What is a gas cylinder reducer: design and operation of a device with a pressure regulator
Not all settlements and dacha areas are connected to the centralized gas supply.Unfortunately, there are still towns and villages in which bottled gas is actively used. For its safe use, a gas reducer is required - a device that reduces the fuel pressure to the values required for stoves and boilers.
We will tell you everything about the guidelines for choosing a reduction device. The information we provide will help you buy the most suitable reducer for installation on a gas cylinder. We describe in detail the types of devices and the criteria according to which preference should be given to a particular model.
Those wishing to independently install and connect the reduction device will be helped by the detailed step-by-step instructions. Here you will find rules, compliance with which will protect you and extend the service life of gas installations. The article is illustrated with photographs and supplemented with video tutorials.
The content of the article:
General rules for choosing a balloon reducer
Stable operation of the gas system depends on the quality and compatibility of all its components. When choosing a gearbox, it is necessary to take into account the compliance of its parameters with the needs of the devices connected through it.
Area of application of devices
For a gearbox, the following indicators are considered as the main characteristics:
- the type of gas that passes through the device;
- method of connection to the system;
- output pressure range;
- maximum performance;
- Operating temperature range.
Cylinders with reducers can be installed inside or outside the house.
The room in which the equipment is installed is subject to increased requirements for air exchange with the ability to quickly ventilate in the event of an emergency. The outdoor option saves space inside the building and is safer in case of flammable gas leaks.

Based on the type of gas passed through, reducers are divided into the following types, each of which is painted in a specific color for additional identification:
- acetylene - white;
- hydrogen - dark green;
- oxygen - blue;
- propane-butane - red;
- methane - red.
The color marking of gearboxes manufactured outside of Russia may differ.

The characteristics of the purchased gearbox must correspond to the parameters and type of gas cylinder and the device with which it will be installed. Correct calibration of the output gas flow power is also important.
If the pressure value goes beyond the permissible range, the automation of a modern gas appliance will turn it off. If it is not equipped with such protection, then an emergency situation may arise.
Gearboxes, as potentially dangerous equipment, are subject to mandatory certification.If you have doubts about the factory origin of the purchased device, you must request a certificate of conformity.
System connection standards
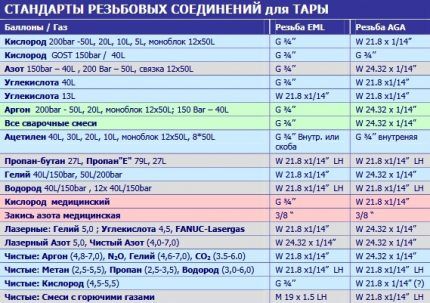
To connect the reducer to a gas cylinder or to a supply line, 3 standards of threaded connections are usually used:
- W 21.8 x 1/14 – cylindrical thread standard DIN 477/T1, in Russia the abbreviation SP 21.8 is often used for it;
- G – cylindrical pipe thread, where the number after the letter indicates the nominal diameter in inches;
- M – metric thread, where the first number after the letter indicates the nominal diameter, and the second – the thread pitch in millimeters.
Symbols "LH" indicate that a left-hand thread is used.
Some simple devices only have one connection option. Thus, the popular Type 724B gearbox from the Italian manufacturer “Gavana Group S.p.A” is equipped with a left-hand input thread W 21.8 x 1/14 for a standard metal cylinder. At the outlet there is a right-hand half-inch internal thread for connecting a bellows liner without any adapters.
A more complex device Type 733 with a pressure regulation function from the same manufacturer already has 6 inlet thread options: for metal and composite cylinders, for a multi-valve gas holder and 3 more connections. This model also has 3 output thread options.
If the input or output threads of the gearbox do not match cylinder valve or eyeliners, then use special adapters. However, the number of such connections must be minimized as they increase the risk of leakage.With standard gas equipment, it is not difficult to find a reducer with a suitable connection format.
Installation and startup procedure
First of all, installation is carried out gas supply hoses without connecting it to the cylinder. Then the reducer nut is installed on the cylinder valve and after that the hoses are connected to it.
During this operation, the taps of the gas consuming device, geyser, floor-standing gas boiler, stove, must be in the “closed” position. Before attaching the gearbox, to loosen the spring, you must turn out the adjusting screw until it stops.

If you use an ordinary flexible hose, then to simplify the procedure, the reducer fitting can be moistened with water. This connection must be secured with a screw clamp. Bellows hoses are connected using a threaded adapter, which is screwed in instead of a fitting.
After installing the system, it is necessary to check for gas leakage with the devices not working. To do this, you need to tighten the gas flow valve (if there is one) and unscrew the adjusting screw to loosen the spring as much as possible.
If, after establishing the pressure difference, the pressure gauge needle shows a gradual increase in pressure, then the reducer cannot be used.
After assembling the entire system, it is necessary to ensure the flow of gas from the cylinder to the reducer and by rotating the adjusting screw to set the required outlet pressure. Then you need to coat the connections from the cylinder to the consuming device with a soapy solution to check them for gas leaks.
If the consuming device is a gas stove, then it is necessary to light the burners sequentially. If the flame on each of the burners is not blue, then you need to reduce the pressure on the reducer.

