Hybrid inverter for solar panels: types, review of the best models + connection features
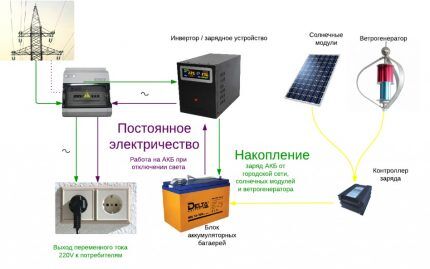
Power supply systems with the simultaneous use of traditional current supply and electricity from the sun are an economically sound solution for private households, cottage and holiday villages and industrial premises.
An indispensable element of the complex is a hybrid inverter for solar panels, which determines the voltage supply modes, ensuring the uninterrupted and efficient operation of the solar system.
For the system to work effectively, you need not only to choose the optimal model, but also to connect it correctly. And we will look at how to do this in our article. We will also consider existing types of converters and the best offers on the market today.
The content of the article:
Assessing the capabilities of a hybrid inverter
Using renewable solar energy in combination with centralized power supply provides a number of advantages. The normal functioning of the solar system is ensured by the coordinated operation of its main models: solar panels, charge controller, battery, as well as one of the key elements - the inverter.
Solar system inverter is a device for converting direct current (DC) coming from photovoltaic panels into alternating electricity. It is on a current of 220 V that household appliances operate. Without an inverter, energy generation is meaningless.

