How to choose an LED lamp driver: types, purpose + connection features
LED lamps have become widespread, as a result of which the active production of secondary power supplies has begun.The LED lamp driver is capable of stably maintaining the specified current values at the output of the device, stabilizing the voltage passing through the diode chain.
We will tell you everything about the types and principles of operation of a current conversion device for operating a diode light bulb. Our article provides guidelines for choosing a driver and provides useful recommendations. Independent home electricians will find connection diagrams proven in practice.
The content of the article:
Purpose and scope of use
Diode crystals consist of two semiconductors - anode (plus) and cathode (minus), which are responsible for the transformation of electrical signals. One area has P-type conductivity, the second – N. When a power source is connected, current will flow through these elements.
Due to this polarity, electrons from the P-type zone rush to the N-type zone, and vice versa, charges from point N rush to P. However, each section of the region has its own boundaries, called P-N junctions. At these sites, particles meet and are mutually absorbed or recombine.
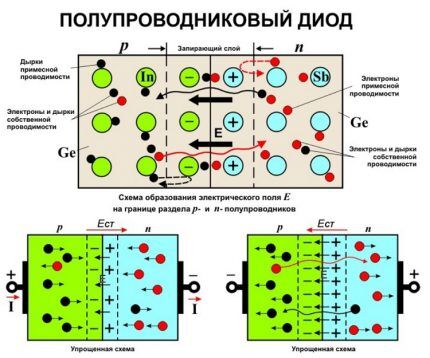
During P-N transitions, the voltage decreases by a certain number of volts, always the same for each element of the circuit. Taking these values into account, the driver stabilizes the incoming current and produces a constant value at the output.
What power is required and what values of losses during P-N passage are indicated in the passport of the LED device. Therefore, when choosing a diode light bulb it is necessary to take into account the parameters of the power supply, the range of which must be sufficient to compensate for lost energy.

Power supplies with voltages from 10 to 36 V are used to equip lighting devices.
Equipment can be of various types:
- headlights of cars, bicycles, motorcycles, etc.;
- small portable or street lamps;
- led strips, ribbons, ceiling lights and modules.
However for low power LEDs, and also in the case of using constant voltage, it is permissible not to use drivers. Instead, a resistor is added to the circuit, also powered from a 220 V network.
Operating principle of the power supply
Let's figure out what the differences are between a voltage source and a power supply. As an example, consider the diagram shown below.
By connecting a 40 ohm resistor to a 12 V power source, a current of 300 mA will flow through it (Figure A). When a second resistor is connected in parallel to the circuit, the current value will be 600 mA (B). However, the voltage will remain unchanged.
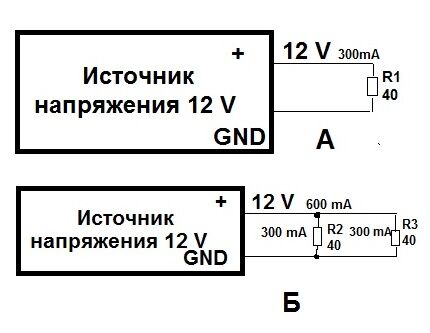
Now let's look at how the values change if resistors are connected to the power supply in the circuit. Similarly, we introduce a 40 Ohm rheostat with a 300 mA driver. The latter creates a voltage of 12 V on it (circuit B).
If the circuit is made up of two resistors, then the current value is unchanged, and the voltage will be 6 V (G).
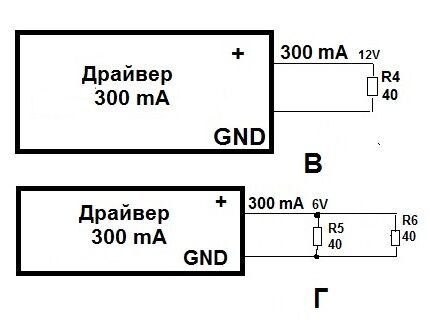
Drawing conclusions, we can say that a high-quality converter supplies the load with the rated current even when the voltage drops. Accordingly, diode crystals with 2 V or 3 V and a current of 300 mA will burn equally brightly with a reduced voltage.
Distinctive characteristics of the converter
One of the most important indicators is the transmitted power under load. Do not overload the device and try to get the best possible results.
Incorrect use contributes to the rapid failure of not only the viewing mechanism, but also the LED chips.
The main factors influencing work include:
- constituent elements used in the assembly process;
- degree of protection (IP);
- minimum and maximum values at the input and output;
- manufacturer.
Modern models of converters are produced on the basis of microcircuits and use pulse-width conversion (PWM) technology.
Such devices are characterized by a high degree of protection against short circuits, network overloads, and also have increased efficiency.
Rules for selecting a current converter
To purchase an LED lamp converter, you should study the key device characteristics. It is worth relying on the output voltage, rated current and output power.
LED power
Let us initially analyze the output voltage, which is subject to several factors:
- the value of voltage losses at the P-N junctions of the crystals;
- number of light diodes in the chain;
- connection diagram.
The parameters of the rated current can be determined by the characteristic features of the consumer, namely the power of the LED elements and the degree of their brightness.
This indicator will affect the current consumed by the crystals, the range of which varies based on the required brightness. The task of the converter is to provide these elements with the required amount of energy.

