Heating supply ventilation in an apartment: types of heaters, features of their selection and installation
The ventilation system is the basis for a favorable microclimate both in the house and in the apartment.Complete air exchange, in which stale exhaust air is regularly replaced with fresh air, contributes to the well-being of household members and reduces the incidence of respiratory diseases.
However, street air entering through the supply valve can significantly lower the room temperature and increase home heating costs. In such cases, it is necessary to heat the supply ventilation in the apartment, thanks to which the temperature will not drop below the desired values.
In this material we will look at popular and ergonomic types of air heating systems for supply air, determine the key characteristics of the heaters and talk about the appropriate stages of installing a ventilation system at which it is appropriate to install these components.
The content of the article:
The need for supply ventilation with heating
Supply ventilation is a proven way to ensure normal air exchange in an apartment. It is necessary to replace heavy stale air not only in the kitchen or in the bathroom: in all rooms where residents spend the bulk of their time, care must be taken in advance to supply fresh air from the street.
According to the old standards adopted back in Soviet times, for each person constantly staying in a living room, a minimum of 60 cubic meters is required. m of fresh air per hour. A similar indicator is relevant for a bedroom or children's room.
For an area with periodic occupancy, for example, a living room, the minimum threshold for the amount of supply air is 30 cubic meters. m/h. Modern European standards for supply ventilation system performance are lower and offer 30 and 20 cubic meters. m/h per person for rooms with permanent and periodic stays, respectively.
However, even a reduced flow of fresh air from the street can significantly affect the temperature in the entire apartment. Cold air masses increase the load on the heating system, reducing its efficiency. As a result, energy is wasted, which is spent on warming up the cooled air.
Additionally, staying in a room with low air temperature can cause hypothermia and provoke the occurrence of certain diseases.

These problems can be solved with the help of an air heater, which is installed on the supply ventilation of the apartment. For the domestic climate, such a unit in the ventilation system is an urgent need. When the temperature outside the window noticeably drops, an air heating element will be the only effective way to prevent drafts and keep the house warm.
A ventilation system with an air heater allows you to simultaneously compensate for heat loss and saturate the internal climate with the necessary volume of fresh air masses.
Methods for heating ventilation air
In fact, you can warm up the air coming from outside using different methods:
- use of a recuperator;
- installation of a special heater or heat fan;
- application of the recycling principle.
These systems for heating outdoor air in supply ventilation are the most popular among users. Let's look at them in more detail.
A fairly effective mechanism for reducing heat loss - recovery heat in ventilation systems. The recuperator is a heat exchanger in which cold air from outside is heated due to the heat transfer of previously heated air masses in the apartment, which are removed by the ventilation system itself. However, a significant disadvantage of designs with a recuperator is their high cost, which does not always pay off quickly by minimizing the cost of operating the supply ventilation system.
A heating element, built into the chain of units of the supply ventilation system, is an equally reliable and effective way to heat cold street air. With this method, the flows are warmed up in the ventilation duct, passing through a thermal heater, and enter the apartment at the required temperature.

Supply ventilation with a heating element is usually cheaper to install, but heating the air itself requires more energy resources than the heat exchange process during recovery.
Air recirculation is in many ways similar to recuperation, in which the heating of air masses occurs due to the heat of exhaust air. However, if air flows do not mix during recuperation, recirculation involves merging indoor air with fresh outdoor air, thereby increasing the temperature of the latter.
For integration into an apartment, the most convenient is a ventilation system with heating of the supply air using a separate heating unit. Such complexes are cheaper to install and are often more compact.
Design and operation of fresh air ventilation
The design of supply ventilation with heated air masses consists of several key links:
- At the entrance to the system there is an air intake grille, which has decorative and barrier functions, preventing large particles of dirt, insects, and dust from entering the system.
- The check valve regulates the volume of air passed through, limiting its flow if necessary.
- Blocks with filters purify air masses.
- A heater, recovery or recirculation unit heats the air.
- The fan directs the flow, promoting the formation of the required level of draft, after which the air enters the apartment.
In addition to these elements, the system may have diffusers that help distribute air, silencers and fans.