When checking the functionality of the burners at minimum heat, there may be a problem with their attenuation. To solve this, you need to either slightly increase the output pressure using the regulator on the gas cylinder reducer, or change the position of the flow screw on the stove itself.
If the problems described above are not typical for all burners, then the jets on the problematic parts of the stove need to be cleaned or replaced. If a gas leak occurs during system startup, the shut-off valve must be completely closed. Then you need to ventilate the room and begin troubleshooting.
Required pressure and volume
The throughput of the reducer must ensure the operation of all devices connected to the system at maximum gas consumption. Some of the problem in determining the required parameters is the use of different units of measurement.
There are two pressure units for gas appliances: pascals (Pa) and bars (br). For a reducer, the inlet pressure is determined in megapascals (1 MPa = 106 Pa) or bars, and at the output - in pascals or millibars (1 mbr = 10-3 br). The conversion of pressure values between these units of measurement is carried out using the formula:
1 br = 105 Pa
The volume of gas passed through the reducer and consumed by the devices can also be represented by two quantities: kilograms and cubic meters.
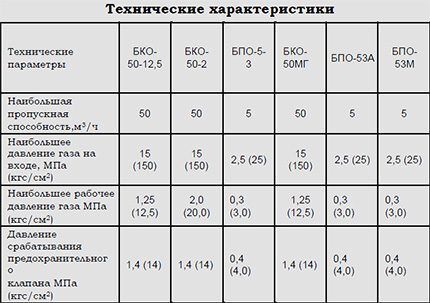
The indicators can be correlated using data on the density of the main bottled gases (kg/m3) at a temperature of 190C and standard atmospheric pressure:
- nitrogen: 1.17;
- argon: 1.67;
- acetylene: 1.10;
- butane: 2.41;
- hydrogen: 0.08;
- helium: 0.17;
- oxygen: 1.34;
- propane: 1.88;
- carbon dioxide: 1.85.
When recalculating indicators for household stoves, a problem may arise related to the proportion of propane and butane in gas cylinders. Their percentage ratio for different climatic regions is regulated by GOST 20448-90.
The density of the gas mixture depends on its percentage composition. For example, with a stated ratio of 60% propane and 40% butane, the gas density can be calculated as follows:
q = 1.88 * 0.6 + 2.41 * 0.4 = 2.09 kg/m3.
So, if the maximum gas flow of a four-burner stove is 0.84 m3/hour, then the gearbox must provide the same volume of passage. In terms of kilograms, this value will be 2.09 * 0.84 = 1.76 kg/hour.
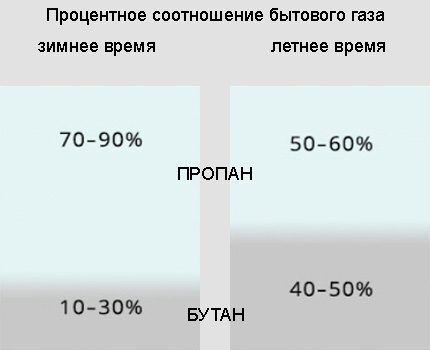
To the calculated value of the maximum throughput of the gearbox you need to add 25%.
This is due to the following reasons:
- gas mixture parameters may vary depending on the region, time of year and supplier;
- The density of the gas, which is taken in the calculations, depends on its temperature;
- there may be a loss of elasticity of the spring, which regulates the volume of the low-pressure chamber in the gearbox, resulting in a decrease in its maximum throughput.
Sometimes, complete with modern equipment, they offer a pressure-tested reducer with a pressure regulator in case of using a propane gas cylinder. This option is optimal from the standpoint of fire safety and system performance.
Design features and maintenance
Problem-free operation of the system is impossible without regular maintenance and elimination of minor gearbox faults. To do this, you need to know the design of the device and the signs of typical problems.
Diagram of direct and reverse acting devices
According to the type of design, gearboxes are divided into direct and reverse acting devices. In the first case, the excess pressure of the incoming gas is directed to open the valve, in the second - the insufficient pressure in the working chamber of the device.
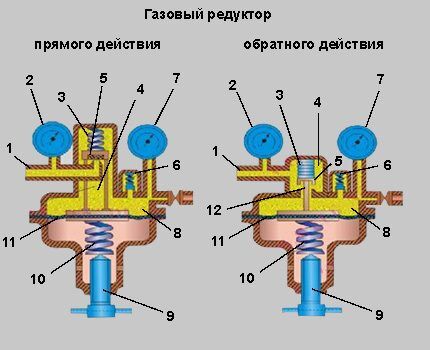
The basic elements of both types of gearbox designs are the same:
- fitting through which gas is supplied;
- high pressure gauge showing the pressure value of the gas supplied to the device;
- a return spring that works to close the valve;
- high pressure chamber;
- a valve whose position regulates the volume of gas passed through;
- a safety valve that is triggered when unacceptable pressure is reached in the working chamber;
- low pressure pressure gauge, which determines the value of the working gas pressure;
- working chamber (low pressure);
- an adjusting screw that determines the position of the membrane;
- main spring;
- working chamber membrane;
- pin between the main spring and the bypass valve.
Reverse-acting gearboxes have become more widespread because they are more reliable.
There are models equipped with a pneumatic pressure sensor, where instead of the main spring, gas acts on the membrane, ensuring the balance of the system.
As a rule, the adjusting screw is tight. This is due to the prevention of spontaneous changes in position under the influence of forces directed at the membrane. When it rotates clockwise, the volume of the working chamber decreases and the pressure of the exiting gas increases.
In ordinary gearboxes, the unevenness of the output pressure depends on the value of the input pressure and, as a rule, reaches 15-20%. Two-stage (or two-chamber) models are used when it is necessary to maintain the exact pressure of the exhaust gases.

