Pipes for water heated floors: a comparative overview of all options + design tips
When planning the installation of a heating system, owners of private houses are increasingly deciding to install a heating water circuit.The option is economical and versatile - it can be used to heat the entire home or as a secondary heat source.
It is used as a main, backup or additional heating source. It is easy to use, efficient, and does not take up useful space in the interior.
To achieve maximum reliability and efficiency, it is necessary to correctly select pipes for water heated floors, comparing the characteristics of each option.
In our material we will consider in detail the requirements for installing a heated floor, and will also tell you how to select pipes and calculate their required quantity.
The content of the article:
Water circuit requirements
Heating floors are a type of heating system. Therefore, design, calculation and installation are carried out in accordance with standard regulatory documents. There is no single regulation for water floors - they are guided by the rules that apply to a specific technological process.
The heating circuit is operated under fairly harsh conditions.The pipes are constantly pressed from the inside by the circulating coolant, and from the outside the coil is subjected to impressive loads: the weight of the screed, flooring, furniture and the residents themselves. Don't forget about thermal effects.

Not all materials are suitable for such specific service conditions.
Most water systems involve pouring cement or concrete mortar, which eliminates the possibility of inspecting the heating branch and carrying out repairs. Any leak is a reason to completely dismantle the floor and replace it.

The quality of the laid pipes should not be in doubt, because the system is designed for long-term operation. Products that meet a set of basic requirements are suitable for use.
Material stability
The material must respond painlessly to constant contact with the coolant liquid - the development of corrosion processes and the deposition of growths on the internal walls of the line are unacceptable.
The service life of the circuit depends on this nuance. High-quality materials can easily withstand high temperatures and have a smooth internal coating that does not accumulate lime deposits.

This requirement also presupposes the presence of the following characteristics:
- Resistance to regular temperature changes. It is optimal if the material is designed for thermal exposure of +90°C and above.
- Chemical inertness. The quality of the coolant cannot be predicted several years in advance, so it is better to use pipes that are not afraid of impurities, suspensions and minimally interact with various reagents.
- Oxygen protection. The most durable are pipe fittings with a “gas barrier”.
The separating layer prevents the flow of oxygen into the line, slowing down the diffusion destructive processes in the heating circuit.
High strength
The circuit must maintain its integrity even under unexpected conditions. water hammer and jumps in the system.
The pipes are subject to high pressure: the coolant presses from the inside, and the screed presses from the outside. In case of possible critical changes, they should be designed for 10 bar.
The “pie” of the heated floor, taking into account the concrete screed, places a significant load on the structural floors of the room. In order not to aggravate the situation, it is better to refuse heavy metal products.

Low coefficient of expansion and good thermal conductivity
As the temperature rises, materials tend to increase in volume, which can lead to damage to the screed and decorative coating. The permissible value of thermal expansion of pipes is up to 0.25 mm/mK.
High heat transfer capacity is welcomed.The higher the thermal conductivity coefficient, the higher the efficiency of the heating floor.
Ideally, the heating loop should be solid - without spliced sections. Welds on bends and tees are potential emergency zones for bursts and leaks. This means that the pipe must have the appropriate length for laying a continuous coil.

The heating line must be smooth from the inside so as not to provoke a loss of pressure. In addition to maintaining hydraulic resistance, an even coating reduces the noise effect from transporting the coolant.
Optimal weight, length and elasticity index
In addition to all of the above, you should not lose sight of a number of factors that allow you to check whether the device meets standard technical requirements:
- Optimal weight. It is prohibited to use heavy steel products in an underfloor heating installation. They overload the floors and are strictly not recommended for use in closed systems by building regulations.
- Acceptable length. Any connections in the circuit made by couplings, welding or fittings are considered a potential area for leaks and clogging. The required pipe length is determined during special calculations. Typically, the material is produced in coils and sold by the meter.
- Flexibility and elasticity. Structures that bend well by hand will not crack or break and will make it easy to achieve the desired curvilinear shape with bends of a suitable radius.
The most common diameters are 16, 18 and 20 mm.When choosing pipes for arranging a warm water floor, one point should be taken into account: a smaller diameter will increase the resistance of the liquid and, accordingly, reduce the efficiency of heat transfer.
By increasing the indicator, you will have to increase the thickness of the screed. Such manipulation will increase the load on the ceiling and raise the floor level, which is not acceptable for every room.

