Thermal relay for an electric motor: principle of operation, device, how to choose
During operation of power equipment, it is constantly exposed to current overloads, which reduce its durability.Protection in such situations is a thermal relay for the electric motor, which turns off the power supply when unusual circumstances arise.
We suggest you understand the design, operating principle, types and nuances of connecting protective devices. In addition, we will tell you what parameters and characteristics should be taken into account when choosing a thermal relay.
The content of the article:
Design of thermal relays
Thermal relays of all types have a similar device. The most important element of any of them is the sensitive bimetallic strip.
The operating current value is influenced by the temperature of the environment in which the relay operates. An increase in temperature reduces the response time.
To minimize this influence, device developers choose the highest possible bimetal temperature. For the same purpose, some relays are equipped with an additional compensation plate.
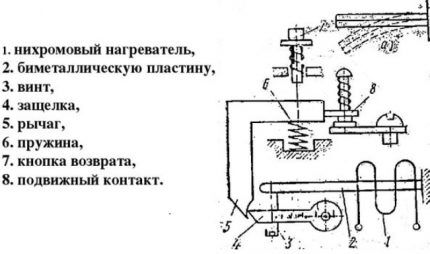
If nichrome heaters are included in the relay design, they are connected in a parallel, series or parallel-series circuit with a plate.
The current value in the bimetal is regulated using shunts. All parts are built into the body. The U-shaped bimetallic element is fixed on the axis.
A coil spring rests against one end of the plate. The other end is based on a balanced insulating block. It rotates around an axis and is a support for a contact bridge equipped with silver contacts.
To coordinate the setting current, the bimetallic plate is connected at its left end to its mechanism. The adjustment occurs due to the influence on the primary deformation of the plate.
If the magnitude of the overload currents becomes equal to or greater than the settings, the insulating block rotates under the influence of the plate. When it is tipped over, the device's normally closed contact is switched off.
The relay automatically returns to its original position. The self-return process takes no more than 3 minutes from the moment the protection is turned on. A manual reset is also possible; a special Reset key is provided for this.
When using it, the device takes its original position in 1 minute. To activate the button, turn it counterclockwise until it rises above the body. The installation current is usually indicated on the panel.
Operating principle of the device
Performing a protective function, circuit breaker disconnects power supply circuits. A thermal relay differs from it in that when the load is exceeded, it simply issues a control signal. With such protection, small currents are switched in one control circuit.
In the circuit in front of the thermal relay there is magnetic switch. When the circuits are opened in an emergency, there is no need to duplicate the operation of the contactor. Consequently, no material is consumed for the manufacture of power contact groups.
The most popular are devices equipped with bimetallic plates. The plate itself consists of two similar elements.
One of them has a significant temperature coefficient, while the other has a slightly smaller one. These two components fit tightly together.
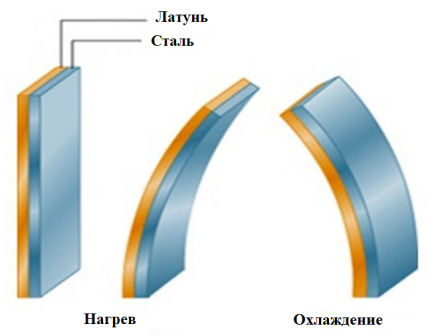
Such rigid fastening is ensured by welding or hot rolling. Due to the fact that the plate is fixed motionless, when heated, it bends towards the element with a lower temperature coefficient. This principle was taken as a basis when creating thermal relays.
In their production, chromium-nickel steel and non-magnetic steel are used, which have a high temperature coefficient. Invar, a compound of nickel and iron, is used as a material with a low value of this parameter.
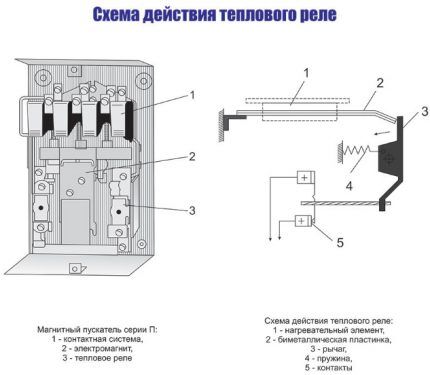
The bimetal plate is heated by load currents. They most often flow through a special heater. There is also combined heating, in which, in addition to the heat given off by the heater, the bimetal is also heated by the current passing through it.
How to connect a thermal relay
The closed contact (normal connected), which is used to connect the thermal module to the magnetic starter, is designated NC or NC, which stands for normally closed. The letter combination NO denotes a normally open contact.
