Ventilation of the attic in a private house: how to make ventilation through gables and dormer windows
Every owner wants the newly renovated or added attic to become one of his favorite places in the house, isn’t it? However, this room may be too hot in summer and cold in winter. The air can stagnate, acquire a musty smell, and the interior decoration can be affected by mold.
The reason for such annoying phenomena is ineffective attic ventilation in a private house, poorly designed during construction. We'll tell you how best to arrange it. We will help you find errors in your system and offer several options for proven solutions.
In our article you will find a detailed description of the causes and consequences of improperly organized or unproductive ventilation. Find out how best to ensure stable air exchange. You will understand what components make up perfect ventilation.
The content of the article:
Types and purpose of attic ventilation
The attic floor often has a non-standard shape and layout, because there are many solutions for both the shape of the roof and the arrangement under it. Ventilation in each specific option is different, as are the temperature conditions and the possibility of outputting communications.
The most common layout that is acceptable in terms of technical requirements is a sloping gable roof. Below it there is a room of a regular square or rectangular shape and three cold triangular segments of the attic.

Living space, attics, gable cladding, and roofing all need ventilation.
To organize it we use:
- Metal, plastic or corrugated pipes and transitions for ventilation ducts;
- Dormer windows built into slopes and gables;
- Overhead, duct and roof fans;
- Deflectors installed on aerators and ventilation pipes;
- Linear and point aerators;
- Soffits that provide flow into the attic space and layers of the roofing system.
- Ventilation gaps between layers of roofing pie.
Air circulation in a residential attic is especially important, since temperature changes and high humidity are possible in this room.
It can be organized according to the same principle as in any other room, or as in a non-residential attic. The choice of scheme depends on the purpose of the attic: for permanent or periodic residence, as well as on its layout.
Even with high-quality ventilation of the living space, mold may appear on the walls and ceiling. The reason for this is the stagnation of moist air in the cold attic triangles that separate the wall and ceiling from the roof slopes.
As a rule, their ventilation is the easiest and cheapest to organize, but you need to remember this even before the structures and finishes become affected by black mold.
Roof ventilation consists of air circulation inside the roofing pie, from the overhangs to the ridge.It removes evaporation and condensation, and also normalizes the temperature under the roof, which according to standards can exceed the street temperature by a maximum of 4 degrees.

This ensures the safety of the wood in the roof frame and metal roofing material, and prevents the appearance of rust and rot.
In addition, thanks to ventilation, the air pressure under and above the roof is equalized in strong winds. Thanks to this, the lifting force that tears off the roof is significantly reduced. The ventilated facade also ensures the safety of the sheathing material and insulation under the cladding.
Ventilation of the attic room
The immediate living area of the attic needs regular and high-quality ventilation, especially if this is a place of permanent residence and not a country house. The air exchange rate for a room is 2–3 times the complete renewal of air per hour, but if there is a bathroom or kitchen under the roof, the multiplicity factor increases to 8–12.
For normal functioning of ventilation, it is necessary to provide air inflow and exhaust paths that are approximately equal in throughput. In the attic, as a rule, it is necessary to take care not only of the removal of exhaust air, but also of the influx of fresh air - an open landing will not be enough.
In addition, it should be taken into account that the length of the air duct leading through the roof is less than that of the ventilation of the 1st floor, and therefore the natural draft is much lower.
Organization of supply ventilation
Even the most powerful hood will not be able to work effectively if fresh air has nowhere to come from. To do this, it is necessary to provide holes in the attic through which fresh portions from the street can freely penetrate.
The sources of inflow can be attic or dormer windows in the slopes, ventilation windows located in opposite gables or ordinary barred openings, supply wall valves. To regulate the flow, they can be equipped with diffusers.
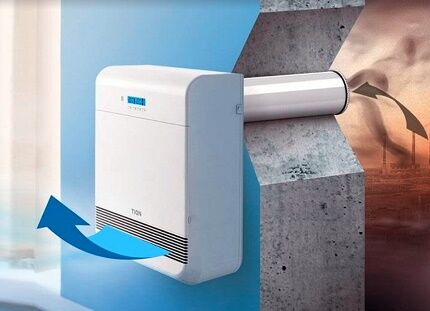
A basic device for fresh air ventilation looks like a round grille cut into the wall through a pipe. They are used where ventilation through windows is impossible or insufficient.
Air is drawn into the valve naturally due to the pressure difference, passes through a structure that absorbs the noise of the flow, and is supplied to the room. There are also universal supply and exhaust valves that allow air to pass in both directions.
A supply valve with a built-in fan is necessary to create a forced supply of fresh air. This is especially convenient and effective for attics of complex geometric shapes. Thanks to it, pressure will be created in the room, which will independently displace the exhaust air, leaving no stagnation zones.
As a rule, supply ventilation valve models are installed directly above the battery so that the incoming air can immediately heat up.In addition, you should not mount the inlets too high, otherwise the air will circulate only under the ceiling.

