Air-to-air heat pump: operating principle, design, selection and calculations
Do you want to install convector heating in your home, where an air-to-air heat pump is used to heat the coolant, providing significant savings on heating costs? Agree that getting full-fledged heating in a company with hot water practically free of charge is a very tempting undertaking.
But you don’t know how to build such a system to heat rooms in an alternative way and obtain hot water for domestic needs?
We will help you sort out this issue - the article covers the principle of operation and design of the pump. Such a system will have to spend energy only on the operation of the compressor, and the main volume of heat will simply be taken from the street from the atmosphere, for which we have not yet been asked to pay money.
The advantages of its implementation into the system and significant disadvantages are also considered. Special attention is paid to the selection and calculation of the pump.
And for those who like to do everything with their own hands, we suggest building such a pump yourself, using available materials. To help, we provide photographic materials and video recommendations on the design and operation of an air heat pump.
The content of the article:
Characteristics of air-to-air heat pump
Any heat pump belongs to equipment from the sphere alternative energy. It takes the thermal energy of air masses on the street, from the surrounding space indoors, in order to heat residential and non-residential objects with it.
It does not use any combustible fuels.
Externally heat pump (TN) air-to-air is similar to an inverter air conditioner, split system from the external and internal block.
And according to the principle of operation, it is more reminiscent of a refrigerator, only it acts “the other way around”. But unlike both of them, this heat pump is capable of both cooling and heating the air masses in the house.
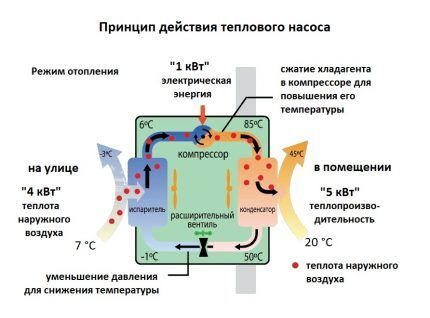
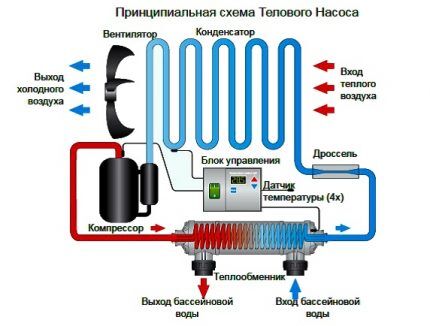
Operating principle and internal structure
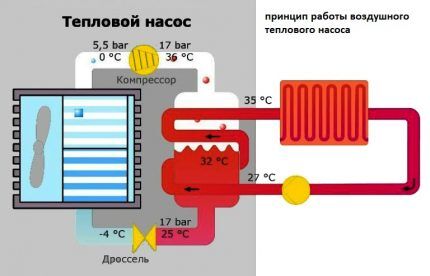
The operation of an air-to-air HP is based on a simple physical phenomenon of thermodynamics - when a liquid evaporates, it cools the surface from which it is dispersed. For example, steam over a mug of hot tea demonstrates the same effect.
A regular refrigerator works on this principle. Inside it are tubes through which refrigerant circulates under high pressure. It takes heat from the inside of the freezer, becoming slightly warmer.
Then the collected heat is released into the air of the room through a heat exchanger (the grille at the back of the refrigerator).
And in order for the refrigerant to cool down to operating temperatures, it is compressed in a compressor. Moreover, during the operating cycle freon inside the system compressor-condenser-evaporator constantly changes from gaseous to liquid and back.
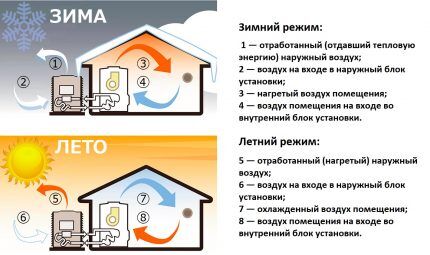
An air source heat pump functions in exactly the same way. Only it takes heat from the street, and not from a closed freezer. Even if it is frosty outside, there is still a lot of thermal energy in the atmosphere.
