Metal-plastic pipes: types, technical characteristics, installation features
In many characteristics, metal-plastic pipes are superior to their closest competitors: polymer, copper, cast iron and steel materials for laying highways. Their properties are especially significant when constructing a heating system.
In order for a metal-polymer composite to fully realize the qualities declared by the manufacturer, it is necessary to select the correct type of pipe. It must be suitable for the upcoming operating conditions and facilitate installation. You will learn everything about pipes made of metal and plastic, as well as guidelines for choosing them, from our article.
The content of the article:
Structure of metal-plastic composite pipes
The metal-plastic pipeline has gained popularity due to its combination of the strength of metal and flexibility polymer. The design of composite pipes is a multilayer “pie” of layers of polymer reinforced with an aluminum layer.
The symbiosis of plastic with metal provides high mechanical strength, prevents the diffusion of oxygen from the atmosphere and minimizes the thermal expansion of the material.
The internal polyethylene “liner” is absolutely smooth, ensuring unhindered passage of the transported medium and preventing the appearance of deposits and scale.The polymer is resistant to aggressive substances and does not corrode.
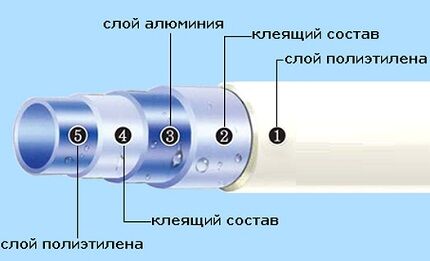
The metal core is responsible for the rigidity of the product and increases the temperature resistance of the pipeline. The ends of the aluminum are joined by laser welding. The thickness of the aluminum sleeve is 0.15-0.75 mm - this allows it to withstand frequent temperature fluctuations and high pressure.
The outer polymer layer is a particularly durable plastic, resistant to mechanical damage, high humidity and aggressive reagents. The outer shell reduces the intensity of condensation formation on the pipes.

The initial characteristics of the product are largely determined by the type of polymer used:
- PEX – high-density polyethylene;
- PE-RT – heat-resistant polymer;
- PE-R – polyethylene;
- PP-R – polypropylene.
The adhesive composition is responsible for the solidity of the entire assembly. Manufacturers introduce their own patented recipes, and the ingredients and ratio of components are not advertised. A high-quality adhesive layer neutralizes the stress inside the structure between the polymer and aluminum, prevents delamination and increases the wear resistance of the pipeline.
Physical and technical characteristics
The properties of metal-plastic pipelines depend on the dimensions of the product (diameter, wall thickness), type of polymer and manufacturer. However, all indicators must comply with the standards of GOST 18599 (2001), R-53630 (2009) and R-52134 (2003).
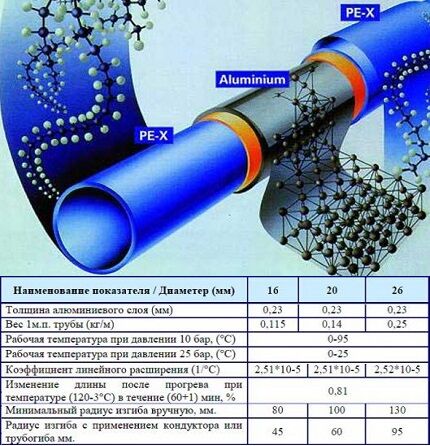
General requirements for metal-plastic mains according to GOST:
- yield strength of the hot plastic layer – up to 0.3 g/10 minutes;
- no delamination of the leading edge when stretched up to 10%;
- minimum permissible resistance to delamination under loads is 15 N/cm, without loads – from 50 N/cm;
- cross-linking of polyethylene layers – from 60%;
- thermal stability of plastic components;
- the limit value of oxygen permeability at a temperature of +40°C is 0.32 mg/sq.m*day, at +80°C – 3.6 mg/sq.m*day;
- the degree of strength of the polymers used is from 8-12 MPa;
- the initial fluidity temperature of the adhesive composition is at least +120°C.
GOST also regulates environmental parameters. The proportion of volatile substances in metal-plastic pipes should not exceed 0.035%.
Basic averaged physical and technical characteristics:
- Assortment. Manufacturers offer metal-plastic moldings with an internal cross-section of 14-60 mm and a wall thickness of 2-3 mm. The length of the bay is 50-200 m.
- Strength. Under lateral load conditions, the minimum tensile strength is 2880 N. The strength of welding to metal and adhesive joints is 57 and 70 N/sq.mm.
- Heat resistance. The composite retains its characteristics within a temperature range of +95°C. Let’s assume a short-term jump to +110°C; at -40°C the thermoplastic freezes.
- Linear parameters. The bending radius is directly proportional to the diameter of the pipe line. For manual installation, the value is 80-125 mm, for machine installation (pipe bender or jig) - 46-95 mm.
The pressure limit in the system depends on the temperature of the transported agent.

