Extruded polystyrene foam: characteristics, features of choice, scope of application
Home maintenance costs a significant amount of money, and you probably know it.Agree that while prices are rising, it would not hurt to optimize costs. You've definitely heard about insulation as one of these options. For example, if we talk about extruded polystyrene foam, the characteristics are at a fairly high level at a relatively low cost. It would be nice to know about all the properties of this material, right?
Postponing everyday issues until later can be a rash decision. You can understand the main properties of all insulation materials by spending just 10 minutes on each one. Don't forget also that sometimes you have to redo something for a long time before starting something again. Keep in mind: a material as simple as extruded polystyrene foam can retain most of the heat that goes to waste.
The extruded polystyrene foam sold is not always the same, so it would be good to know what the differences are and how to choose the best material. This article is about exactly this, and also about the scope of its application and various physical features. We have provided you with the information you need in the most convenient form.
The content of the article:
Basic properties of extruded polystyrene foam
One of the types of polystyrene foam is polystyrene foam. They are a mass of small air bubbles in shells. There are extruded polystyrene foam (extruded, penoplex, EPS, extrusion), regular or non-pressed, pressed, autoclaved and other types.
The usual version of expanded polystyrene consists of polymer - 2% and air - 98%. For extruded material, the solids content is about 10%. Strength penoplex 2.5 times more, and it increases as the number of sheets increases.

In the USA, Western Europe and Russia today they note that extruded polystyrene foam is less harmful. In European countries, insulation using conventional polystyrene foam is increasingly prohibited, as it emits more harmful substances when burned.
The following parameters are characteristic of penoplex:
- thermal conductivity: 0.029—0.034;
- water permeability: 0.2-0.4%;
- specific gravity: 25–45 kg/m³;
- bending strength: 0.3-0.45 MPa;
- compressive strength: 200-500 kPa.
Penoplex is made by extrusion. That is, through mixing the granules at high pressure and temperature, with further extraction from the extruder.
First, the base in the form of styrene copolymers is melted, and then a hydrocarbon or nitrogen-containing type foaming agent is added. Then the mass is processed with tools, compressed and shaped. During the process, the material cells are saturated with carbon dioxide or natural gas. The cells are closed, and the surface of the insulation is relatively flat and smooth.
At the same time, penoplex and other types of polystyrene foam can be produced from the same raw materials.
High-quality penoplex is characterized by a closed porous structure with a uniform surface and cells of 0.1-0.2 mm. Due to the air-containing composition, penoplex has low thermal conductivity, which gives the material ideal thermal insulation properties. It retains heat 3 times better than wood and up to 20 times better than other building materials.
The extruded material has high mechanical resistance, low water and vapor permeability. It allows less air and moisture to pass through than conventional foam, and when using it, you can do without a vapor barrier. Extrusion is produced in the form of plates, flexible material and rolls.
Extruded polystyrene foam has a great advantage over mineral insulation and the like, because it hardly changes when exposed to water, while mineral materials generally become unusable. In general, you will need 3-4 times more mineral insulation than extruded polystyrene foam.
Both penoplex and ordinary polystyrene foam are lightweight and have good technical parameters; they are convenient for installation work. Penoplex is denser than many other types of foam.

TO thermal insulation place high demands on safety, stability and technical parameters.
There is a method for determining durability. It provides for compliance with the capabilities of the foundation blocks. Their normal service life is 40 years. Materials that cannot be replaced during the process must provide the same service life.The service life of extruded polystyrene foam potentially reaches more than half a century.
IN Federal Law No. 123 regulated toxicity indicators of combustion products. According to it, extruded polystyrene foam is included in the flammability groups G3 and G4.
The best polystyrene foam has a G2 rating - moderately dangerous. In fire hazardous areas and with high fire safety requirements, G3 penoplex is chosen. At the same time, the material must maintain the same service life - 40 years.
Modern polystyrene foam contains fire retardants, the function of which is to neutralize the effect of pyrene. The material burns quickly, but does not support the flame and goes out. Any type of polystyrene foam has this quality, but the rate of attenuation can vary greatly. Sometimes the extruded material is not in favor.
Pros and cons of penoplex
Extruded polystyrene foam has many positive qualities.
It has low thermal conductivity - this is the main feature that makes the material an ideal insulation.