Dormer windows are ventilation openings closed with blind or hinged sashes with glazing or louvres. Ordinary double-glazed windows can also serve as dormer windows, if they are regularly opened slightly or equipped with ventilation valves.
The easiest way is for windows to cut into gables, and in small and medium-sized houses with gable roofs this is usually done. Then the air circulates both directly between the two gables and is removed by ventilation through the ceiling.
However, not every roof design implies the presence of gables, and if the room is large, windows only at the ends will not be enough. In this case, skylights are inserted into the roof or built into Dormers.
Panoramic windows cut directly into the slope, at an angle, continuing the plane of the roof. They provide a lot of light and can be installed in an already assembled roof without dismantling it. Such windows fit well into any exterior style, and their relatively high cost is compensated by the lack of costs for additional buildings on the roof.
Although this is the most popular solution, it has disadvantages: panoramic roof windows are prone to leaking, especially budget options or if installed incorrectly.

In addition, skylights can be used for ventilation. True, this is possible if they are equipped with opening transoms. These structures will serve not only to improve natural lighting, but also to remove household fumes, smoke, and exhaust air.
Dormers - these are small projections - “houses” on the roof for installing ordinary, vertical windows. Such “cuckoos” make the roof more beautiful and increase the interior space; in addition, a standard window with a window sill is added in the attic.
Myself dormer can be of different shapes and configurations:
- Triangular - with a gable roof at an angle of 64 degrees, descending to the main roof. It looks most organic in most cases.
- Square - with two vertical walls and a pitched roof, the easiest to build and allows you to install a rectangular window. And also with small vertical walls and a gable roof - in such buildings it can be difficult to waterproof the joints of the walls and the main roof;
- Arched - with a rounded roof. One of the most difficult to arrange, but on a rounded roof with a soft roof this is the only option that looks good.
Ventilation will also be provided by an anti-dormer – a window “recessed” into the roof. This design is cheaper, but it uses indoor rather than outdoor space for installation. They are especially popular in roofs with a large slope - for example, sloping roofs.
IN Dormers Most often, glazed windows are installed, which, in addition to ventilation, will provide lighting and the possibility of access to the roof.

Arrangement dormer – the best solution for a large attic or under the floorhip Danish roof. However, they cannot be installed on flat slopes with a slope of less than 350. It is also undesirable to point the windows to the north - it will be both dark and cold.
If we talk about sizes and spacing, it is not recommended to use windows smaller than 120x80cm. You should also not install them lower than 1 m from the floor of the veranda or closer than 80 cm from each other. For ventilation to be effective, windows, or rather their opening parts, must be at a distance of 80 - 100 cm from the ceiling or roof.
Arrange the doors in Dormers necessary at the design and roofing stage. When drawing up a roof plan, recalculate the total width of the windows - it should be no less than half the length of the attic. Also check that the vertical part dormer was located exactly above the outer wall of the house, and its frame could be fixed to the main rafters without cutting into them.
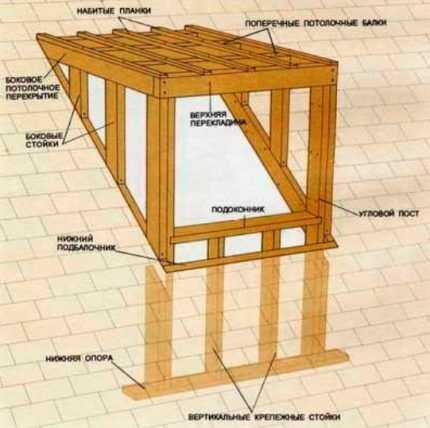
Regarding the relationship with the rest of the windows of the house, Dormers placed exactly above the windows of the previous floor - this is both beautiful and safe.
Hood through the gable
If there are gables in the house, not only fresh ventilation should be installed through them, but also an exhaust hood. Making a hole in them is always easier and cheaper than making a hole in the roof, but this is not always acceptable.
Firstly, this option is probably not suitable for those who have absolutely the entire space under the roof as living space - with open crossbars and without a cold attic above.The reason is simple: there is nowhere to lay a ventilation duct, and the hood directly on the pediment will only be sufficient for a very small one-room attic.
Secondly, it is advisable to avoid horizontal channels for those who have a bathroom or kitchen under the roof: these rooms need powerful exhaust hood, and moisture and soot from them can accumulate as condensation in the attic, inside ventilation duct and at its end, on the facade of the house.
The result is that condensation freezes in the attic and in the pipe, and the thaw floods the insulation, the attic ceiling, and the facade.
If you are setting up a living room in a well-insulated attic, and there is a cold triangle above it of at least a minimum height, effective ventilation of the attic is possible through the gables, and not through the roof.

