready-made modular system or assembled it yourself.
Calculation of circuit parameters
The list of requirements for grounding arrangement contains several indicators, the algorithm for obtaining which may be incomprehensible to a beginner in the electrical business - for example, exactly how many electrodes are required for the correct operation of the system or how to measure the resistance of the circuit. Let's try to clarify the basic principles for determining these parameters.

Grounding is carried out after gas boiler installation in a country house. The physical parameters of the grounding loop are selected mainly experimentally. This practical method is suitable for those who are afraid of getting bogged down in complex theoretical calculations.
The algorithm for performing the work is as follows:
- Let's take as a basis a contour in the form of an isosceles triangle of three metal rods 3 meters long.
- We connect the conductors.
- We take an ohmmeter (a device for measuring resistance) and measure the indicators for the circuit. The ideal value is 4 ohms.
- If the result obtained significantly exceeds the optimal value, we add another element to the circuit and check the resistance again. We continue until we get the ideal value or at least the maximum permissible value for the boiler circuit of 10 ohms.
But you can determine the required number of electrodes using formulas, choosing the appropriate options for your case.

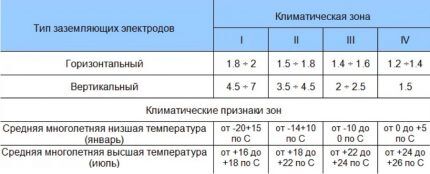
In the formula you need to substitute the average value of resistivity, depending on the type of soil in which the ground electrode will be located:
- wet sand – 500 Ohm*m;
- hard sandy loam – 300 Ohm*m;
- clay-sand mixture – 150 Ohm*m;
- loam – 100 Ohm*m;
- semi-solid clay and chernozem – 60 Ohm*m;
- garden soil – 40 Ohm*m;
- refractory loam – 30 Ohm*m;
- peat – 25 Ohm*m;
- plastic clay and salt marsh – 20 Ohm*m.
Stone and rocky soil are least suitable for installing a ground loop. In this case, an artificial embankment will have to be erected.

The value of the seasonal climatic coefficient of soil resistance depends on the area where your home is located. They are conventionally divided into 4 groups.
There are also more complex algorithms for accurately determining the parameters of the electrodes and even special programs for their calculations.But for the gas boiler to operate correctly, it will be enough to follow the general recommendations for arranging a standard grounding loop.
The use of copper-plated steel grounding conductors allows the construction of systems in soils with any physical and mechanical properties:
Installation of a grounding system for the boiler
To install the circuit, you will need to allocate a free space, which is located at a distance of no closer than one, but no further than 5 meters from the house foundation.
This area cannot be used in the future for the construction of various extensions, planting work, and in general it is unsafe for a person to be on it, because if triggered, it can be fatal. Therefore, it is worth enclosing the contour with a border and decorating the place with some kind of stone composition or decorating it with a garden sculpture.
We bring to your attention an article on how to do Do-it-yourself grounding in the garage.
Design and preparatory work
To ground a gas boiler, first a model of the future circuit is drawn on a selected area. The most commonly used scheme involves placing grounding conductors on the sides of an isosceles triangle.
But the contour can also be in the form of a line, square or polygon - it all depends on the estimated number of electrodes and the location of the building itself.
To assemble a homemade structure you will need the following tools:
- welding machine for connecting metal elements of the system;
- grinder for cutting and sharpening pipes or rods;
- a hammer drill or drill for installing a grounding cable into the house.
You also need to prepare a digging tool. The minimum set that the owners of a private house will probably have in stock is a bayonet shovel and a heavy sledgehammer. But if the site has hard soil, it is better to get a hole drill or a motor drill, which will greatly facilitate the “deep” stage of the work.
Installation and connection of the circuit
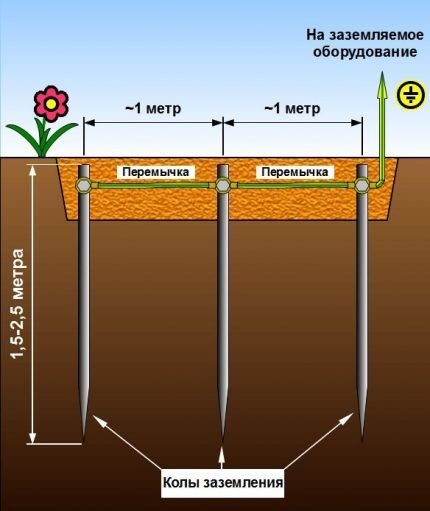
Now let's look step by step at how to make a triangular-shaped circuit for grounding a gas boiler. First you need to dig trenches along the lines of a pre-drawn layout. The optimal width of each groove is 35-40 cm, depth - 50-70 cm. From the vertex of the triangle closest to the house, a straight trench is drawn to the foundation.

