Solar heating of a private house: options and design diagrams
The use of “green” energy supplied by natural elements can significantly reduce utility costs.For example, by arranging solar heating for a private home, you will supply low-temperature radiators and underfloor heating systems with virtually free coolant. Agree, this is already saving money.
You will learn everything about “green technologies” from our proposed article. With our help, you can easily understand the types of solar installations, the methods of their construction and the specifics of operation. You will probably be interested in one of the popular options that are actively working in the world, but are not yet in great demand here.
In the review presented to your attention, the design features of the systems are analyzed and the connection diagrams are described in detail. An example of calculating a solar heating circuit is given to assess the realities of its construction. To help independent craftsmen, photo collections and videos are included.
The content of the article:
"Green" heat technologies
Average 1 m2 The earth's surface receives 161 watts of solar energy per hour. Of course, at the equator this figure will be many times higher than in the Arctic. In addition, the density of solar radiation depends on the time of year.
In the Moscow region, the intensity of solar radiation in December-January differs from May-July by more than five times. However, modern systems are so efficient that they can work almost anywhere on earth.
Task of use solar radiation energy with maximum efficiency is solved in two ways: direct heating in thermal collectors and solar photovoltaic batteries. Solar panels first convert the energy of the sun's rays into electricity, then transmit it through a special system to consumers, for example an electric boiler.
Thermal collectors, when heated by the sun's rays, heat the coolant of heating and hot water supply systems.
Thermal collectors come in several types, including open and closed systems, flat and spherical designs, hemispherical concentrator collectors and many other options. The thermal energy obtained from solar collectors is used to heat hot water or heating fluid.
The industry produces a wide range of collector systems for inclusion in an independent heating network. However, the simplest option for a summer residence is easy to do with your own hands:
Although there has been clear progress in developing solutions for harvesting, storing and using solar energy, there are advantages and disadvantages.
Efficient use of solar energy
The most obvious advantage of using solar energy is its universal availability. In fact, even in the gloomiest and cloudiest weather, solar energy can be collected and used.
The second advantage is zero emissions. In fact, it is the most environmentally friendly and natural form of energy. Solar panels and the collectors do not produce noise. In most cases, they are installed on the roofs of buildings, without occupying the usable area of a suburban area.
The disadvantages associated with using solar energy are the variability of illumination. At night there is nothing to collect, the situation is aggravated by the fact that the peak of the heating season occurs during the shortest daylight hours of the year. It is necessary to monitor the optical cleanliness of the panels; slight contamination sharply reduces the efficiency.
In addition, it cannot be said that operating a solar energy system is completely free; there are constant costs for equipment depreciation, operation of the circulation pump and control electronics.
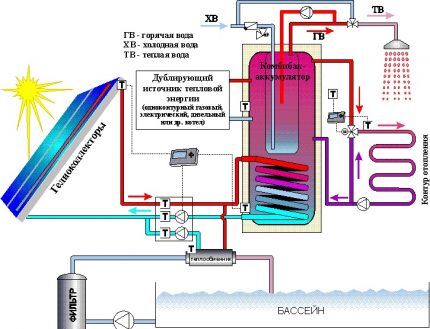
Open solar collectors
An open solar collector is a system of tubes, unprotected from external influences, through which coolant heated directly by the sun circulates.
Water, gas, air, and antifreeze are used as coolants. The tubes are either fixed to the supporting panel in the form of a coil, or connected in parallel rows to the outlet pipe.

Open collectors usually do not have any insulation. The design is very simple, therefore it has a low cost and is often made independently.
Due to the lack of insulation, they practically do not store the energy received from the sun and are characterized by low efficiency. They are used mainly in the summer to heat water in swimming pools or summer showers.
Installed in sunny and warm regions, with small differences in temperature of the ambient air and heated water. They work well only in sunny, windless weather.

Tubular collector varieties
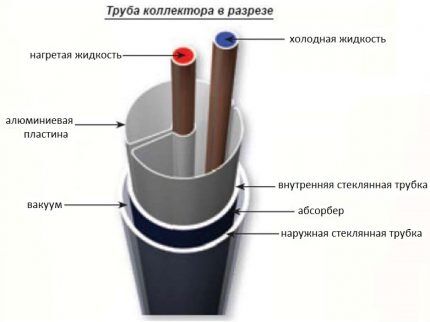
Tubular solar collectors are assembled from individual tubes through which water, gas or steam flows. This is one of the types of open solar systems. However, the coolant is already much better protected from external negativity. Especially in vacuum installations, designed on the principle of thermoses.
