Types of cables and wires and their purpose: description and classification + explanation of markings
The existing variety of cables and wires for the most part amounts to three-digit numbers.Therefore, it is not possible to describe the entire range in one article.
Meanwhile, it is not at all necessary to describe all types of cables and wires and their purpose. It is enough to have an idea of labeling standards and be able to extract the necessary information from the characteristics in order to select the appropriate option from the variety of cable products according to its purpose.
Let's consider the main points on how you can learn to distinguish electrical wires among an array of such products, and also provide descriptions of the most popular wires and cables.
The content of the article:
- Structural basis of the cable product
- Wire and cable insulating component
- Distinctive features of cable and conductor
- Basic types of electrical wires
- Type #1 - PBPP wire (flat)
- Type #2 - modification of PBPPg
- Type #3 - aluminum conductor APUNP
- Type #4 - two-three-wire PPV
- Type #5 - variety under the APPV brand
- Type #6 - APV aluminum with PVC insulation
- Type #7 - modification PV1 - PV5
- Type #8 - PVC patch cord with PVC insulation
- Type #9 - flat cord SHVVP in PVC sheath
- Types of electrical cables
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Structural basis of the cable product
The design of the cable or electrical wires determines the technical and operational characteristics of the product. Actually, the design of cable or wire products is, in most design variations, a fairly simple technological approach.
Classic version:
- Cable insulation.
- Core insulation.
- Metal core – solid/bundled.
A metal core is the base of a cable/wire through which electric current flows. The main characteristic, in this case, is the throughput, determined by the transverse core cross-section. This parameter is influenced by the structure - solid or bunched.
Such a property as flexibility also depends on the structure. In terms of the degree of “softness” of bending, stranded (bundled) conductors are characterized by better properties than single-core wires.

The cores of cables and wires in electrical practice, as a rule, have a cylindrical shape. At the same time, it is rare, but there are several modified shapes: square, oval.
The main materials for the manufacture of conductive metal cores are copper and aluminum. However, electrical practice does not exclude conductors whose structure contains steel cores, for example, a “field” wire.
While a single electrical wire is traditionally built on a single conductor, a cable is a product where several such conductors are concentrated.
Wire and cable insulating component
An integral part of cable and wire products is the insulation of the metal current-carrying base. The purpose of insulation is quite clear - to ensure an isolated state for each current-carrying core, preventing the effect of a short circuit.

Depending on the purpose of the cable (wire) products, the insulating part may have different designs.
The dielectric material can be:
- ceramics;
- glass;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- celluloid;
- polymers, etc.
In addition to purely electrical protection, the insulating material also provides mechanical protection, protecting the electrical wire (cable) from moisture and other destructive factors.
There is also a special insulating construction applied to electrical wires and cables, giving the products "armored" or "anti-chemical" properties.

Distinctive features of cable and conductor
Often, in non-professional practice, the term “cable” is equated to any type of electrical wire. Meanwhile, the concepts of “cable” and “wire” should be distinguished. And, first of all, the separation involves the factor of transmitted power.
Cable - a product whose structure combines at least three conductors in insulation, additionally protected inside the shell with a special material - parchment, rubber, lead, etc.
The wire - a product consisting of one, maximum, five conductors (cord), in the latter case, united by a common casing.
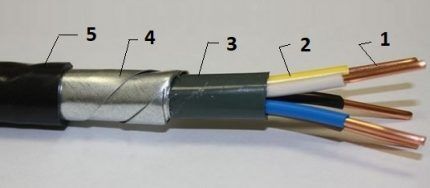
The priority use of cables is industrial and economic facilities. Wires are actively used in everyday life, as well as in other areas.
Separately, bare wires that do not have insulation should be highlighted. The main use of such products is in the installation of centralized power lines.
Basic types of electrical wires
Electrical network wires are classified based on load power and application conditions. For everyday use, the use of the following types of wires is typical: PBPP, PBPPg, APUNP, PPV, APPV, APV, PV1 - PV3, PVS, ShVVP.
Type #1 - PBPP wire (flat)
A product with a polyvinyl chloride insulating sheath, under which a solid copper core is hidden. This electrical material is manufactured with conductors with a cross section of 1.5 - 6.0 mm2.