Using a sledgehammer or a hole drill, electrodes - steel conductors from pipes or angles - are driven vertically along the vertices of the triangle. To make this process easier, you can first sharpen the bottom edge of each section with a grinder.
They need to be installed at such a depth that the distance from the bottom of the trench to the upper edge of the conductor is within 15-20 cm (that is, subsequently the entire structure will be covered with a layer of soil of 30-55 cm).
Next, the electrodes must be connected to each other. Lay a steel conductor with a cross-section of 4.8-5 cm2 or a strip 4 cm wide and at least 4 mm thick along the trenches dug along the sides of the triangle.
The entire procedure for installing a grounding loop includes a number of standard steps:
Ready-made grounding kits can be connected with the bolts provided in the kit. And for homemade structures, the best solution is spot welding.
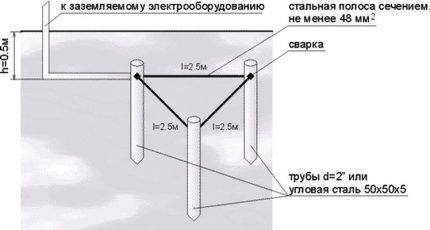
Then you need to weld a horizontal metal strip to the steel conductor, which will be led through the trench to the planned location for introducing grounding into the building itself. It rises above the level of the blind area by approximately 50 cm (a steel pin can also be used).
Now you need to install grounding into the house. To do this, use a hammer drill to make a hole in the wall through which a copper wire is threaded. An M8 bolt is welded to the strip. The copper wire is fixed at one end to a terminal on the grounding bus, and at the other end to a metal plate on the base.
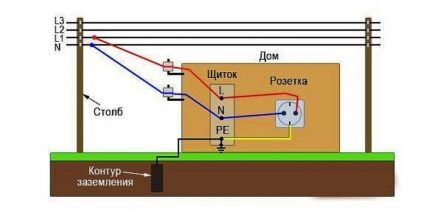
Then the gas boiler is connected to the panel through an individual circuit breaker using a three-wire wire. Additionally, it is recommended to install a voltage stabilizer.
How to check the work and obtain a grounding certificate?
Using a measuring device, determine the resistance of current flow along the circuit. If the result ground resistance measurements does not exceed the maximum permissible value of 10 ohms, then trenches can be buried.
If deviations are found, add the required number of electrodes, make sure that the resistance is normal. The grounding is ready, you can bury the circuit and call for inspection.

By the way, there is another way to check the functionality of the system. To do this, you will need a simple light bulb with a power of 100 W (or more), which is screwed into a socket with a carrying case. Then one end of the carrier is connected to one of the horizontal strips of steel installed on the sides of the grounding triangle, and the other to the 220 volt phase.
Let's compare the results:
- The lamp burns brightly, as if connected to a socket - the circuit is working.
- The lamp is on, but the light is dim or flickering - weld the joints of the structure again.
- The lamp does not light - you need to check the integrity of the entire circuit, from the quality of welding to the connection to the panel.
Representatives of regulatory authorities are usually guided when checking the readiness of equipment for operation by the recommendations of the PUE specified in paragraphs 1.7-1.8. They determine the resistance of the soil and ground loop, the correct connection to the gas boiler panel and other parameters.
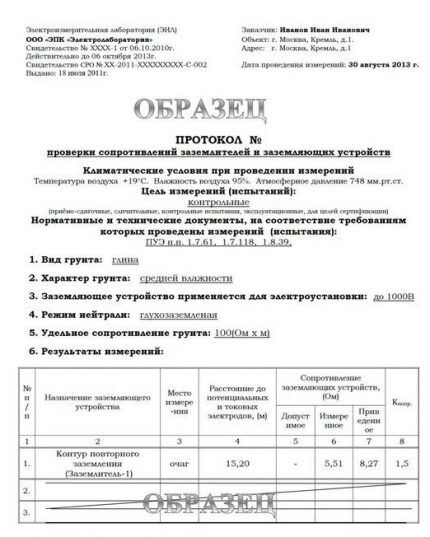
If all indicators are normal, a grounding certificate will be issued. It is a set of technical documentation from a test report indicating the list of measuring instruments used, a laboratory registration certificate, a protocol for checking the circuit between the ground loop and the boiler, and a defective statement.
He will introduce you to the features of grounding a bathtub in an apartment in a multi-storey building. next article, which we recommend reading.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
And finally, we offer a selection of videos where you can get a visual idea of how to safely ground a gas boiler in a private home.
In this video you can see the construction of a grounding loop of 4 rods with the task of achieving a resistance of up to 7 ohms:
Another option for arranging a gas boiler circuit for a private house connected from a pole:
The grounding system is an important step that should not be neglected when installing a gas boiler. And if you are not sure that you can correctly install and connect the circuit to the panel, it is better not to take risks and turn to builders, because not only the safety of expensive equipment is at stake, but most importantly, your safety and even life.
Tell us about how you built a grounding system on your suburban area. It is possible that you have information that will be useful to future independent installers of grounding systems. Please write comments, post photos on the topic and ask questions in the block below.




So there should be grounding in every house, and not only for the boiler, but for all electrical equipment. Such things are conceived at the stage of construction or major repairs, and the wiring is already three-wire along with sockets. In principle, the boiler will work without grounding, but still for such a powerful consumer it makes sense to drive the circuit into the ground.
I don’t know about you, but in Moscow there is an order from Mosgaz and gas workers require the gas boiler to be grounded.
And we bought a house without grounding. I didn’t think anything about it right away, and then, when the refrigerator and boiler burned out after a thunderstorm, I, of course, was upset. Although there was a transformer on the house, which was supposed to save the equipment, it did not work.It turned out to be a Chinese fake, but after the fight they don’t wave their fists. Now I’m reading a lot about this and I’m going to do the grounding myself, I think I should be able to handle it.
Did I understand correctly, Konstantin, that you have your own 10/0.4 kV step-down transformer? If so, then it does not protect against lightning overvoltages. It is necessary to install arresters on the high and low sides, supplemented by RCDs. The dischargers will “cut off the top of the wave”, the RCD will turn off the home network while the charge flows to the ground.
If the boiler does not have electrical mechanisms, is there a pump on the side, which is grounded from an outlet, is it necessary to ground the boiler body in this case?