Safety valve in the heating system: types, purpose, diagrams and installation
Due to improper operation, temperature changes and pressure surges, failures may occur in the operation of autonomous heating systems.The negative consequences in such situations are critical: from the breakdown of individual components to the destruction of buildings and a serious threat to life.
A safety valve in the heating system will help eliminate dangerous risks. What is it and what is its principle of operation? We will consider these questions in our article. We will also analyze the types of such valves and indicate the main differences between them, consider the rules for installation in the heating system and provide recommendations for selecting and configuring safety valves.
The content of the article:
What is a safety valve for?
Heating systems are filled with water, the temperature of which is approximately 15 degrees. Circulating in a closed circuit, the coolant heats up, significantly increasing in volume. At this time, the pressure exerted on the inner surface of the pipes and the devices installed in the system increases significantly.
Exceeding the permissible limit, in most cases more than 3.5 bar, results in:
- leakage at the junctions of pipeline parts;
- damage or rupture of connecting elements and pipes made of polymers;
- boiler tank explosion;
- short circuit of electrical equipment in the boiler room.
The highest risk of emergency situations is typical for solid fuel boilers, in which it is difficult to regulate the heat transfer power.
The performance of electrical and gas equipment is quickly adjusted from starting to maximum values and vice versa. They often contain automatic security, which turns off operating elements when the temperature rises excessively.
The intensity of combustion of wood, coal and other types of fuel in a solid fuel boiler is adjusted by opening/closing the damper. In this case, the heat transfer force does not change immediately, but gradually. Due to the inertia of the heat generator, the coolant liquid can become very overheated.

When the firewood in the chamber heats up well, bringing the water in the network to the required temperature levels, the air supply is blocked, and the active flame begins to die out.
However, in a hot state, the firebox continues to release accumulated heat. Reaching 90-95 degrees, the coolant boils and triggers inevitable intense vaporization. As a result, a sharp rise in pressure is provoked.
It is in such circumstances that the safety valve comes into operation. When the limit pressure parameter is reached, it opens the shutter, clearing the way out for the formed steam. Once the values have stabilized, the valve automatically closes and goes into sleep mode again.
Its installation is mandatory not only for solid fuel boilers, but also for steam boilers, as well as furnaces equipped with a water circuit. Many modifications of heating equipment are equipped with these devices at the production stage. Often this valve is one of the elements security groups. Typically, the device is embedded directly into the heat exchanger or installed in a pipeline near the boiler.
Types of devices and principle of operation
The design of the bleed valve includes two mandatory components: a shut-off part, consisting of a seat and a valve, and a force adjuster. There are several types of equipment that have their own characteristics. They are classified according to certain criteria.
Classification #1 - by clamping mechanism
In heating systems of private houses, apartments and low-power industrial installations, preference is given to the spring type of product.
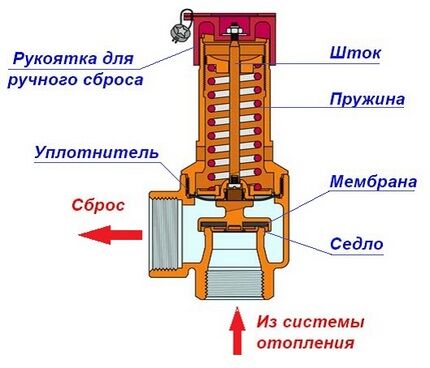
The device has a simple and reliable structure, compact dimensions, the ability to be combined with other elements of the security unit, and an affordable price. The compression force of the spring mechanism depends on the pressure parameter at which the valve operates. The tuning range is affected by the elasticity of the spring itself.
The operating principle of spring fuses is as follows:
- the valve of the device is affected by the flow of water;
- the movement of the coolant is limited by the spring force;
- critical pressure exceeds the compression force, lifting the spool rod upward;
- the liquid is sent to the outlet pipe;
- the internal volume of water is stabilized;
- the spring closes the bolt, returning it to its original position.
The body of the springy device is made of high-quality, high-strength brass using hot stamping technologies and techniques. Steel is used in the production of springs.The membrane, seals and handle are made of polymers.
Some brands produce equipment with factory settings already installed. The range also includes models that can be adjusted at the installation site during commissioning.