The diameter of the product affects the maximum length of the contour.
The larger the footage, the more obvious the risk becomes of exceeding the capacity of the circulation pump and causing fluid to stagnate in place. and how to correctly calculate the number of pipes for a heated floor, read this material.

Pipe variety: technical performance assessment
Referring to the listed requirements, we will conduct a comparative analysis of the most popular products for arranging a heating water circuit.
Manufacturers make pipes from many different materials. Among them there are budget and expensive models. They all have their advantages, disadvantages and limitations. The chosen material determines how often the need to open the floor for repairs will arise.
Metal-plastic - practicality and reliability
Heated floors are equipped with metal-plastic in every 2-3 cases.This is due to its affordable price and good technical characteristics. The composite material is made from thin aluminum strip, ultrasonically butt or overlap welded.
Thanks to the combination of two materials, it was possible to achieve high technical characteristics. Composite pipes have a complex five-layer structure, where each element is responsible for a separate task.
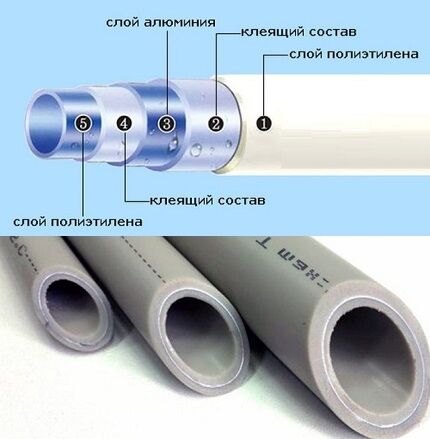

An aluminum shell located in the middle increases the rigidity of the product, compensates for the thermal expansion of the polymer, and prevents the penetration of air from the environment. The inner polyethylene layer provides smoothness and protection against corrosion.
The layers of polyethylene are fixed inside and outside with special adhesives. The adhesive composition is responsible for reliable fixation of all layers, forming a single structure. The durability of the product largely depends on the quality of the glue.

Metal-plastic products can withstand up to 110 degrees when heated without changing their original appearance.
Thanks to the bending radius of the pipes, it is possible to lay turns more often during installation, thereby achieving greater heat transfer from the system.

The aluminum layer provides good thermal conductivity, the polymer part increases resistance to damage and overgrowth by deposits from substances contained in water, and the influence of an aggressive environment. The walls of the material are well insulated, so the sound of coolant movement does not reach the room.
Composite pipes are excellent for water heated floors, as they meet a number of basic requirements.
Main advantages:
- low degree of thermal expansion;
- corrosion resistance, chemical inertness;
- high temperature tolerance;
- anti-oxygen protection;
- good flexibility, ease of installation;
- multilayer - ensures silent transportation of the coolant.
Among the disadvantages, it should be noted the detrimental effects of sudden temperature changes on the inner surface of the pipes. When it comes to bending, special care must be taken. Repeated bending and unacceptable twisting may result in damage to the aluminum layers.

