Ventilation in the cellar: technology for constructing a proper ventilation system
The safety of the items placed there, and sometimes the well-being and health of the owners, depends on how well the ventilation in the cellar functions.To create a properly functioning air exchange system, an understanding of certain physical processes and knowledge of device technology is required.
We will tell you how to organize a system for removing exhaust air from underground premises and ensure the supply of fresh air from the street. The article presented for review describes in detail the options and implementation methods tested in practice. Taking into account our recommendations, you can perfectly arrange cellar.
The content of the article:
The task of ventilation of underground premises
Cellars are used for long-term storage of items with special requirements for environmental conditions. The temperature in closed underground rooms almost always ranges from +5 to + 12 degrees Celsius.
Humidity indicators can vary significantly depending, as a rule, on external conditions. With the help of ventilation it is possible to regulate these parameters to the required values.
Temperature compliance
The temperature regime of a properly constructed and insulated cellar is formed due to heat exchange between the walls, floor and the air in it.The ceiling, as a rule, is insulated, so its influence on the temperature change inside the structure is minimal.
Seasonal fluctuations in soil temperature are significantly less than atmospheric fluctuations, which makes it possible to establish a constant microclimate in the room. Heating or cooling of the air inside the cellar occurs slowly due to the low thermal conductivity of the earth.
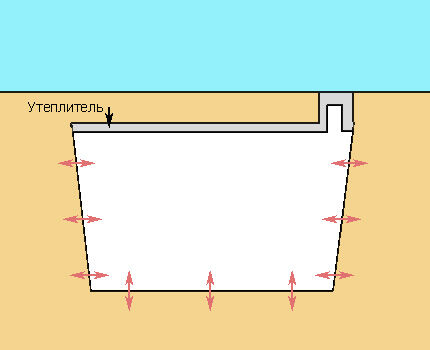
If necessary, ventilation can be used to change the temperature. Considering that the structure is underground, natural air movement is sufficient to cool the cellar in winter, while in summer it is better to stimulate air flow using fans.
Solving the problem of excess moisture
The most common problem with the cellar microclimate is excess moisture. It cannot be evaporated by solar radiation or wind, so ventilation is the main way to dry rooms buried in the ground.
Methods of moisture entry can be divided into three types:
- Moisture can enter the cellar in the form of water through the walls, floor or ceiling if the waterproofing layer is missing or damaged. Most often this happens in the spring when the snow melts.
- An internal source of moisture can be objects or products located in the room. Vegetables and fruits, especially at the initial stage of the storage process, emit fumes.Also, air humidification occurs during the fermentation process, during the breathing of bees, if the cellar is used as a cellar and in many other cases.
- In the spring-autumn period, when the temperature in the cellar is significantly lower than the street temperature, the source of moisture is condensation. Therefore, for the correct use of ventilation, knowledge of the physical laws of condensation and evaporation is necessary.
The process of removing moisture through ventilation is slow. Therefore, before starting this procedure, it is necessary to determine the cause of the increase in humidity in the cellar and, if possible, eliminate it.

Reducing the concentration of hazardous gases
Another reason for indoor ventilation is the need to change the chemical composition of the air. So, as a result of storing agricultural products, all kinds of odors are released, and when they rot, as well as when bees or fermentation tanks are kept in the cellar, carbon dioxide is released abundantly, replacing oxygen.
In poorly ventilated cellars, gases of a different nature may accumulate. Excessive concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, carbon monoxide (CO) or hydrogen sulfide can cause a person to lack oxygen in the blood, suffocate and, as a result, lose consciousness. If immediate assistance is not provided, death is possible.
In the absence of internal air circulation, the concentration of dangerous heavy gases occurs at the lowest point of the cellar.Therefore, if simple ventilation is sufficient to remove extraneous odors, then to reduce the concentration of gases whose specific gravity in relation to atmospheric air is more than one, ventilation is required with the air intake hole located at a short distance from the floor.
If there are prerequisites for excessive concentration of heavy gases in the cellar, it is necessary either to carry out mandatory ventilation of the room before visiting it, or to use sensors or gas analyzers to determine the need for ventilation.