In a simple circuit, it is used to provide a signal indicating that the engine protection has tripped due to exceeding the threshold temperature.
When implemented in complex control circuits, it is capable of generating an emergency signal to deactivate the conveyor.
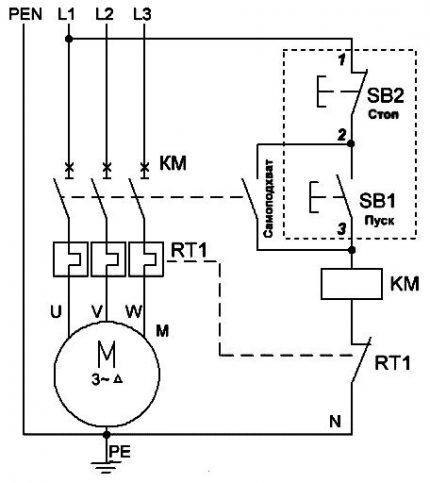
The designation of contactor terminals is dictated by GOST: normally closed - 95-96, normally open - 97-98. A starter is connected to the first pair, the second is used for signaling circuits. Since the motor and thermal relay need to be protected from short circuits, the circuit must contain a circuit breaker.
The device circuit includes “Test” and “Stop” or “Reset” buttons. The first one is used to check the functionality, and the second one is used to manually disable the protection.
Using the rotary cocking switch, after turning on the protection, the electric motor is restarted. The glass cover of the product is marked and sealed.
Based on the type of connection, two large groups of thermal relays can be distinguished:
- first group - devices mounted behind the magnetic starter and those connected using jumpers;
- second group — devices installed directly on the starter contactor.
In the latter case, during startup, the main load falls on the contactor.Here the thermal module is equipped with copper contacts connected directly to the starter inputs.
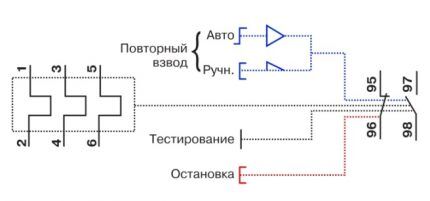
Wires from the engine are connected to the TP. The relay itself in such a circuit represents an intermediate unit that analyzes the current flowing in transit to the motor from the magnetic starter.
Nuances when installing the device
The response speed of the thermal module can be affected not only by current overloads, but also by external temperature indicators. The protection will work even in the absence of overload.
It also happens that, under the influence of forced ventilation, the engine is subject to thermal overload, but the protection does not work.
To avoid such phenomena, you need to follow the recommendations of specialists:
- When choosing a relay, focus on the maximum permissible operating temperature.
- Install the protection in the same room as the protected object.
- For installation, choose places where there are no heat sources or ventilation devices.
- You need to configure the thermal module based on the actual ambient temperature.
- The best option is to have built-in thermal compensation in the relay design.
An additional option for the thermal relay is protection in the event of a phase or complete power supply failure. For three-phase motors this point is especially relevant.

If there is a problem in one phase, the other two take on a larger current. As a result, overheating quickly occurs, and then shutdown.If the relay does not operate effectively, both the motor and the wiring may fail.
Existing device types
The class of thermal relays includes several types: TRN, RTL, TRP, RTI, RTT. The use of each is determined by the design features.
Two-phase current relay (TRN), are used mainly for electrical protection of asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor. As a rule, they operate from a network with a rating of up to 500 V, a frequency of 50 Hz.
The relay is equipped with a manual contact control mechanism. The dimensions of the TRN make it possible to integrate them into complete devices of both closed and open type stations that coordinate the operation of drives. They do not perform the function of short circuit protection and need it themselves.
TRP relay They have a vibration-resistant mechanism and a shock-resistant body. Designed to protect asynchronous three-phase motors operating under conditions of heavy mechanical loads.
They are designed for a maximum current of 600 A and a maximum voltage of 500 V, and in circuits with direct current - 440 V. The automation is insensitive to external temperature and operates when the indicator exceeds 200°C.
RTL devices — three-phase, in addition to protecting the motor from overloads, protects the rotor from jamming. They insure it against damage in the event of phase imbalance during a prolonged start-up.
They work autonomously with KRL terminal blocks and in a modification with a PML magnetic starter. Current operating range - from 0.10 to 86 A.

PTT — the device protects asynchronous motors from current surges, phase imbalance, jamming and other emergency situations.It is used both as a stand-alone device and as an integral part of PMA and PME starters.
