Ventilation in a wooden house: rules for providing a log house with an air exchange system
In low-rise construction, houses made of timber or logs are now leading. Wood attracts with its affordability and environmental friendliness.Its disadvantages quite rightly include sensitivity to condensation and household moisture, but well-organized ventilation in a wooden house will help minimize their harmful effects.
We will tell you how to create stable air exchange in structures made of lumber. An optimal microclimate in your home is the key to health. In addition, in a wooden building, ventilation will help protect structures from damage by fungus and premature failure.
The content of the article:
Arguments in favor of a ventilation device
Is a specially organized air exchange system needed in a wooden building as such? The opinion that wooden houses “breathe” does not give grounds to completely abandon systems that remove excess moisture and exhaust air from the premises.
Just as in the construction of buildings made of concrete and brick, the construction of houses made of lumber uses technologies that reduce heat loss. It’s just that instead of synthetic materials, natural seals made of jute, flax, and felt are used in the inter-crown joints. Mineral wool is placed in the ceilings.

Insulated wooden building structures do not allow air masses to circulate naturally.In addition, builders and owners began to actively replace the usual window and door frames with sealed plastic analogues.
As a result, fresh air does not enter inside, and exhaust air does not exit outside. The inhabitants are not supplied with the required amount of oxygen for breathing. Mold fungus settles on undried wooden structures, destroying buildings with amazing speed.

In addition, wood perfectly absorbs moisture! If you do not deal with humidity, heat loss will at least double. After all, water is an ideal conductor for heat waves.
The tree does “breathe,” but not so much that air exchange occurs in full without a specially organized ventilation system. Walls made of wood will not be able to fully remove household fumes. They will not provide the opportunity to remove dust suspended in the air with microorganisms.

Organizing ventilation in a house made of timber or logs will eliminate the influence of the listed negative circumstances on the organisms of residents and building structures. It is simply necessary to create a natural scheme, but you can also build an artificial one. And if supply and exhaust system If you also equip it with a recuperator, then the exhaust air can be used to heat a fresh portion from the street.
Regulatory requirements for air exchange
The presence of ventilation must be provided for at the design stage of the house itself.The study of building codes (SNiP) is recommended for both independent builders and customers of construction crews.
Not all migrant workers can be trusted; most have to be carefully monitored.

SNiP number 41-01-2003, which regulates the rules for the design of ventilation and heating systems, sets standards for air circulation speed both in the building itself and in its individual rooms:
- for living rooms, living rooms, bedrooms the norm is 30 m3/hour;
- for kitchens and bathrooms where humidity is high, the norm is from 50 to 70 m3/hour;
- for utility rooms the norm is 15 m3/hour.
Regardless of the type of ventilation system, it must provide the required volume.
The designer's task is to select the type that suits the needs. You also need to immediately decide on the equipment and calculate the area of the air ducts if they are planned for use.
Types of ventilation systems
Ventilation systems are divided into groups according to the methods of stimulating air movement and the type of action. The optimal option is selected depending on the tasks being solved, the area and number of floors of the building. To a large extent, the choice is influenced by the financial capabilities of the future owner.
Classification by method of motivation
For wooden houses and log cabins, the following types of ventilation are most often used:
- Natural (gravity). Provides for the presence of ventilation vents (vents) and an exhaust duct that form air flow circulation based on the laws of physics. It should be taken into account that the rate of natural air exchange depends on weather factors, because movement is possible only if the air density outside the window is higher than inside.
- Artificial (mechanical). In it, the movement of air flows is stimulated by fans installed either in the supply components or in the exhaust components. Its undeniable advantage is the stability of operation in any weather. The mechanical system is absolutely independent of the physical parameters of the air mass outside and inside the house.
- Mixed (combined). In essence, it is a modernized version of the natural type of ventilation. To organize it, either the exhaust or the supply is mechanized with a fan. If an exhaust fan is installed, then the influx is carried out naturally. And vice versa: supply with a fan, exhaust - natural.
It is important to take into account the layout of a wooden house in order to properly provide ventilation, both natural and artificial. Determining the locations for vents, hoods and separate air ducts directly depends on where the kitchen and bathrooms will be located. It is in them that the exhaust holes are located.
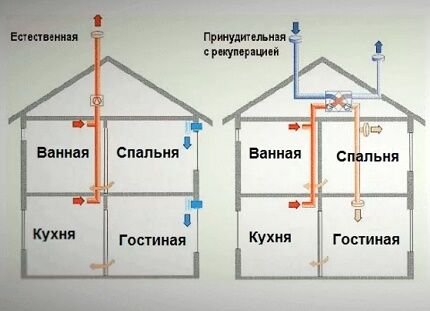
Exhaust ducts in private houses most often lead into a common ventilation shaft. Therefore, kitchens with baths and toilets are usually grouped in one area.However, there are other solutions, for example, recycling waste through an air duct into the attic or directly through a wall exhaust valve to the street.
If you plan to build a complex architectural form, many owners of wooden houses choose an artificial air exchange system. The mechanical scheme does not oblige the components of the system to be located at a certain height and the kitchens and bathrooms to be tied to each other.
Division by principle of action
It is also necessary to distinguish ventilation systems by type of action, namely:
- Supply. Ensures efficient operation of the entire ventilation system designed to supply air inside. Fan-driven supply ventilation fresh air displaces the waste mass outside through exhaust openings located in the bathroom, kitchen, and toilet.
- Exhaust. Ventilation hoods are found in any house/apartment. They can be with or without fans. In order to be able to regulate the air exchange rate, hoods are equipped with valves, dampers or fans that operate from the mains. If the fan is running in the hood, then fresh air itself comes in to replace the removed air.
- Supply and exhaust. Mechanical draft is provided not only by exhaust and supply fans, but also by the construction of air ducts. The effectiveness of these systems has been proven in large wooden houses. Those. where natural air exchange is difficult or impossible to achieve.
Despite the fact that in supply and exhaust systems fans operate for both exhaust and supply, usually only one direction is used. The home owner always has the opportunity to choose what to use more intensively.
Ventilation air handling unit can be equipped with a control device that makes it possible to adjust the air speed inside the room. The downside is that such equipment is quite expensive, and its installation requires specialized tools and certain qualifications.
Nowadays, owners of wooden houses prefer a supply and exhaust air exchange system with the possibility of recovery.

