LED lamp circuit: simple driver design
LED light sources are quickly gaining popularity and replacing uneconomical incandescent lamps and dangerous fluorescent analogues.They use energy efficiently, last a long time, and some of them can be repaired after failure.
To properly replace or repair a broken element, you will need an LED lamp circuit and knowledge of design features. And we examined this information in detail in our article, paying attention to the types of lamps and their design. We also provided a brief overview of the devices of the most popular LED models from well-known manufacturers.
The content of the article:
How does an LED lamp work?
A close acquaintance with the design of an LED lamp may be required only in one case - if it is necessary to repair or improve the light source.
Home craftsmen, having a set of elements on hand, can assemble the lamp yourself on LEDs, but a beginner can’t do it.

But, having studied the circuit and having basic skills in working with electronics, even a beginner will be able to disassemble the lamp, replace broken parts, restoring the functionality of the device.To find detailed instructions on how to identify a breakdown and repair an LED lamp yourself, please go to via this link.
Does it make sense to repair an LED lamp? Undoubtedly. Unlike analogues with incandescent filaments for 10 rubles apiece, LED devices are expensive.
Let’s assume that a GAUSS “pear” costs about 80 rubles, and a better alternative OSRAM costs 120 rubles. Replacing a capacitor, resistor or diode will cost less, and the life of the lamp can be extended by timely replacement.
There are many modifications of LED lamps: candles, pears, balls, spotlights, capsules, strips, etc. They differ in shape, size and design. To clearly see the difference from an incandescent lamp, consider the common pear-shaped model.
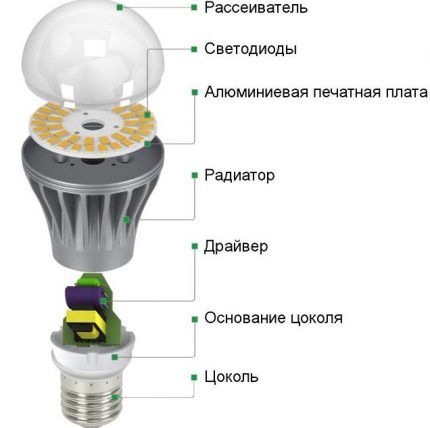
If you look away from the usual form, you can notice only one familiar element - plinth. The size range of socles remains the same, so they fit traditional sockets and do not require changing the electrical system. But this is where the similarities end: the internal structure of LED devices is much more complex than that of incandescent lamps.
LED lamps are not designed to operate directly from a 220 V network, so a driver is located inside the device, which is both a power supply and control unit. It consists of many small elements, the main task of which is to rectify the current and reduce the voltage.
Types of schemes and their features
To create the optimal voltage for diode operation, driver assembled based on a circuit with a capacitor or step-down transformer.The first option is cheaper, the second is used to equip high-power lamps.
There is a third type - inverter circuits, which are implemented either for assembling dimmable lamps, or for devices with a large number of diodes.
Option #1 - with capacitors to reduce voltage
Let's consider an example involving a capacitor, since such circuits are common in household lamps.
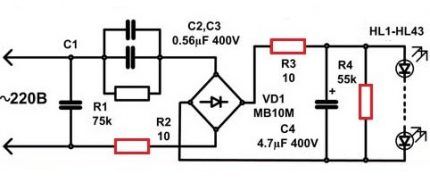
Capacitor C1 protects against power line interference, and C4 smoothes out ripples. At the moment the current is supplied, two resistors - R2 and R3 - limit it and at the same time protect it from a short circuit, and the VD1 element converts alternating voltage.
When the current supply stops, the capacitor is discharged using resistor R4. By the way, R2, R3 and R4 are not used by all manufacturers of LED products.
For capacitor checks A multimeter is often used.
Disadvantages of a circuit with capacitors:
- Diodes may burn out, since stability of the current supply is not observed. The load voltage is completely dependent on the supply voltage.