It is better to evaluate the capabilities of a hybrid model in comparison with the operating features of its closest competitors - autonomous and networked “converters”.
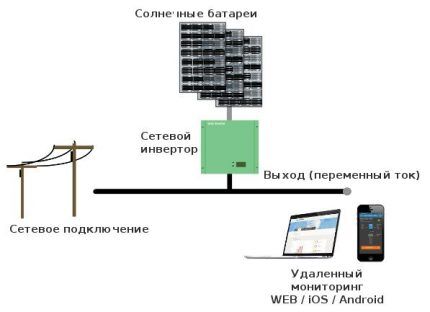
Network type converter
The device operates on the load of the general electrical network. The output from the converter is connected to electricity consumers, the AC network.
The scheme is simple, but has several limitations:
- operability when AC power is available in the network;
- The mains voltage must be relatively stable and within the operating range of the converter.
This variety is in demand in private homes with a current “green” tariff for electrification.
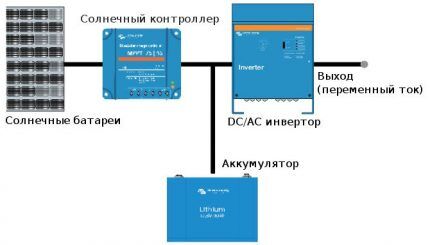
Autonomous version of the device
The device is powered from battery, which receives charge from solar panels through an MPPT controller.The system uses different types of batteries, including high-tech lithium batteries.
At maximum “filling” of the storage device, excess electricity is transferred to the input of the inverter, the output of which is connected to the end consumers of the AC.
In case of insufficient solar activity, energy is taken from the batteries and undergoes “conversion” through a voltage inverter.
Features of the autonomous installation:
- possibility of independent operation in the absence of mains alternating current;
- some models support the feed-in tariff;
- The efficiency of the installations is 90-93%.
To ensure absolute autonomy of an object, precise solar panel power calculation and sufficient battery capacity.
Hybrid inverter type
The model differs from the devices described above in its special manufacturing “architecture”. A special electrical circuit is provided inside, which allows it to operate in parallel with a current source (network, generator) in converter mode.
At the same time, the load is powered from the central network and solar panels, with priority given to the DC supplier.
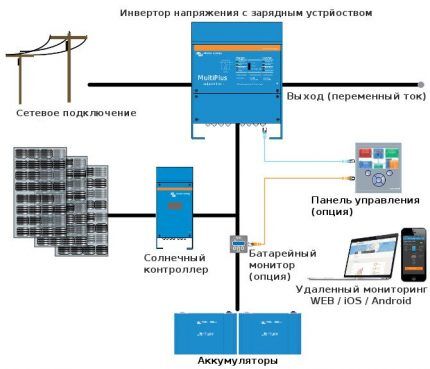
Competitive advantages lie in the versatility of hybrid inverters:
- Net - a kind of capacious battery with an efficiency of 100%.All surplus generated by photovoltaic plates can be redirected to the central grid at a “green” tariff.
- Ensuring uninterrupted power supply. When the main power supply is turned off, the system switches to autonomous mode, protecting all consumers from voltage surges.
- Increasing the network power limit during peak loads by adding energy from the battery-inverter complex.
When consumption declines, the solar complex switches to charging mode and after a while is ready for use again. The double power function can be designated: Smart Boots, Power Shaving, Grid support.
Adding power occurs according to the following principles:
- if the power used is below the maximum network consumption, then in addition to powering the load, the storage battery is charged;
- in the absence of voltage in the network, electricity received from the battery and converted by the inverter is consumed;
- if the load exceeds the limit value of the network power, then the deficiency is filled with accumulated electricity from the solar battery.
The listed operating modes are capable of supporting hybrid models with a charger.
Types of current converters
When choosing the “heart” of an autonomous power supply system, you should correctly compare the tasks assigned to the equipment with its potential capabilities.
The main features of the classification of hybrid inverters are: an algorithm for changing operating modes, the shape of the output voltage and the ability to service a single- or three-phase network.
Comparison of PSU and hybrid installation
Some companies unwittingly mislead consumers by calling an uninterruptible power supply unit (UPS) a hybrid inverter. It would seem that both devices perform similar tasks, but there is a significant difference.
The BPS is an inverter with a charger. The module primarily ensures energy consumption from the photovoltaic installation, and if there is insufficient energy, it switches to consumption from the network.
The functioning of the system in a “jerky” mode provokes additional cycling of the battery and accelerates its wear. In most inexpensive PSUs, the threshold voltage is set without the possibility of regulation.
In models of hybrid inverters for solar panels, such jumps are excluded - the unit adapts to the required power and works simultaneously with different current sources.
You can choose your priority consumption yourself. Typically, the emphasis is on energy consumption from solar panels.Some hybrid units have the option of limiting the power supplied from the city network.
Varieties according to the inverter signal shape
Solar cell current converters are classified by the type of output signal.
There are:
- pure sine wave;
- modified sine (quasi-sine wave);
- meander.
The latter option is practically not used in practice, since a sharp change in polarity causes malfunctions in the equipment.
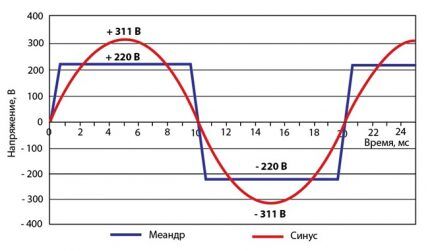
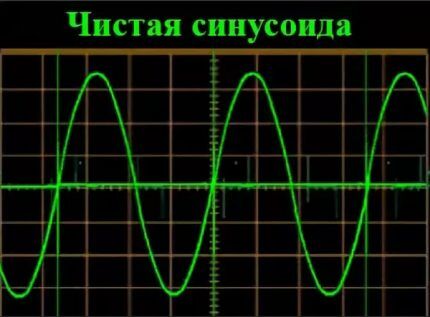
What is a pure sine wave?
The converter produces a high quality signal that is superior to the mains current waveform. This is the best option for ensuring the operation of “sensitive” equipment: heating boilers, compressors, electric motors, medical equipment and devices based on transformer power supplies.
Features of quasi-sine
Transmission of signal energy in the form of a modified sine wave can reduce the efficiency of some devices, provoke the appearance of noise, cause interference or lead to equipment failure.
When powering low-frequency transformers, asynchronous, synchronous motors, a power loss of 20-30% is visible.This “flaw” is converted into thermal energy, excessively heating the devices.
Inverters with a pseudo-sine wave signal are compact and affordable. Their use is advisable for powering devices without inductive loads, designed to consume active components of electrical power.
This group includes: thermoelectric heaters, incandescent lamps for lighting systems and other resistive structures.
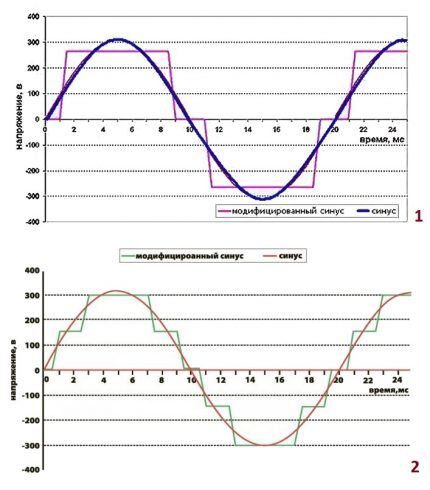
The shape of the output signal is indicated in the passport of the inverter or uninterruptible power supply. Possible designations: “Back” – a guarantee of the absence of a pure sine wave, “Smart” – the probability of receiving high-quality current at the output.
Some manufacturers note the harmonic distortion factor (nonlinear distortion index) in the accompanying document. If the parameter is less than 8%, then the unit produces an almost perfect sine.
Single-phase and three-phase models
Single-phase inverters are mainly integrated into the circuit of a residential photovoltaic system with a standard voltage of 220V.
The output voltage range when connected to one phase in different models ranges from 210-240V, output frequency - 47-55 Hz, power - 300-5000 W.
Single-phase inverters are produced for standard battery voltages: 12, 24 and 48 V. To ensure that the converter does not operate at its maximum capacity, it is necessary to match the power of the “converter” with the voltage of the solar battery or battery.
Three-phase inverters are used to supply three-phase current to power electric motors. Primary use: production, workshops, commercial purposes.
Three-phase inverters are distinguished by high power (3-30 kW), a wide range of output alternating voltage (220V/400V).
Combination models are also available on the market. These include single-phase inverters with the ability to synchronize the converter outputs with a phase shift - this allows you to power three-phase loads. We reviewed all types of equipment for converting current from solar panels in our other article.
Solar Inverter Selection Parameters
The efficiency of the converter and the entire power supply system largely depends on the correct choice of equipment parameters.
In addition to the characteristics described above, you should evaluate:
- output power;
- type of protection;
- operating temperature;
- installation dimensions;
- efficiency;
- availability of additional functions.
Let us next consider all these characteristics in more detail.
Criterion #1 - device power
The rating of the solar inverter is selected based on the maximum load on the network and the expected battery life. In start-up mode, the converter is capable of delivering a short-term increase in power at the time of commissioning capacitive loads.
This period is typical when turning on dishwashers, washing machines or refrigerators.
When using lighting lamps and a TV, a low-power inverter of 500-1000 W is suitable.As a rule, it is necessary to calculate the total power of the equipment being used. The required value is indicated directly on the device body or in the accompanying document.