Theoretical basis of moisture removal
If the main purpose of air exchange is to dry the room, then from the point of view of physics the problem can be formulated as follows: it is necessary to install ventilation in the cellar according to such a scheme so that the absolute mass of moisture entering inside is less than that coming out.
Physical description of the processes of condensation and evaporation
There are three main terms, the essence of which must be understood to understand the nature of condensation and evaporation of moisture from the air:
- Absolute humidity shows the mass of water vapor contained in one cubic meter of air. This value is expressed in g/cub.m.
- Relative humidity shows the ratio of the current mass of water vapor to the maximum possible, at constant pressure and temperature. Expressed as a percentage.
- The dew point temperature shows the temperature value below which the water vapor contained in the air reaches a state of saturation and the condensation process begins.
In relation to the cellar, the condensation process can be described as follows. At a certain temperature, the air has certain values of absolute and relative humidity.
As the temperature decreases, the absolute humidity remains unchanged, but the relative humidity increases. When the relative humidity reaches 100%, the dew point occurs and moisture begins to be discharged in the form of condensation.
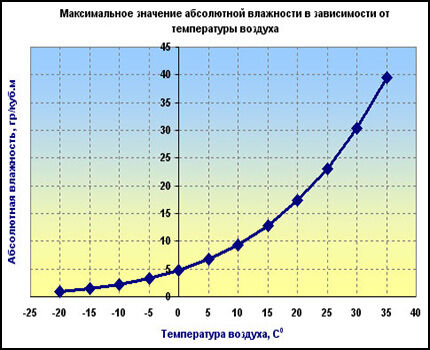
The evaporation process is as follows: when air, whose relative humidity is less than 100%, comes into contact with water, it becomes saturated with moisture, which can continue until the relative humidity reaches 100%. The higher the air temperature, the more moisture it can absorb during evaporation.
Drainage of underground premises in summer
In dry and hot weather, it is tempting to temporarily open a damp cellar and let in warm, dry air to remove condensation. This is one of the most common mistakes that leads to the opposite effect - the flow of moisture from the atmosphere into the underground.
For example, during the day, with an anticyclone and an air temperature reading of +32 degrees Celsius and a relative humidity of 40%, there is a feeling of dry air. In a cellar with a temperature of +12 degrees and a relative humidity of 100%, there is a feeling of dampness. However, the absolute humidity outside at these parameters will be higher than indoors.
As warm air enters, it will begin to cool. The dew point temperature at the above outdoor air parameters will be 16 degrees. Consequently, during the period when the temperature drops from 16 degrees to 12, moisture condensation will occur, and the relative air humidity will be equal to 100%.
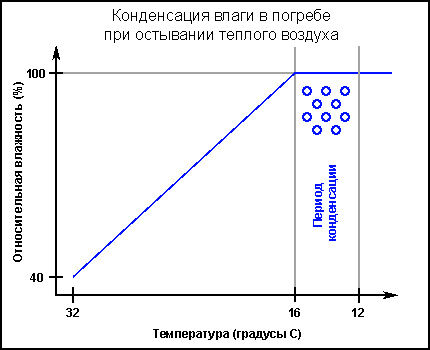
Drainage underground rooms due to ventilation produce correctly for a long time. At the same time, the volume of air passing through the premises must ensure a minimum temperature drop, so that at low values of its relative humidity the process of evaporation occurs.
However, after the completion of the ventilation period, due to heat exchange with the walls and floor, there will be a gradual decrease in temperature and condensation of water in the air.
Therefore, temporary removal of moisture using ventilation during the warm season is carried out in the following cases:
- the amount of moisture in the cellar clearly exceeds the volume that will end up there after condensation of water from the atmospheric air;
- it is necessary to create conditions to stop intensive processes of decay, the spread of mold and mildew;
- it is necessary to carry out antifungal treatment, which is most effective when applying an antiseptic to dry surfaces.
Removal of condensate from the cellar during the warm season is carried out using alternative methods. You can collect moisture using substances that have good hygroscopic (water-absorbing) properties, such as ash or sawdust.
In this case, if possible, it is necessary to exclude external air exchange, if this does not contradict compliance with other parameters of the microclimate of the room.

Freezing moisture in winter
At subzero temperatures, absolute air humidity is low. Therefore, the most effective method of removing dampness using ventilation, which is not entirely correctly called “freezing,” is to ensure an influx of frosty air into the cellar.
So, even if at a temperature of -10 degrees Celsius the air has the maximum possible humidity (2.36 g/cub.m), then after heating it in the room to +5 degrees, the relative humidity will become only 30%. One cubic meter of such air will be able to evaporate 4.5 grams of water in the cellar.
Since it is undesirable for almost any cellar to lower the temperature to negative values, the intake of frosty air should be carried out in small portions.
It displaces humid air from the room and mixes with the remaining air. Then you need to wait until the temperature rises to normal values and you can carry out this procedure again.