If it complies with the passport operating standards, the service life of the metal plastic is 50 years. When used in “hot” utility networks (coolant temperature above 25-30°C), the operating period is reduced to 25 years.
Performance and scope of application
The structure and technical characteristics of metal-plastic determined a number of strengths of the composite highway.
Positive aspects of operation include:
- anti-corrosion – the inner surface does not rust or silt;
- good throughput due to low hydraulic resistance of the pipeline;
- chemical inertness to most toxic substances and aggressive environments;
- flexibility, which makes it possible to minimize the number of connectors and corner pieces;
- gas tightness - elements of the pipeline system (radiators, boilers, pumping equipment) are protected from the harmful effects of oxygen;
- noise absorption – quiet transportation of liquid along utilities;
- wear resistance, ease of use and no need for additional maintenance.
The pipes are lightweight and therefore easy to transport and install. Additional advantages: aesthetics, affordable cost and virtually waste-free use.

Along with the positive aspects, metal plastic also has disadvantages:
- Thermal expansion difference. Plastic “adjusts” faster to changes in water temperature than aluminum. This difference negatively affects the material - over time, the joints weaken and the risk of leakage increases.
- Bending requirements. Repeated bending/unbending or one-time bending beyond the norm can lead to deformation of the layers of metal-plastic molding.
- Susceptibility to UV rays. The polymer outer layer loses its protective properties with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The metal-polymer pipeline is installed using compression fittings.

These deformations may result from freezing of the coolant in the pipe. Solution to the problem: insulating the main line at the installation stage or replacing the transported water in the heating system with anti-freeze water.
The performance properties of metal-polymer pipes allow them to be used in private, industrial construction and other areas of business.
Main Applications:
- communications of water supply systems;
- supply of aggressive liquids and gas in agriculture and industrial facilities;
- arrangement of insulated “water floors”, including for heating the soil in greenhouses;
- insulation of electrical cables and wires.
Metal-plastic composite fittings are widely used in the construction of ventilation, air conditioning and well irrigation systems.