Lever-weight fuses are not so widespread. They are rarely installed in private autonomous systems with a boiler. Operation is concentrated in the industrial sector in large production facilities, where the diameter of pipelines is at least 200 mm.
The force on the rod in such mechanisms is provided not by a spring, but by a weight hung on the lever. It moves along the length of the lever, adjusting the force with which the rod will be pressed against the seat.
The lever-load valve opens when the pressure of the medium from the bottom of the spool exceeds that coming from the lever. After this, the water leaves through a special discharge hole.

The actuation pressure, as well as the range of settings, is determined by the length of the lever and the weight of the load. Lever fuses are not inferior to spring devices in terms of reliability, but are more expensive. The devices are installed on flanged connecting parts of pipes with a nominal diameter of 50 or more.
Classification #2 - according to the height of the shutter lift
In low-lift safety valves, the shutter rises no higher than 0.05 of the seat diameter. The opening mechanism in such equipment is proportional.
It is characterized by low throughput and the most primitive design. Low-lifting equipment is used on vessels with liquid media.

Full-lift devices have a higher shutter lift. This means that their throughput capacity is much better than that of the previous version, so they are able to discharge larger volumes of excess coolant.
Classification #3 - by response speed
The shutter cover of the proportional safety valves opens gradually. Typically, the amount of opening is proportional to the increase in pressure exerted on the inner surface. Simultaneously with the rise of the mechanism, the volumes of discharged coolant gradually increase.
The design of the devices does not limit the possibility of their use in a compressible medium, but they still predominate in systems with water and other liquids.

A feature of two-position valves is instantaneous operation with full opening after reaching the pressure limits in the system at which the safety valve opens.
Experts recommend using these devices in compressed environments. Their main disadvantages include the presence of characteristic self-oscillations of the shutter.
When installing a two-position valve in a heating system with a liquid coolant, it should be taken into account that during a sudden opening of the valve, a large amount of water will be discharged.
This will cause the pressure to drop too quickly. The valve will close instantly, which will entail water hammer. Proportional devices do not cause such risks.
Features of three-way safety valves
We should also talk about a device that is not so well known to consumers - a three-way valve with a manual or electric switch. It is used in heating systems with low temperature circuits.
The fuse design is equipped with three holes, one of which is input, two are output. The flow of the medium is controlled by a damper made in the form of a ball or rod. The moving fluid is redistributed by rotations.

Let's imagine a situation: the house has a heating scheme with a system of conventional radiators and heated floors. The technical requirements for the operation of the second option provide for not too high coolant temperatures.
The boiler heats water at the same temperature for all systems. In such conditions, there is a need for a redistributing device, the tasks of which are perfectly handled by a three-way valve.
It is responsible for the following functions:
- delimitation of areas;
- distribution of flux density by zones;
- facilitating the mixing of coolant from the main supply/return branches to send colder water into the underfloor heating pipeline than into the radiators.
In order not to constantly control the temperature of the medium yourself, you need to pay attention to valve models equipped with a servo drive.
This device operates from a sensor installed in the low-temperature circuit. When the temperature changes, a shut-off mechanism is activated, opening or closing the liquid supply from the return line.
We talked in more detail about the types of three-way valve for heating and the criteria for its selection in the next article.
Tips for choosing the optimal model
Before choosing a specific safety equipment, you must familiarize yourself in detail with the technical characteristics of the boiler installation.
Do not neglect to study the manufacturer’s instructions, which indicate all the limit values.
Several criteria play a decisive role in choosing a heating device:
- Boiler performance.
- The maximum permissible medium pressure for the thermal power of heating equipment.
- Safety valve diameter.
You should check that the pressure regulator in the device has a range that includes the parameters of a particular boiler. The response pressure should be 25-30% greater than the operating pressure required for stable operation of the system.