Each tube is connected to the system separately, parallel to each other. If one tube fails, it is easy to replace it with a new one. The entire structure can be assembled directly on the roof of the building, which greatly simplifies installation.

A significant advantage of tubular solar collectors is the cylindrical shape of the main elements, thanks to which solar radiation is captured all day long without the use of expensive systems for tracking the movement of the luminary.
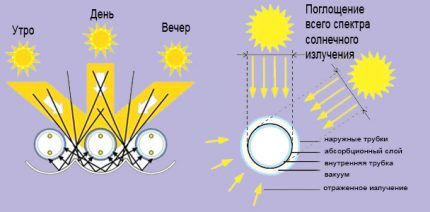
Based on the design of the tubes, feather and coaxial solar collectors are distinguished.
The coaxial tube is a Diaur vessel or a familiar thermos. Made from two flasks between which air is evacuated. A highly selective coating is applied to the inner surface of the inner bulb, effectively absorbing solar energy.
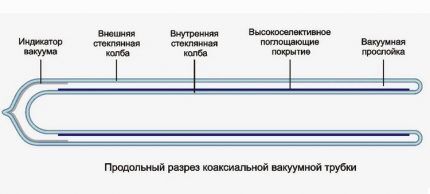
Thermal energy from the internal selective layer is transferred to a heat pipe or internal heat exchanger made of aluminum plates. At this stage, unwanted heat loss occurs.
The feather tube is a glass cylinder with a feather absorber inserted inside.

For good thermal insulation, the air has been evacuated from the tube. Heat transfer from the absorber occurs without loss, so the efficiency of feather tubes is higher.
According to the method of heat transfer, there are two systems: direct-flow and with a heat pipe. Thermal tube is a sealed container with an easily evaporating liquid.
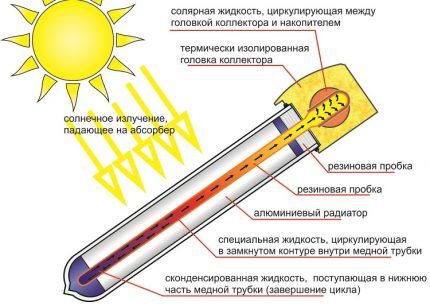
Inside the heat tube there is an easily evaporating liquid that receives heat from the inner wall of the flask or from the feather absorber. Under the influence of temperature, the liquid boils and rises in the form of steam. After the heat is transferred to the heating or hot water supply coolant, the steam condenses into liquid and flows down.
Water is often used as an easily evaporating liquid at low pressure. A once-through system uses a U-shaped tube through which water or heating fluid circulates.
One half of the U-shaped tube is intended for cold coolant, the second removes the heated one. When heated, the coolant expands and enters the storage tank, providing natural circulation. As with heat tube systems, the minimum angle of inclination must be at least 20⁰.
Direct-flow systems are more efficient because they immediately heat the coolant. If solar collector systems are planned to be used all year round, then special antifreeze is pumped into them.
The use of tubular solar collectors has a number of advantages and disadvantages. The design of a tubular solar collector consists of identical elements that are relatively easy to replace.
Advantages:
- low heat loss;
- ability to work at temperatures down to -30⁰С;
- efficient performance throughout daylight hours;
- good performance in areas with temperate and cold climates;
- low windage, justified by the ability of tubular systems to pass air masses through themselves;
- possibility of producing high temperature coolant.
Structurally, the tubular structure has a limited aperture surface.
It has the following disadvantages:
- not capable of self-cleaning from snow, ice, frost;
- high price.
Despite the initial high cost, tubular collectors pay for themselves faster. They have a long service life.
