Pipe for drip irrigation: what to look for when choosing + rules for working with it
Plants need water just as much as people.With insufficient watering, they also experience stress, which slows down growth and disrupts metabolic processes in the stems, leaves and root system. To constantly supply water to the roots in measured quantities, a tape or pipe for drip irrigation is increasingly being used.
In this article, we will look in more detail at the types of this equipment found on the market and the features of choosing the appropriate option.
We will also pay attention to the features of self-assembly of a drip pipeline, and provide recommendations for using the system and its storage in the winter. We will also consider the main problems that most often arise during operation and ways to eliminate them.
The content of the article:
Components of drip irrigation systems
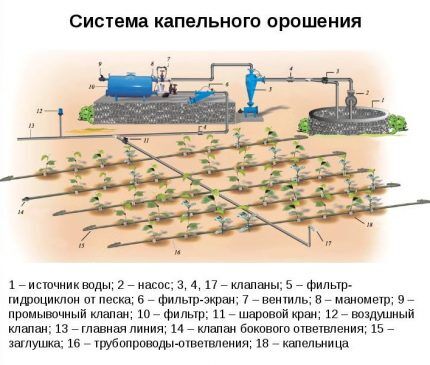
The drip irrigation system for plants is not simply connected to a water tap, but has many special components and devices.
The optimal equipment configuration includes the following components:
- Pressure regulating valves. They are located in front of the drip pipes and reduce the water pressure. High pressure can cause tubing damage and uneven watering along its length.
- Filter system. The outlet holes in the pipes are very small, so they easily become clogged with the smallest particles of sand and dirt. Filters are used to prevent clogging.
- Water meter. Device for determining and accounting for real consumptionnecessary to calculate the actual water requirement.
- Fertilizer application unit. It consists of a container for mixing fertilizers and pumping equipment that supplies water to the pipe system.
- Controller. A device that regulates the operation of the water meter and pumping equipment. Serves to regulate the volume and time of watering.
- Main pipe system, supplying water to the irrigated area.
- Drip pipes and droppers. Devices that directly distribute water.
Due to the maintenance and setup requirements of drip irrigation systems, their cost is largely determined by the price of additional equipment. It often costs much more than the polyethylene pipes themselves, so when choosing an irrigation system, the financial factor should be taken into account.
Main advantages and disadvantages
There is a wide selection of different types of pipes for irrigation plants, so choosing the right option is not so easy.
The choice of a drip system as the best option for irrigating plants should be made only after weighing all the advantages and disadvantages. After all, the method using a hose with suitable watering nozzle will cost much less than maximum automation of the watering process.
Benefits include:
- No sunburn of leaves. When watered by rain, the water focuses light on the leaves, which leads to damaging sunburn. Drip irrigation releases water directly into the soil, eliminating sun damage to plants.
- Low minimum operating pressure. During the summer season, water supply pressure often drops, and water the plants with a hose uncomfortable. The drip system has enough pressure of 0.2-0.3 atmospheres to operate.
- Possibility of supplying warm water from storage tanks, which eliminates temperature stress in plants.
- Save 60% water compared to rain irrigation.
- Possibility of applying insecticides directly to the soil, without contact with vegetables and berries.
- Reduced fertilizer consumption due to their better digestibility and reduced soil losses.
- Possibility of night watering. Water supply is carried out automatically without the participation of site owners.
- No physical costs for watering and control over the amount of water spent.