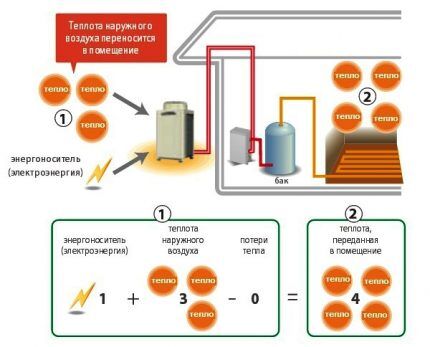
An air-to-air heat pump consists of the following elements:
- compressor;
- evaporator with forced air fan;
- expansion valve;
- copper pipes for pumping freon between the street and the house;
- condenser with a fan supplying heated air to the room.
The first three elements make up the external unit, and the last one belongs to the internal part of the heat pump. Thermally insulated copper tubes are designed for continuous movement of coolant between these split system modules.
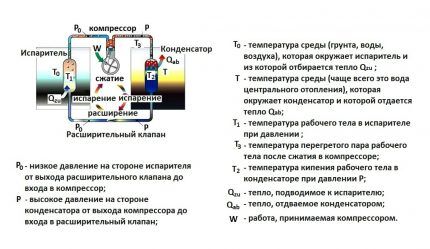
The operating algorithm of an air-to-air heat pump is as follows:
- Outdoor air is drawn into the outdoor unit by a fan and forced through the fins of the external evaporator. Freon circulating through the heat exchanger absorbs the thermal energy available in it, while passing into a gaseous state.
- The gas then enters the condenser, where it is compressed. And then it is pumped through copper pipes to the indoor unit.
- In a condenser located in the house, the gas turns back into liquid, transferring heat to the indoor air.
- Then the excess pressure is released through the expansion valve, and the liquid freon is again sent to the primary evaporator.
The temperature of freon entering the external unit is always lower than the ambient temperature. Therefore, it always takes heat from the atmosphere.
But the level of “cooling” of the coolant in the system is constant, and the outside temperature constantly fluctuates.For this reason, in severe frosts, TN loses its effectiveness.
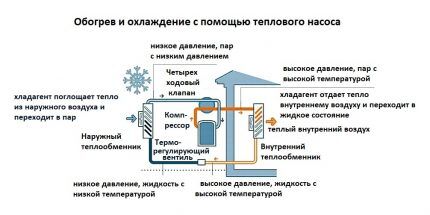
To increase the power of the heat pump, the surfaces of the condenser and evaporator are made as large as possible. And for uninterrupted operation in winter, the external heat exchanger is equipped with its own defrosting system.
Pros and cons of an air heat pump
Each technically complex system has its own advantages and disadvantages. Advertising brochures are one thing, but in reality, owners of heat pumps run the risk of encountering certain problems.
Air-to-air heating/cooling units are beneficial for a number of reasons.
The main advantages include:
- Versatility. The systems allow you to heat and cool rooms depending on the purpose of the room, needs and the climatic season.
- Environmental friendliness. They make it possible to completely stop burning natural gas, coal, firewood, etc., which pollute the natural environment with combustion products.
- Easy to install. Assembling a system from factory-produced components is not difficult. You can build a heat pump yourself using available materials.
- Fire safety. The process of generating heat does not involve the use of fuel. Even disruptions in the operation of the installation will not lead to fires.
- Economical. They are attractive due to their high heat transfer coefficient at minimal costs (for 1 kW of electricity consumed they produce 4–5 kW of heat). In addition, they pay for themselves quickly.
- Affordability. The cost of factory-made systems allows almost everyone to purchase a heat pump. A self-made installation will be practically free.
- Ease of use. The most technically complex device in the system is the compressor, the maintenance of which is difficult to cope with. With the typical load of heat pumps, compressors rarely fail before the time promised by the manufacturer.
To organize heating in one room it is enough install a split system, hanging an external module on the facade, and a convector on the internal wall. To heat several rooms, you will have to install heated air distribution channels.
All control of the air-to-air heat pump is carried out by built-in automation. You will not have to pay special attention to the operation and configuration of this system. You will only need to regularly clean the air filters and change them occasionally.
Among the negative aspects of heat pumps are:
- albeit insignificant, but still background noise;
- direct dependence of system efficiency on external temperature;
- increase in power consumption when it gets cold outside;
- dust constantly hanging in the air due to the continuous operation of the fan and air convection in the room;
- dependence on power supply (for uninterrupted operation a generator will be required).
At outside temperatures down to -10°C, everything works perfectly; the heat taken from the street is quite enough to create comfortable conditions in the house. But with further cooling, the efficiency of the cutting pump decreases.
If the cottage is built in an area with a cold climate and severe frosts in winter, then you cannot do without an additional boiler or fireplace.