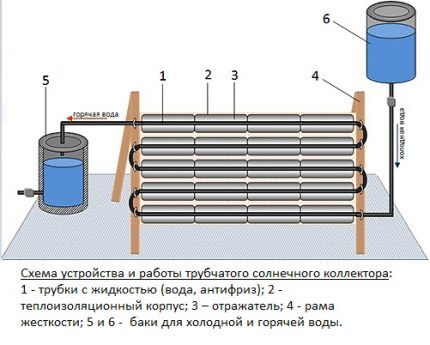
Flat closed systems
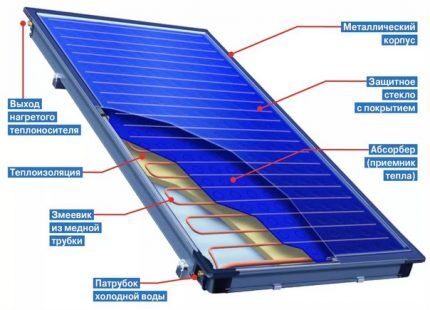
A flat-plate collector consists of an aluminum frame, a special absorbent layer - an absorber, a transparent coating, a pipeline and insulation.
Blackened sheet copper is used as an absorber, which has ideal thermal conductivity for creating solar systems.When solar energy is absorbed by an absorber, the solar energy it receives is transferred to a coolant circulating through a tube system adjacent to the absorber.
On the outside, the closed panel is protected by a transparent coating. It is made of shockproof tempered glass with a transmission band of 0.4-1.8 microns. This range accounts for the maximum solar radiation. Shockproof glass provides good protection against hail. On the back side the entire panel is reliably insulated.
The list of advantages of closed flat panels includes:
- simplicity of design;
- good performance in regions with warm climates;
- the ability to install at any angle with devices for changing the angle of inclination;
- the ability to self-clean from snow and frost;
- low price.
Flat-plate solar collectors are especially advantageous if their use is planned at the design stage. The service life of quality products is 50 years.
The disadvantages include:
- high heat loss;
- heavy weight;
- high windage when the panels are positioned at an angle to the horizontal;
- performance limitations when temperature changes exceed 40°C.
The scope of application of closed collectors is much wider than that of open-type solar systems. In summer they are able to fully satisfy the need for hot water. On cool days, when utilities do not include them in the heating period, they can work instead of gas and electric heaters.
For those who wish make a solar collector To build a heating system in your dacha with your own hands, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with practice-tested diagrams and step-by-step assembly instructions.
Comparison of solar collector characteristics
The most important indicator of a solar collector is efficiency. The useful performance of solar collectors of different designs depends on the temperature difference. At the same time, flat collectors are much cheaper than tubular ones.
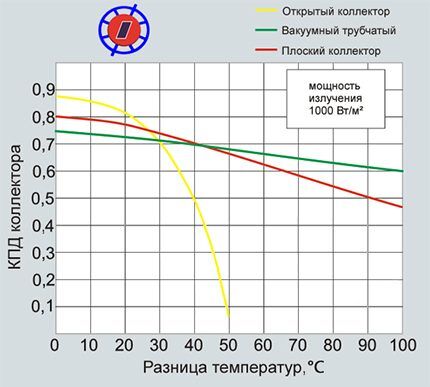
When choosing a solar collector, you should pay attention to a number of parameters showing the efficiency and power of the device.
There are several important characteristics for solar collectors:
- adsorption coefficient - shows the ratio of absorbed energy to total;
- emission coefficient - shows the ratio of transmitted energy to absorbed energy;
- total and aperture area;
- Efficiency
The aperture area is the working area of the solar collector. A flat-plate collector has a maximum aperture area. The aperture area is equal to the absorber area.
Methods for connecting to the heating system
Since solar-powered devices cannot provide a stable, round-the-clock energy supply, a system that is resilient to these shortcomings is needed.
For central Russia, solar devices cannot guarantee a stable flow of energy, so they are used as an additional system. Integration into an existing heating and hot water system is different for a solar collector and a solar battery.
Scheme with water collector
Depending on the purpose of using the heat collector, different connection systems are used. There may be several options:
- Summer option for hot water supply
- Winter option for heating and hot water supply
The summer option is the simplest and can be done even without circulation pumpusing natural water circulation.
The water is heated in the solar collector and, due to thermal expansion, enters the storage tank or boiler. In this case, natural circulation occurs: cold water is sucked out of the tank instead of hot water.