A metal-plastic coil will do the job perfectly. The main thing is not to try to save money by purchasing pipe fittings of dubious quality. It is better to play it safe and choose products from reliable manufacturers: Rehau, Henco, Valtec.
Polyethylene based products
To organize underfloor heating, a water circuit is often made from polyethylene pipes.
Two categories of polymer products are used in the work:
- cross-linked polyethylene pipes (REX or XLPE);
- fittings made of heat-resistant or linear PE (PE-RT or LPE).
Both options have good physical and chemical properties and are direct competitors of metal plastic in terms of price/quality ratio. Let's take a closer look at the distinctive features of each material.
Cross-linked polyethylene
Pipes made of advanced polyethylene, compressed under high pressure, have increased density compared to conventional material. Thanks to the innovative technologies used in production, hydrocarbon molecules are interconnected, which gives PEX products unique properties.
The material is not afraid of temperature changes, is not damaged over time and is resistant to external influences. In many ways, its quality and durability are determined by the degree and method of stitching.
The optimal indicator for heated floors is 65-80 percent crosslink density. The higher this value, the higher the price of the product. An insufficient degree is negatively reflected in performance characteristics.
The properties of a polymer are a consequence of its structural filling. In ordinary polyethylene, molecular threads are in free “floating”. The lack of bonds explains the vulnerability of the material to thermal influences - it begins to melt.
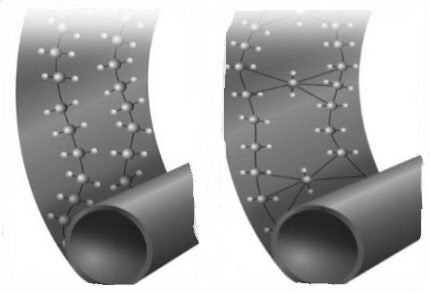
Crosslinking technology has endowed the polymer with a number of distinctive characteristics:
- high compressive/tensile strength - excellent ductility and softness;
- molecular memory that returns to its original form after heating;
- immunity to acids, most organic solvents, alkalis;
- excellent dielectric properties;
- normal performance at temperatures 0-95 degrees;
- good tolerance to pressure changes;
- lack of sensitivity to chemicals, fungi, bacteria;
- preservation of physical properties during sudden changes in environmental conditions;
- safety for health, eliminating the possibility of releasing harmful compounds.
In addition, the material has high melting temperature limits (150 degrees) and combustion temperatures (400 degrees). Despite the recommended operating range of 0-95, XLPE pipes can maintain strength from -50 to +150 degrees. However, it is worth considering that with regular increased loads, the service life of the products is reduced.
PEX polyethylene has good flexibility - the smallest loop radius is 5 diameters. This is sufficient for any circuit laying scheme.
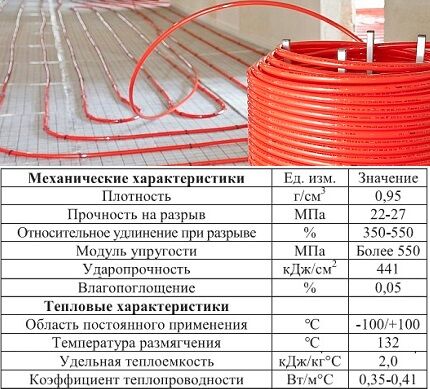
Suppliers produce pipes in bulk coils that can hold up to 600 meters. This is very convenient for installation: they can be easily laid into a single contour without using solders.
Due to the special elasticity of the device, it should be fixed with additional fasteners that will help avoid unwinding.
Weaknesses of PEX polymers: instability to UV rays and the destructive effect of oxygen that has penetrated inside the polyethylene structure. To solve the latter problem, some manufacturers produce multilayer pipes with an anti-diffusion barrier.
The technique for creating a molecular network determines the density of lateral bonds, and therefore the strength of the finished product.
Depending on the crosslinking technology, there are four groups of pipe fittings, which are divided according to the method of joining the molecules:
- peroxide - PEX-a;
- silane - PEX-b;
- radiation - PEX-c;
- nitrogen - PEX-d.
The most reliable, but also the most expensive option is models marked PEX-a. PEX-b products will be a little simpler and more affordable. But let's look at all these 4 types separately.
PEX-a. The chemical method of bond formation is fixation using organic peroxides. The reaction occurs at high temperature in molten polyethylene.