- There is no galvanic isolation, so there is a risk of electric shock. It is not recommended to touch current-carrying elements when disassembling lamps, as they are under phase.
- It is almost impossible to achieve high glow currents, because this will require an increase in capacitor capacities.
However, there are also many advantages, which is why capacitors remain popular. The advantages are ease of assembly, wide range of output voltages and low cost.
You can safely experiment with making it yourself, especially since some of the parts can be found in old receivers or televisions.
Option #2 - with a pulse driver
Unlike a linear driver with a capacitor, a pulsed one effectively protects LEDs from voltage surges and network interference.
An example of a pulse device is the popular electronic model CPC9909. Let's take a closer look at its features. The efficiency of its use reaches 98% - an indicator at which we can really talk about energy saving and savings.
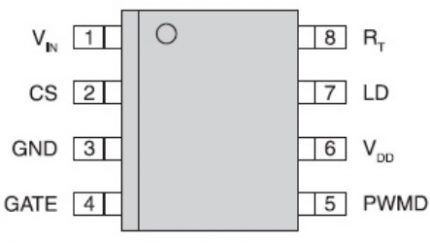
The device can be powered directly from high voltage - up to 550 V, since the driver is equipped with a built-in stabilizer. Thanks to the same stabilizer, the circuit has become simpler and the cost is lower.
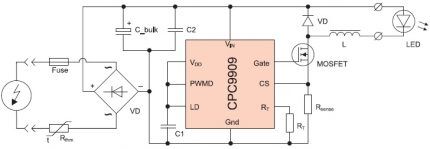
The microcircuit is successfully used for the development of electrical networks for emergency and backup lighting, since it is suitable for boost converter circuits.
At home, lamps powered by batteries or drivers with a power not exceeding 25 V are most often assembled based on the CPC9909.
Option #3 - with a dimmable driver
Adjusting the brightness of lighting fixtures allows you to set the desired level of lighting in the room. This is convenient when creating separate zones, reducing the brightness of light during the day, or for highlighting interior items.
By using dimmer the use of electricity becomes more rational, and the service life of the electrical appliance increases.

There are two types of dimmable drivers, each with their own advantages. The first ones work with PWM control.
They are installed between the lamp and the power supply. Energy is supplied in the form of pulses of different durations. An example of using a driver with PWM regulation is a creeping line.

Dimmable drivers of the second type act directly on the power source and are used for devices with stabilized current.
When regulating the current, the shade of the glow may change: white diodes begin to emit slightly yellow light when the current decreases, and blue when it increases.
Brief review and testing of popular LED lamps
Although the principles of constructing driver circuits for various lighting devices are similar, there are differences between them both in the sequence of connecting the elements and in their choice.
Let's look at the circuits of 4 lamps that are sold in the public domain. If desired, you can repair them yourself.
If you have experience working with controllers, you can replace the elements of the circuit, resolder it, and slightly improve it.
However, meticulous work and efforts to find elements are not always justified - it is easier to buy a new lighting fixture.
Option #1 – LED lamp BBK P653F
The BBK brand has two very similar modifications: the P653F lamp differs from the P654F model only in the design of the emitting unit. Accordingly, both the driver circuit and the design of the device as a whole in the second model are built according to the design principles of the first.
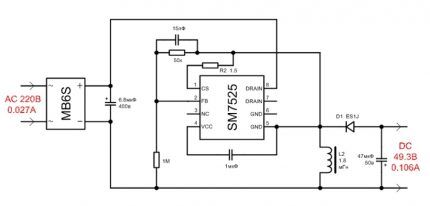
It's easy to spot flaws in the design. For example, the installation location of the controller: partly in the radiator, if there is no insulation, partly in the base. The assembly on the SM7525 chip produces an output of 49.3 V.
Option #2 – Ecola 7w LED lamp
The radiator is made of aluminum, the base is made of heat-resistant gray polymer. On a half-millimeter thick printed circuit board there are 14 diodes connected in series.