Criterion #2 - level of protection
A high-quality solar inverter should have several stages of protection. Possible options: forced cooling system, short circuit prevention, protection against voltage dips and surges in the network.
It is also important to have a sealed, reinforced housing that prevents dust and moisture particles from getting inside. The protection indicator of electrical equipment is standardized according to the IEC-952 standardization.

For outdoor operating conditions, models with the index “IP65” are suitable - the strength and reliability of the inverter allows its use in the external atmosphere.
Criterion #3 - operating temperature and dimensions
A wide range of values is an indicator of decent build quality of the inverter. The value of the indicator is especially relevant when placing the converter in an unheated room.
Weight is an indirect indicator of the quality of the inverter. There is an opinion - the heavier the converter, the more powerful it is. This is explained by the presence of a transformer in high-power equipment.
In “lightweight” models, the absence of a transformer can cause the inverter to break down when a high starting current is supplied.

Criterion #4 - efficiency
Experts recommend purchasing current “converters” with an efficiency of 90% or more. Only with this parameter will the operation of the solar system be effective and its arrangement expedient. Losing 10% of solar energy is an unacceptable luxury.
Additional functionality. Advanced capabilities affect the cost of equipment and are not always in demand. However, some options are worth the money spent.
Useful and necessary “devices” include:
- automatic addition of inverter power to the grid electricity;
- adjusting the battery charging period;
- selection of priority current source;
- maintaining work with different types of batteries (alkaline, lithium iron phosphate, helium, AGM, acid);
- possibility of combined operation with a network converter;
- setting the voltage indicator - preventing “jumps” in the mains voltage;
- possibility of upgrading the inverter by updating the firmware.
Modern converters can be connected to a PC for programming and monitoring.