For arrangement of air heating Such systems are ideal. Minimum energy consumption, installation effort and maintenance problems. But they cannot heat water. To do this, you will have to additionally install a boiler or connect to centralized networks.
Air-to-air heat pumps are the optimal way to heat buildings made of wood or SIP. Such buildings have low heat losses, and the air heat pump capacity for heating them is abundant.
Fundamental differences from air conditioning
Externally, an air-to-air heat pump is similar to a household air conditioner. But it has its own distinctive design features and technical characteristics.
The first device is used as the main source of heating, operating year-round. And the second is more intended for cooling the air in the summer heat.
The main function of a heat pump is heating. However, many models are also capable of cooling indoor air. But in this operating mode they are significantly inferior to the air conditioner in terms of energy efficiency. This is rather an extreme case of their use.

On the other hand, many inverter air conditioners can heat indoor air. But they consume much more electricity than heat pumps. Each device has its own purpose.
The use of air-to-air HP is primarily a transition to renewable energy sources.
These systems are cost-effective, despite the large initial investment of money. The reduction in heating bills pays for all initial costs.
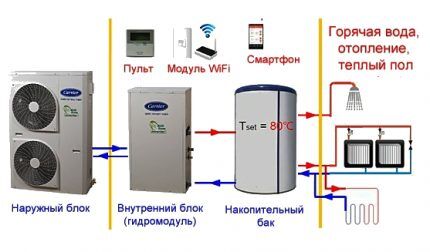
Selection and calculations of a heat pump
An air-to-air heat pump will only be effective if it is selected correctly. It is necessary to calculate its power in advance depending on the square footage of the house. And only then look at the prices of different manufacturers.
The calculations use the energy efficiency coefficient COP (the ratio of the HP power to the energy expended).
Under “greenhouse conditions” it often reaches 4–5 points, and the most modern models reach 7–8. However, when the outside temperature drops to -15–20°C, this figure drops sharply to only two.
At calculation of air heating must be taken into account:
- thermal insulation and insolation of premises;
- area of rooms;
- number of people living in the cottage;
- general climatic conditions of the area where the house is located.
For most homes, about 0.7 kW of heat pump power is needed for every ten square meters. But everything here is quite arbitrary. If the ceilings are higher than 2.7 m or the walls and windows are poorly insulated, then more heat will be required.
There are many manufacturers of air-to-air heat pumps in both Asia and Europe.
The systems have good reviews from Daikin, Dimplex, Hitachi, Vaillant, Mitsubishi, Fujitsu, Carrier, Aertec, Panasonic And Toshiba. Almost all of their models are adapted to domestic operating conditions and have proven themselves well.
Even with voltage surges, they do not break and continue to work properly after turning on the electricity.
The price of running air heat pumps varies from 90 to 450 thousand rubles. Here, a lot depends not only on the power of the unit, but also on the additional functionality and country of manufacture.
Selected models complement:
• filters for air purification and disinfection;
• backup heaters;
• electric generators;
• GSM modules for system management;
• ionizers and ozonizers.
Practice shows that at frosts below -15 ° C, rooms heated only by a heat-air pump become cool. And without an additional heater, the rooms frankly do not smell comfortable.
However, in the southern regions, where such frosts are rare, HP is quite effective and more than justifies the money spent by saving energy resources.
Homemade from an old refrigerator
It is quite difficult to assemble an air-to-air heat pump from individual compressors and condensers without specialized engineering knowledge. But for a small room or greenhouse, you can use an old refrigerator.

To do this, you need to make two holes in the front door of the refrigerator. Through the first one, street air will enter the freezer, and through the second lower one, it will be discharged back to the street.
At the same time, during its passage through the inner chamber, it will give off part of the heat present in it to freon.
You can also simply build the refrigeration machine into the wall with the door open to the outside, and the heat exchanger at the back into the room. But it should be taken into account that the power of such a heater will be small, and it consumes a lot of electricity.
The air in the room is heated by a heat exchanger at the back of the refrigerator. However, such a heat pump can only operate at outside temperatures not lower than plus five Celsius.
These household appliances are intended for indoor use only.