This method is effectively used in the fall after planting the crop, opening the ventilation for some time at night.
Technical aspects of the ventilation device
A technically correct implementation of a ventilation system for a cellar, along with an understanding of the rules for its use, will ensure the desired microclimate in the room. For small structures, you can complete all the work yourself, having basic construction skills.
You can get acquainted with the features of calculating the ventilation system for various types of premises by reading recommended article.
Air duct placement and maintenance
Plastic or metal pipes are usually used as air ducts. Plastic is required to withstand low temperatures. This is necessary to avoid damage to it in winter due to mechanical stress, such as cleaning out the kurzhak.
Usually for purposes ventilation of underground premises they use two pipes, one of which works for air supply, and the second for exhaust.The use of a single pipe results in a much smaller volume of circulating air.
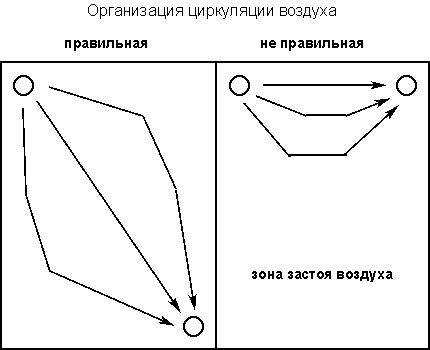
It is advisable to place the pipe exit points at different ends of the cellar. In this case, the entire area of the room is uniformly ventilated, without the formation of air stagnation zones.
The entry point of the supply ventilation is usually located near the floor of the room, and the air intake point is closer to the ceiling. This is necessary to comply with the physical laws of natural air circulation. An exception is placing the entrance to the exhaust pipe near the floor for more efficient outflow of dangerous heavy gases.
When placing external outlets near the ground, it is necessary to monitor the snow level, since the formation of a snowdrift above the level of the pipe can cause the ventilation to stop. Humid air leaving the room causes the formation of smoke in the exhaust pipe, which can reduce the speed of air movement or even cause ventilation to stop.
Cleaning kurzhak is sometimes a difficult task due to the presence of ice or high-density deposits in it. To simplify the work, in the fall you can insert a rigid metal rod with a diameter of 8-12 mm inside the pipe. If the cross-section of the pipe is completely covered by the kurzhak, the procedure for cleaning the hood can begin with translational movements and rotation of the rod.
If the exhaust pipe is located vertically, then under its end, located in the cellar, it is necessary to place a container into which condensate and fragments of snow and ice that fall off when cleaning the pipe will fall.

Natural and forced air circulation
In the vast majority of cases, natural ventilation of small underground rooms is used. In winter, the physics of the air mass turnover process is based on the difference in density of cold and warm air. To do this, the outlet from the supply pipe is located closer to the floor, and the entrance to the exhaust pipe is located under the ceiling.
The cross-sectional area of the air ducts is calculated based on the volume of air circulation required for a particular room and the estimated speed of its movement through the pipes.
To adjust the ventilation volume, it is better to use a pipe cross-section slightly larger than the calculated one, complete with a valve. It can be installed on both the supply and exhaust pipes.

Natural ventilation does not work well in the summer, and also takes a long time to remove gases with a specific gravity greater than that of ordinary air. In this case, to create air pressure, they build forced ventilation type by installing axial fans.
Fans can be installed on both the exhaust and supply pipes, as well as on both at once. If there is high humidity in the cellar, it is recommended not to install a fan on the exhaust pipe due to its possible rapid breakdown as a result of exposure to moisture.
Removing moisture using condensation zones
There is a way to remove moisture from the cellar in winter, which does not require pipes and holes for air inflow and outflow. It consists in the formation of zones for moisture condensation and its subsequent removal. This method does not relate to ventilation, but to circulation, since there is no air exchange between the room and the atmosphere.
The most basic implementation of this method is to use a canopy outside the slightly open cellar door. Warm air, penetrating from the cellar through a small hole, cools when it comes into contact with a cold canopy, on which condensation remains in the form of frost and curd. Cold, dry air is returned back into the room.
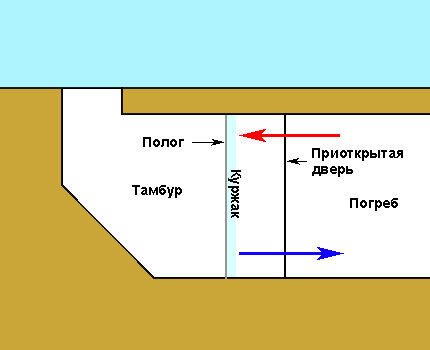
When using this method, it will be necessary to periodically move back the canopy, close the door, knock down the kurzhak and remove it to the street.As a canopy, you must use a thick rag that can withstand the weight of up to 20 kg of adhered snow per 1 square meter of its area.
Will familiarize you with the rules and technologies for constructing ventilation systems next article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. The problem of moisture condensation in summer and methods for eliminating it:
Video #2. Assembly and installation of the fan on the exhaust pipe:
For high-quality operation of the ventilation system, it is necessary to carefully approach the issue of studying the physical principles of air circulation, as well as its condensation and evaporation. The technological air exchange device is not complicated and for small rooms its implementation is possible on its own.
Please comment on the information we provide. You can leave a comment, ask a question and post photos on the topic in the block below. Perhaps you want to talk about your personal experience in installing a ventilation system?