Review of popular hybrid converters
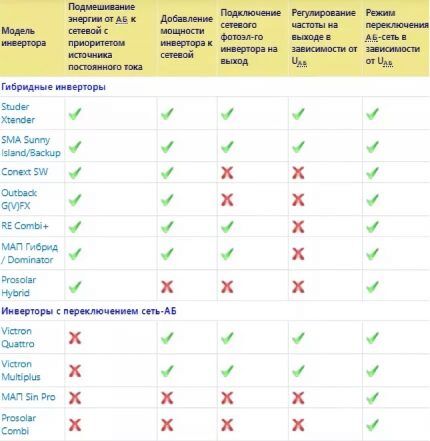
Among consumers, inverters from foreign companies received good reviews: Xtender (Switzerland), Prosolar (China), Victor Energy (Holland), SMA (Germany) and Xantrex (Canada). Domestic representative - MAP Sine.
Xtender range of multifunctional inverters
The Studer hybrid converter from Xtender is the embodiment of the Swiss quality standard in power electronics. The Xtender series solar inverters are distinguished by their impressive strength characteristics and extensive functionality.
Variety of models: XTS - low-power representatives, XTM - medium-power models, XTN - high-power inverters.

Each Xtender Hybrid Series offers the following features and options:
- pure sine wave feed;
- “addition” of power to the network from the battery;
- when the mains voltage decreases, consumption from the central power supply is reduced;
- two priority selection modes: the first is “soft” with power supply within 10%, the second is a complete switch to the battery;
- variety of installer settings;
- management of the backup generator;
- standby mode with a wide control range;
- remote monitoring of system parameters.
All modifications have the Smart Boost function - connection to different power suppliers (generator set, network inverter) and Power Shaving - guaranteed coverage of peak loads.
Optimal Prosolar Hybrid converters
The Chinese-made model has good characteristics and an acceptable cost (about 1200 USD). The converter optimizes the operation of solar panels by storing unused energy in the battery.

Distinctive features:
- option to track the limiting power point of a solar battery;
- information LCD display displaying operating parameters of the system;
- 3-level battery charger;
- maximum current adjustment up to 25A;
- inverter communication.
The converter is connected to a PC via software (supplied as a kit). It is possible to modernize the inverter through innovative flashing.
Sine wave inverters Phoenix Inverter
Phoenix inverters meet high demands and are suitable for industrial applications. The Phoenix Inverter series is released without a built-in charger.
The converters are equipped with the VE.Bus information bus and allow operation in parallel or three-phase configurations.
The power range of the model range is 1.2-5 kW, efficiency is 95%, voltage type is sinusoid.

Competitive advantages:
- “SinusMax” technology supports the launch of “heavy loads”;
- two energy saving modes – load search option and no-load current reduction;
- presence of an alarm relay - notification of overheating, insufficient battery voltage, etc.;
- setting programmable parameters via PC.
To achieve high power, up to six converters can be connected in parallel to a phase. For example, a combination of six devices with a rating of 48/5000 is capable of providing an output power of 48 kW/30 kVA.
Domestic MAP devices Hybrid and Dominator
The MAP Energia company has developed two modifications of the hybrid converter: Gibrid and Dominator.
The power range of the equipment is 1.3-20 kW, the time period for switching between modes is up to 4 ms, the possibility of “pumping” electricity into the city network is provided.

