Air exchange rates per person for premises for various purposes
The residence of people in city apartments or country houses is determined by a list of conditions dictated by the requirements of health care institutions, construction and installation standards. It has long been proven that any violation immediately affects the comfort or health of residents.
One of the necessary conditions is fresh air with a certain oxygen content. To create a microclimate favorable for life, a ventilation system will be equipped, having previously made some calculations.
Calculations require regulatory data, among which air exchange per person occupies an important place. We will consider in more detail what is hidden behind this concept, and also find out what air exchange standards are acceptable for residential premises.
The content of the article:
What is air exchange and multiplicity?
People often confuse or do not see the difference between air exchange and its frequency, although in fact these are two different, albeit related, concepts.
The term “air exchange” is used when it is necessary to characterize the ventilation system in a closed room. There is a second meaning - this is the process of air replacement that occurs inside the building, and the parameters differ for different interior spaces.
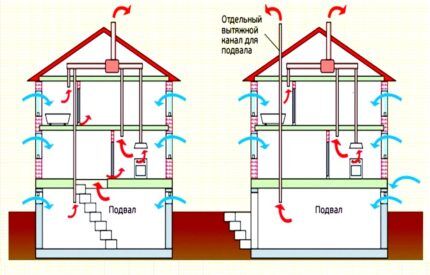
The amount of air exchange is calculated in m³/h.The units indicate how much air must be changed within 1 hour. For example, if the air exchange is 60 m³/h, then in 1 hour 60 m³ of air should be exchanged in the room.
Multiplicity means how many times in 1 hour the air is completely changed to new one. Simply put, air exchange is the volume of air, and the multiplicity is the number of changes of this volume.
In the calculation tables given in the SNiP or GOST documentation, both values can be indicated.
To draw up a ventilation project, calculations are made using special formulas. But there are also average standards that you can rely on when choosing ventilation pipes or climate control equipment.
For example, in SNiP 01/31/2003 There is a table with the norms of multiplicity and the amount of air exchange in 2 modes, non-working and servicing:
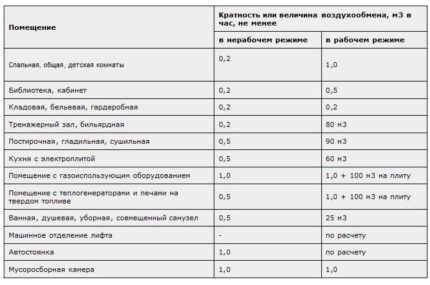
When working on more complex ventilation systems of medical institutions, public institutions or production workshops, additional factors are taken into account in the calculations: the presence of harmful impurities in the air, the number of staff and visitors, temperature and humidity parameters, heat generated by electrical appliances, etc.
Air exchange standards for a residential building
Apartment in multi-storey building consists of premises for very different purposes, and in connection with this, the requirements for standards are also different. They are dictated by the length of time residents spend in a particular room (corridor, bathroom), and the quality of the air itself.
Let's consider what air exchange standards per person should be followed when installing ventilation for specific rooms, and what needs to be done if the actual parameters differ from the standards.
#1 – bedroom and living room
For premises in which residents spend most of their time, the same standards have been adopted. It is believed that this is the living room where the whole family gathers, and the bedroom where people relax - that is, they spend, on average, 8 hours a day. This category also includes residential rooms in dormitories.

According to standard calculations, air flow in frequently used premises there should be 30 m³/h or more for each resident. The multiplicity in non-operating mode is 0.2, in operating mode – 1.0 (in other sources – from 0.35). The unit indicates that every hour the air in the bedroom or living room should be completely replaced once.
If the enclosing structures are considered tight for the passage of air, and a fireplace or mechanical hood is installed in the room, additional devices are required to ensure sufficient air flow.

