Rules for checking gas analyzers: frequency and methodology of work
It is likely that you have encountered government control over gas appliances.Perhaps you are an entrepreneur, and even the smallest aspects related to expenses matter to you? We believe that very few people know the rules for checking gas analyzers, and meanwhile, an unsuccessfully chosen device will ultimately cost tens of thousands of rubles in overpayment.
We tried to collect all the useful information together. We are talking about all the key points: norms, frequency, verification stages. You will thoroughly approach the choice of a gas analyzer if you read the material we have presented.
Gas analyzers are subject to government regulation, as they ensure safety at facilities in various fields of human activity. This primarily concerns verifications that are performed to ensure compliance with metrological characteristics. Let's figure out together how verification activities are carried out.
The content of the article:
Features of gas analysis instruments
A gas analyzer is a device for determining the quantitative and qualitative composition of a gas mixture. That's what science says. Hand-held absorption analyzers, in which reagents gradually absorb gas components, have become widespread. Automatic devices continuously determine the physical and physicochemical values of mixtures and their components.
Gas analyzers are divided into 3 groups.All devices operate on physical methods of analysis, and the difference is expressed in the ability to take into account chemical processes.

Type 1 devices monitor, among other things, accompanying chemical reactions. Analyzers determine changes in the pressure of the fuel mixture and its volume after chemical interaction between the components.
Type 2 gas analyzers provide indicators of physical analysis, which covers chromatographic, photoionization, electrochemical, thermochemical and other physical and physicochemical processes.
Type 3 devices operate only on the principle of physical analysis. Their measurement methods are magnetic, densimetric, thermal conductometric and optical.
Instruments for analyzing gas mixtures are also classified:
- by appointment;
- by the number of measuring channels;
- by the number of measured components;
- by design;
- by functionality.
It is worth knowing more about devices that differ in this latter characteristic. Gas analyzers perform the functions of conventional measuring instruments, as well as alarms, leak detectors, and indicators.
Areas of application of gas analyzers
Gas meters are used in explosive objects, thermal power plant boilers, chemical industry enterprises, and vehicles. Analyzers are also used before hot work in wells and basements.

The devices benefit owners of gas, vacuum and refrigeration equipment: thanks to the meters, leaks, leaks, and the concentration of flammable gases are determined. Doctors use gas analyzers to monitor concentrations in the breathing circuit during pain-relieving procedures. In the field of nature conservation, these devices have also found useful applications.
Read more about the operating principle of the gas analyzer in this material.
Verification of gas analyzers in Russia
Measuring instruments subject to state supervision are inspected for compliance with metrological characteristics. Ordinary citizens and entrepreneurs should know that since 2008, activities in this area have been regulated by Federal Law No. 102 “On Ensuring the Uniformity of Measurements”. A gas analyzer or other metering device is checked at a certain frequency, usually once a year.
Preparation for calibration of a gas meter
Calibration gas mixtures (CGMs) in cylinders are kept for 24 hours in the testing room. The gas analyzer itself is stored there for at least 2 hours. At the same time, inspection equipment is prepared, which is discussed in the operational documentation.
Based on the documents and operating instructions for a specific product, the analyzer’s equipment is checked, after which the device is prepared for operation. Preparatory measures are a component of the verification methodology for any type of gas analyzer; in the technical documentation it corresponds to point 5.

The essence of the verification is that the ASG is passed through gas analyzing equipment at the required speed.When the number of cylinders is more than 1, a multi-way valve is used. The composition is switched by simply turning the tap.
Equipment inspection sequence
The verification begins with an external inspection, and visible problems and damage are taken into account. They also look at the clarity of the inscriptions on the front panel and the condition of the threads on the fittings. According to the instructions for a specific gas analyzer, a check is carried out for serviceability.
During the process, the gas mixture will pass through the reducer and enter the line to the sensor. The check will come to its logical conclusion when the specialist determines the main indicators of metrological characteristics: errors in measurements, as well as variations in indicators with different gas contents.
The verification organization will issue a certificate or leave a mark on the device. Due to the design of some gas analyzers, the mark is sometimes placed directly on a paper document.
There are 5 types of verification:
- primary;
- periodic;
- extraordinary;
- inspection;
- expert.
The primary one is implemented before starting to operate the analyzer. Also, after repairs, owners will have to repeat the procedure.
Periodic inspections are carried out according to plan. The schedules are indicated in the documentation, and these schedules are compiled by the metrological services of enterprises. After the plan is approved by Rosstandart, it will still have to be approved by the head of the company.

