Solenoid solenoid valve: where it is used + types and principle of operation
In addition to the usual manual valves, you can also see an automatic solenoid valve in the store.It allows you not only to control the flow of liquids and gases in pipelines at a distance, but also to automate this process.
Such devices differ in internal design and purpose. However, the principle of operation for all of them is the same - the closing/opening of the tap occurs due to the operation of an electromagnet.
In this article we will look at why such a valve is needed and how it works. We will also talk about the main types of solenoid valves.
The content of the article:
Why is a solenoid valve needed?
Solenoid valves are a category of modern shut-off valves for pipelines for a wide variety of purposes. In everyday life, such electric valves are used in cars, special equipment, water supply systems and automatic watering and heating systems.
They are also widely used in industry to regulate current and control the transport of a variety of liquids and gases.
The solenoid valve for water or gas does not have any sensors inside. With its help, you can only regulate or completely block the flow of the working environment. If automation of these processes is required, then you will have to additionally install external measuring instruments, tying the operation of the electrovalve to them.
For example, use an additional controller and water leakage sensorso that when a leak is detected, the solenoid valve receives the appropriate command from the controller and shuts off the pipeline.
The advantages of using solenoid valves include:
- quick adjustment of the working medium current through the pipeline;
- versatility and reliability of the device;
- long service life;
- small size and light weight;
- variety of instrument types.
The valve operates literally within a split second after the signal is given. It is designed to work with liquids under different pressures, from 0 to 25 bar, and with varying temperatures, from -20 to +120 ° C. At the same time, in a de-energized state, such an electric valve can remain either in a closed or open position - it all depends on the modification of the device.

In water supply systems, it allows you to automatically shut off the water supply if the pipes burst. And in heating systems, such a valve is used as a device for regulating the flow of coolant.
Here, using an external temperature sensor, it independently reduces or increases the flow of heated liquid from the boiler to the radiators.
How does a solenoid valve work?
The solenoid valve consists of:
- steel, cast iron, brass or polymer housings;
- induction coil with core (solenoid);
- working locking element;
- seal;
- damping spring.
The copper induction coil inside the shut-off device is located in a sealed housing, where access to water is closed.The blocking or opening of the working medium current channel occurs due to the rod and membrane extending under the action of the solenoid.

In a de-energized state, under the influence of a spring, the valve completely shuts off the current channel or leaves it completely open. Further, after applying voltage to the coil, the core and the rod are displaced, as a result of which the cross-section of this duct increases/decreases.
The general principle of operation of the electromagnetic valve under consideration is simple - the movement of the rod occurs in it due to electromagnetic induction. When electric current flows through the coil, the core located in its center is affected by an electromagnetic field, the strength and direction of which depend on the applied voltage in volts.
As a result, the shut-off element is displaced and the flow area of the valve changes.
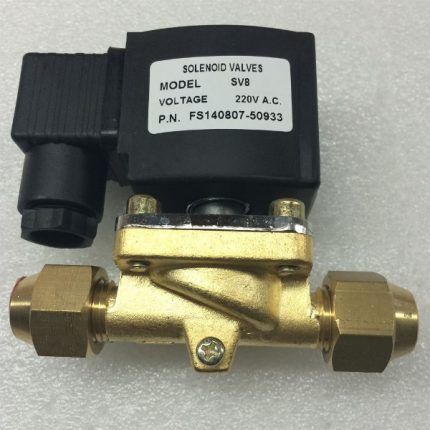

Electrovalves with low control voltage are designed to operate in small diameter pipelines and with low pressure of the working medium. The scope of their application is quite limited.
But such valves are easier to integrate into a control system on low-voltage semiconductor devices and connect to various microcontrollers. They are usually used in water supply systems and heating circuits of private houses.
Types of solenoid solenoid valves
There are several varieties of the device in question.Such devices are classified according to the material of the body, design and de-energized position of the lock inside, type of seal and method of connection to the pipes.
Each of these options is designed to work with a specific medium in terms of composition, temperature and pressure. The solenoid valve must be selected carefully. If you take a device that does not meet the requirements, it will not last long.

According to the method of connection, solenoid electrovalves are divided into:
- flanged;
- coupling;
- fittings.
And in size they can be from 6 to 150 DN (from 1/8 to 6 inches). There is an option for any pipeline.
The body of the electrovalves in question is made of:
- plastic (reinforced PPA, PVC, nylon);
- of stainless steel;
- brass;
- cast iron
Each of these options has its own characteristics for pressure and temperature of the working environment. These numbers should be carefully studied in the device passport so as not to make a mistake with your choice. At the same time, any of the above variations is suitable for plumbing or heating in a private house.
Classification #1 - by internal structure
Based on the design of the control element, valves are divided into three groups:
- Spool valves.
- Membrane.
- Piston.
Household solenoid valves are usually made with a membrane. This is a cheap and reliable option that can easily cope with regulating the flow of water in domestic heating and water supply systems.
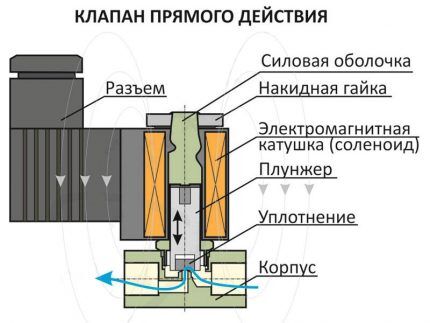
The main separation of solenoid valves is carried out according to the position of the locking mechanism when the electromagnet is de-energized.
According to this parameter, solenoid electrovalves are divided into:
- normally closed, valve closed (NC);
- normally open, valve open (NO);
- bistable.
In the first case, until voltage is applied to the solenoid, the core is lowered down due to spring pressure and there is no water flow. In the second case, when the device is de-energized, the channel, on the contrary, is completely open, and it closes only after power is applied.
The third option is that the position can be either open or closed.
Classification #2 - based on operating principle
Functionally, solenoid electrovalves for water at 220 V and other voltages are:
- one-way;
- two-way;
- three-way.
The first ones have only one connection pipe to the pipeline. This safety devices, designed to release steam or water when the pressure in the pipes is too high.