The power of the device depends on the strength of each LED element, their color and quantity.
To calculate the energy consumed, use the following formula:
PH = PLED *N,
Where
- PLED – electrical load created by one diode,
- N is the number of crystals in the chain.
The obtained indicators should not be less than the driver power. Now it is necessary to determine the required nominal value.
Maximum power of the device
It should also be taken into account that in order to ensure stable operation of the converter, its nominal values must exceed the obtained P value by 20-30%.H.
Thus the formula takes the form:
Pmax ≥ (1,2..1,3) * PH,
where Pmax — rated power of the power supply.
In addition to the power and number of consumers on the board, the load strength is also subject to the color factors of the consumer. With the same current, depending on the shade, they have different voltage drops.

Let's take, for example, LEDs from the American company Cree from the XP-E line in red.
Their characteristics are as follows:
- voltage drop 1.9-2.4 V;
- current 350 mA;
- average power consumption 750 mW.
A green analogue at the same current will have completely different indicators: losses at P-N junctions are 3.3-3.9 V, and the power is 1.25 W.
Accordingly, we can draw conclusions: a driver rated at 10 W is used to power twelve red crystals or eight green ones.
LED connection diagram
The choice of driver should be made after determining the connection diagram for LED consumers. If you first purchase light diodes and then select a converter for them, this process will be accompanied by a lot of difficulties.
To find a device that ensures the operation of exactly this number of consumers with a given connection diagram, you will have to spend a lot of time.
Let's give an example with six consumers. Their voltage loss is 3 V, current consumption is 300 mA. To connect them, you can use one of the methods, and in each individual case the required parameters of the power supply will differ.
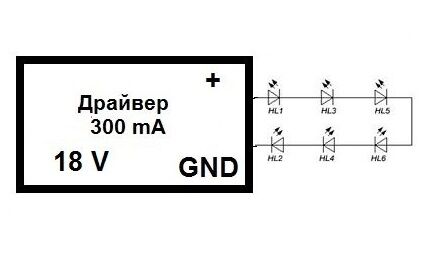
In our case, when connected in series, an 18 V unit with a current of 300 mA is required. The main advantage of this method is that the same power passes through the entire line, and accordingly, all diodes burn with identical brightness.
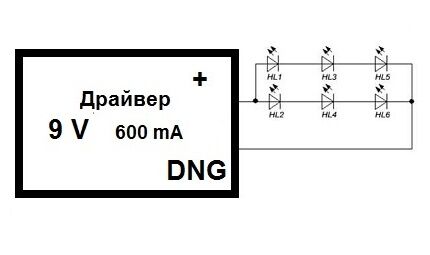
If parallel placement is used, it is enough to use a 9 V converter, however, the consumed current will be doubled compared to the previous method.
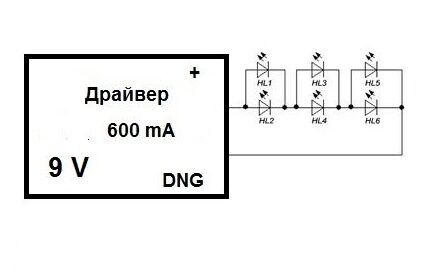
If a sequential method is used with the formation of pairs of two LEDs, a driver with similar performance is used as in the previous case. In this case, the brightness of the lighting will be uniform.
However, even here there are some negative nuances: when power is supplied to the group, due to the variation in characteristics, one of the LEDs can open faster than the second, and accordingly, a current twice the nominal value will flow through it.
Many types LEDs for home lighting are designed for such short-term jumps, but this method is less popular.
Types of drivers by device type
Devices that convert 220 V power to the required indicators for LEDs are conventionally divided into three categories: electronic; based on capacitors; dimmable.
The lighting accessories market is represented by a wide variety of driver models, mainly from Chinese manufacturers. And despite the low price range, you can choose a very decent option from these devices. However, you should pay attention to the warranty card, because... Not all products presented are of acceptable quality.
Electronic view of the device
Ideally, the electronic converter should be equipped with a transistor. Its role is to unload the control microcircuit. To eliminate or smooth out ripple as much as possible, a capacitor is mounted at the output.
This type of device belongs to the expensive category, but it is capable of stabilizing current up to 750 mA, which ballast mechanisms are not capable of.