Extraordinary verification will be required in case of loss of equipment inspection document, damage or prolonged downtime of the device.
Gas analyzers are also subject to inspection.This means a visit within the framework of state metrological supervision.
In case of disagreement on metrological characteristics, expert verification is resorted to. It can be appointed by the prosecutor's office or the court, but sometimes the consumer's desire is enough.
Regulatory guidelines for testing gas analyzers
The devices must operate correctly in the presence of radio interference with values within the limits of Standards 1-72-9-72. As for the indicators of the gas analyzers themselves, if necessary, not only the flow rate, but also the flow rate instead of it can be subject to standardization. If something happens, the main error is replaced by random and systematic components.
Metrological standards are established in technical or standard conditions for a specific gas analyzer, depending on the scope of application and indicating the conditions for verification work on GOST 8.401-80. Under normal conditions, the difference between the extreme measurement values for the permissible basic error is within 25%.
Conditions for work
The first thing is to ensure safety. Only those premises where there are supply and exhaust ventilation. After fulfilling this requirement, the content of harmful substances in the working area of the enterprise is checked, and the norm is indicated in GOST 12.1.005.

Employees are protected from electrical shocks based on GOST 12.2.007.0 and according to other requirements from safety regulations. Usage gas mixtures in cylinders normalize PB 03-576-03, they are also the Rules for the design and safe operation of pressure vessels.
To carry out verification, you will have to comply with the following requirements and restrictions:
- voltage 220 V;
- ASG consumption at the level of 0.18–0.35 dm³/min;
- atmospheric pressure is not lower than 84 kPa and not higher than 106;
- relative air humidity within 30-80%;
- ambient temperature from +15 to +25 °C.
Verification is carried out only by certified employees in measuring instruments according to PR 50.2.012-94. Before doing their work, they must read the gas analyzer manual and also operate the instruments.
During the process, the specialist will keep a protocol and enter the following data:
- Document Number;
- date;
- name of the owner of the gas analyzer;
- number of the device being verified;
- instrument readings and error parameters.
As a result, the owner of the meter will receive a signed certificate with the mark “Pass”, but if you are unlucky with the quality of the device, then a notice with the note “Not Pass”.
Representatives of the Center for Standardization and Metrology will immediately stop verification if they receive an unsatisfactory result in terms of variation in readings, basic or absolute error, or alarm response time.

Before verification, fuel metering equipment must have an information block, a charger and a passport. The same applies to the report on the last verification, if it was carried out, as well as replaceable cassettes and remote probes, if any.
What do you need to know about frequency?
Legislators at the state level have obliged all organizations that own gas analyzers to provide these devices for verification.The work is carried out by representatives of the State Metrological Service and certified services of private organizations. The frequency indicator for checking the sensor depends on the model of the gas analyzer, but the law says a period of 6 to 12 months, but at least once a year. However, some devices require inspection at least once every 6 months.
The period for inspection of equipment can be set by local metrological service structures. Employees of the Centers for Standardization and Metrology sometimes abuse their position and increase the frequency of inspections. The FMC may set a six-month verification period without compelling reasons.
There is also calibration - a set of measures for gas analyzers that are used outside the scope of government regulation. The interval between calibrations is not clearly established. At the same time, the methodology sometimes indicates technically sound recommendations regarding the timing of the next such procedure.
What is the essence of the testing methodology?
The verification procedure is a document with detailed operations described to confirm the suitability of the gas analyzer. The approach is different for different brands and models.
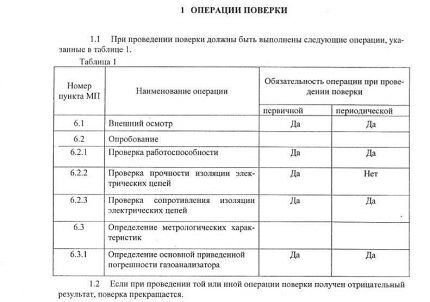
The document usually includes 7 points:
- Verification operations. We are talking about the main indicators, including errors.
- Facilities. These include instruments and gas mixtures for testing and determining metrological characteristics.
- Safety requirements.
- Conditions for carrying out.
- Preparation.
- Carrying out.
- Registration of verification results. At this stage, the verifier draws up a protocol and issues a certificate document.
Direct verification begins by connecting a cylinder with test gas to the control valve. Then a rotameter is brought to the exit. The latter is connected with an adapter for calibration work. The mixture is then allowed to enter the gas analyzer, and when the device gives readings, they are recorded.
The specialist will calculate the error and determine the time it took to establish the readings. The inspector will compare the indicators with the standards and formalize the results.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Review of a household gas analyzer, connection, principle of operation, testing:
Verification of gas analyzers and gas alarms using modern equipment:
The verifications themselves will not cause organizational difficulties, especially if due attention was paid to safety issues. A device for determining gas composition is considered suitable after the basic and absolute errors are acceptable. It is quite possible that the timing for calibrating the gas analyzer will become a problem. The consumer should seek a one-year interval instead of an unreasonably short period. An unsatisfactory result based on metrological characteristics can also be challenged.
Leave your comments, ask questions about the topic of the article, share your experience and exchange useful information. The contact form is located below the article.



