Do-it-yourself heating boiler piping: diagrams for floor-standing and wall-mounted boilers
Autonomous heating allows you not to depend on established consumption standards, the pricing policy of heat suppliers and their mood. This makes it possible to independently control the heating process and maintain the most comfortable temperature in the house, while saving resources.
And if you wire your heating boiler with your own hands, then it will last longer and will take up less financial resources, isn’t it? But have you never engaged in tying, and the word itself seems incomprehensible to you at first glance?
Don’t be intimidated by the abundance of pipes, devices and technological steps - after reading the article, you will be up to the task. Here we consider piping schemes for floor and wall types of heating equipment, select illustrative photos and recommendations from specialists for piping at home.
The content of the article:
- Selecting the power of the heating boiler
- Types of heating boilers
- Types and schemes of heating
- Implementation of a heating system
- Step #1 - purchasing the necessary equipment
- Step #2 - installation of heating boilers
- Step #3 - selection and installation of an expansion tank
- Step #4 - installing a circulation pump
- Step #5 - Automatic Vent Valves
- Step #6 - choosing a location and installing the collector
- Step #7—installation of the pipeline
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Selecting the power of the heating boiler
A heating boiler piping is a system of pipelines and equipment designed to provide radiators with coolant. Simply put, it's everything except the batteries.
The first step is choosing a heating boiler, the performance of which must be determined in advance.
The calculation of the required power of the heating unit is influenced by many factors, these are:
- volume of the building;
- number of windows and total glazing area;
- number and area of doorways;
- thermal conductivity of materials used in the construction of walls;
- degree of insulation of load-bearing structures;
- average annual temperature in the construction region;
- location of the building, i.e. Which side of the world faces the main, traditionally most glazed, façade?
However, there is an average indicator that, without in-depth calculations, allows you to determine the required performance.
For the middle zone, 1 kW per 10 m² of heated area can be taken as a starting point (but not a guide to action!). It is imperative to add a reserve of at least 20% to the design power of the heating boiler.
Next, you need to decide on the type of heating boiler: autonomous or manual loading.

Types of heating boilers
Conventionally, heating boilers can be divided into autonomous and manual loading.
Depending on the fuel used, autonomous boilers are:
- solid fuel;
- electric;
- gas;
- liquid fuel.
The order in the list determines the cost of heating depending on the type of fuel: gas boilers will be the cheapest to operate.
These boilers are equipped automation maintaining the specified coolant temperature. They can work all year round throughout their service life. There are wall mounting And floor type installation.
Manual loading boilers include solid fuel boilers. Firewood, peat and coal are used as fuel. Requires human intervention to load fuel.
Maintaining the required coolant temperature is also a person’s responsibility.
Boiler design is floor-standing. Equipped with a minimum set of automation. Heating boilers are single- and double-circuit. A water supply is connected to the double-circuit boiler, which is built to heat hot water.
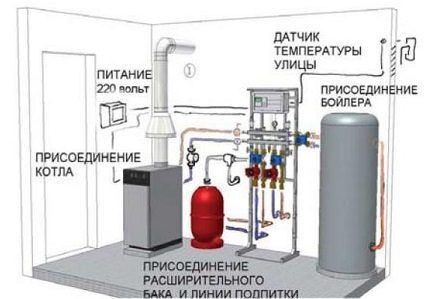
No. 1 - features of automatic type boilers
In most modern gas boilers for autonomous heating, the coolant temperature is maintained automatically.
Inside the unit there is a heat exchanger heated by a burner using liquid or gaseous fuel. The boiler temperature sensor constantly monitors the temperature of the coolant.
As soon as the temperature reaches the set point, the burner goes out and heating stops. When the coolant temperature drops below a preset limit, the burner is re-ignited.
Such ignition-extinguishing cycles can occur quite often, there is nothing wrong with that.
The vast majority of installed heating boilers heat the coolant by processing gas or liquid fuel.
This is facilitated by widespread gasification and high reliability of boilers.
Advantages of gas and liquid fuel boilers:
- ease of maintenance;
- many security systems, often redundant;
- Some equipment is included in the kit (circulation pump, pressure gauge).
The undoubted advantage is the high efficiency, which averages 98%.
