Insulation for warm water floors: rules for selection and installation
Are you installing a water-heated floor system in a country house and it’s time to lay the insulating underlay? Agree that among the variety of offers of heat-insulating materials offered by manufacturers, it is sometimes not easy to make the right choice.
We will help you determine which insulation for a warm water floor is better. Together with you we will understand all the intricacies of assembling heat-insulating systems. We will examine the characteristics of popular materials and evaluate the key advantages and disadvantages.
Do-it-yourselfers will find installation instructions here. To make it easier to navigate the assortment offered by the building materials market, we have selected videos with recommendations for choosing insulation and installation.
The content of the article:
The need for thermal insulation of the system
Any instructions for installing a water heated floor for DIYers indicate that it is necessary to use insulation.
The insulation layer when installing a water floor performs several significant functions. It helps not only to ensure uniform heating of the room, but also, acting as a heat shield, can significantly reduce the energy losses of the system.
A screed laid on top of an insulating layer acquires the properties of a solid heat-transmitting element with a large surface area.
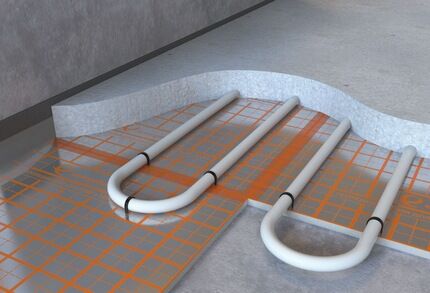
Thanks to the uniform distribution of energy, the ordered convection heat flow begins to move at the same speed and in the same direction. As a result, evenly distributed heat waves will not form cold and hot areas on the floor, creating the most comfortable conditions for household members.
In addition, thanks to the direction of warm air flows along one course, it is possible to reduce energy costs for operating the system, while maintaining its power unchanged.
Modern thermal insulation mats are equipped with convenient latches in the form of bosses, with the help of which laying and subsequent fixing of pipes can be done quickly and at the same time reliably.
Types of insulation for water heated floors
There are many options for insulation for underfloor water heating systems on the modern market. The choice of substrate thickness is limited only by the material capabilities of the owner and the technical parameters of the room.
Absolutely all thermal insulation materials prevent the movement of sound waves through their thickness, and therefore are characterized by high noise absorption rates.
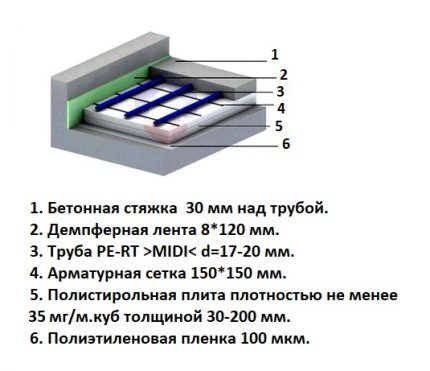
Regardless of the design option, special requirements are imposed on the heat-insulating material:
- it must have a low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- absorb the load created by water-filled pipes;
- withstand the load of the screed laid on top of the pipeline;
- be resistant to dynamic influences that may arise during operation of the system, and after pressure reduction it must return to its original shape.
The desired effect can be achieved by using insulating material with a density of at least 35 kg/m3.
Option #1 - heat-insulating boards
In rooms where the ceiling height reaches 260 centimeters or higher, you can safely give preference to insulation materials based on a rigid polymer base.
Polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam. The basis for the manufacture of thermal insulation boards can be polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam.
The first option was created using a non-extrusion method; between its polymer cells there are channels for the passage of air and steam. Polystyrene foam has a low specific gravity and high vapor permeability.
In the production of expanded polystyrene, the extrusion method is used, due to which the cells of the material are firmly sintered by the walls with each other. Because of this, the vapor permeability of the insulation is practically zero. But it has high strength and the ability to withstand significant mechanical loads.
The specific heat capacity of expanded polystyrene is slightly higher than that of polystyrene foam. In the first case it is equal to 1.34 kJ/(kg°C), in the second it is calculated at 1.26 kJ/(kg°C). The difference is small, but during calculations it can significantly affect the overall thickness of the floor heating system.
Standard size of thermal insulation Penoplex sheets, for example, 120 cm × 240 cm. GOST number 15588-86 regulates the width from 50 cm to 130 cm, length from 90 cm to 500 cm.
The density of foamed polystyrene is 150 kg/m³, the same characteristic of polystyrene foam is 125 kg/m³.Depending on the specifics of production and the properties put into products by manufacturers, the characteristics of materials may vary.

If we compare both types of material, then foam plastic is disadvantageous because it is inferior extrusion product in terms of density. Due to this, it is less resistant to deformation under mechanical loads.
This significantly reduces its thermal insulation properties. It is recommended to lay polystyrene foam in the structures of decking systems between joists.
Cork. Often as thermal insulation substrate Cork is used for water and electric floors. Thanks to its special structure, which consists of miniature prisms of the correct shape, cork insulation is distinguished by significant compressive strength and lack of adhesion to cement mortar.
Due to the high cost of the material, cork is often chosen for residential premises, in which the base is already well insulated. Otherwise, to achieve the desired effect, you will need to purchase a technical cork with a thickness of at least 30 mm, which can significantly “hit your wallet.”