Such gearboxes have a more complex design and slightly larger dimensions. They cost more than their single-stage counterparts. Therefore, if there is no need, their use is inappropriate.
Periodic inspection and service work
For long-term and proper operation of the gearbox, it is necessary to periodically carry out simple procedures with it. Once a week you need to record the pressure gauge readings. As the elasticity of the springs decreases, a slow but constant decrease or increase in pressure is possible.
The following actions must be performed once a quarter:
- Check the tightness of the mating gaskets, safety valve and pressure gauges with the device body. This procedure can be performed by applying a soap solution to areas of possible gas leaks.
- Bleed the safety valveand to prevent it from sticking. To do this, it is necessary to connect the gearbox to a source of compressed air and, with the outlet closed, increase the pressure until the protective mechanism is activated.
Repair and maintenance work that involves physical impact on the device body (including tightening threaded connections) cannot be carried out when the gearbox is under pressure.
This is dangerous due to the release and ignition of flammable gases. In addition, a sudden depressurization of the device may occur with possible physical harm to people in the room.

Typical faults and their repair
Gas leaks and pressure deviations outside the standard range can be eliminated independently. The first problem may be caused by the following reasons:
- depressurization of the housing;
- membrane damage.
The passage of gas through a loose connection of the housing elements can be eliminated by replacing the liner or using silicone sealant. The damaged membrane must be replaced with a similar element from the repair kit.
The reasons for deviation of the pressure value may be:
- Spring problem. It is necessary to disassemble the gearbox and determine the cause of the malfunction. If the spring is displaced, it must be corrected; if broken, it must be replaced.If there is a loss of elasticity, then it is enough to place a hard gasket under it.
- Leakage of compressed gas in devices with a pneumatic principle of pressure on the membrane. It is very difficult to fix the problem on your own. The gearbox needs to be replaced.
- Membrane problem. If a rupture occurs, it is necessary to replace the device assembly, and if there is a loss of tightness at the connection points with the washers, this malfunction must be eliminated by tightening the edges.
- Bypass valve problem. If the rubber gasket is worn out, it must be replaced. If the movement of the rocker arm is disrupted, the hinges must be replaced.
Considering the low cost of gearboxes, it is advisable to repair it only if a quick replacement is impossible. If, as a result of actions with the device, it was disassembled, then for safety reasons it is necessary to check its tightness during the first start-up.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Design of a simple gearbox for five-liter cylinders:
Video #2. An example of repair of common gearboxes of the BKO series:
The selection of a reducer for a system based on liquefied gas must be made taking into account the required pressure parameters and the volume passed through. Simple maintenance and timely elimination of minor faults will allow the device to perform its functions for a long time and efficiently.
Please write comments in the block below. Tell us about the choice of reducer that you installed on the gas cylinder, write about the rules for operating the device. Ask questions, share your opinion and photographs on the topic of the article.




In our village, not all houses have gas supply; at first we tried small gas cylinders for cooking during a power outage, this was especially true in the summer. Then they stopped bringing and exchanging small gas cylinders for us (empty ones were taken away and full ones were given out for a small price) and we purchased a large cylinder. We needed a gas reducer, but we were forbidden to install it ourselves and gas workers were visiting our houses. Is it true that purchasing and installation can be done independently?!
In general, this is the first time I’ve heard from you that there are any legislative obstacles to installing a reducer on a gas cylinder yourself. If they took money from you for installation, then I think that’s the only problem. Invented to make money.
Hello. The rules for using gas in everyday life are the same for everyone: “The population is prohibited from: 3.1. Carry out independent gasification of a house (apartment, garden house) by rearranging, replacing and repairing gas appliances, cylinders and shut-off valves.«
A simple reducer for a 50L cylinder - now you can fill such a cylinder at gas filling stations with different gases - methane, propane, butane - will it cope with the task - a safe reduction for the Gorenie gas stove? And one more thing - sometimes you can smell the smell of gas from the hole on the top cover of the gearbox - is this a malfunction, or the operating process of the device?