An integral part of the design is the thermal insulation of the channel, thanks to which the system itself and the wall in which the hole is made for air intake and exhaust do not freeze.
We discussed in more detail the design and principle of arrangement of supply ventilation in next article.
Types of heaters for ventilation systems
Two types of air heaters can be built into the air heating system in the supply ventilation: water and electric. Let's look at their features in more detail.
Type #1 - water heater
The water heater is most often used in central ventilation and is interconnected with the heating system. Integration with the heating system allows you to save energy, since the air is heated using the coolant.
The block is a radiator with tubes containing coolant. The surface of the pipeline itself has fins, which increases the area of contact of the heater with the air masses. Heat exchange occurs as follows: the coolant heats the tubes, which transfer the resulting heat to the fins. The latter directly heats the air.
We examined in more detail the design and operating principle of a water heater in this publication.

However, installation of such a complex costs significant funds and requires significant intervention in the premises itself, after which repairs may well be required. The design of such ventilation systems must be carried out by specialists. In addition to these disadvantages, there is always a risk of water freezing in the heater with minimal radiator operation.
Type #2 - electric heater
The electric heater operates from the mains and is no less efficient. Such a unit slightly, but still increases energy consumption. However, heating the air using an electric heater is the most acceptable solution for a small apartment.
Like a water heater, an electric heater can have fins to increase the area of contact with air.
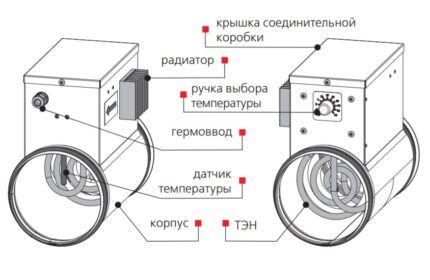
Additionally, electric and water heaters differ in shape. Depending on the configuration of the ventilation duct, they can be round, square or rectangular.
We wrote about the rules for calculating the power of water and electric heaters in the article: Heater calculation: rules for calculating the power of water and electrical units.
Integration of the heater into the ventilation system
It is possible to properly install the necessary heating in the inlet at the stage of installation of the entire ventilation system, since disassembling a ready-made complex to integrate a separate unit is a rather labor-intensive process. But to install a water heater, this procedure is practically impossible, since this unit must be connected to the heating system of the apartment.
To install an electric heater into a ready-made and functioning ventilation system, it is necessary to disassemble the latter up to and including the unit with the fan.
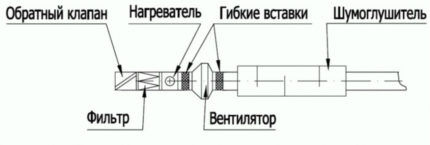
The heater is installed in front of the fan immediately after the filters.
This location is due to the fact that in winter the lubricant of bearings in radial fans tends to thicken, which can cause jamming of parts and overheating of the winding. The heating element neutralizes the effects of cold and prevents damage to such an important unit.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below provides recommendations for choosing heated supply ventilation and discusses the key differences between a stacked ventilation system and a monoblock:
The author of the following video examines the advantages and disadvantages of the supply ventilation system and the breather, which is popular among apartment owners:
Air exchange and removal of carbon dioxide from the room are the basis for a healthy microclimate in the apartment. The maximum possible air circulation can be achieved using a supply ventilation system. Effective heating of the air coming from the supply ventilation is practically irreplaceable in our climate.
A rationally selected heater will make it possible to save energy resources and maintain the optimal temperature in the apartment, providing the room with the necessary volume of fresh air.
What method of heating the supply air do you use? Do you think your option is the most rational - share your opinion and useful information on installing the heater with other users in the comment block below.