Three-phase RTI product endowed with the same functions as the previous one, but is used in a modification with KTM and KMI starters.
How to choose a thermal relay
The motor needs a relay for protection when, for technological reasons, there is a potential threat of overload. The second case is the need to limit the start-up time under reduced voltage conditions.
These requirements are contained in the relevant instructions. Which sets out a request to equip a protective product with a time delay. All this is realized using thermal relays.
Basic characteristics of devices
The basic data of the device protecting the engine are:
- Contact performance depending on current parameters - time-current indicator.
- Operating current at which the TP is triggered.
- Limit current setting adjustments. In all devices produced by different manufacturers, this parameter differs slightly. Exceeding the nominal value by 20% entails the operation of the device after 25 minutes.
- Rated current value of the working bimetallic plate. This refers to a value above which the relay does not switch off immediately.
- Current range in which the relay operates.
Information about the thermal relay can be obtained by deciphering its markings. The symbol indicating the type of execution may vary.

The locations of domestic TPs are regulated by GOST 15150.Their work is influenced by such factors as the altitude above sea level, vibration, shock, and acceleration.
Manufacturers reflect all these nuances in the labeling of their products. Some of them additionally include information about the ability to work in the presence of harmful substances and explosive gases.
Selecting a device according to the rules
The requirements for the thermal relay are set out in the instructions. It is also stipulated here that the protection must have a time delay. All requests are fulfilled using special devices.
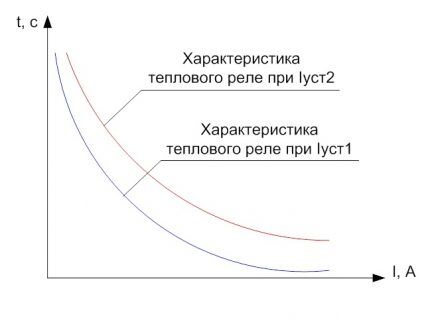
When analyzing the time-current characteristics of a TR, it is necessary to take into account that operation can occur from an overheated or cold state.
Impeccable protection assumes that the curve depicting the optimal dependence of the duration of current flow on the current value for the relay and the motor for trouble-free operation of the equipment is different. The first should be lower than the second.
The correct selection of a protective product is carried out on the basis of such a parameter as the operating rated current. Its value is related to the rated load current of the electric motor.
Both international and domestic standards stipulate that the rated current of the motor is similar to the setting of the thermal relay operating current.
This means that the device is put into operation at an overload of 20 to 30% or at Iav.x1.2 or 1.3 no later than 20 minutes.
Based on this, the choice must be made so that the non-operation current of the TR exceeds the rated current of the covered object by an average of 12%. The In value is displayed in the device passport and on a plate attached to the body.
Based on it, both the TR and the starter corresponding to it are selected. The relay scale is calibrated in amperes and, as a rule, corresponds to the setting current value.
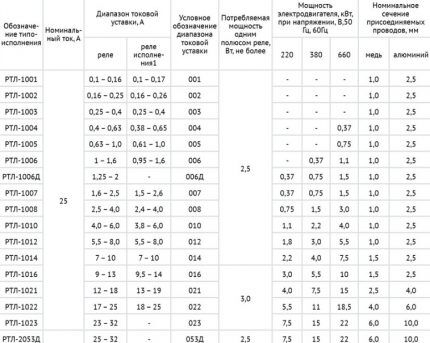
An example is the selection of a thermal relay for an asynchronous motor connected to a 380 V network with a power of 1.5 kW.
The operating rated current for it is 2.8 A, which means that for a thermal relay the threshold current will be equal to: 1.2 * 2.8 = 3.36 A. According to the table, the choice should be made on RTL-1008, whose adjustment range is in ranging from 2.4 to 4 A.

When the motor's nameplate data is unknown, the current is determined by using special devices - a current clamp or a multimeter with the appropriate option. Measurements are carried out on each of the phases.
When choosing, it is important to pay attention to the voltage indicated on the device. If you plan to use a TP-starter tandem, you need to take into account the number of contacts.
When connecting the device to a three-phase network, a module is required that has a protection function in cases of conductor burnout or phase imbalance.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Effective motor protection scheme:
Components of a thermal relay:
The principle of interaction between various devices in different connection options for a thermal relay is the same. For better orientation in diagrams, you need to be able to “read” device markings.Ideally, all connection work should be performed by a technician certified to work in high voltage conditions.
Do you have anything to add, or do you have questions about the selection and use of a thermal relay? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience of using the devices. The contact form is located in the lower block.