I have a cellar in my garage, and the ventilation in it is just some kind of nightmare. After rain it becomes too damp there, moisture is not drawn out at all. I tried to clean it - nothing seems to interfere with the air exchange, there is draft, but the humidity is still too high. A friend advised us to arrange forced ventilation using a fan. I would like to ask, how effective will it be to use a fan in a ventilation system?
Forced supply ventilation in the cellar is normal. If the natural air flow is insufficient, then storing food in the cellar or anything else at all is not worth it. The situation is similar for exhaust ventilation.Forced supply ventilation using a special fan is the optimal solution.
Only you can determine exactly what is causing the problems in the cellar; it is possible that the air flow is normal, but your natural exhaust is poor. In this case, you need to use forced exhaust rather than installing a fan on the inlet. Ideally, install two fans at once, one for supply and one for exhaust. I am attaching photo instructions.
It’s strange, of course, who makes a cellar without ventilation!? If you store food there (potatoes, carrots, onions, etc.), then it’s easier to immediately throw them out of the garden or process them. In addition to removing stale air, a good ventilation system also removes excess moisture. In theory, the natural ventilation option should work flawlessly in the cellar, but if it fails, it is better to organize a forced one. Regarding the fan: a small amount of power will be enough. I can also recommend doing waterproofing, a very good and useful thing.
Dear Alexey, hello!
I have the following problem: an unheated utility block, a basement underneath, its dimensions are 4x6 m, height 2.5 m. The foundation blocks are also the walls of the basement, waterproofing is done, the ceiling is concrete floors, everything is plastered. Well, in the spring and summer, the ceiling and walls are covered in drops of water - that is, problems with condensation. There is ventilation, but it is done incorrectly - 110 mm pipes (supply and exhaust, spaced apart in height) are mounted side by side approximately in the middle of the basement. I tried to spread them with elbows and straight sections of pipes to different ends of the basement. It's late autumn now. There is no water, but this is understandable - it is now warmer in the basement than outside.
I'm going to paint the walls and ceiling with insulating paint - is this correct? I think that if you use polystyrene foam, mold may appear between the wall and the insulation sheet. Or not to do this and try to get rid of condensation only by ventilation? With which, too, not everything is clear... You can put a forced fan on the hood or punch two additional holes in the base (diagonally) for additional natural ventilation. But by increasing air exchange in spring and summer, we increase the flow of warm air from the street into the cold basement... We increase condensation. So it’s not clear how to get rid of condensation.. 🙁
In a good way, you need to cool the incoming air while simultaneously removing fallen water from it, but this is essentially an air conditioner - a little expensive for a basement. I’m sitting here racking my brain, maybe you can recommend something?
Good afternoon, Arthur.
Let's start solving your problem by checking whether the cross-sectional area of the supply/exhaust pipes is sufficient. In other words, we will determine what diameter pipe is needed.
The cross-sectional area is simplistically determined by the following ratio: each square meter of basement floor requires 25 square centimeters of pipe cross-sectional area.
Your basement has a floor area of 24 square meters. meters. This means the cross-sectional area of the supply/exhaust pipe = 24 sq. meters × 25 sq. cm = 600 sq. centimeters.
Let's first determine the square of the radius of the pipe using the well-known formula - S = πR×R.
Then R×R = 600/3.14 = 191 sq. cm. Extracting the root, we get - the radius is 13.8 cm, and the diameter is 27.6 cm.
As you can see, one of the problems is the diameter of the pipes is almost three times lower.
You didn’t include a ventilation diagram, so I attached a screenshot of what it should look like.Please note that the flow of the supply pipe through the utility unit should be minimal. If possible, avoid it altogether. The elevation of the inlet above the floor is a maximum of 500 mm. The protrusion of the hood from the ceiling is determined by the design of the latter - pay attention to the device for draining condensate from the exhaust pipe.