There are also disadvantages:
- in the event of a lack of electricity, the entire system stops, creating the threat of defrosting;
- high price;
- the circulation pump operates around the clock;
- can only be used in closed systems.
When installing an autonomous boiler, you need to take into account the constant costs of electricity. The circulation pump runs constantly, regardless of whether the coolant is being heated or not.
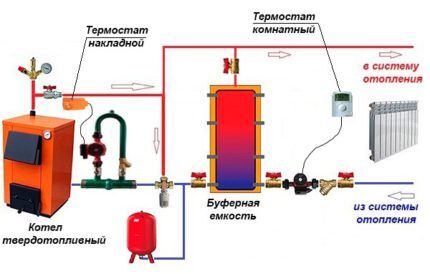
No. 2 - manually loaded solid fuel boilers
In solid fuel boilers, fuel is loaded and ignited manually. The combustion intensity can be adjusted within a limited range. The operating time is determined by the fuel burning time of one load.
Solid fuel boilers are the most universal solution; their advantages include:
- independence from electricity;
- can be used in closed and open systems;
- low price.
Units of this type operate on the most accessible type of fuel.
There are significant disadvantages:
- as a rule, they are supplied with a minimum set of equipment;
- require constant human supervision;
- have low efficiency.
To solve traditional “winter” problems, one option may be to use two boilers of different types in one heating circuit.
In normal mode, the autonomous boiler operates, and in the event of an accident on the gas or electric line, the solid fuel heating unit is manually started.
This scheme will not allow the heating system to overcool and freeze. The second option may be to use a special non-freezing coolant - antifreeze.
The choice of heating boiler piping scheme largely depends on the type of heating unit.

Types and schemes of heating
The purpose of the heating system is to transfer thermal energy from the boiler to the heating radiators. Energy transfer is carried out through coolant circulation.
The heating circuit can be implemented in the following ways:
- open single-pipe circuit;
- closed single-pipe circuit;
- closed two-pipe scheme.
The two-pipe closed heating circuit is the most progressive and has the highest efficiency. However, it is the most expensive and difficult to implement.
When heated, the volume of coolant in the heating system increases; excess coolant is collected in the expansion tank.
When cooling, the reverse process occurs: the coolant decreases in volume, the heating system sucks coolant from the expansion tank. According to the method of organizing the expansion tank, systems are divided into open and closed.
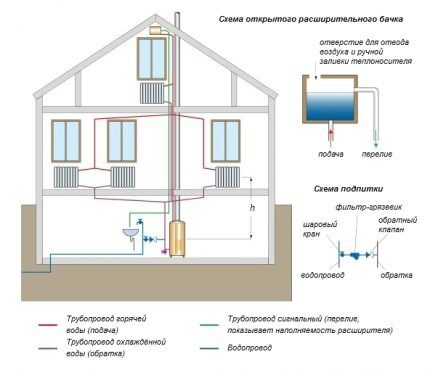
Open diagram of the heating system
With an open system, the expansion tank is open and communicates freely with the atmosphere.The general layout is as follows: the heating boiler is located at the lowest point, the expansion tank is at the highest point, relative to the heating radiator.
The greater the difference in height between the expansion tank and the topmost heating radiator, the better.
The circulation of the coolant in an open single-pipe system occurs naturally; heated water or a mixture of it with antifreeze moves due to gravity.
As the coolant cools, it becomes heavier, which is why it gradually sinks to the lower level of the system. The heavy substance pushes out the lighter, hotter coolant.
So they constantly alternate, i.e. the coolant moves around the heating system ring.
This arrangement of the heating system has its advantages:
- the simplest scheme;
- there is no need for electricity, because the coolant moves by gravity;
- low sensitivity to emergency pressure increases (for example, when boiling).
Installing a system with natural coolant movement will require the least amount of money, because there is no point in equipping it with automation, bypass valves, or a circulation pump.
Unfortunately, there are significant disadvantages:
- constant contact of the coolant with air leads to gas contamination;
- the ability to cool the coolant in cold weather;
- relatively slow coolant circulation;
- it is impossible to achieve the same temperature of heating radiators;
- a large volume of coolant is required.
With an open system, constant contact of the coolant with atmospheric oxygen leads to increased corrosion of pipelines and radiators. The formation of various contaminants reduces the overall efficiency of the heating system.
This system does not work well with aluminum and bimetallic radiators.