Distinctive features of PEX-a:
- stitching uniformity;
- rigidity and strength of pipe fittings;
- high price.
PEX-b. A more accessible alternative method for the production of modified polyethylene using organosilanides. The technology provides a degree of cross-linking up to 65%. An interesting feature is that in PEX-b polymer there is a constant sluggish process. Over time, the material “shrinks” and becomes stiffer. In the structure of a metal plastic, b-polymer in tandem with low-quality glue can lead to delamination.
Only PEX-b organosilanide polyethylene pipes that have a hygienic certificate are suitable for domestic use. Products based on hydrogen silica are prohibited for use in heating and water supply systems.
PEX-c. The technology involves passing a mass of polyethylene through an electron accelerator, where the polymer is exposed to gamma radiation. To reduce the cost of the process, unscrupulous manufacturers emit radioactive cobalt, which casts doubt on the safety of using such pipes.
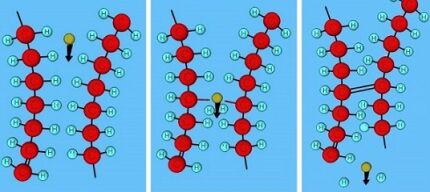
The crosslinking percentage of PEX-c polyethylene reaches 60%. The material is used as the outer/inner shell of metal-plastic pipes. However, even taking into account the reinforcement, such products are not recommended for laying a water circuit.
PEX-d. Cross-linking by nitriding is a chemical method using nitrogen radicals, the bond density reaches 70%. Rarely used due to limited production - the technology requires certain reaction conditions.
Heat-resistant polyethylene
The material was created as an alternative to cross-linked polymer, which, along with high technical qualities, is labor-intensive to produce and has some limitations in use - it cannot be welded and recycled.
Buyers often mistake PEX pipes for heat-resistant polyethylene. It should be understood that these are different materials. Cross-linked polyethylene is ahead of its analogue in terms of service life, degree of strength and resistance to aggressive operating conditions.
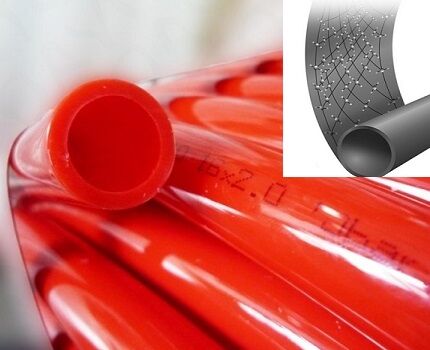
Distinctive features of a heating circuit made of heat-resistant polymer in comparison with PEX polyethylene:
- the material is not afraid of negative temperatures - the pipes retain their integrity when the water in the system freezes;
- maintainability of the coil;
- silent operation of heated floors, no squeaks when walking;
- maximum permissible peak temperature – 125°C;
- possibility of connecting pipes with fittings and welding.
PE-RT pipes are mainly produced with reinforcement or an anti-diffusion barrier. Both options are perfect for a water floor. To determine which pipe is best to use for a warm water floor in a particular case, you need to evaluate the expected load on the system.
If “wet” pouring and a heavy finishing coating (tile) are used, then a contour made of rolled metal-plastic – PERT/Al/PERT – is suitable.
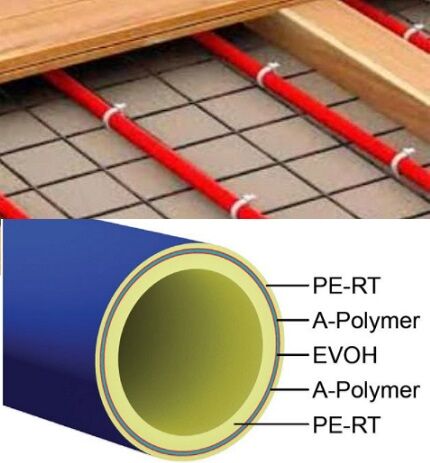
Polypropylene - saving is harmful
Polypropylene is not suitable for creating warm floors for a number of reasons:
- High linear expansion rate. The reinforcement poured into the screed will be constantly subject to internal stress at high temperatures, which over time will negatively affect the pipes themselves and the floor covering. The situation is not particularly improved by reinforcement with fiberglass or a metallized layer.
- Lack of flexibility. Polypropylene is a rigid material, the permissible bending radius is about 9 diameters of the reinforcement.This requires increasing the step between branches, which is not always acceptable. Some craftsmen resort to welding the joints of the circuit, greatly increasing the risk of leaks. For example, if the diameter of a polypropylene tube is 16 mm, then the minimum pitch for laying sections for it is 128 mm. This distance does not always fully provide the required thermal power.
- Low thermal conductivity. Polypropylene will not ensure proper heat transfer from the coolant to the floor, which means the heating system will be ineffective.
The main argument for PP pipeline is low cost. However, in this case, cost savings are not practical.