Penoplex retains its original properties for a long time. Thermal insulation performance remains at the same level after 1000 freeze/thaw cycles. Thermal resistance changes by no more than 5%. The physical and mechanical properties remain unchanged for a long time even when the temperature changes in the range of -50…+75 °C.
Penoplex is easy to use. Its installation is simple and the need for tools is minimal.
Extrusion is resistant to a number of substances and factors common in everyday life: vegetable oils, ammonia, cement, organic and inorganic acids, rodents, dyes, alkali. The material is also not in danger of biological decomposition. Unlike regular polystyrene foam, extrusion does not crumble when compressed, stretched or impacted.
Extruded polystyrene foam absorbs water minimally. Penoplex immersed in water will be filled with moisture no more than 0.5% by volume. He will completely stop absorbing it after 10 days. We are talking about quality material.
To the advantages, and at the same time to the disadvantages, it is worth adding low vapor permeability. In terms of its ability to pass steam, 1 layer of extrusion 2 cm thick corresponds to 1 layer of roofing felt. In this regard, extruded polystyrene foam is better than all other materials of its type.

Like all materials, extruded polystyrene foam has its weaknesses.
When arranging saunas and heated roofs, the use of this material is usually not available. If the temperature next to the penoplex exceeds 75 °C, it will begin to release many harmful compounds. The material is also vulnerable to sunlight. Penoplex also ignites, and self-extinguishing lasts about 10 seconds.
Extrusion has low frost resistance - small cracks sometimes appear in the structure. Most thermal insulation materials are preserved in frosts better than penoplex.
Loss of integrity also occurs due to contact with hydrocarbons such as polyvinyl chloride. Penoplex is susceptible to oxidation in air, but ordinary polystyrene foam oxidizes even faster.
Material selection criteria
Expanded polystyrene is a lightweight, comfortable, warm and relatively cheap material. However, it can vary significantly in quality.
Check the material standard. Ideally, take it in compliance with GOST. Manufacturers also have products according to their own specifications.
In the second case, the properties may differ significantly, and the specific gravity of the same modification may be in the range of 28–40 kg/m³. Therefore, request documents indicating physical parameters.

Be sure to feel the material and make sure it is durable. It should not lose integrity if you pressed it but did not apply significant force. In a normal extrusion, no balls will be visible at the fracture site, but only polyhedra of the correct shape. In addition, penoplex is easy to cut with a knife.
At the point of sale, you can check the storage location of penoplex. Foam plastics cannot be left uncovered in the open air, and sometimes ordinary fabric is enough; packaging is not necessary. Make sure that there is no acetone, dichloroethane, benzene, paints or varnishes near the penoplex.
Check all certificates, inspect the packaging, if any, for integrity. Find the marking sticker. It is placed on the packaging or on the material itself if it is not packaged. It is better not to buy a product without a sticker with markings.
Pay attention to the color.Only pure shades are suitable, and the less they approach a uniform color, the lower the original quality of the penoplex, or the storage option was unsuitable and the material has deteriorated. The smell of extrusion should not be unpleasant.
Check the thickness of the sheets. Determine whether the granules in each are the same.
Select penoplex depending on the intended use:
- for roofing, take penoplex with the highest specific gravity: from 33 to 45 kg/m³;
- for arranging the floor, an indicator of 33 kg/m³ is enough;
- for internal walls, 28 kg/m³ is sufficient.
Give preference to XPS penoplex, grade 40 and above. Keep in mind, the ideal extruded material is strong, but elastic and slightly pliable.

According to GOST 30244-94, polystyrene foam is the most dangerous materials in the event of fire - due to the substances released. In this case, the material fades, unlike wood. Extrusion is generally more resistant to ignition, but dies out more slowly. Its hot burning pieces will spread the flame, and in the case of strong fire, the self-extinguishing property will not help in any way.
Expanded polystyrene with increased fire safety is designated by the letter “C”. They contain fire retardants that protect against burning. Despite the fact that such material is included in the G2 flammability group, it soon becomes corresponding to G3-G4.
Fresh penoplex releases a certain amount of styrene. At temperatures above 80 °C, in addition to styrene, carbon monoxide, benzene, ethylbenzene and toluene are released.
The thickness of the sheet should be correctly calculated.Large numbers do not guarantee high reliability. It often happens that thick sheets are more likely to develop microcracks and irregularities.
In European countries, it is not customary to use foam sheets thicker than 3.5 cm on the external surfaces of buildings.