Open single pipe heating system is the easiest to implement and the least effective. Used with manual loading boilers. It is used mainly for heating small private buildings of one or two floors.
Closed diagram of the heating system
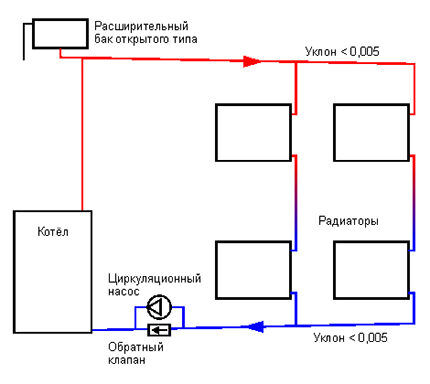
With a closed heating system, the expansion tank is made in the form of a steel container, inside of which there is a rubber bulb or membrane under air pressure. When the coolant expands, the bulb contracts and releases additional volume.
Forced circulation of the coolant allows you to warm up all heating radiators much faster and more evenly.
At the same time, the coolant, through special air vent valves, once gets rid of all the gases present in it. The pipelines remain clean and no corrosion occurs.
Boiler layout and expansion tank can be anything: the boiler can be in the basement or on the first floor. The expansion tank is usually installed next to the boiler.
Advantages of a closed system:
- clean coolant;
- guaranteed circulation
- free arrangement of equipment;
- minimum amount of coolant;
- small diameter pipelines.
Disadvantages of a closed system: constant overpressure, increased cost.
A closed, single-pipe heating system remains quite inexpensive, allowing the use of all types of boilers.
Single pipe heating system
According to the method of movement of the coolant along the pipeline diagram and the devices included in it, heating systems are divided into one- and two-pipe.
With a single-pipe heating system, a large-diameter main line runs from the boiler - the supply. It acts as a transporter of hot coolant and collector of it when cooled.
Heating radiators are connected in series to the main line by two thinner pipes. One of them receives the coolant, the second releases it.
The coolant passes through all the batteries one by one, parting with some of the thermal energy along the way.
The single-pipe category is divided into two subtypes:
- Flow-through. In the flow circuit there is no supply riser as a structural element. The radiators on the upper floor are connected to their counterparts on the floor below. In this scheme, control valves cannot be used so as not to block the access of the coolant to the following devices.
- With bypasses. According to this option, the radiators are connected by risers, but separated from the circuit by closing links. The coolant comes from the supply riser. It is distributed in portions over all devices into which it is supplied almost at the same time, due to which it cools down less.
A heating circuit with bypasses allows you to regulate the temperature and repair a faulty device without shutting down the entire system.
In this regard, the flow-through option loses in the same way as in terms of coolant cooling rate. But the flow-through version is easier to implement.
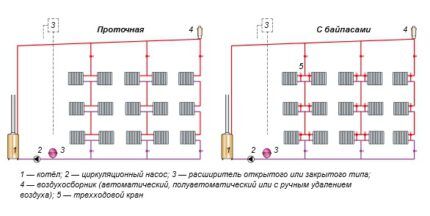
If a single-pipe circuit is used in a heating circuit with natural circulation of coolant, there are no return risers at all, and only upper wiring is used to connect devices.
Two-pipe heating system
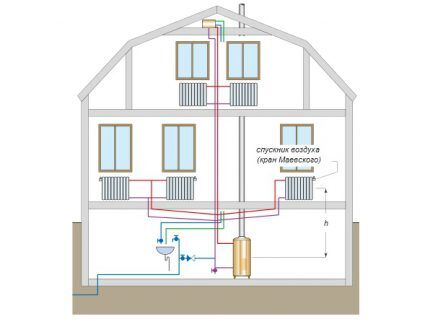
With a two-pipe heating system, one line supplies hot coolant heated by the boiler. The second one receives and transports it cooled back to the heating unit.
The receiving pipe is called the supply pipe, the collecting pipe is called the return pipe. Heating radiators are connected in parallel.
The coolant in the coldest radiator has the lowest temperature, and accordingly presses harder than the others. The greater the difference in temperature between the supply and return lines, the more intense the circulation of the coolant.
As a result, a cold radiator will warm up faster. Thus, the temperature in all devices connected to one collector is equalized.