Between the heatsink and the board there is a layer of heat-conducting paste. The base is fixed with self-tapping screws.
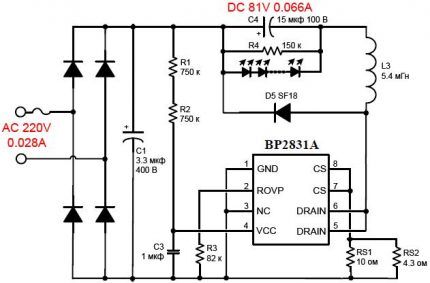
The board is completely placed inside the base and connected with shortened wires. The occurrence of short circuits is impossible, since there is plastic around - insulating material. The result at the controller output is 81 V.
Option #3 – collapsible lamp Ecola 6w GU5.3
Thanks to the collapsible design, you can independently carry out repairs or improve the device driver.
However, the unsightly appearance and design of the device spoils the impression. An oversized radiator increases the weight, so additional fixation is recommended when attaching the lamp to the socket.
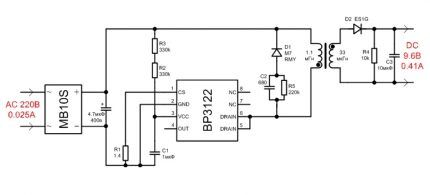
The disadvantage of the circuit is the presence of noticeable pulsations of the light flux and a high degree of radio interference, which will certainly affect the service life. The controller is based on a BP3122 microcircuit, the output value is 9.6 V.
We reviewed more information about Ecola brand LED light bulbs in our other article.
Option #4 – Jazzway 7.5w GU10 lamp
The external elements of the lamp are easily detached, so you can get to the controller quickly enough by unscrewing two pairs of screws. The protective glass is held in place by latches. The board contains 17 diodes with serial communication.
However, the controller itself, located in the base, is generously filled with compound, and the wires are pressed into the terminals.To free them, you need to use a drill or use desoldering.
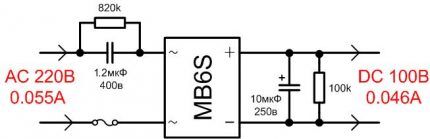
There is no radio interference - all thanks to the absence of a pulse controller, but at a frequency of 100 Hz there are noticeable light pulsations, reaching up to 80% of the maximum value.
The result of the controller is 100 V output, but according to the general assessment, the lamp is more likely to be a weak device. Its cost is clearly overestimated and is equal to the cost of brands that are distinguished by stable product quality.
We have listed other features and characteristics of lamps from this manufacturer in next article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How drivers for LEDs are designed, what their features and functions are, can be found in the videos below.
Analysis of the MR-16 LED lamp circuit:
Driver circuit for self-assembly of lamps with power up to 15W:
What the FT833A driver looks and does:
Homemade from scrap elements:
Nowadays, on commercial Internet sites you can purchase kits and individual elements for assembling lighting fixtures of various powers.
If desired, you can repair a failed LED lamp or modify a new one to get a better result. When purchasing, we recommend that you carefully check the characteristics and suitability of parts..
Do you still have questions after reading the material above? Or do you want to add valuable information and other light bulb diagrams based on your personal experience in repairing LED lamps? Write your recommendations, add photos and diagrams, ask questions in the comments block below.




When electricity prices started to rise, I replaced all the lamps in the apartment with LED ones. Several of them broke down, but I didn’t know that they could be repaired. After reviewing the information you offered, I tried to repair it. I did everything gradually, as written here, and I managed to restore two LED lamps, at the same time saving some money on buying new devices.
No matter how prices rise, health is more expensive. It is better not to use the G.. that is now sold in stores in the house. The color rendering index is usually less than 80. This is for the plebs. As a last resort: LED lamps will not harm your eyesight when used in conjunction with several conventional incandescent lamps in one chandelier.