It is allowed to use PBPP wire in ambient temperatures from -15°C to +50°C. The wire is designed for the installation of networks with a voltage not exceeding 250 V. The traditional use of PBPP is the installation of socket lines in the domestic sector. This type of wire is often used for organizing wiring in the apartment.
Type #2 - modification of PBPPg
In fact, the product is presented in the same design as described for the PPPP, with the exception of one nuance, which is indicated by the letter “g” of the standard marking.
This nuance lies in the more pronounced properties of flexibility. In turn, improved flexibility properties are provided by the core structure of this type of wire, which is “bundled” and not solid.
Type #3 - aluminum conductor APUNP
The presence of an aluminum conductor under the insulation is directly indicated by the product marking - the first symbol “A”. This product is produced in the core cross-section range of 2.5-6.0 mm2.
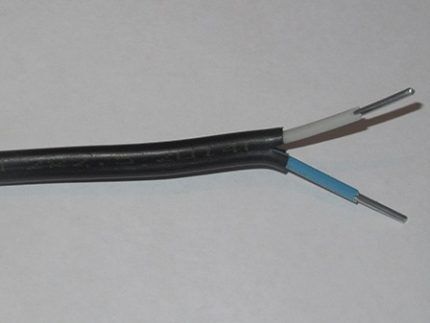
This type of conductor is not recommended for use by professional electricians. The only advantage of this brand is its low cost. However, for the construction of temporary low-load circuits it is quite acceptable to use.
Type #4 - two-three-wire PPV
A product of a two- or three-conductor configuration, where the current-carrying conductors are placed under PVC insulation and held next to each other by means of an insulating jumper based on the same polyvinyl chloride.
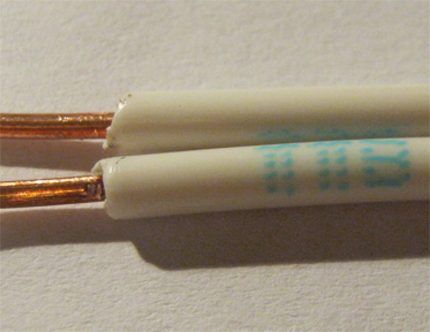
Wire strands (copper) can have a cross-section in the range of 0.75-6.0 mm.
According to the technical specifications, operation is maintained at frequencies up to 400 Hz at voltages up to 450 V. Temperature limit -50/+70°C.
Type #5 - variety under the APPV brand
In fact, the same type of performance as demonstrated by the PPV brand, with the exception of the presence of aluminum conductors instead of copper conductors. Manufactured in different sections, starting from a section of 2.5 mm2.

This type of electrical wire is widely used in a wide variety of installation cases. It is allowed to use APPV for the device open type wiring.
Type #6 - APV aluminum with PVC insulation
It is produced in two configurations of cores - single-cast or bundled (multi-core).
At the same time, the single version is represented by products where the range of sections is 2.5-16 mm2, and the multi-core version is available in the range of 25-95 mm2.

This is one of those modifications that can be used in high humidity conditions. A wide temperature range is supported - from -50°C to +70°C.
Type #7 - modification PV1 - PV5
In fact, it is an analogue of automatic reclosure, but is produced exclusively with copper conductors. The difference between indexes 1 and 5 is that the first option is a product with a solid core, and the second option is, accordingly, multi-core.

This variety is often used when assembling control cabinet circuits. Comes with multi-colored insulation.
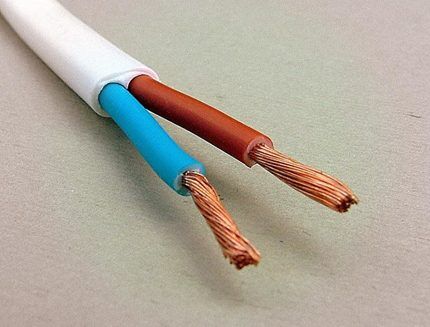
Type #8 - PVC patch cord with PVC insulation
A type of conductor representing the configuration of an electrical cord. Available with a number of cores 2-5 in the cross-section range 0.75 - 16 mm. The structure of the cores is multi-wire (bundled).
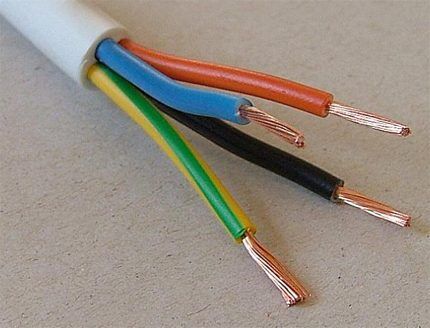
Designed for operation in networks with voltages up to 380 V at a frequency of 50 Hz.
A special feature of the PVS design is a high degree of flexibility. However, the temperature regime is somewhat limited - from -25°C to +40°C.
Type #9 - flat cord SHVVP in PVC sheath
Another variety in a “corded” design. A variation in the number of wires united by a PVC sheath is supported, in the amount of two or three.