The best device diagram is organized like this. In each living room or at the farthest point from the air supply (if there is only one room), a hole is cut in the ceiling. The grille and outlet are installed in this hole ventilation duct - corner or tee.
In the attic, all these openings are connected by a ventilation duct. In this case, a check valve is installed at the branch for each room, and the passage of the duct through the outer wall is also surrounded by check valves.
Preferably in the last part ventilation pipe, after connecting all parts, install a duct fan to force the hood to operate. To minimize the formation of condensation due to temperature changes, all ventilation duct pipes are insulated.
It is not advisable to install ventilation on the street level with the facade: perhaps the protruding pipe does not look particularly aesthetically pleasing, but condensation leaks on the pediment will be even worse. Also, the pipe exit must be covered with a special canopy - a façade exit.
The insidiousness of the arrangement hoods through gables from the attic space is that the construction of a high-quality system according to all the rules will cost almost the same amount as the output through the roof.

Natural ventilation of the attic floor through the gables will work well if there is a noticeable difference between the atmospheric pressure outside the structure and inside. In this case, you can even build a channel from a corrugated pipe with minimal or no insulation: it is cheaper and easier than using conventional pipes or flat channels.
Option with insert wall exhaust valve or simply a ventilation window for a residential attic, we do not consider it, since it involves the circulation of cold air directly through the room, from the supply openings to the exhaust openings. This scheme is unacceptable for a heated room: the heat will simply be blown out.
Ventilation outlet through the roof
This is exactly the solution that heating engineers recommend. And not at all because they want to get more money from you. The fact is that each horizontal section of pipe reduces natural draft, and therefore the efficiency of ventilation.
It is better to entrust the design of the ventilation shaft of a private house and its access to the roof to builders: not only the cross-sectional area and height above the roof are important here. The area and type of premises, the material and shape of the duct, the type of ventilation, pipe insulation, temperature in the attic, weather conditions and other factors are important.