Pros of heating with two pipes:
- adjusting the temperature parameters of one radiator does not affect the others;
- hydrodynamic stability of the entire system;
- easily allows you to connect devices to regulate the supply of hot water;
- all pipelines can be hidden in floors or walls;
- high speed and efficiency.
Two-pipe systems come with upper and lower distribution, with dead-end and associated transportation of coolant. They come with natural movement and with forced circulation, stimulated by circulation pumping devices.
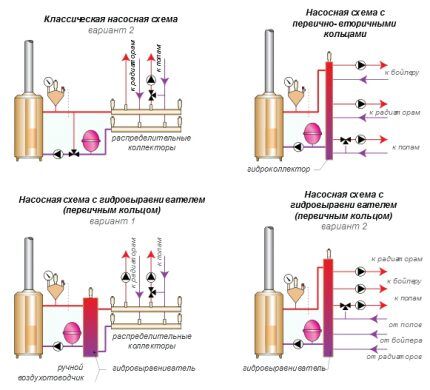
In circuits with natural circulation, the boiler is installed
The disadvantages include the following:
- double number of pipelines;
- relatively high price;
- the need to use shut-off and control valves.
The two-pipe system, despite its complex design, is the preferred solution, especially when used with autonomous boilers.
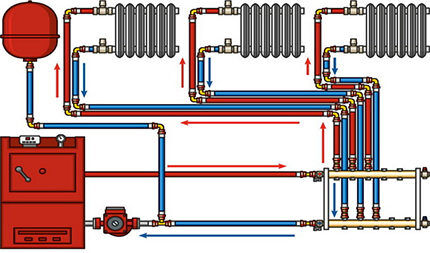
If you do not resort to complex thermal calculations, you can take advantage of many years of construction experience in the middle zone.
For the construction of the supply and collecting lines, it is recommended to use two-inch pipes (Ø 50 mm) connected to the boilers. The risers are made of pipes of the same size.
Depending on the number of sections, batteries are connected to the supply and return pipes with 1.5" (for 25-35 sections), 1" (for 10-25 sections), 3/4" (less than 10 sections).
When constructing an autonomous heating system with one or more boilers, a two-pipe system is suitable to achieve the greatest efficiency and comfortable microclimate.
It can be used on any objects. Works with any types of heating radiators and any boilers. The choice of heating scheme depends on the desired price-quality ratio and the purchased heating boiler.
Implementation of a heating system
Armed with the necessary knowledge about the principles and advantages of each heating scheme, you can create a procedure:
- selection of heating scheme;
- choice of heating boiler;
- acquisition of necessary equipment;
- installation.
To install an open, single-pipe heating circuit, it is enough to have a thermometer (in the vast majority of cases, it comes with the boiler) and an expansion tank, usually homemade.
For closed systems, the minimum required equipment is similar and is discussed below.
Step #1 - purchasing the necessary equipment
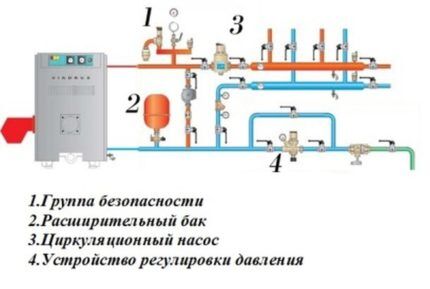
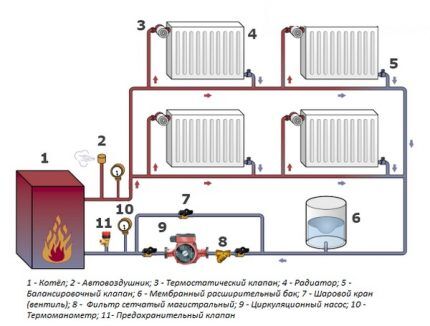
The mandatory list of equipment for closed heating systems includes:
- expansion tank;
- overpressure relief valve;
- circulation pump;
- automatic air vent valve;
- in the case of a two-pipe system, collectors (another name is combs);
- pipes.
When purchasing a heating boiler for autonomous water supply, some of the equipment may not be purchased. Equipment offered for sale, as a rule, is already equipped with a circulation pump, safety valve, expansion tank, and pressure gauge.