Pulsation is not the only drawback of converters. The second can be called electromagnetic interference in the high frequency (HF) range. So, if other electrical appliances are connected to the socket connected to the lamp, for example, a radio, you can expect interference when receiving digital FM frequencies, television, router, etc.
The optional device of a quality device must have two capacitors: one is electrolytic to smooth out ripples, the other is ceramic to reduce RF.However, such a combination can be found rarely, especially when talking about Chinese products.

Due to their high efficiency (up to 95%), such mechanisms are suitable for powerful devices used in various fields, for example, for car tuning, street lighting, and household LED sources.
Capacitor based power supply
Now let's move on to less popular devices - those based on capacitors. Almost all low-cost LED lamp circuits that use this type of driver have similar characteristics.
However, due to modifications by the manufacturer, they undergo changes, for example, the removal of some circuit element. Especially often this part is one of the capacitors - a smoothing one.

Such mechanisms have only two advantages: they are available for self-assembly, and their efficiency is equal to one hundred percent, since losses will only occur at p-n junctions and resistances.
There are the same number of negative aspects: low electrical safety and high degree of pulsation. The second disadvantage is around 100 Hz and is formed as a result of rectification of the alternating voltage. GOST specifies a norm of permissible pulsation of 10-20%, depending on the purpose of the room where the lighting device is installed.
The only way to mitigate this drawback is to select a capacitor with the correct rating. However, you should not count on completely eliminating the problem - such a solution can only smooth out the intensity of the bursts.
Dimmable current converters
Dimmer drivers for dimmable LED bulbs allow you to change the incoming and outgoing current indicators, while reducing or increasing the degree of brightness of the light emitted by the diodes.
There are two connection methods:
- the first involves a soft start;
- the second is impulse.
Consider the operating principle of dimmable drivers based on the CPC9909 chip, used as a regulating device for LED circuits, including those with high brightness.
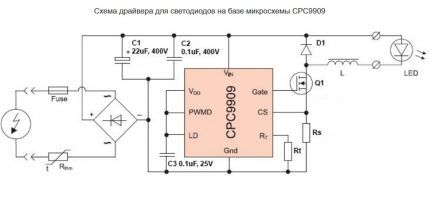
During a soft start, the microcircuit with the driver ensures gradual switching on of the diodes with increasing brightness. This process involves two resistors connected to the LD pin, designed to perform the task of smooth dimming. This is how an important task is achieved – extending the service life of LED elements.
The same output also provides analog regulation - the 2.2 kOhm resistor is replaced with a more powerful variable analogue - 5.1 kOhm. In this way, a smooth change in output potential is achieved.
The use of the second method involves supplying rectangular pulses to the low-frequency output of the PWMD. In this case, either a microcontroller or a pulse generator is used, which are necessarily separated by an optocoupler.
With or without housing?
Drivers are available with or without a housing.The first option is the most common and more expensive. Such devices are protected from moisture and dust particles.
Devices of the second type are used for hidden installation and, accordingly, are inexpensive.