Remember that expanded polystyrene foam has soundproofing properties. The spread of noise can be reduced by using a more or less thick layer of material.
Areas of application of extruded polystyrene foam
It is used in frame construction using LSTK technologies and wood construction methods. In Europe, expanded polystyrene is preferred in 80% of cases when it comes to insulation for buildings.
Penoplex is used for layered masonry, on roofs, for example, inversion, and in floor coverings. The ideal option for thermal insulation with penoplex or ordinary polystyrene foam is to create a layer in the thickness of the building wall.
Insulating a facade using penoplex can be difficult due to the low adhesion of the material, low vapor permeability and problems with dew point calculation.
It often happens that the extrusion option is used externally, but only at the base level. For internal insulation, extruded and regular polystyrene foam may not be suitable due to a shift in the dew point and associated inconveniences. Experts consider the use of expanded polystyrene inside a building without an intermediate layer to be impractical and risky.
Penoplex is often used in basements and at foundation level, not least because mice do not chew on extruded materials. It will be just as useful when arranging the roof.

On balconies and loggias, penoplex will be better than ordinary foam. Usually these rooms are not spacious, so extruded material will save space there. Large and thick foam sheets are, on average, 5 cm thinner than regular foam sheets.
Floors are insulated with both penoplex and ordinary polystyrene foam. The benefits will be approximately the same: whether in residential, technical or utility premises.
In developed countries, extruded polystyrene foam is widely used for laying railway tracks and highways. The material reduces the likelihood of freezing of the subgrade soil and further swelling of the soil.
Penoplex copes well with the tasks encountered in the construction of sports surfaces, ice complexes, and refrigeration units. A type of material with a density of 38-45 kg/m³ is used in the construction of airfields and runways.
Construction areas where penoplex is used:
- Private, civil, industrial. Foundations, roofs, floors, walls, fences, household communications, underground structures.
- In agriculture. In greenhouses, greenhouses, storage facilities, greenhouses, farms.
- Road. Repair, reconstruction and construction of runways, roads and railways.
Extruded polystyrene foam is used as the main material in refrigeration units, containers, and refrigeration sections.
Edible and inedible food is packaged in it. This insulation is used to make various types of sandwich panels used in architectural elements.

Penoplex is combined with different materials, and it has a multi-purpose purpose:
- thermal insulation of pipelines and sewerage: pipeline, expanded clay or gravel, penoplex, soil;
- foundation insulation, on which groundwater presses: geotextiles, extruded polystyrene foam, waterproofing, foundation wall;
- external insulation of the foundation or basementa: soil, penoplex, waterproofing, wall, floor, polymer cement protection;
- pitched roof: waterproofing, lathing, extruded polystyrene foam, rafter system, drywall;
- flat roof reconstruction: gravel, filtration layer, penoplex, new waterproofing, old waterproofing, heat-insulating material, reinforced concrete slab;
- thermal insulation of inversion roof: gravel, filter layer, foam sheets, waterproofing, slab;
- thermal insulation of the first floor floor: dense soil, sand cushion, waterproofing, extruded polystyrene foam, screed;
- creating a heated floor: finished floor, penoplex, subfloor, logs;
- design of heated floors: penoplex, heating pipes, separator layer, screed;
- wall cavity insulation: facing brickwork, pressure washer, wire anchor, extruded polystyrene foam, wall;
- internal wall insulation: drywall, guides, penoplex, wall.
When thermally insulating a façade, plaster and dowel mesh are required. But the main thing is that the dew point is not on the border of the insulation.
Otherwise, the plaster may collapse due to condensation, followed by the thermal insulation. On facades it is more appropriate to use ordinary polystyrene foam.
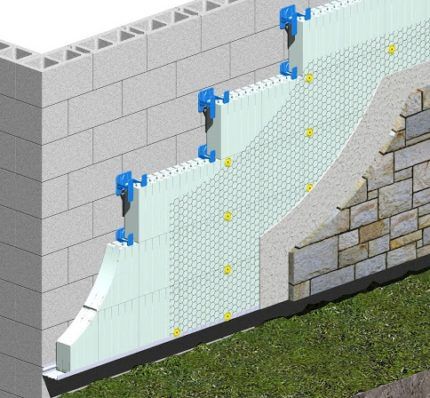
The use of expanded polystyrene foam outside provides for their protection from ultraviolet rays and atmospheric conditions. To do this, use plaster with the addition of cement.
The coating is made dense, without the slightest gaps. If you neglect this, direct and reflected rays of the sun can ruin the entire thermal insulation.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Floor insulation using penoplex - analysis of the process:
Testing different types of extruded polystyrene foam for strength:
Nuances for insulating the attic with penoplex:
Extruded polystyrene foam has long been known as an effective heat-insulating material. It is denser than ordinary polystyrene foam and other types of foam. Consider all the positive and harmful properties of the extruded version and expanded polystyrene in general.
In most cases, penoplex should be fine. On the street and where the impact of external aggressive factors is low, you can use regular polystyrene foam.
Write comments on the topic of the article.Perhaps you have some questions or information that would be valuable to other readers. The feedback form is located below the article.