- Possibility of automating the irrigation process. A convenient function that allows you to care for plants with minimal labor costs, because you do not need to walk around the site, “dragging” a hose behind you.
- Increase in productivity by 2-3 times. It becomes possible due to constant water supply and reduction of stress in plants.
Despite the obvious benefits of use, the pipe drip irrigation system also has its disadvantages. Which are such only upon superficial examination.
These include:
- High cost of drip irrigation systems. It must be taken into account that the initial cost of the equipment is offset by savings on water consumption and income from increased productivity.
- Difficult to install. It is easy to install a simple dosed irrigation system.You can do this in one day, and then save time on irrigation all summer.
- Clogging of droppers. Properly installed drippers rarely become clogged with soil, and the supplied water can be purified using passive filters.
The above advantages of a drip irrigation system are not exhaustive. This technique has many additional positive aspects for professional farmers. Therefore, installing pipes for drip irrigation is an ideal option for watering a summer cottage.
Types of drip systems
Despite the apparent similarity of all water hoses for drip irrigation of plants, they are all divided into two groups: tapes and pipes.
Features of drip tapes
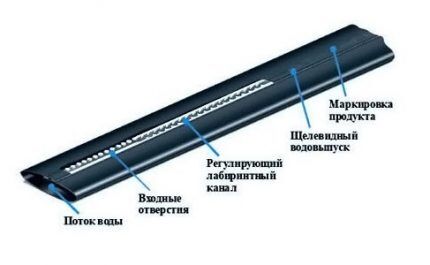
Polyethylene drip tapes have a wall thickness of up to 0.4 mm, so they are easily flattened and wound onto a drum. Due to the low material consumption, the price of the tapes is quite low.
According to the mechanism of water outflow, they are divided into labyrinth, slot and emitter.
Pipes for drip irrigation
Pipes for assembling the drip system are made of polyethylene or PVC and they have walls with a thickness of 0.4 to 1.5 mm. The hoses do not collapse and always maintain a circular cross-section.
These products themselves will be discussed further.
Classification and application of drip pipes
Drip pipes, unlike tapes, are guaranteed to last 5-6 seasons, so their use is effective when growing perennial plants and trees. Due to the wide variety of designs and types of pipes for drip irrigation, it is worthwhile to dwell in more detail on the areas of application and selection of this or that type of equipment.
Most drip pipes on the market have an outer diameter of 16 mm, although products are sold in 12 and 20 mm thicknesses.
Otherwise, drip systems can be divided according to the following functional and structural differences:
- by pressure uniformity in the pipe;
- by type of dropper;
- one step at a time between droppers;
- by the location of the equipment relative to the ground;
- by the presence of holes for droppers;
- by water consumption.
Next, we will consider the classification of drip tubes according to the listed characteristics.
Criterion #1 - pressure uniformity in the pipe
According to the uniformity of pressure distribution, the tubes are divided into:
- Compensated. The flow rate of outgoing water at the end and beginning of the tube remains unchanged and does not depend on the pressure.
- Not compensated. The water flow varies depending on the pressure applied at the beginning of the hose.
- Adjustable.
It makes sense to buy compensated pipes when the length of irrigation lines is more than 20 meters and at a minimum operating pressure of at least 1 atm. For Spanish drippers, the opening threshold is 0.3 atm, for Israeli ones - 1 atm, that is, at lower pressure, water simply will not leave the system. We talk about ways to increase pressure in the system talked here.
And with a short length of pipes, watering will be uniform along the entire length.