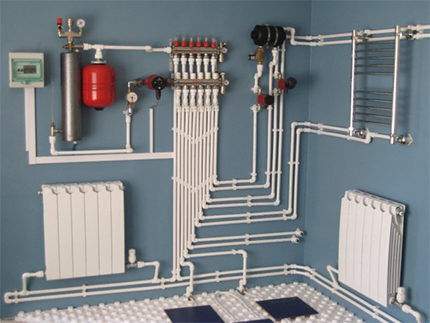
Step #2 - installation of heating boilers
Heating boilers are available in floor-mounted and wall-mounted versions. They are mounted depending on the version.
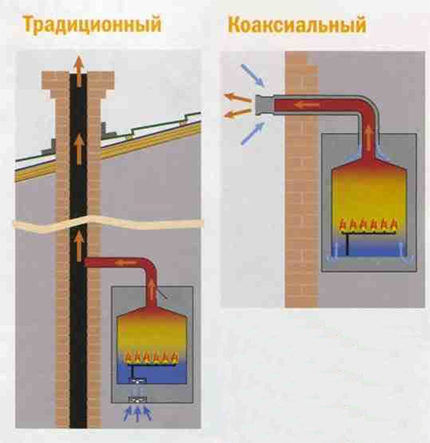
Among the wall-mounted boilers there are turbocharged ones. These are boilers that forcibly remove exhaust gases and supply air to the combustion chamber.
In such boilers, ultra-efficient fuel processing occurs, as a result of which the exhaust gases have a low temperature.
Gas removal and air supply are carried out using a special coaxial pipe. The pipe is laid out horizontally with a slight slope to the street. The slope is necessary to allow the resulting condensate to drain outside and not inside the boiler.
The choice of piping scheme for a wall-mounted boiler can only be of a closed type, since all wall-mounted boilers are autonomous.
In all other boilers, including floor-mounted manual loading ones, exhaust gases are discharged into a vertical chimney. The part of the chimney facing the street must be insulated to prevent the formation of condensation.
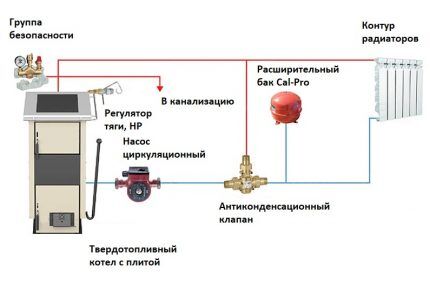
For a floor-standing, solid fuel heating boiler, you need a solid base and a platform made of fireproof material (iron sheet, ceramic tile). The piping scheme for a floor-mounted manual loading boiler can be open and closed, single-pipe and double-pipe.
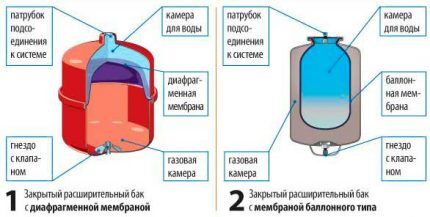
Step #3 - selection and installation of an expansion tank
Even if an expansion tank is already installed in the heating boiler, it is strongly recommended to install an additional one. The volume of the expansion tank is selected based on the volume of coolant.
A good option for installing an expansion tank would be to install it on a standard comb, along with an automatic vent valve and a pressure gauge.
Before installing the expansion tank, it must be pumped with air to the recommended pressure, usually 1.5-2.0 Atm. It is better to install the expansion tank next to the boiler.
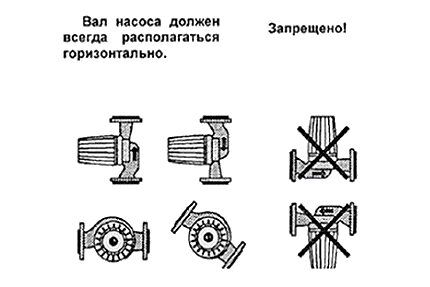
Step #4 - installing a circulation pump
The need to use an additional circulation pump, its parameters are determined by hydraulic calculations. There are a few general comments.
Operation of the circulation pump is designed for temperatures of about 60 °C.Therefore, it is advisable to install the pump on a return pipe with a colder coolant.
Also, for safety reasons, if the coolant overheats to the point of steam formation, when installing the pump on a straight pipe, the pump impeller will stop working, which will lead to even greater overheating.