Operating restrictions:
- premises classified according to fire safety standards as category “G” - substances are located, the processing of which is accompanied by heat generation or the appearance of sparks;
- buildings with heat sources, if their heating temperature exceeds 150°C;
- centralized heating with an “inset” of the elevator unit;
- when supplying hot coolant with a working pressure of 10 bar or more.
It is not recommended to install metal-plastic components into open utility lines. Temperature surges and operation in cold weather will lead to destruction of the pipeline.
Selection of metal & plastic products
The quality and operating conditions of metal-plastic products depend on the type of polymer component, size, technology for connecting the aluminum sleeve and the reliability of the manufacturer. According to the listed criteria, the entire range of pipe products can be classified.
Type of polymer used
Based on its composition, plastic for pipe production is conventionally divided into two groups: high- and low-pressure polymers.
The first group includes:
- PEX- cross-linked polyethylene;
- PE-RT – heat-resistant polymer.
PEX is polyethylene with “cross-linked” molecular chains. Cross-links transform a linear structure into a stable three-dimensional connection.
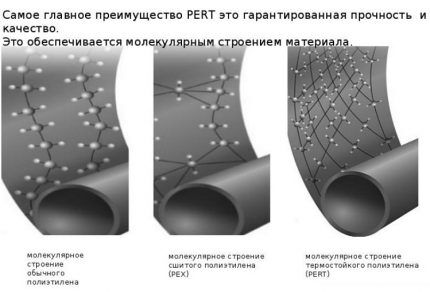
This property increases the resistance of pipelines to water hammer.
The type of intermolecular bonds is determined by the crosslinking catalyst used:
- PEX-A. New chains inside the structure are the result of treating polyethylene with peroxide. The maximum level of “firmware” is achieved - up to 85%. Pros: preservation of elasticity, high strength and pronounced molecular “memory”. The downside is the high cost of the technology, and as a result, the high price of pipes.
- PEX-B. The optimal alternative to A-links. Crosslinking technique using silane. The main advantage is the reduction of production costs. Technological nuances: degree of cross-linking - 65%, reduced elasticity, more stringent restrictions on pipe bending. PEX-B polymers retain a sluggish crosslinking process - the material changes its original characteristics over time.
- PEX-C. Formation of new bonds under the influence of electron radiation. The quality parameters of the finished product are significantly inferior to pipes of the PEX-A category. Plus - low cost.
- PEX-D. Intermolecular bonds are the result of nitrogen treatment. PEX-D pipes cannot compete with their counterparts, and their production has been reduced.
RE-RT pipes are characterized by long-term thermal resistance. Thermally stable polyethylene has numerous stable intermolecular bonds. The production involves the technique of controlled processes of spatial formation of macromolecules.
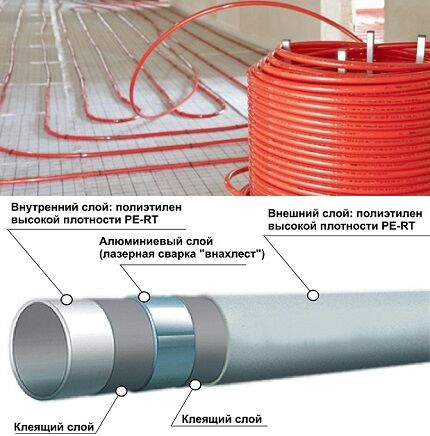
Thanks to the high technical characteristics of metal-plastic pipes with RE-RT polymer, their scope of application has been expanded. The main line can withstand temperatures up to +124°C and is not afraid of freezing.
For the installation of a “cold” pipeline, models made of low-density polyethylene are suitable. Possible designations: PE-RS, PE, PEHD, HDPE. Features of materials:
- a temperature of 70°C is critical - the pipes are deformed;
- maximum system pressure – 8-10 bar;
- deterioration due to exposure to the sun.
A composite material made of metal and low-pressure polymers is chosen in order to “cut” the budget for pipeline construction.
Pipe dimensions: diameter and thickness of reinforcement
The size of the pipeline is determined by its scope of use. The range of leading manufacturers includes modifications with an outer diameter of 16-50 mm.
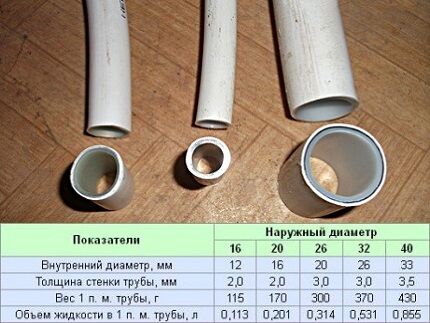
Below are the characteristics and features of the use of pipes with a diameter of XX*YY, where XX is the external section, YY is the internal diameter.
16*12. Pipes are used primarily for arranging the water circuit (supplying water to meters, mixers) and the heating system of the house. Larger diameter products may be used for the main pipeline.
20*16. Installation of "warm floors" and water supply systems. The fittings have better throughput compared to previous analogues, so they are recommended to be installed when the water pressure is unstable.
26*20. Wall thickness – 3 mm.This option is preferably used in a private home for autonomous systems, where it is important to provide some reserve capacity in case of possible pressure “interruptions”.
32*26. The dimensions of the pipe allow it to be used as a riser or main pipeline for low pressure systems. The volume of the transported unit is increased due to the large cross-section.
40*32. Thickness – 3.9 mm. Pipes have found application in laying long routes of utility networks in civil and industrial construction. Suitable for water treatment, air conditioning, individual and centralized water supply systems.