The diameter of the safety valve cannot be less than the connector of the inlet pipe. Otherwise, constant hydraulic resistance will not allow the fuse to fully perform its immediate tasks.
The optimal material for manufacturing equipment is brass. It has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which prevents destruction of the housing from exposure to strong pressure.
The control unit is made from heat-resistant plastic materials that maintain the required rigidity even when in contact with boiling liquid.
Installation and configuration rules
When planning to independently install a safety valve for heating, you should prepare a set of tools in advance. The work cannot be done without adjustable wrenches and wrenches, a Phillips screwdriver, pliers, a tape measure, and silicone sealant.
Before you begin, you need to determine a suitable location for installation. It is recommended to install the safety valve on the supply pipeline near the boiler outlet pipe. The optimal distance between elements is 200-300 mm.

In the regulatory documentation that comes with each device, the installation process is usually described step by step.
Some key installation rules are the same for all types of valves:
- if the fuse is not mounted as part of a safety group, a pressure gauge is placed next to it;
- in spring valves, the spring axis must have a strictly vertical position and be located under the device body;
- in lever-load equipment, the lever is placed horizontally;
- Installation is not allowed on the pipeline section between the heating equipment and the fuse. check valves, taps, valves, circulation pump;
- to prevent damage to the body when rotating the valve, you need to select the wrench from the side where the screwing is carried out;
- the drain pipe, which discharges the coolant into the sewer network or return pipe, is connected to the outlet pipe of the valve;
- the outlet pipe is not connected to the sewer directly, but with the inclusion of a funnel or pit;
- in systems where fluid circulation occurs through natural pattern, the safety valve is placed at the highest point.
The nominal diameter of the device is selected on the basis of methods developed and approved by Gostekhnadzor. In resolving this issue, it is wiser to seek help from professionals.
If this is not possible, you can try using specialized online calculation programs.
The valve adjustment is affected by the type of clamping structure. Spring devices have a cap. The pre-compression of the spring is adjusted by rotating it. The adjustment accuracy of these products is high: +/- 0.2 atm.
In lever devices, adjustments are made by increasing the mass or moving the load.
After 7-8 operations in the installed emergency device, the spring and plate wear out, as a result of which the tightness may be broken. In this case, it is advisable to replace the valve with a new one.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How does a safety valve work and what does it consist of:
Emergency valve as part of a safety group:
More information about choosing and installing the optimal safety valve:
A safety valve is a simple and reliable equipment that will protect your home from unforeseen emergencies that occur in heating systems. To do this, it is enough to choose a high-quality device with suitable parameters, and then carry out its proper configuration and installation.
Are you choosing the right safety valve for your heating system? Maybe you still have questions the answers to which you did not find in the material presented above? Ask our experts by leaving a comment below the article.
Or maybe you want to supplement the material with interesting facts and useful recommendations? Or share your experience of installing the valve into the system yourself? Write your opinion about the need for such a protective device, share tips on choosing, based on your personal experience.




I installed heating in my house using an electric boiler. When assembling the system, it is indeed important to pay attention to the safety valve. My heated room area is small, the slope is set according to the standard, so I set the pressure in the system to 1.8 bar. Nevertheless, he did not neglect safety and installed the valve. When the pressure rises to 2.1 bar, it automatically releases air. I didn’t install any more because the radiators are Chinese and it’s unknown how they will behave. At least I am sure that there will be no breakthrough in the system due to excess pressure.
The topic is useful for those who like to install certain devices and structures on their own. For example, when purchasing a water heater, in most cases a safety valve is not included in the package.A person carries out independent installation and connection, and out of ignorance does not add a valve. In any heater, the guaranteed protection against overheating may not work; as a result, without releasing the pressure, overheating or water hammer will occur; then there is no need to even predict the result.