However, polypropylene has very attractive characteristics: low specific gravity, ease of installation, environmental friendliness, non-corrosion, plasticity and sound insulation.
These properties are quite sufficient for arranging a water supply system or a classic heating branch with radiators. After heat welding with a soldering iron, the products become ultra-strong, almost monolithic. They should be taken only for small rooms.
Copper piping – durability and efficiency
Copper heating pipes are characterized by maximum durability and excellent thermal conductivity. Today, many new technologies are being developed, but copper retains its position and does not lose its relevance.
Bacteria do not multiply on its surface, it is not afraid of the corrosive processes inherent in the humid environment created by the coolant liquid, and it withstands almost any mechanical stress.

The arsenal of copper piping characteristics is dominated by positive qualities:
- resistance to liming, non-corrosion;
- complete impermeability to gases;
- stability and durability of matter;
- mechanical strength - pipes can easily withstand water hammer, temperature surges and pressure within 400 atm;
- high thermal conductivity, ensuring the efficiency of the heating system.
The copper circuit can bend along a small radius. Such pipes are suitable for any method of laying heated floors, regardless of the given shape of the coil.
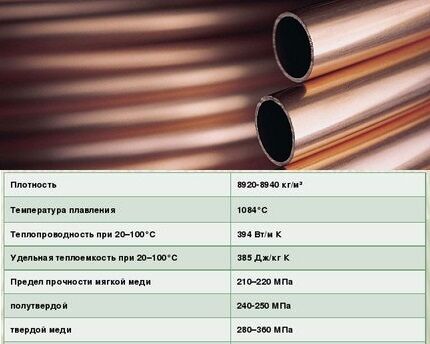
Copper also has several disadvantages. The most noticeable of them is the high capital investment at the floor installation stage. To install the coil, you will need special equipment and connecting elements made of brass.
In addition, the material is sensitive to water quality. If it is too hard or acidic, negative electrochemical processes are triggered, reducing the operating time by several times.
The last limitation is the complexity of installation. To complete this, you will need a machine or pipe bender. Since this equipment is expensive, you will have to invite a team of specialists to install a heated floor.
Combination of stainless steel and corrugation
Relatively recently, stainless steel corrugated pipes began to be installed in heated floors. Thanks to the symbiosis of the manufacturability of the corrugation and the rigidity of the metal, it was possible to obtain an easily bending, durable channel for coolant circulation.
The design features of the metal hose pipe give the thermal circuit a number of advantages:
- variability of the bending radius - you can set any configuration of the coil manually;
- maintaining capacity at the bend;
- corrosion resistance of stainless steel;
- high thermal conductivity;
- light weight of the system and low noise threshold;
- temperature range – from -50 °C to +110 °C;
- burst pressure at +20 °C – 210 bar.
In fact, stainless corrugation has a full range of required qualities along with a more affordable cost compared to copper products.
Optimal diameter of pipe fittings
When choosing a circuit cross-section, it is necessary to take into account the length of the heating branch and the heat transfer rate of the material. The most commonly used rolled products are 16, 20, 25 mm in diameter.
Nuances of determining the optimal size:
- as the diameter decreases, the hydraulic resistance increases and the heat transfer intensity decreases;
- an increase in the cross-section of the pipeline must be accompanied by an increase in the thickness of the screed - this leads to a rise in the floor level and an increase in the load on the floor.
If the parameters of the length and diameter of the heating circuit do not match, the hydraulic resistance may exceed the technical capabilities of the pumping equipment.
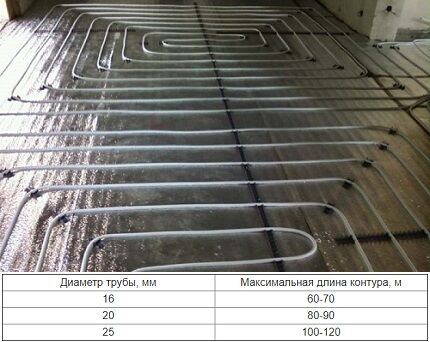
The thermal conductivity of materials should also be taken into account. When laying a coil made of copper or metal-plastic, it is permissible to use pipe fittings of small diameter - 14, 16 mm. Installation of polymer products – 20, 25 mm.
We also recommend reading our other article, where we examined in detail the options for pipes for heated floors. Read more - read Further.
How to calculate the required number of pipes?
After choosing the optimal type of pipeline, you should not rush into the purchase. The first step is to calculate how much material will be needed to install a high-quality heated floor.