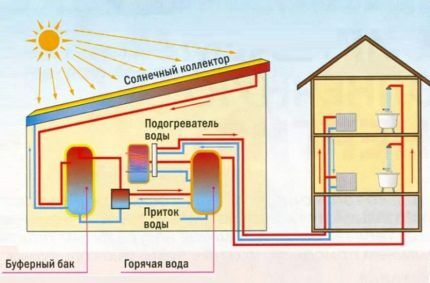
Like any system based on natural circulation, it does not work very efficiently, requiring compliance with the necessary slopes. In addition, the storage tank must be higher than the solar collector. In order for the water to remain hot for as long as possible, the tank must be thoroughly insulated.
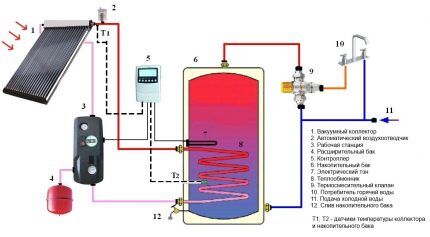
If you really want to achieve the most efficient operation of the solar collector, the connection diagram will become more complicated.
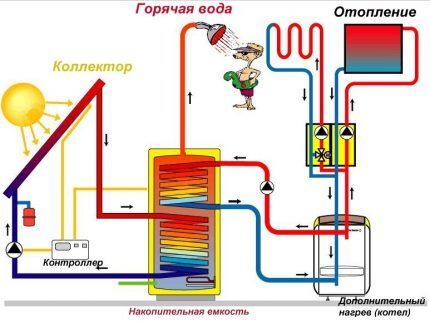
Non-freezing coolant circulates through the solar collector system. Forced circulation is provided by a pump controlled by a controller.
The controller controls the operation of the circulation pump based on the readings of at least two temperature sensors. The first sensor measures the temperature in the storage tank, the second - on the hot coolant supply pipe of the solar collector.
As soon as the temperature in the tank exceeds the temperature of the coolant, the controller in the collector turns off the circulation pump, stopping the circulation of coolant through the system. In turn, when the temperature in the storage tank drops below the set value, the heating boiler turns on.
A new word and an effective alternative to solar collectors with coolant have become systems with vacuum tubes, the principle of operation and design of which we suggest familiarizing yourself with.
Scheme with solar battery
It would be tempting to apply a similar solar battery connection diagram to the power grid, as is implemented in the case of a solar collector, accumulating the energy received during the day. Unfortunately, for the power supply system of a private home, it is very expensive to create a battery pack of sufficient capacity. Therefore, the connection diagram looks like this.
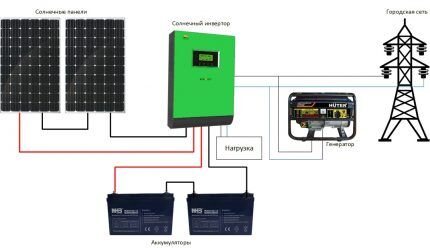
From the solar panels, the charge is supplied to the charge controller, which performs several functions: ensures constant recharging of the batteries and stabilizes the voltage. Next, the electric current is supplied to the inverter, where 12V or 24V direct current is converted into single-phase alternating current 220V.
Alas, our electrical networks are not suitable for receiving energy; they can only work in one direction from source to consumer. For this reason, you will not be able to sell the extracted electricity or at least make the meter spin in the opposite direction.
The use of solar panels is advantageous in that they provide a more versatile type of energy, but at the same time they cannot compare in efficiency with solar collectors. However, the latter do not have the ability to store energy, unlike solar photovoltaic batteries.
You will find everything about options for organizing heating of a private house using solar panels. In this article.
Example of calculating the required power
When calculating the required power of a solar collector, calculations are often mistakenly made based on the incoming solar energy in the coldest months of the year.
The fact is that in the remaining months of the year the entire system will constantly overheat. In summer, the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the solar collector can reach 200°C when heating steam or gas, 120°C for antifreeze, 150°C for water. If the coolant boils, it will partially evaporate. As a result, it will have to be replaced.
Manufacturers recommend proceeding from the following figures:
- provision of hot water supply no more than 70%;
- provision of the heating system no more than 30%.
The rest of the required heat must be generated by standard heating equipment. Nevertheless, with such indicators, an average of about 40% is saved per year on heating and hot water supply.
The power generated by a single tube of a vacuum system depends on geographic location. Indicator of solar energy falling per 1 m per year2 of the earth is called insolation.