Three-way devices come with three pipe connections for connection to pipes. Such options are designed to redirect flow from one pipeline to another.
Most widely three way valves used in heating systems. Such devices make it easy to transfer coolant from one circuit to another to mix the working environment.
As a result, the temperature of the water in the system changes, but the source of thermal energy continues to operate without changing the mode.
Also, solenoid valves are:
- direct action;
- indirect action.
In the first, the core moves solely under the influence of an electromagnet. Secondly, its movement is also affected by the pressure of the working environment.
Classification #3 - based on the material of the seal and membrane
Inside the body of the solenoid valve there is a membrane that blocks the flow of water. Plus, there is a seal between the coil and the main one with the pipes. Both of these elements are made of elastic polymer materials.
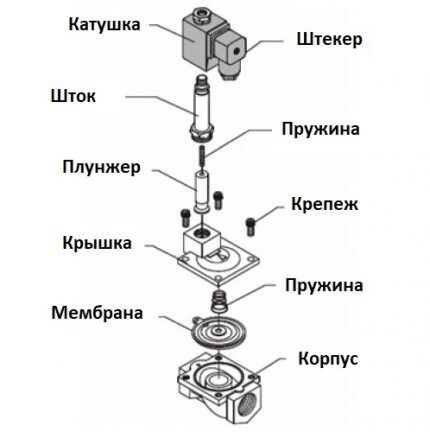
The seal in solenoid valves can be made of:
- FPM (FKM, VITON) – fluoroelastomer;
- EPDM – ethylene-propylene elastomer;
- NBR – nitrile butadiene rubber.
The first option is characterized by a high maximum operating temperature and resistance to oils and gasoline. The second is cheap and resistant to salts, alkalis and acids dissolved in water. The third one calmly tolerates contact with petroleum products and is usually used in industry and automobiles.
This material does not greatly affect the price of the solenoid valve. Its parts are too small in size. The type of seal and membrane should be selected based solely on the characteristics of the working environment.
The thermal properties of the seals are presented in the following table:
| Seal designation | FPM | EPDM | NBR |
| Material name | Fluorine rubber | Ethylene propylene rubber | Butadiene nitrile rubber |
| Operating temperature range, °WITH | -30…+150 | -40…+140 | -10…+80 |
In any case, when operating the solenoid valve, special attention should be paid to the absence of impurities in the water.
Sand and rust in pipes will sooner or later ruin any membrane, regardless of its material. The device in question can only be installed if there is a filter in the pipeline.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Solenoid valve device overview:
How a 220 V direct acting solenoid valve works and works:
Types of solenoid valves according to the operating principle:
The remote control solenoid valve is unpretentious and reliable in operation. It is designed for several tens of thousands of operations (it will work properly for 20–25 years) and does not require specialized maintenance.
Such a device for water costs between 3-6 thousand rubles, but it helps solve many problems. At the same time, it is not difficult to install it yourself; you just need to choose the right valve according to the characteristics and materials.
Would you like to add useful information to the above material or point out an inconsistency or error? Or would you like to give recommendations on choosing the optimal model of solenoid valve? Please write your tips and comments in the comments block.
If you still have questions about the topic of the article, ask our experts below under this publication.





Such valves are useful in a leakage protection system. A simple sensor on the floor - and you're done. As soon as water flows where it should not be, the pipes automatically shut off.
Hello. Please tell me. I need to remotely open the supply and return of heating pipes to the second floor. The first floor is constantly heated.
I plan to give a signal to open and close taps using SMS using the ZONT H-1000 heating controller. Use it to change the boiler temperature and open/close electromagnetic valves on the second floor. What are the best solenoid valves for me to use? And is this even possible? Thank you.
Hello. From personal experience I can recommend the solenoid valves of ODE S.r.l. (Italy). The project you want to implement is quite realistic, but instead of the ZONT H-1000 heating controller with SMS control, I recommend using a thermostat. The latter connects to the Wi-Fi network in the house, and can be controlled remotely with an Internet connection.
When it comes to thermostats, look no further than the IMIT range. It makes no sense to recommend anything specific regarding solenoid valves and thermostats, since I do not know the technical characteristics of your heating system. Based on your data, you can easily select the necessary equipment.
Hello. Need help classifying a 3 way solenoid valve for a washing machine. After reading the article, I still can’t figure out which valve to classify it as - pressure reducing or shut-off valves.
In the normal position, when there is no power (the machine is turned off), the valve is closed and water from the water supply does not flow into the machine drum. When you turn on the machine and select a washing program, water flows into the drum, and also according to the program into the compartment for powder and fabric softener.
Moreover, the liquid flow in the detergent compartment is adjusted. As a result, it is unclear which valves it should be classified as. A specialist's opinion is very necessary.Thanks for the help.
Hello! I am finishing the wiring of a small pool (indoor) and it will have a water heating system. The coolant is supplied to the pool heat exchanger through a hydraulic arrow by a circulation pump. I also have a solenoid valve. I can't get enough of the water temperature control unit. Is there a way to turn the circulation pump on and off together with the solenoid valve using, for example, a timer or thermostat? Thank you.