The only drawback of cork mats is that they are hygroscopic and are also available as single-component heat insulators. Therefore, when laying them, it is necessary to use an additional layer that will provide steam and water protection.
Mineral wool. An alternative, affordable option is to use mineral wool. It is available in the form of a flexible mat or a rigid slab.
Since, when laid in a screed, mineral wool is crushed under weight, which negatively affects its heat-shielding properties, this material is also best combined with decking structures assembled from wooden logs.

The only drawback of the material is the presence of penofol in the composition, which poses a danger to human health, and low moisture resistance. But properly executed waterproofing easily eliminates these shortcomings.
Option #2 - profile systems with guides
Profile systems help facilitate the installation of water circuits. They are created using hydropellent stamping technology, as a result of which shaped protrusions are formed.
Products come in two types: regular and laminated, which are covered with a vapor barrier film.

The basis for their production is extruded polystyrene foam, which is created by squeezing the molten composition through the holes of the extruder.
The polymer base is famous for its resistance to moisture and high mechanical strength. The thickness of the plate itself can vary from 10 to 35 mm. The main thing is that it is proportional to the thickness of the finishing screed.
The side faces of each plate are equipped with locks, which make it convenient to adjust the elements, forming a continuous field, devoid of thermoacoustic seams.
The height of the cylindrical protrusions located on the surface of the plates reaches 20-25 mm. This is enough to conveniently place and securely fix water circuits with a diameter of 14 to 20 mm. Densely planted rows of bosses eliminate the possibility of shifting the laid contours during the process of pouring the cement screed.

A special feature of the installation of profile systems is that after laying the water circuits in them, the structures are filled on top with a small layer of adhesive. And only after a day or two, when the glue has completely dried, the system is put into operation.
Option #3 - roll insulation
Roll insulation is chosen for rooms where the distance to the ceilings is critical. Using thin foil layers with a protective lavsan coating, you can significantly reduce the thickness of the “pie”. The maximum thickness of such a substrate is only 9-12 mm.
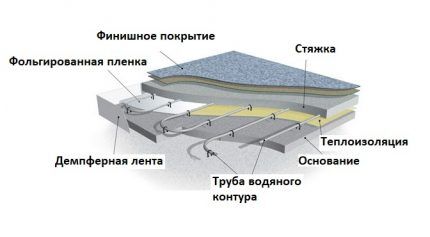
Rolled thermal insulation is equipped with a heat-reflecting shell made of lavsan or thermal insulation. Thin metallized materials perfectly reflect heat rays, so you can safely reduce the thickness of the insulation without fear of reducing the insulating qualities.
An important requirement when using foil options is that materials with aluminum foil cannot be used in the construction of floors with cement-sand screed. The alkaline environment of the mixture when pouring will simply corrode the aluminum layer.
However, if a protective film is applied over the foil, installation is possible. Use is permitted if the solution is mixed with gypsum and not with cement powder. Some manufacturers replace the foil layer with lavsan or polypropylene film, adding metallized inclusions to it.
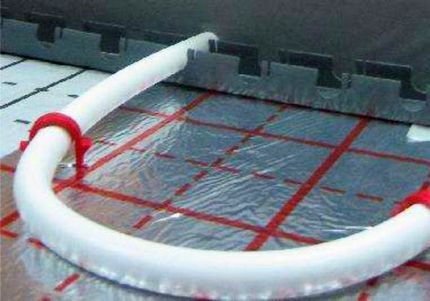
The disadvantage of foil materials is that they reflect heat well, but do not insulate well enough. If the floor is laid above a basement, thin roll solutions are not enough.
Some craftsmen solve the problem by laying hard insulating mats not in one layer, but in two. But at the same time, the sheets are placed in such a way that the seams of the lower substrate overlap the seams of the upper one. This allows you to minimize heat loss.
Features of laying insulation
The substrate installation scheme depends on the type of materials used. But in any case, it must be placed on the most flat surface possible.
No. 1 - slab laying technology
The substrate, constructed from slabs with a mounting chamfer, is assembled easily - according to the principle of a designer. The slabs are easy to adjust and measure. You can cut the slabs to the appropriate sizes with a regular knife.
The simplicity of laying the substrate is convenient because during installation you can change the configuration of the circuits and the length of the pipelines at any time. To prevent the slabs of material from moving relative to each other during installation and operation, their joints are glued with construction tape.

Sequence of actions when laying insulation boards:
- Foam boards are laid on the cleaned and leveled base, fixing them with special plastic brackets, anchor dowels, or by placing them on an adhesive composition.
- A foil layer is laid on top of the laid and joined slabs.
- The top layer is lined with a reinforcing mesh, onto which the pipes are subsequently mounted.
If the concrete screed of the base floor is poured with significant deviations from the level or has rough cracks and unevenness, or the concrete slabs are laid with irregularities, it is better to build a frame before laying the substrate.To do this, wooden logs are assembled from dry and even timber with a section of 50x50, 50x100 or 100x100 mm.