Each of them differs in the permissible temperature during operation - this must also be taken into account when selecting.
Classic driver circuit
To independently assemble an LED power supply, we will deal with the simplest pulse-type device that does not have galvanic isolation. The main advantage of this type of circuit is simple connection and reliable operation.
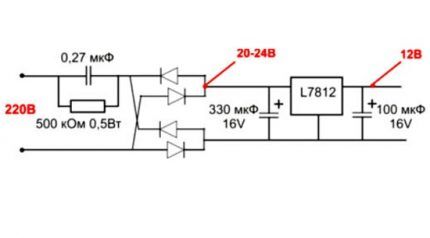
The scheme of such a mechanism is composed of three main cascade areas:
- Capacitive voltage separator.
- Rectifier.
- Surge Protectors.
The first section is the resistance provided to alternating current on capacitor C1 with a resistor. The latter is required solely for self-charging of the inert element. It does not affect the operation of the circuit.

When the generated half-wave voltage passes through the capacitor, current flows until the plates are fully charged. The smaller the capacity of the mechanism, the less time it will take to fully charge it.
For example, a device with a volume of 0.3-0.4 μF is charged during 1/10 of the half-wave period, i.e., only a tenth of the passing voltage will pass through this section.
The second stage is an electrical device that converts (rectifies) alternating current into pulsating current. This process is called full-wave. Since one part of the half-wave has been smoothed by a capacitor, the output of this section will have a DC current of 20-25 V.
The third stage operates on the basis of a smoothing stabilizing filter - an electrolytic capacitor. The choice of its capacitive parameters depends on the load strength.
Since the assembled circuit reproduces its operation immediately, you cannot touch the bare wires, since the conducted current reaches tens of amperes - the lines are first insulated.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
All the difficulties that a radio amateur may encounter when selecting a converter for powerful LED lamps are described in detail in the video:
Key features of independently connecting a converter device to an electrical circuit:
Step-by-step instructions describing the process of assembling an LED driver with your own hands using improvised means:
Despite the tens of thousands of hours of uninterrupted operation of LED lamps declared by the manufacturer, there are many factors that significantly reduce these indicators.
Drivers are designed to smooth out all current jumps in the electrical system. Their selection or self-assembly must be approached responsibly after calculating all the necessary parameters.
Tell us about how you selected the driver for the LED light bulb. Share your arguments and ways to stabilize the voltage supply to a diode lighting device. Leave comments in the block below, ask questions, post photographs on the topic of the article.




The driver is needed to stabilize the voltage and maintain the output current value. When purchasing, you need to start from the parameters of the power supply. But if the LEDs in the device are low-power, a driver is not needed. Then a resistor is included in the circuit.
The drivers we sell are mostly made in China (as are most everything else). The prices for such drivers are low, and the quality is tolerable.
Good day, please help me choose a driver for an LED lamp with the following parameters: 24V DC 18x 0.14W 2.8W
Is a driver suitable with the following parameters: Model LED (4-7)x 1W
Output DC 12-25V 280 mA
We need an analogue of the following driver
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF DRIVER 027-002-0036
power: 36W
network connection: 185-265V / 50-60Hz
output voltage: 65-110V
output current: 230mA
I just didn’t understand one thing: if the driver is AC/DC, then does the output voltage matter? Logically, yes, but everyone focuses only on current and power. But if I have a driver with an output of 110-130VDC and not 40-60 volts, then what should I do? Just look at the current and power?
If the range of 110-130V is stated for the driver, this is a line of 40 LEDs (120V divided by approximately 3V per LED). If there is only one line with a current of 280-300 mA, then the driver must provide such a current and a power of 40W. Accordingly, if the range 40-60V is specified - this is 14-18 LEDs, perhaps 20, you need to look at the voltage drop across the LED at the nameplate current.