The thickness of the armor layer determines the strength, flexibility and thermal conductivity of the pipes.
When choosing, the following nuances are taken into account:
- the thicker the aluminum layer, the stiffer the pipeline;
- self-assembly is easier to perform from products with a metal layer of 0.15-0.2 mm;
- with an increase in the proportion of reinforcement, the loss of thermal energy during transportation of the coolant increases.
For performing internal household work, the optimal size of the reinforcing layer is 0.3-0.5 mm.
Nuances of manufacturing technology
There are two basic methods for producing metal-polymer pipes: English and Swiss. The main difference between the technologies is the connection option for the aluminum sleeve.
You can often hear from marketers about the classification of pipes into “seamless” and “seamless” depending on the manufacturing technology. However, delving into the basics of production, you can understand that the joining seam is present in both options, the difference is in its execution.
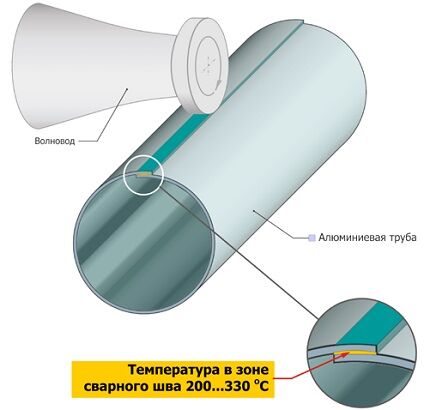
English technology - overlap welding. A pipe is formed from a metal strip, the edges of the “sleeve” are welded overlapping with ultrasound. Layers of glue and polymer are simultaneously applied to the outer and inner sides of the aluminum pipe.
Swiss technology – butt welding. Production stages:
- Production of polymer pipes by extrusion.
- Applying adhesive to the outer surface of the plastic.
- Formation and “rolling” of a metal layer from aluminum tape.
- Bonding the edges of the reinforcing material end-to-end using argon-arc or laser welding.
- Consecutive application of glue and polymer to the aluminum surface.
The final stage is cooling of the finished product.
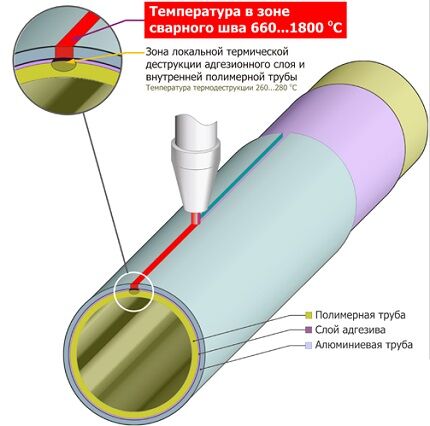
Assurances from sellers of “seamless” pipes about higher strength compared to “seamless” pipes should not be taken as an axiom. Welding experts know that the strength of an overlap weld is always higher than that of a butt joint.

Review of manufacturers: quality and price ratio
An informal rating of manufacturers of metal-polymer pipes is presented by domestic and foreign companies.
Valtec (Italy, Russia). Metal-polymer pipe systems are manufactured using the organosilanide method (PEX-b).The degree of cross-linking of the working layer is 65%, the protective outer layer is 55%. Combining the characteristics made it possible to obtain a flexible material.
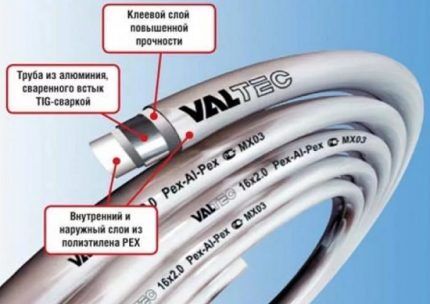
Approximate price of a product 16*2 mm – 1 USD/m, 32*3 mm – 4.5 USD/m.
Henko (Belgium). Five-layer pipes manufactured using “seamless” technology. The production uses cross-linked polyethylene PEX-C, the degree of cross-linking is 60%. Pipes are produced with a diameter of 14-40 mm, thickness - 2-3.5 mm, coil length - 5-200 m.