Uncompensated and adjustable drippers can operate at any pressure and even in gravity systems. Adjustable pipes require initial fine adjustment, which is time consuming.
Criterion #2 - type of dropper
Pipes may have the following types of droppers:
- rigid, in the form of an elastic tube;
- soft, in the form of a tape;
- built into the wall.
Pipes with built-in drippers are used mainly in dense gardens, artificial landscapes and shrubs, where the poured water will be available to the root system anywhere.

Drip hoses with built-in external drippers are used for watering plants in the following areas:
- ornamental plant growing;
- hydroponic systems;
- industrial berry orchards;
- nurseries.
They can also be found in vertical gardening systems.

Drippers allow you to supply water to each root separately.
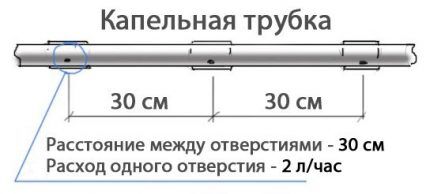
Criterion #3 - step between droppers
The pitch between the emitters in the drip tubes must be selected based on the crops being grown. There is no need to buy equipment without a clear understanding of the list of plants that it will water.
Pipes can have the following pitch between emitters:
- 10-20 cm — installed for irrigating grass lawns, onions, garlic, parsley, lettuce, etc., used on sandy soils when high water consumption or linear irrigation is required.
- 30 cm — used for irrigating potatoes, strawberries, cucumbers, and peppers.
- 40 cm or more (up to 150 cm) — used for irrigating tomatoes, pumpkins, zucchini, watermelons.
The latter species is often used in a nesting scheme for planting shrubs.
If there is no planting plan, then it is best to buy a blind pipe and subsequently determine the insertion locations for the droppers yourself. In addition, reducing the pitch between emitters leads to higher equipment costs.
Criterion #4 - equipment location relative to the ground
Based on their location relative to the soil, pipes are divided into:
- superficial;
- subsoil.
Pipes laid underground have a special design that prevents them from quickly becoming clogged with earth.
They are used in the following cases:
- It is necessary to hide watering for aesthetic beauty.
- There is a possibility of pipe theft.
- In artificial landscape systems.
They are also relevant for preventing damage from machinery during land cultivation.

Installing an underground system requires additional labor and financial costs.
Criterion #5 - presence of holes in pipes
According to the presence of special places for connecting droppers, pipes are divided into:
- blind — these are solid pipes, holes for droppers in which you can make yourself in any place;
- emitter, with built-in outlets.
Both types are actively used.

Blind drippers are convenient for watering chaotically located berry bushes and artificial landscape elements. Using a drill or a tip, you can always make a hole in them in the right places and insert a drip tube into it. There are plugs to plug extra holes.
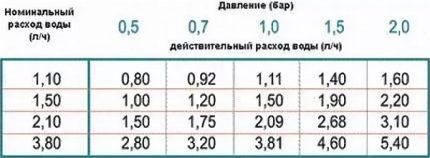
Criterion #6 - water consumption
There is no clear division of drip pipes in terms of water flow, but for each product this parameter is specified in the instructions.
Equipment with different capacities has its own areas of application.
- Emitters with a water flow rate of 2-4 l/hour are installed on beds that require double-sided watering from one hose, as well as on sandy soils with high absorbency.
- Water in an amount of 1-1.5 l/hour is enough for most grass lawns and vegetable crops.
- Low flow rate of 0.6-1 l/hour is used on long irrigation lines and clay soils.With such pressure, good water filtration is required, otherwise the pipes may become clogged.
If desired, the water flow can be adjusted.
Before choosing pipes for drip irrigation, consultation with specialists is required in order to purchase exactly the equipment that matches the existing conditions and plants.
DIY irrigation system construction
You can make an effective automated irrigation system with your own hands. Its installation will cost much less than assembling and installing a ready-made set of pipes and fixtures. In addition, applying your own strength and skills will bring undoubted pleasure:
An automated irrigation system made of polyethylene pipes can be laid openly; it is not afraid of sunlight.
It is not recommended to install pipelines from PVC pipes in open areas; it is not advisable to use polypropylene if there are sources of open fire nearby.
Have you decided to install the summer water supply at your dacha yourself, so as not to waste extra time and effort watering the plants by hand? We recommend that you read step by step guide for laying an automatic irrigation system using pumping equipment.
Recommendations for using drip systems
There are time-tested recommendations for the use of drip pipelines that increase their efficiency.
- It is best to add fertilizers and bioadditives to the soil by dissolving them in water supplied through a drip system.
- Watering should begin 2 hours after sunrise, and end 2 hours before sunset.
- The optimal water temperature for irrigation is 20-23 degrees.
- You cannot immediately supply cold water after the supply of warm water has been exhausted.
- In a gravity system, the water tank should be at least 1 meter from the ground.
- It is necessary to ensure that the diameter of the wet spots around each dropper is uniform. Their increase or decrease may indicate, respectively, a rupture or clogging of the pipeline.
If it is impossible to water during the day, it is recommended to give the plants 2/3 of the daily water requirement in the morning, and 1/3 in the evening.

