Ventilation in a two-story private house: options for organizing trouble-free air exchange
The microclimate in the house is of great importance, and its condition depends on how properly the ventilation system is equipped.This affects not only the well-being of the inhabitants. Without effective air exchange, humidity increases, as a result, condensation appears, wood begins to rot, and metal begins to rust.
To avoid such troubles, you need to know how to properly ventilate a two-story house so that life in it is comfortable.
From the article we have proposed, you will learn all about the options for installing systems that provide the air exchange necessary for life. We will introduce you to the features of organizing ventilation of two-story buildings. Let's talk about how calculations are made for the correct selection of equipment.
The content of the article:
Existing types of air exchange
Based on the method of inducing air movement, three types of air exchange are distinguished:
- natural;
- forced;
- mixed.
Each of these types has advantages and disadvantages. To figure out which option has more advantages, you need to familiarize yourself with everything in more detail.
Natural ventilation of housing
For natural air exchange in a two-story house, there is no need to install equipment that stimulates air movement. Everything here is based on the rules of physics - gravity, the principles of changing gas pressure.
Gravitational circulation occurs due to leaks between structural components in windows and doors. Due to changes in the physical state, air masses that have penetrated inside from the street independently move into the vents, the system ventilation ducts. At the same time, the heat transfer of the premises increases.
A typical solution for private two-story houses is a ventilation duct located vertically and exposed to the roof. This is an ideal option for a newly built house, since the box must be included in the design and installed during the construction process.

Uninterrupted service of the natural ventilation system in a private two-story house is impossible without good draft.
It depends on a number of indicators:
- temperature differences inside the room and outside its external walls;
- the height of the shaft and its cross-section;
- wind that worsens or improves traction;
- quality of channel thermal insulation;
- the presence of turns, bends in the air duct.
When the temperatures inside and outside are balanced, draft deteriorates. A significant increase in outside temperature leads to reverse draft. The way out is a high-height ventilation shaft.
Air enters rooms such as the dining room, bedroom, living room, and is removed through utility rooms. The first of them are called dry, and the second are called wet. Thus, dry air enters the house and humid air is removed.
Supply air masses enter the house through supply valves installed in the walls. When necessary, they can be blocked. When installing the system, incoming channels are made from below, and outgoing channels are made from above so that they go out onto the roof.
This construction is based on the fact that cold air, which tends to displace warm air, will always be at the bottom, and warm air at the top. Air circulates between rooms through a gap at the bottom of the door of at least 1.5 cm.

The use of a natural air exchange scheme is justified if the house is located in an area where the air is truly clean. The operation of such a system does not require additional energy costs. If the scheme meets all the requirements, the intensity of air exchange can be adjusted.
Forced ventilation of a two-story house
The operational parameters of a forced-type hood in a two-story private house are much higher than those of a natural one, since additional equipment is involved in air exchange. There are three types of forced air exchange systems based on the operating principle: supply, exhaust, supply and exhaust.
According to their functional purpose, mechanical ventilation is divided into two categories - local and controlled. The first works only in one specific place, while the second in the future can ventilate the house completely. An example of local exhaust ventilation is a kitchen hood.
Exhaust air flows are removed through a channel with access to the roof. As in the case of natural ventilation, air inlet openings are located in dry rooms, and exhaust openings are located in rooms with high humidity.

The advantages of forced ventilation are expressed as follows:
- intensive air circulation due to high discharge speed;
- eliminating the influence of external factors;
- controllability process;
- the ability to pre-prepare incoming air masses.
To install the supply circuit, the same supply valves are used as for natural ventilation. The only difference is the presence of a fan forcing air into the room. Install it in an air duct laid in the wall. From the side of the room, the channel is closed with a lid, and from the street - with a grill, so that dust, various living creatures, and precipitation do not get inside.
Install supply valve not difficult. A hole is made in the wall using a drilling machine or hammer drill. Then they clean it, lay the air duct, install the valve and the protective grille.
Has more advanced functionality breather. A fan, protective grilles, and air duct are also present here. But besides this, there are sensors that monitor humidity and temperature, and if necessary, they automatically start the equipment.
Majority breathers equipped with a built-in convector that heats the air entering the room. This allows you to maintain a constant temperature, which is not only comfortable, but also reduces heating costs.
Equipment for organizing a ventilation system in a private house with two floors is installed in places where air removal is extremely necessary - in the kitchen, sanitary unit.

A fan is also used as exhaust equipment for the bathroom. Place it at the entrance to ventilation duct, then masked with a protective grille. It does a good job of normalizing the humidity level in the room.
It is necessary to remove unpleasant odors and grease from the kitchen along with moist air. Kitchen hood mounted above the hob and connected to the ventilation duct.A fan located inside the equipment pulls and removes exhaust air masses from the room.
In a large two-story house, a forced exhaust system may not be effective enough. This is explained by the fact that dirty air is forced out, and fresh air comes in naturally in a small volume. In these conditions, a more acceptable option is supply and exhaust ventilation.
To use this combined system, air is supplied and discharged by means of fans. The building envelope must be highly airtight. Often the role of supply equipment is played by breathers, and in wet rooms exhaust mechanisms are installed.
Thus, the intensity of air exchange increases, and the volume of air masses both input and output will be under control. In more powerful systems, in addition to supply and exhaust equipment, there is heating or cooling. Sometimes humidifying and air-filtering devices are additionally installed. Most complex systems are equipped with a recuperator.