The average cost for pipe fittings with a cross-section of 20 mm is 0.8 USD/m.
Oventrop (Germany). The company specializes in the production of heat-resistant pipes based on PE-RT polymers. Due to their excellent technical and operational characteristics, the products are considered universal and are used in various fields of construction. Price – about 1.2 USD/m.
Comap (France). Metal-plastic pipeline using PEX-C and PEX-B polymer compounds. The products are characterized by absolute electrochemical stability and low wear rates. Pipes of the Multi-Skin series absorb noise well and maintain a given bend shape.
Nanoplast (Russia). A domestic manufacturer has launched the production of metal-polymer pipes using Swiss technology. A special feature of the product is a reinforced reinforcing layer (metal thickness is 0.3-0.55 mm).

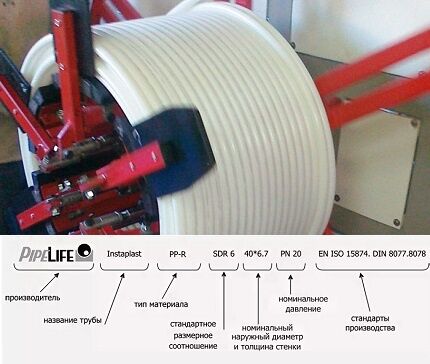
Decoding of production markings
The marking contains basic information about the characteristics and purpose of the pipeline. The sequence of values may differ from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Standard designations:
- name of the manufacturing company;
- production standard, certificate number;
- type of materials used;
- nominal dimensions;
- maximum permissible pressure;
- environment suitable for transportation;
- additional operating conditions (temperature).
At the end, the batch number, shift number and production date are displayed.
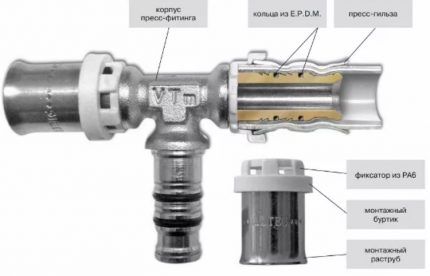
Features of installation of a metal-plastic pipeline
Assembly of the main line from metal-polymer pipes is carried out using three types of shaped fittings: detachable, compressor, press fittings. To make connections by crimping, you need press jaws, allowing the formation of an absolutely sealed unit.
Connecting pipes using press fittings is done as follows:
In addition to traditional crimp connections, another technology and type of fittings called push-on fittings are used when working with metal-plastic pipes. To form a sealed unit in this case, in addition to press pliers, an expander is also used, which is used to expand the socket. This technique is used to assemble systems laid in a screed or with grooves.
Pressing a sliding sleeve onto an expanded pipe installed on a fitting allows you to achieve a tight connection, but for a one-time assembly it is not always advisable to purchase the entire tool.
Detachable (collet) fittings consist of a body, an open ferrule and a rubber gasket. A thread is provided for connection to household appliances.
Installation procedure:
- Mark the fitting location and cut the pipe.
- Place the nut and ferrule on the pipeline.
- Install the fitting and tighten the nut.
- Check the tightness of the joint.
The compressor fitting is considered conditionally detachable. To assemble a pipeline using this type of fitting, you need a minimum of tools, just a couple of wrenches are enough:
The fittings are easy to install:
- Align the pipeline at the mounting location within a range of 10 cm.
- Cut the pipe straight.
- Process the ends, put on the nut and ring.
- Cover the shank with sealant and insert it into the pipe.
- Tighten the union nut.
The most reliable connection in assembly of metal-plastic pipelines achieved by using press fittings.The method is optimal for installing hidden communication lines. To install the pipeline you will need a press machine, a calibrator and pipe cutter.
You will get acquainted with valuable tips for performing crimping of metal-plastic pipes. next article, in which all installation nuances are analyzed in detail.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of the resistance of metal-plastic and polypropylene lines to high pressure:
Training video about step-by-step installation of a metal-polymer pipeline using press fittings:
Metal-plastic pipes are a symbiosis of the advantages of both materials. The combined structure expands the scope of application of metal-polymer products in engineering communication systems of various construction sites. Strong arguments in favor: durability and affordable price.
Would you like to tell us how you selected metal-plastic pipes and installed them with your own hands? Do you have useful information on installing or upgrading communication systems? Please write comments in the block below, ask questions, share useful information and photos on the topic of the article.