Proper watering saves water and guarantees a high yield and beautiful lawn.
Pipe problems and their elimination
The effectiveness of drip pipes is highly dependent on operating conditions. The equipment can last a month, or maybe five years - it all depends on following the basic rules of its use.
The main causes of problems with drip pipes are:
- clogging;
- root germination;
- improper storage during the off-season.
Next, the listed problems will be considered in more detail, and options for their prevention will also be proposed.
Clogging and flushing the system
Country irrigation is often carried out with water from wells or natural bodies of water, so periodic clogging of pipes is understandable.
To purify groundwater, a mesh filter will be sufficient, but when watering from reservoirs, you need to install an additional disk filter device.In the absence of preliminary cleaning, clogging of the droppers can occur within a few days.
Regardless of the presence of filters, drip pipes must be regularly cleaned of mechanical sediment using water pressure. To do this, you need to open the far end of the pipeline and supply water to the system at a speed of 6-7 l/min. Washing continues until the sediment is completely cleared.

Elimination of bacterial mucus from the system is carried out by flushing with a 0.5% sodium hypochlorite solution. It is necessary to fill the system with the mixture and leave for 12 hours. After this, drain the chlorine liquid and rinse the pipeline with clean water for 10 minutes.
As contamination occurs, the drip system is also cleaned of salt deposits with 0.6% nitric, orthophosphoric or perchloric acid. The water used should be as warm as possible. The pipeline is washed with an acid solution for 50-60 minutes. After the procedure, you should rinse the system with clean water for half an hour.
Preventing roots from growing into pipes
Drip systems with round holes for water outlet are most susceptible to germination. The more moisture deficit plants experience, the stronger their roots are drawn to its source. Therefore, the basis for preventing root germination is sufficient watering.
Additionally, you can periodically move the pipes a few centimeters to the side so that the roots do not concentrate near the droppers.

If the problem cannot be solved by these methods, then it is possible to use special chemicals that inhibit the growth of the root system. But it is recommended to use them carefully so as not to destroy the plants being grown.
Storing pipes in winter
You need to plan cleaning of the drip line in advance so that unexpected cold does not freeze the water in the system and damage the pipes.

Before cleaning the pipeline for the winter, it is necessary to clean it of mechanical sediment, mucus and lime deposits. You need to wind up the drip system slowly, raising the hoses high to drain the water. Rolls should be stored in a dry place, preventing the entry of rodents that can chew on the equipment.
Compliance with these rules will allow you to operate drip pipes without problems during the entire warranty period.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The presented videos demonstrate irrigation systems in field conditions. Viewing them will help you better understand the processes of installation, operation and automatic control of drip pipes.
Installation of a blind drip pipe:
Working with a drip irrigation tube:
Automated drip system:
In skillful hands, drip irrigation turns into a powerful tool for saving finances and personal time while simultaneously improving the growth dynamics and well-being of plants.
These systems do not require special equipment or skills for installation, so anyone can assemble them. And certain financial expenses will pay off many times over in just a couple of years.
Do you irrigate all the plants in your yard using a drip system? Tell us what pipes you chose to install the system, approximately how much it cost you, and are you satisfied with the results? Share your successes in growing vegetables and increasing their yield with beginners - leave your comments under our article.




Generally great! After all, if the irrigation system is fully equipped, it will be able to function without human intervention at all. I smiled slightly at the mention of summer residents and their harvest. I just remembered the old people with backpacks and buckets on commuter buses, who will certainly introduce an automatic watering system on their 6 acres. This is, of course, more relevant for small agricultural farms.
You shouldn’t be so skeptical, Egor. Among these gardeners there may well be good Soviet-trained engineers who are quite capable of making such an irrigation system. Perhaps a little simplified, not autonomous, but still. I remember very well from my childhood how my grandparents had a hanging irrigation system made from plastic bottles at their dacha.
Ivan, you don’t need engineering knowledge to install the system. Typical options have already been developed and calculated - you just need to do everything according to the instructions.
Cool. What brand of drip tube?
I took galvanized BSHGD pipe, it’s perfect for my hundred-hectare land.
Immensely grateful for the information. Laconically. Intelligible. Effective! I am planning to build something similar here too. Once I do it, I'll let you know the result. I'll send you a photo. Well, with God)