The direction of movement of the coolant is clearly marked on the body of the circulation pump. The circulation pump can have any orientation, but the rotor must always remain in a horizontal plane.
Step #5 - Automatic Vent Valves
Even if air pockets form, one valve will be sufficient to remove gases. Sooner or later, the air, dissolving in the coolant, will come out through the valve. However, the dissolution rate is low and such gas removal can take up to several months.
Correct adjustment is only possible on a completely de-aerated system. To avoid waiting several months, it is necessary to install several automatic valves.
A good place to install automatic valves is on manifolds and manifolds.

Step #6 - choosing a location and installing the collector
The purpose of the collector is to distribute coolant to consumers. Consumers can be heated floors, heating radiators, and coils in bathrooms.
Structurally, the collector is a section of pipe with several bends. The number of taps must correspond to the number of consumers.
For a two-pipe system, the number of collectors is at least two. For each outlet, adjustment of the volume of supplied coolant is provided.
When organizing heating for a two-story or more house, each floor has its own pair of collectors. If there are heated floors, a separate collector must be allocated for them.
Separate collectors are required for the following reasons:
- due to the difference in the hydrodynamic resistance of pipelines between the nearest and distant heating radiators;
- with different characteristics of consumers;
- for reliable configuration of the entire system.
Due to different hydrodynamic resistance, it may be necessary to install an additional circulation pump in the heating boiler piping circuit, for example, on a heated floor manifold.
For ease of adjustment, the collectors are mounted in one place, in a special cabinet.

Step #7—installation of the pipeline
The next stage of the arrangement is the installation of heating pipes. Depending on the type of system, this stage of work will differ slightly. We propose below to consider the features of pipeline assembly for a one- and two-pipe system.
Pipes for one-pipe system
For single-pipe systems, steel pipes are the most common. A large selection of diameters and low cost make this a preferable choice.
When installing pipes, a slope of at least 5 mm per linear meter must be observed. Aesthetically, inclined pipes look worse, but ensure reliable circulation of coolant, even if the circulation pump is turned off.
Heating radiators are connected in an open system using a pipe with a minimum diameter of 32 mm. The forward and return lines are made of pipes of larger diameter, at least 50 mm.

Pipes for a two-pipe system
The two-pipe system does not require large diameters. The material of the pipes can be varied: polypropylene, metal-plastic, etc.
The main thing is that the pipes can withstand pressure and temperature. Since a two-pipe system does not require natural circulation, the pipes are hidden in the underground space or in the walls. All pipes must be insulated to prevent heat loss.
The pipes connecting the collector have a diameter of 20-25 mm, connecting heating devices 16-20 mm. respectively.

Each bend in the pipe adds flow resistance and should be avoided whenever possible. A large difference in the hydrodynamic resistance of the branches of one collector will make regulation difficult or impossible.
After installation of all components, high-pressure testing must be performed. The pressure should remain constant for at least 24 hours.
If the heating system has successfully passed the tests, the heating boiler piping can be considered complete.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparative analysis of heating system design options:
Examples of gross errors when piping a boiler:
Installation of a boiler room with a double-circuit gas boiler:
Correct connection of a long-burning solid fuel boiler:
At first glance, heating systems seem complex. However, the principles by which the heating system works are very simple. A properly designed and implemented system can work for years without any intervention.
If you have any questions about piping the boiler or the nuances of connecting individual elements of the system, ask them in the comments. Or you have just recently done your own tying and want to share your new experience with other people, please leave your comments on this material.




In my opinion, it is better to entrust such an important task as piping a boiler to specialists, because it will be difficult for a person who has never encountered this to do everything efficiently, only then will he need to redo everything. In addition, you will also have to buy equipment for soldering, and you won’t use it all the time anyway, you’ll just throw money away.
Using the example of the plumbers who do work in our apartment building, I can say that everything is not so simple. Among the specialists, we also still need to find normal ones. I had one piece of equipment installed by one elderly technician, and a few years later another piece of equipment was installed by another, younger one. Everything that the first one did still works without any complaints or leaks, but the second one has to fix leaks every year.
The most comprehensive article of all presented on the Internet today. There are controversial issues, but overall everything is fine and without advertising. Very correct organization of the article, thanks to the editors!