The main application is the domestic sphere, outdoor wiring. Operating voltage up to 380 V, core structure – bundled, maximum cross-section 0.75 mm2.
Types of electrical cables
If we consider exclusively cables for power electrical circuits, the main types here are the following power cables:
- VVG;
- KG;
- VBBShv.
Of course, this is not a complete list of all existing cable products.However, using the technical characteristics as an example, you can form a general idea of the electrical cable.
Execution under the VVG brand
Widely used, popular and reliable brand. The VVG cable is designed to transmit current with a voltage of 600 - 1000 volts (maximum 3000 V).
The product is manufactured in two modifications, with current-carrying conductors of a solid structure or a bundle structure.
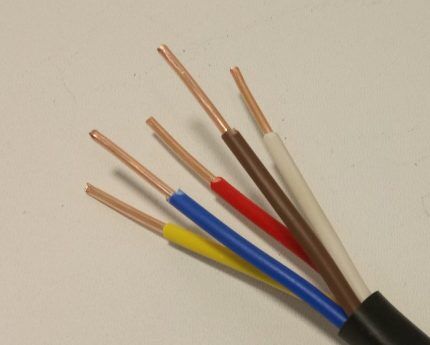
According to the product specification, the range of core sections is 1.5 - 50 mm. PVC insulation allows the cable to be used at temperatures of -40…+50°C.
There are several modifications of this type of cable products:
- AVVG
- VVGng
- VVGp
- VVGz
The modifications are distinguished by a slightly different design of insulation, the use of aluminum conductors instead of copper conductors, and the shape of the cable.
Power flexible cable type KG
The design of another popular cable, characterized by a high degree of flexibility due to the use of a bundle structure of current-carrying conductors.

The design of this type provides for the presence of up to six current-carrying wires inside the shell. Operating temperature range -60…+50°С. Mainly, the KG variety is used to connect power equipment.
Armored cable VBBShv
An example of the design of special cable products in the form of a product under the VBBShV brand. The conductive elements can be bundled or solid conductors.In the first case, the range of sections is 50-240 mm2, in the second 16-50 mm2.
The cable insulation is constructed by a complex structure, including belt insulation, tape screen, steel armor, bitumen and PVC.
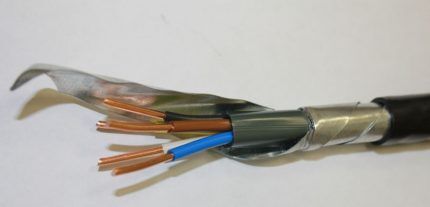
There are several modifications of this type:
- VBBShvng — non-combustible insulation;
- VBBShvng-LS — when burning does not emit harmful substances;
- AVBbShv – presence of aluminum conductors.
The ability to read cable product markings is useful when selecting products and wiring electrical networks.
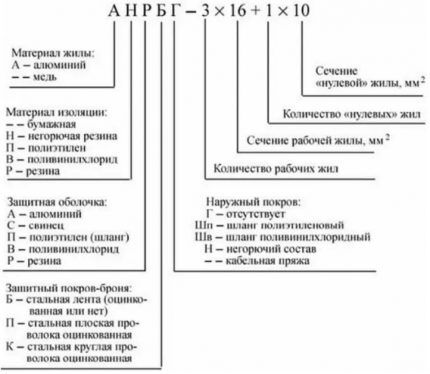
Features of the type of core material - Letter 1: "A" – aluminum core. In any other case, the vein was copper.
As for the purpose (Literature 2), the decoding here is as follows:
- "M" – for installation;
- "P(U)", "MG" – flexible for installation;
- "SH" – installation; "TO" - for control.
The designation of insulation (Liter 3) and its interpretation is as follows:
- "В(ВР)" – PVC;
- "D" – double winding;
- "N (NR)" – non-flammable rubber;
- "P" – polyethylene;
- "R" - rubber;
- "WITH" - fiberglass;
- "TO" – nylon;
- "SH" – silk polyamide;
- "E" – shielded.
The features indicated by Letter 4 have their own interpretation:
- "B" – armored;
- "G" – flexible;
- "TO" - wire braid;
- "ABOUT" – the braid is different;
- "T" – for pipe laying.
The classification also provides for the use of lowercase letters and Latin letters:
- "ng" - non-flammable,
- "z" - filled,
- "LS" - without chemicals combustion emissions,
- "HF" – no smoke when burning.
Markings, as a rule, are applied directly to the outer shell, and along the entire length of the product at regular intervals.

On our website there are articles devoted to the choice of cable products for arranging electrical networks in an apartment and house, we recommend that you read:
- Which cable to use for wiring in an apartment: overview of wires and choosing the best option
- Which wire to use for wiring in the house: recommendations for choosing
- Which cable to use for wiring in a wooden house: types of non-flammable cable and its safe installation
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below demonstrates a “beginner electrician” lesson.
Quite useful video material is shown, which is recommended for viewing as an acquisition of general knowledge on wires and cables:
Given the existence of a wide range of wire and cable products, a potential electrician has many options for solving any problems in the electrical field.
However, even with such diversity, it is quite difficult to choose the right product for specific purposes if you do not have the appropriate knowledge. Let's hope this article will help you make the right choice.
Do you have anything to add, or do you have questions about choosing electrical cables and wires? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience of using cable products. The contact form is located in the lower block.