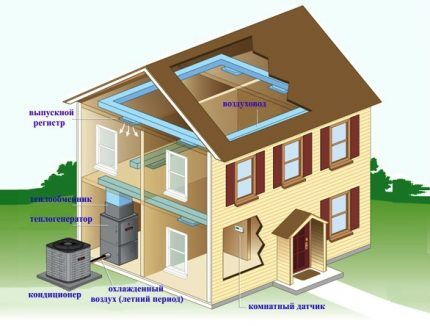
Installation of an air-to-air heat pump is extremely simple. It is necessary to install the external and internal blocks, and then connect them to each other with a circuit with coolant.
The first part of the system is installed outdoors: directly on the facade, roof or next to the building. The second one in the house can be placed on the ceiling or wall.
It is recommended to install the outdoor unit a few meters from the entrance to the cottage and away from the windows; do not forget about the noise produced by the fan.
And the internal one is installed so that the flow of warm air from it spreads evenly throughout the room.
If you plan to heat a house with several rooms on different floors using an air-to-air heat pump, you will have to install a system of forced-air ventilation ducts.
In this case, it is better to order the project from a competent engineer, otherwise the power of the heater may not be enough for all the premises.
The electricity meter and protective device must be able to withstand the peak loads generated by the heat pump. When there is a sudden cold snap outside, the compressor begins to consume electricity many times more than usual.
It is best to lay a separate supply line from the distribution panel for such an air heater.
Particular attention should be paid to the installation of freon pipes. Even the slightest chips inside can damage the compressor equipment.
You can't do without copper soldering skills here. In general, refrigerant refilling should be entrusted to a professional to avoid problems with refrigerant leaks later.
Step-by-step instructions for making a heat pump from a refrigerator are described in this article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Operating principle of the air-to-air thermal split system:
Air heat pump in the heating system of a two-story house:
Inverter air conditioner or air heat pump - which is better?
Air-to-air heat pumps are highly efficient devices. They are easy to maintain, convenient to use and economical.
There is now a huge range of similar systems on sale; you can choose a heating installation for any home. You just need to correctly calculate its power, then it will serve effectively for many years.
What do you think about the efficiency and feasibility of using air-to-air heat pumps? Share your opinion, leave feedback on the use of the units and ask questions. The comment form is located below.




Due to the constant rise in energy prices, we have finally paid attention to how we can use technology to save on this type of expense. An air source heat pump also has its drawbacks, but they are more than compensated by the positive effect it brings. The only negative: if the region is dominated by days with low temperatures, then this pump is not for you.
We have quite a few places with a climate warm enough for such pumps. Take the Black Sea coast for example: there is no frost, and gas supply, especially in the foothills, is very expensive. Here, such a pump is just right!
An air-to-air heat pump uses the atmosphere as an energy source.This is where the dog is buried, the lower the air temperature, the less energy is generated for heating the interior. This property limits the cost-effective use of the pump to areas with t>-10 C. If winter is severe in your area, pay attention to our mother earth (below the freezing level), you can use a nearby body of water (preferably a river, natural washing of the pipes). It's an extra cost, but keeping your home warm is worth it.
Heat pumps have one feature - the greatest efficiency is achieved when the coolant is heated to relatively low temperatures - about 45C. To work with conventional heating radiators, this temperature is not enough, or you will have to install large batteries of 20 sections. But for heated floors, this temperature is just right. In conventional systems (with a gas boiler, for example), it is specially lowered to such values so as not to overheat the floor and, accordingly, the room.
And Victor and Alexander - you are not entirely right. For example, cost-effective application to -10 is outdated information. Engineers work, invent, and have now achieved an air-to-air system COP > 3 at -15 degrees. And the work was tested at temperatures > -30 degrees (naturally with a slight decrease in efficiency and COP). That is, it pays off in a couple of years maximum!
Next about heating the coolant. The engineers worked hard here too. For example, they managed to squeeze more powerful compressors on samarium magnets into the size of the old units (which immediately made it possible to almost halve energy consumption with the same power as squirrel-cage motors), and the efficiency also increased from the use of scroll compressors (by 10 percent).The internal(!) fins of the freon pipes and the double-row piping of the radiators themselves (the latest top-end Daikin has a five-row radiator of the indoor unit) made it possible to maximize the efficiency of the radiators of both the external and internal units. All this made it possible to reduce the difference in operating temperatures between the external and internal units, and accordingly increase the COP. And also transfer heat pumps to the A+++ energy efficiency zone!
Accordingly, in the summer you will have a very economical air conditioner, which also speeds up the payback!
I would like to ask a question, what if you place the external unit underground and make a water jacket for it, or place it in a container with water?