There are people who do not delve into construction or sanitary standards - they are comfortable living either with the windows tightly closed, or, conversely, with the vents constantly ajar.Here you need to be guided by your own well-being, but the second option is preferable, especially if gas equipment is installed in the house or apartment.
#2 – children's room
A children's room is a room in which a child sleeps, plays, does homework, trains, that is, spends all his free time.
He also sleeps in it, so the norms for children are the same as for the bedroom or living room:
- air exchange rate – 30 m³/h;
- multiplicity in non-working mode – 0.2;
- maintenance ratio – 1.0.
If there are 2 children living in a room, then we also multiply the air exchange by two and get an air exchange equal to 60 m³/h.

We remind you that the standard parameters are calculated for rooms with normal humidity and room temperature, and these indicators should not change after installing ventilation devices.
#3 – kitchen with gas or electric stove
Both options are suitable for city apartments: if multi-storey buildings, according to the new rules, are provided with electric stoves, then 5-storey and 2-storey buildings of old buildings are more often equipped with gas equipment.
Requirements to rooms with gas stoves and ovens are tougher:
- air exchange rate – 90 m³/h (in kitchens with 4-burner stoves);
- multiplicity – 1.0 + 100 m³, if a stove is installed.
If the kitchen is part of a living room or studio apartment, the parameters are calculated taking into account specific conditions, and mechanical equipment is equipped supply and exhaust ventilation.

For electric stoves, the standards are different:
- air exchange rate – 60 m³/h (in kitchens with 2-burner stoves) and 75 m³/h (in kitchens with 3-burner stoves);
- multiplicity – 0.5 in non-working mode.
If gas equipment is actively used in the kitchen, the maximum air exchange is 180 m³/h; if the stove is used infrequently, it is reduced to 45 m³/h.
#4 – toilet and bathroom
Despite the traditionally small size of bathrooms, toilets and toilets, the air exchange in these rooms must be sufficient to compensate for the increased humidity.

If the bathroom is a separate room, then the following requirements are relevant for it and the toilet:
- constant mode – 25 m³/h;
- maximum mode – 90 m³/h;
- minimum mode – 10 m³/h.
Maximum regime means enhanced service for residents. This happens when a large family lives in the apartment or many guests are present at the same time.
The minimum mode is “turned on” when the homeowners are absent for a long time, as well as when there is 1 person living who rarely uses the shower and bathtub.
For a combined bathroom, the standard values increase:
- constant mode – 50 m³/h;
- maximum mode – 120 m³/h;
- minimum mode – 20 m³/h.
All data are averaged and are acceptable if the premises listed above are in use and not idle in a non-residential apartment.
#5 – other premises
There are no special requirements for dressing rooms and pantries, it is only stated that the air exchange rate should be 1.0-1.5.
Considering that these rooms do not have windows, air flows in and out through slightly open doors or holes specially made in the doors.

For example, for a sauna or gym, parameters are calculated taking into account the activity of residents and the quality of the air environment. The same applies to garage, if it is located in the basement. For swimming poolIn addition to the design standards, it is necessary to install mechanical ventilation.
Air replacement rate standards for other premises in multi-storey buildings and dormitories:
- laundry room – 7;
- ironing room, room for drying clothes – 3;
- utility room – 1.5;
- garbage collection chamber – 1.0;
- office or library – 0.5.
For lobbies, staircases, front and common corridors, no requirements are imposed, since air circulation occurs constantly through openable doors and windows.
How to increase air exchange with your own hands?
What to do if the natural air ventilation in the apartment does not meet the norm for a person or does not perform its functions at full capacity? You will have to improve the conditions on your own, and this is not difficult to achieve.
There are several effective ways to increase air flow, and special electrical appliances are usually used for exhaust.
We offer several devices that can significantly increase the performance of the ventilation system:
The advantage of all the devices and devices listed is that you can install them yourself.
There are many models of fans, hoods, and various supply valves on sale.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
About calculating the air exchange rate:
Few owners of city apartments or houses are concerned about the compliance of air exchange in housing with the requirements. Most often, engineers, builders and installers are interested in standards when designing or installing ventilation systems.
But we recommend that you familiarize yourself with existing standards - by focusing on proven values, you can create the most favorable and comfortable microclimate in your home.
If you have questions or can share valuable tips on the topic of this article, please leave your comments in the box below.