Knowing the length and diameter of the tube, you can calculate the aperture - the effective absorption area. It remains to apply the absorption and emission coefficients to calculate the power of one tube per year.
Calculation example:
The standard tube length is 1800 mm, the effective length is 1600 mm. Diameter 58 mm. Aperture is the shaded area created by the tube. Thus, the area of the shadow rectangle will be:
S = 1.6 * 0.058 = 0.0928m2
The efficiency of the middle tube is 80%, solar insolation for Moscow is about 1170 kWh/m2 in year. Thus, one tube will produce per year:
W = 0.0928 * 1170 * 0.8 = 86.86 kWh
It should be noted that this is a very rough estimate. The amount of energy generated depends on the orientation of the installation, angle, average annual temperature, etc.
With all kinds alternative energy sources and ways to use them you can find in the presented article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Demonstration of the operation of a solar collector in winter:
Video #2. Comparison of different models of solar collectors:
Throughout its existence, humanity consumes more and more energy every year. Attempts to use free solar radiation have been made for a long time, but only recently has it become possible to effectively use the sun in our latitudes. There is no doubt that solar systems are the future.
Would you like to report interesting features in organizing solar heating for a country house or cottage? Please write comments in the block below. Here you can ask a question, leave a photo demonstrating the system assembly process, and share useful information.




Recently, people have started thinking about installing solar panels in their home. Firstly, in order to save money, as I am shocked by gas and electricity bills, especially in winter. Secondly, we need to think about the environment. Everything in the article is beautifully written, but this is for those who have at least a little understanding of technical issues. We are a complete zero. Explain to me in Russian. We have a two-story house, 120 square meters on each floor. We live in Bashkiria, where there are few sunny days, and in winter it is always cloudy. What kind of batteries do we need and how much will it cost? How long will it take for them to pay off? And will solar panels save us in winter? After all, we spend a lot of gas and electricity in the winter, but in the summer we don’t seem to need them. So maybe it’s not worth bothering with, but continue to pay through the nose for gas and electricity?
First of all, Svetlana, insulate your house, make it a kind of thermos. That is, provide thermal insulation to walls, windows, and roofing systems.Only then think about alternatives to gas and electricity.
I'm not ready to switch to solar heating. This is only suitable for those who live in warm regions, where there is summer and warm nights all year round. In the Russian central zone, thermal batteries are of little use. This is perhaps combining conventional heating in winter and the use of solar energy in summer. Then there will be at least some savings on utilities, but still the effect is partial, you cannot heat the house completely with solar energy.
Can you clarify your coordinates (city, village), I have a similar situation and question..
And I’m ready to switch to combined heating. This article discusses the general principles of constructing solar heating systems and hybrid ones. You can also use wind energy to additionally heat the heat storage tank. The battery tank is a very powerful thermal energy storage device; no electric battery can compare in terms of the amount of energy stored. And in order to empty it of accumulated energy, it is advisable to use a heat pump.
You are right, Gregory. Combined heating is an ideal option. We use solar collectors and a gas boiler, which saves a lot of money.
They say correctly, you need to use a battery to make a coolant tank in your house. Calculate based on minimum insolation. The excess is dumped into the cooler automatically. You can combine...
Hello!
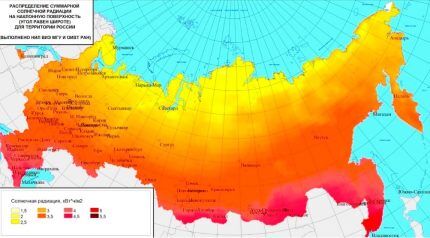
Firstly, I completely agree with Alexey, first you need to insulate the house and only then think about solar heating. First, you need to look at the solar energy distribution map (it is shown at the very beginning of the article).I'll tell you about my hybrid system.
Geographically, I am in the Primorsky Territory, where, judging by the distribution map of solar activity, there is a red zone, that is, a lot of sun. I designed and installed a hybrid heating system, which includes, firstly, a solar system, secondly, a solid fuel boiler and, of course, an electric boiler (since we don’t have gas). The area of the heated room is 240 m2. So Sergei said that the house cannot be completely heated with solar energy, I want to disappoint you a little. In winter, during the daytime, solar energy is enough to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room from 10 to 18. In the evening, I use a solid fuel boiler, and at night, an electric boiler. All circuits are started, not the heat exchanger.