A distance of 60 cm between the logs is considered the most optimal option, since this “step” does not require the creation of additional sheathing. The main thing is that the logs are located in the same plane and lie strictly level.
Thermal insulation boards must be tightly laid between wooden joists. If there are cracks, they must be filled with foam.
When laying slabs of extruded polystyrene foam, it is necessary to observe some nuances:
No. 2 - installation of roll materials
The roll material is laid on a carefully leveled base and fixed to the base using tile adhesive or double-sided tape.Cutting strips of the required size is done with ordinary office scissors.
To compensate for the thermal expansion of the screed, it is recommended to place the foil layer slightly overhanging the wall.

When laying rolled materials, they are guided by the markings of the printed installation markings. It determines the distance between contours and facilitates pipe laying. Typically, rolled materials have allowances of foil polymer film at the edges to allow connection of adjacent webs.
When laying sections, pay special attention to expansion joints. To do this, the joints of the laid strips are glued with one-sided construction or metallized tape. If cork is used as a substrate, then before laying it it is necessary to take care of reliable vapor and waterproofing.
No. 3 - mat installation diagram
The stage preceding the laying of mats is the installation of film waterproofing. After laying it around the perimeter of the room, strips of damper tape are glued along the bottom of each wall.
Mats are laid on the prepared base, fastening the slabs together using a locking system. To reliably fasten slabs of small thickness and light weight, use the adhesive method and use plastic harpoon staples.

An important point: when laying mats, it is not allowed to use metal fasteners, since they can damage the integrity of not only the heat insulator, but also the waterproofing.
The choice of the optimal base option for a thermal insulation substrate depends on your capabilities. Yes, a good substrate will not be cheap. But it will significantly increase the functionality of the equipped water floor system.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Choosing insulation for cement screed:
Video #2. A clear example of laying mats:
Video #3. Installation of roll insulation:
In order not to make a mistake in choosing insulation for a water floor, be guided by the technical characteristics of the room, taking into account not only the thickness of the product, but also the maximum permissible compressive load.
By choosing a heat insulator wisely and observing all the details of installation, you can create a reliable foundation for arranging a functional floor water system.
Would you like to talk about how you selected and installed insulation under the heating floor in your home? Have questions or valuable recommendations? Please write comments in the block below.




Perhaps I am somewhat old-fashioned, and perhaps even this is all out of envy. In principle, I don’t understand the purpose of heated floors in a private house (there is an option with wooden joists). I looked at the photos, good insulation, why heat it up further? I have a private house, the floors were laid with a 15cm layer of mineral wool insulation. And it's beautiful! Feet are warm. I can understand how, again, from the article, comfort is created in an apartment building due to the cold contours on the floors. Well... it's the owner's business.
Well, you know, houses are also different, just like people. Some may feel comfortable on an insulated floor, but others need to even turn the heated floor regulator to maximum so that it is not just cold. In addition, the floor covering can be different; if it is tile, for example, then you simply cannot do without a warm floor.
When installing a heated floor, insulation is used to “not heat” the foundation. That is, so that the heat does not go anywhere, but gets exclusively into the house. For example, I have heated floors throughout the house, and insulation is also used. Heating is by electric convectors, and this whole system is connected to a thermostat, which can be used to regulate the temperature in the house.
If you haven't noticed, the thermal insulation is laid directly under the water circuit pipes. This ensures higher efficiency when using water heated floors.
Igor, it’s all about saving money while increasing efficiency. The insulation under the finished floor protects against the cold from below, but it does not warm the floor itself. Heating devices bring warmth into the house. But what type they will be and where they will be located will all affect the indicators of efficiency, optimality and personal comfort. The heat from the heater located under the feet is most comfortable for a person and is more evenly distributed over the height of the room; there is no excess heat under the ceiling when there is cold at the floor level.
Quite the contrary, by arranging a heated floor in this way, you “invite” the cold from the floor into the room, and besides, you additionally pay for the heat. With the internal insulation method, there is a problem of thermal heterogeneity of the external enclosing structure with thermal bridges at the junctions of the external wall with the ceilings and internal walls. But the main problem is different, the freezing and thawing of structures typical for the cold period of the year leads to a loss of strength properties, which affects the durability of the building in general and the floor in particular.
There are these words from a famous song: “As long as there are fools in the world, we can live by deception.”
It’s very easy for people who don’t want to be friends with physics to “sell” about the miraculous heat-reflecting properties of foil. It is well known that heat can be transferred in three ways: conduction, radiation and convection. Thus, foil can partially reflect only the heat that is transferred to it by radiation (through the air). In another case, foil perfectly transmits (rather than reflects) heat. For example, if the foil lies under a screed (or other) without an air gap and directly (physical contact) perceives heat, then there can be no “heat reflection”! This is physics!
And sales managers are “sharpened” to “sell” about the wonders of heat reflection. Often they themselves believe...