A laying diagram drawn on graph paper will help you make accurate calculations. A scale plan of the room is transferred to it, where the existing household appliances and large-sized furniture are displayed. The heating circuit is drawn in a section of free space.
There are two main laying schemes:
- Spiral. The pipe is laid in turns at double intervals, which gradually go to the middle of the room, constantly repeating the contour of the perimeter. Having reached the central point, they return to the collector.
- Snake. The pipeline is laid along the entire perimeter and then parallel to the wall. The segments meet at the starting point.In this scheme, the zone close to the insertion can warm up more than the remote area.
- Double helix Most often used in rooms of complex shape, when it is necessary to select an area based on heating intensity.
The recommended length of the pipeline in one circuit is no more than 80 meters. Otherwise, the coolant will cool down, reducing heating efficiency.
If the room is too large, it is advisable to divide it into separate sectors. The boundary gap between adjacent lines for uniform heating is no more than 35 centimeters - the interval should decrease in places of large heat loss. You should also take into account a 15-20 cm distance from the walls.

When the drawing is ready, you can start making calculations. Everything is extremely simple: first, the total length of the contours is measured, then the resulting value is multiplied by the scale. It is better to add a few spare meters to the final figure.
Which brand should you prefer?
In order not to make a mistake in choosing and to understand which pipe for a heated water floor is better, in addition to assessing the physical properties of the materials, you should also pay attention to the name of the manufacturer.
Many companies offer a complete set for organizing underfloor heating, including a pumping and mixing unit, pipe fittings and auxiliary elements - power supply, temperature sensors, thermostat, etc.