However, this option has both advantages and disadvantages. Firstly, you need to understand that additional equipment will be required to prepare the air before supply and to dispose of the waste air mass. All devices are volatile, which means they need power, the consumption of which will have to be paid for.
The following components will be used:
- air intake fan;
- electric heater;
- humidifier;
- filtration system;
- soundproofing systems.
In the presence of recuperation systems You can refuse an electric heater, since it is a priori equipped with a heat exchanger. It uses exhaust air removed from the room for heating.
Hence the main advantage - home owners can significantly save on energy consumption. In addition, such a ventilation system can be used in the summer, when you need to cool the air and use air conditioning.
The air circulation rates of supply ventilation systems are the highest.They can be used for heating and cooling the premises of a wooden house, but they will have to invest significantly financially.
Ventilated floor installation
An important component of organizing air exchange in a log house is the ventilation of the floor, foundation and lower crowns of the log house. The system will dry the lumber of the base of the house, which means it will protect the entire building from rot and fungus.

Basic principles and rules for base ventilation:
- Installation of vent holes (diameter - 10 cm) on the windy and opposite side of the log house base. The distance from the ground to the center of these holes should be at least 33 cm.
- Construction of the floor using a floating scheme with gaps around the perimeter of the premises. The gaps are loosely covered with a plinth, so that the air entering the vents can freely escape.
- Formation of ventilation holes in the floor structure that communicate with the underground. They are covered with gratings, suitable if the floor covering was not natural floorboards, but linoleum, carpet, laminate and similar material that does not allow air to pass through.
During the frosty period, the vents selected in the base or foundation are closed with dampers, which significantly reduce air exchange, and in the summer, grilles are placed on them.
The distance between the vents themselves is about 2 meters if the house is located in a lowland. If the log house stands high, then this distance should be increased, since the strength of the wind increases, and therefore the intensity of the blowing.

Particular attention should be paid to the air exchange system of attics and attics, on which the condition and durability of the roof largely depends. Ventilation of the attic and attic will increase the total amount of vents to 500th share of the total area of the entire house.
To organize natural air exchange in the attic or attic, pediment ventilation and dormer windows are installed. The type of ventilation structure is selected based on the shape of the roof. It is clear that in pitched versions it is easier to create an opening in the pediment; hip and hipped ones are equipped with dormer windows.
To remove the exhaust air mass, ventilation shafts will be required. They are most often planned in the center of the building, closer to the ridge. In summer, ventilation shafts can be equipped with fans, so the operation of the entire system on hot, windless days will be ensured.

Roof ventilation requires careful attention to the following nuances:
- Between the insulating layers, insulation and roofing it is necessary to leave gaps of 3-5 cm.
- The specified distance is ensured by the installation of lathing and counter-lattice.
- Thermal insulation from the inside must be protected by a layer of vapor barrier.
- The insulation layer in the roofing pie must be protected from the outside by waterproofing, separated from the roofing by a ventilation gap.
Compliance with established norms and rules is necessary to develop a competent project ventilation in a private house. Knowledge of building regulations and pre-prepared drawings will help you do without designers, and at the same time achieve your goal - to keep a wooden house in a habitable condition.
Air conditioners against natural air exchange
Can air conditioners replace the natural circulation of air masses in a room?
Any, even the most expensive, climate systems are significantly inferior to simple ventilation. Want to think fast to keep you productive? Ventilate the room more often, and even better, do not skimp on the ventilation system, since, for example, in winter it is not always possible to open the window for a long time.

All split-systems have two blocks that operate synchronously:
- External - this is a compressor that condenses the refrigerant;
- Interior is a radiator that heats the air that is forced to circulate around it.
The air, which will subsequently be cooled, is also taken indoors. It means that split- the system cools and passes through the same air masses.
Some models also take in outside air, but its amount does not exceed 5%, so oxygen, even in this case, does not enter the room in the required volume. The price of such innovations is much higher than standard technologies, and they do not solve the problem.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The conclusion suggests itself, the ventilation system is an integral part of wooden houses:
If you figure out in advance how to properly make ventilation in a log house and organize it correctly, the building will last for many years without the slightest problem.
Tell us about how you installed a stable air exchange system in your own house, built from timber or logs. Share technological nuances that may be useful to site visitors. Please leave comments in the block form below, post photographs related to the topic of the article, and ask questions.