Before entering the house, the supply air streams pass through the heat exchanger, meeting the warm air rushing out. Structurally, the unit is designed so that air avalanches do not mix, but a warm stream heats a cold one. The last one comes to the house already warm.
In all respects, forced centralized ventilation with recovery is the most advanced way of arranging a ventilation system, since it allows you to solve many problems at once:
- establish optimal air exchange throughout the house without focusing on weather conditions;
- prepare supply air;
- automate and regulate air exchange over a significant range, based on different microclimate indicators in individual rooms;
- save thermal energy.
The implementation of a forced scheme is associated with considerable financial costs. The equipment that is part of it requires periodic maintenance. In addition, this ventilation model requires the constant presence of power supply to operate.
It is advisable to provide backup power when installing a forced ventilation system in a two-story house. It will be useful not only for maintaining the indoor microclimate, but will also allow you to enjoy all the other benefits of civilization.
Specifics of mixed type
The mixed type of ventilation involves the use of both gravitational and mechanical schemes, i.e. forced. Typically, in such ventilation systems that provide air exchange in a two-story house, fans are installed on both the exhaust and supply components.
Depending on the state of the atmosphere and microclimate inside the house, mixed systems include either exhaust or supply. At activating the hood air masses from the street will spontaneously flow into the vacated rarefied space. If the inflow is started, the forced air will itself displace the excess.
Features of the organization of ventilation of the second floor
Natural ventilation of the second floor can be organized in two ways. The first of them provides for the presence of an entrance door that blocks the flow of air from below. Thus, the airspace is divided into independent blocks.

You can also divide the air space of the floors using a door installed in front of the stairs leading up.
The scheme of natural ventilation of the second floor is similar to the scheme of the first:
- Clean air enters the rooms through a wall or window supply valve.
- Through leaks or transfer grates allow air to flow from the rooms into the bathroom and other auxiliary rooms.
- “Dirty” air flows escape through the ventilation shaft.
Supply valves are installed in living rooms, exhaust valves are installed in the dressing room, hall, and bathroom. They leave at the doors of all rooms transfer cracks or install gratings.
For ventilation to function properly, it is necessary not only to ensure the tightness of the entrance door to the floor. It is necessary to eliminate other ways of possible flow of air jets between floors - places where communications pass, leaks in ceilings.
The second method is used when the layout is made in such a way that there is no door from the stairs to the second floor. Here, individual isolation of the air space of each room is performed.
For this purpose, supply valves are installed in all rooms on the second floor, and the doors are made airtight and kept closed at all times. To remove contaminated air masses, natural ventilation channels are provided in the premises.
The disadvantage of the second method is the need to increase the number of ventilation ducts. Ideally, each room should have an individual duct ending at the roof.
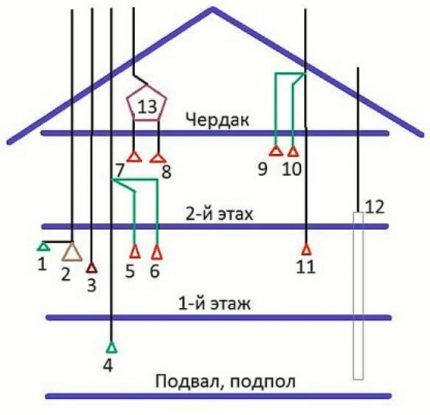
Combining ventilation ducts impairs the performance of the system. There are times when it is still necessary to do this, but even if this option is chosen, the design will turn out to be quite complex.
There are circumstances in which it is not always possible to create the necessary air exchange using natural ventilation on the upper floor:
- It is almost impossible to completely eliminate air exchange between floors.
- The ventilation ducts on the second floor have a smaller height, therefore, the traction force in them is lower compared to the ducts on the lower level.
Based on these reasons, to ensure a comfortable environment here, it is better to use forced exhaust ventilation.
Calculation of the main parameters of the ventilation system
To install effective ventilation in a two-story house, a preliminary calculation is required, based on the air exchange standards specified in SP 55.13330.2011. The main purpose of the calculation is to determine the size of the channels in accordance with the volume of air removed.

The calculation is made for each floor, following the following sequence:
- Find from Table 1 of the Building Rules the total minimum volume of air (Qp) coming from the street in the amount necessary for ventilation of rooms equipped with supply valves.
- From the relevant section of the standards, select the total minimum volume of air masses to be removed (Qв) from all rooms equipped with an exhaust duct.
- The obtained minimum parameters (Qп and Qв) are compared. A large value will be the lowest calculated air capacity (Qр) of all exhaust shafts on the floor.
- Based on the height of the house, choose the vertical size of the shaft on the floor.
Based on the height of the ventilation shaft and the minimum productivity of the channels located on the second floor, the number of shafts is selected using a special table.
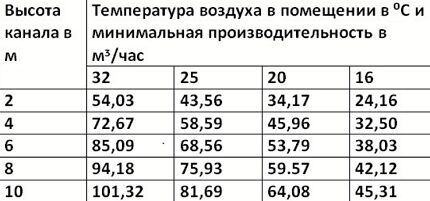
The selected standard channels must have a total capacity in mᶾ/hour no less than the calculated Qр. The shafts are distributed between rooms so that standard air exchange is ensured in each of them.
If it turns out that air speed and the performance of the air duct is insufficient, then increase the shaft length or cross-section. To ensure equal draft in each air duct, all channels on the floor must have the same length.
It should be noted that the above calculation scheme is a simplified version. A professional calculation is much more complicated and can only be performed by a specialist.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The author of this video spoke about creating ventilation in a private house and solving problems that arise during its installation:
The process of installing supply ventilation is shown in the video:
A reasonably designed ventilation system in a house is the key to the health of the people living in it. But this is not its only task - it must preserve the structural elements of the building from gradual destruction under the influence of high humidity.
Information about the types of ventilation systems and operating features will help you choose the best option for optimal air exchange in the house.
Please write comments in the block form below. Tell us about how you installed a ventilation system in your own country house or two-story dacha. Share useful information on the topic of the article, because it can be very useful to site visitors.