General characteristics of the Hybrid and Dominator voltage converters:
- transformer based on a torus;
- There is no input voltage stabilization;
- power “pumping” mode;
- output is pure sine;
- generation of excess energy into the network;
- limitation of current consumption at the AC input;
- class IP21;
- consumption in “sleep” mode is 2-5W.
The efficiency of the converters reaches 93-96%. The devices have successfully passed tests for use at ultra-low temperatures (limit value -25°, short-term reduction to -50 °C is acceptable).
Possible connection diagrams
When building a photovoltaic complex combined with a central network, there are different options for connecting an inverter.
Option #1 - circuit with DC charge controller
The most popular option is where the battery is charged through a solar controller MPPT (peak power point analysis).
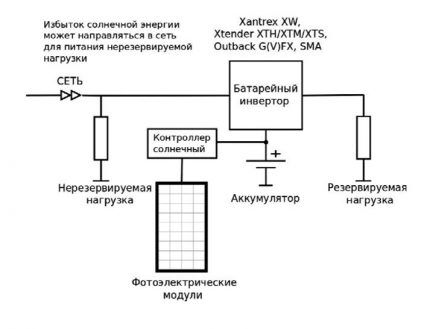
Features of the solution:
- efficient use of renewable energy when the grid is on/off;
- the ability to activate operation from the solar system after the battery is discharged.
And another solution is slightly increased losses for energy conversion in the “controller-battery-inverter” section.
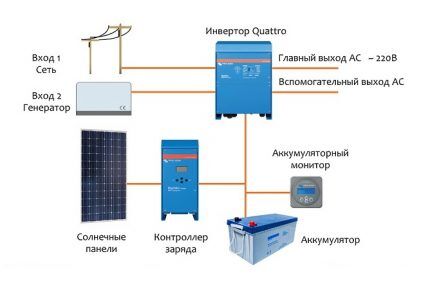
Option #2 - scheme with a hybrid and network converter
Network converter at the output of the battery inverter. According to the diagram, two converters are connected to different solar panels.
The hybrid converter is connected to the optional photovoltaic panel to recharge the battery, and the network converter is connected to the main solar module.
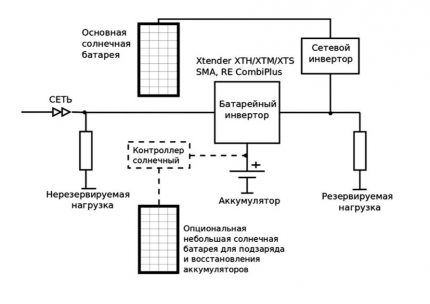
System characteristics:
- uninterrupted operation regardless of the presence of central mains voltage;
- high efficiency and minimization of losses on the DC side due to a sufficient voltage level of the solar battery;
- batteries almost always operate in buffer mode, which increases their service life;
- the use of hybrid inverters designed to charge the battery from the output;
- the need to adjust the operation of the network inverter.
The total power of the network converter should not exceed the power of the hybrid “converter” - this allows you to utilize the energy of solar panels in the event of a battery discharge or a network outage.
Regardless of the chosen circuit, a number of nuances should be taken into account when connecting the inverter:
- Wire connections for DC do not need to be long. It is advisable to place the inverter in close proximity (up to 3 m) to solar panels, and then “build up” the main line with AC.
- The converter must not be mounted on structures made of flammable materials.
- The wall inverter is located at eye level for easy reading of information from the display.
There are special requirements for connecting models with a power of more than 500 W. The connection must be rigid with reliable contact between the device terminals and the wires.
Also on our website there are other articles on solar energy and connecting individual components and modules when assembling an autonomous system.
We recommend you read the following materials:
- Connection diagram for solar panels: to the controller, to the battery and serviced systems
- Solar battery charger: device and operating principle of solar charging
- How to make a solar battery with your own hands: methods for assembling and installing a solar panel
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The concept of a “hybrid inverter”, its structure, functions and options:
Overview of the capabilities, operating modes and efficiency of using the 3 kW InfiniSolar multifunction converter:
Designing a solar power supply system is a complex and responsible task. It is best to entrust the calculation of the necessary parameters, selection of solar complex components, connection and commissioning to professionals.
Mistakes made can lead to system failures and ineffective use of expensive equipment.
Are you choosing the best converter option for operating an autonomous solar energy supply system? Do you have questions that we did not cover in this article? Ask them in the comments below - we will try to help you.
Or maybe you noticed inaccuracies or inconsistencies in the material presented? Or do you want to supplement the theory with practical recommendations based on personal experience? Write to us about this, share your opinion.




If you choose the right and high-quality inverter, you can even make money on your eco-home. The biggest problem for Russia in the case of organizing a completely energy-independent home is the lack of a “green tariff”, thanks to which it will be possible to sell excess energy to the network. And so the concept of an eco-house is very attractive for the Far East, where there is a lot of sun and undeveloped territories.
What's the problem? There is not so much sun in a year, you can save energy to use later. This is not a problem at all. Do you want to blame the country for everything? And then, for example, if such a law existed, you would sell all the electricity in case of need, and then what to do in the winter or some other time? This is also a very controversial possibility. Another thing is that in general we are far behind. But there is no point in exaggerating the problems in everything.
The problem is that the “green tariff” has not been adopted in Russia at the legislative level. For the third year now, the bill has been actively discussed, which, by the way, is quite well thought out.
The essence of this bill is that the government wants to regulate the production of electricity at microgeneration facilities with a capacity of up to 15 kW. This particular power was chosen because the connection of such stations will not entail excess load on the electrical network.
For example, in neighboring Ukraine, residents have been enjoying the benefits of the “green tariff” for several years now, selling excess electricity to the state. This is especially true during the peak productivity of solar panels, from May to August, when it is actually possible to sell excess electricity at a “feed-in tariff”.
Anatoly, how can you save energy so that you can use it later in winter? Share your secret with the global energy community.
Please tell me how/where to connect a hybrid inverter to supply electricity to the network if there are single-phase triac voltage stabilizers at the input: before or after the stabilizers? It is planned to install an inverter on one phase with subsequent expansion of the system to three-phase.