A vertical pipe leading to the roof will save the house owner from problems with condensation in the attic and on the facade, and a deflector or roof a fan installed at the top of the pipe will provide the required level of draft.
Arrangement passage through an already assembled roof - it’s not an easy, costly and thankless task, so it’s better to provide a ventilation outlet on the roof at the stage of its construction.
Air exchange in a cold attic
In most cases, the shape of the attic room does not follow the shape of the base of the sloping roof, because it will not be easy to equip such a non-standard room and make it comfortable. After covering the vertical posts of the rafter frame and crossbars from the inside, there are always triangles separated from the usable area.
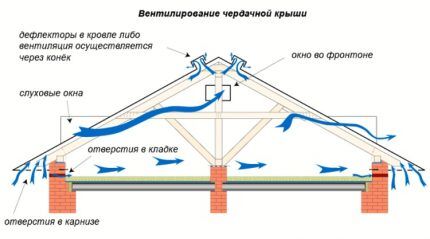
Solving the problem is not difficult: it is enough to install ventilation grilles, dormer windows, inlets or facade ventilation outlets on each gable so that air can penetrate through each cold triangle.
Don't let them bother you heat loss: they will be minimal, but you will prevent the appearance of mold and musty smell on the walls and ceiling of the attic, not to mention the safety of the roof and ceilings.
How to choose what to cover the ventilation holes of the cold triangles above and on the sides of the attic? Ventilation supply and exhaust valves are rarely used in this case: they are more expensive and their area is relatively small, and in sound absorption there is no need here.
Facade ventilation outlets are distinguished by the presence of a canopy that reliably protects from snow and slanting rain. The check valves from them need to be removed or perforated so that when the wind changes, the supply and exhaust openings can change roles.
Ventilation grilles and dormer windows essentially differ only in size and shape. The ability to adjust the opening of blinds and swing doors is of no use here.
Well-designed attic roof
In modern construction, they try to provide all structures with maximum thermal insulation, sealto reduce heat loss. This concerns structures enclosing the attic, perhaps most of all. After all, it is through the roofing system that the greatest amount of heat can escape.
If the layers of hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation in the roofing pie are folded without ventilation gaps, the insulation system will practically not work. Moisture that falls out in the form of condensation due to temperature differences, household fumes, and rainwater that has penetrated under the roof will not have the opportunity to escape outside.
Water is an excellent conductor; due to its content in the insulation, heat waves will freely pass outside.In addition, it provokes rotting of the wood from which the rafter frame is made, and often the cladding of the attic.
Draining the roofing pie is perhaps a separate extensive topic. However, its effectiveness significantly affects the microclimate of the attic, especially in the summer heat, when the top layer of the roof warms up to +1000S. Therefore, we will briefly talk about how this should be arranged.
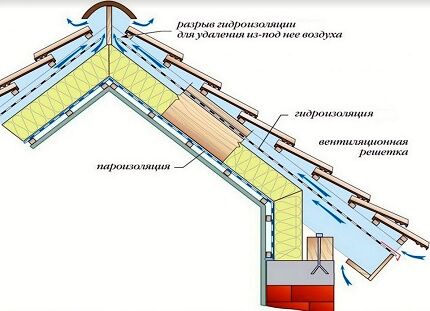
The purpose of any roof ventilation devices is to ensure air movement from the overhangs to the ridge. The easiest way to do this is under a slate roof or ondulina: under the waves of roofing material, the air freely rises to the ridge; in this case, the overhangs are not tightly hemmed.
WITH metal tiles And corrugated sheeting the situation is almost the same, but it is advisable to provide their cornices with ventilation grilles or close them with an air-permeable seal. The relief roof must be separated from the waterproofing by a spacer bar - it forms a ventilation gap required to remove fumes and atmospheric water accumulated under the coating.
Other materials, in particular soft tiles or sheet metal, require the artificial creation of 1 or even 2 ventilation layers of 3–5 cm, separating vapor barrier from the insulation, and the waterproofing film - and from the coating.
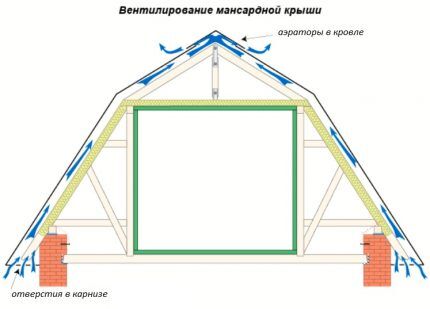
For this purpose, ventilation ducts are arranged by laying sheathing and counter-lattice. Air will rise between the slats. If the thickness of the rafters is not enough to lay all layers of the roofing pie and provide ventilation gaps, the rafter legs are extended with bars.
For influx into hemming roof overhangs use perforated inserts - soffits or ventilation grilles, at regular intervals along the entire length of the overhang. For exhaust, a special ridge with aeration or point aerators are installed.
The total cross-sectional area of all holes for ventilation of the under-roof space should be 1m2 for every 300 – 500m2 roof slope area.

Ventilation of the gables is carried out between the sheathing and the façade cladding material. If the sheathing is installed horizontally, then the sheathing supports are vertical, and they do not interfere with natural ventilation.
If the frame slats need to be fixed horizontally, there are several solutions for gable ventilation:
- Fasten small sections of slats horizontally in a checkerboard pattern. It's economical and efficient, but it can be difficult to get everything level.
- Install long slats, but make holes in them in a checkerboard pattern.
- Construct a vertical counter lathing. Ventilation in this case will be most effective, but the most material will be required.
If the sheathing is diagonal, preference should be given to the vertical arrangement of the slats.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
We discussed the principles and theory of attic ventilation in detail in the article, and you can clearly see the process of installing attic ventilation in the following videos.
Ventilation of cold triangles through façade ventilation outlets:
How to design dormer to install a dormer window in the roof:
How to arrange attic ventilation yourself:
To summarize, let us recall that it is equally important to arrange ventilation not only for the living space of the attic, but also for the cold attic triangles and the roof itself. Otherwise, problems may arise both with indoor comfort and interior decoration, and with the durability of the roof.
Have you already installed ventilation in the attic? Did you manage to create an effective system on the first try? Share your experiences, tips and additions to the article in the comments below.