It is better to stick to brands that have already proven themselves positively in the construction market. Purchasing proven products will guarantee proper and efficient operation of the equipment.
Today, buyers identify the following pipe manufacturers:
- Rehau (Germany). The priority direction is warm systems made of PEX polyethylene with noise absorption and an anti-oxygen barrier. Product warranty – 10 years. Under normal operating conditions (coolant temperature 60°C), the service life is over half a century. The pipes are equipped with a silent design, have high heat resistance and thermal insulation. They are durable, elastic, do not burst under stress, and can withstand loads of up to 100 degrees in emergency situations. Rehau brand products, connected by sliding sleeves, are enjoying record popularity among customers - with their participation, underfloor heating systems of a wide variety of configurations are installed.
- Sanext (Italy). Pipes made of PEX polymer with a multilayer structure - include protection against noise and gas penetration. Warranty – 10 years. The company equips pipes for underfloor heating with a reinforced oxygen barrier and applies a three-layer coating to them, which reduces noise levels. The minimum bending diameter of products is 10 cm. The company claims that its product is designed for 50 years of uninterrupted service.
- Uponor (Finland). Comprehensive solutions for organizing underfloor heating. The assortment includes polyethylene and metal-plastic fittings of different contents and all standard sizes.Pipes of this brand do not reduce the internal diameter due to corrosion and overgrowth, and are resistant to chemical additives contained in water. The products do not lose their characteristics when in contact with building materials - concrete, lime, gypsum mortar. Additional layers of protection protect against mechanical stress and oxygen penetration into the system.
- Emmeti (Italy). The manufacturer strictly controls all stages of the technological process, the manufacturing method is certified to the ISO standard. PEX-polyethylene and metal-plastic pipes are available.
- Valtec (Italy/Russia). Fittings adapted to non-standard conditions. The company has developed standard kits for certain room parameters and comprehensive solutions. Ready-made kits are convenient for self-installation. Pipes of this brand conduct heat well, are lightweight and easy to install, and allow you to create different circuit sizes without unnecessary elements. The products work well in aggressive environments and are not susceptible to the destructive effects of chemicals.
- Aquatherm (Germany). A German factory producing polyethylene pipes made using the extrusion method. The finished product is characterized by increased elasticity and a small bending radius. The products are not prone to temperature aging, corrosion, or oxidation. They operate at pressures up to 10 bar and provide good sound insulation. Components for heating systems of the Aquatherm brand occupy ranking positions in terms of technical characteristics and quality. Even with a small thickness, the products can withstand maximum temperatures and pressures.
The leaders in the production of polymer and composite pipes rightfully include: Henco Industries (Belgium), Oventrop (Germany), Kermi (Germany), Purmo (Finland), Termotech (Sweden), Neptune (Russia).
Among the producers of rolled copper, it should be noted Hydrosta (South Korea) and KME (Germany), corrugated stainless pipes – Kofulso (South Korea), Neptune (Russia).
We also recommend that you read the articles where we tell you which heated floor to choose for a particular coating:
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video review discusses in detail the structural features, physical and operational properties of various types of pipe fittings. Attention is paid to assessing the quality of metal-plastic products and PEX polymers:
What parameters should be taken into account when choosing pipe products for the heating circuit:
Tips for choosing equipment for underfloor heating:
Video on how to choose the diameter of a product:
Strength test for different types of pipes:
If the budget allows, then the ideal solution is to install a floor made of copper pipes. However, it is not necessary to overpay for the excess strength of the metal. You can make a reliable, durable and efficient heating system from metal-plastic fittings based on heat-resistant polyethylene. A worthy, more budget-friendly alternative is PEX pipes.
The efficiency of the water heated floor service will depend on the quality of materials and components. The right choice will allow you to equip the most economical, comfortable and aesthetic heating system in your home.
We hope our material helped you decide on the choice of pipes for heated floors. If you have any questions, you can ask them in the block below.




We live in a private house. They didn’t build it themselves, but purchased a ready-made version, in which the previous owners had lived since 2008. There is a heated floor. The connection to the manifold is made of metal-plastic. During the three years of our residence, a pipe made of this material has already cracked twice, fortunately it happened within the manifold cabinet. The master says that the structure of metal-plastic is very loose. What will happen next can only be expected, since all the main communications are under the screed. I would categorically not recommend metal-plastic material for this kind of communications.
As an option for underfloor heating, a water circuit is the most economical and efficient. This way, not only the entire room will be heated, but also the floor in particular. When designing, do not forget that you are doing this for more than one year and therefore the material must be durable and not subject to corrosion and, in addition, conduct heat well. Of course, not everyone can afford copper pipes, but metal-plastic is quite suitable.
In order to choose a material for arranging a heated floor, you need to take into account a number of conditions and technical characteristics, consult with a good specialist, study the topic well, I can recommend another resource “Pipe for heated floors” topikotel.ru