Sectional heating radiators: types, description, how to choose and connect
Despite the massive dominance of “warm floors”, economical electrical panels and climate systems, sectional heating radiators are still in stable demand among everyone who is determined to make heating comfortable and economically profitable.
The reason for its popularity is that nothing more reliable, easy to repair and effective than water radiators has yet been invented. What advantages and disadvantages do they have?
The content of the article:
What types of sectional radiators are there?
Consumer choice is strongly influenced by advertising. There is an opinion that sectional heating radiators are not so efficient, are morally and technologically outdated, and are unreliable in operation. In addition, the appearance of the batteries is inferior to the design of the panels, halogen or infrared heaters. The buyer is also deterred by the fact that assembling and connecting a sectional radiator requires the knowledge and skills of a specialist.
In other respects, the radiator heating system looks much more attractive:
- The battery body is heated by the heat of hot water or a steam-water mixture. Therefore, the sectional model is safer than its competitors. Heating is provided through simple heat transfer. The design does not contain electrical wiring or red-hot radiating spirals.
- A properly assembled sectional radiator will last longer than underfloor heating and electric heaters.Metal ages an order of magnitude longer than plastic, and if necessary, repairing or expanding the heating system is cheaper than replacing damaged ducts heated floor.
But the main advantage of batteries is their sectional structure. This solution makes it possible to accurately calculate and supply the required number of sections that provide the desired level of comfort and at the same time save money spent on heating.
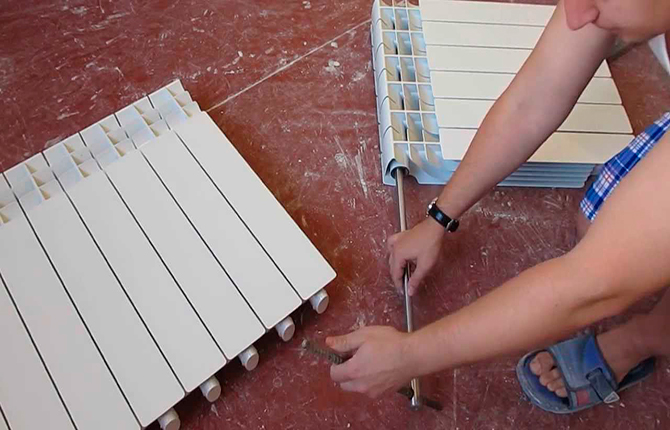
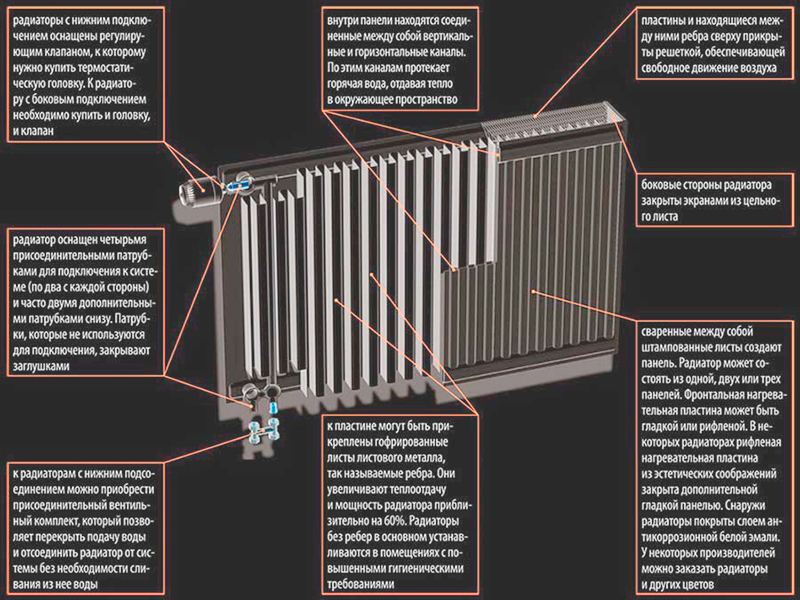
A sectional radiator is a set of individual sections or registers cast from metal, interconnected into one panel using threaded inserts and gaskets. The number of register sections in one battery is limited only by common sense and the capabilities of the heating system.
Inside each such section there is a system of vertical thin channels that circulate hot water from top to bottom, along the metal body. In addition, each register has two pairs of large diameter holes at the top and bottom. After joining with other sections, two horizontal channels are formed inside the heating radiator, ensuring the flow of hot water with minimal hydraulic losses.
The battery inlet and outlet may be located at opposite ends or on the same side. The inlet to a sectional radiator is usually made in the upper part, the outlet can be located at the same level or in the lower part.
Each such section is a self-contained unit of a heating radiator - threaded bushings, seals and tightening nuts are supplied with it. To assemble the battery, other than tools, no other parts are required.
Sections differ in body height and heat output. The thermal characteristics of the registers depend on the material from which the housing is cast.Heating radiators are made from gray cast iron, aluminum, and steel.
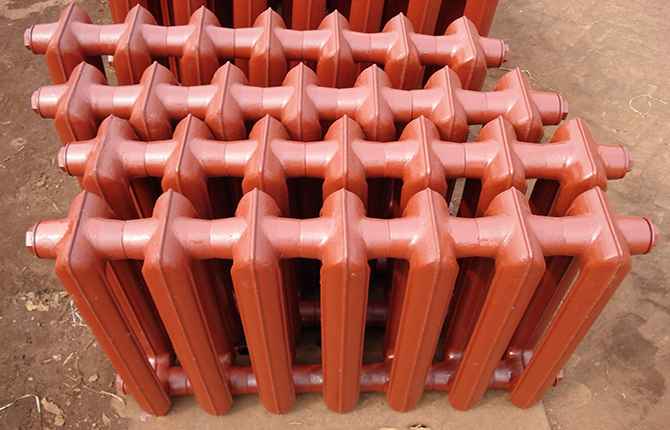
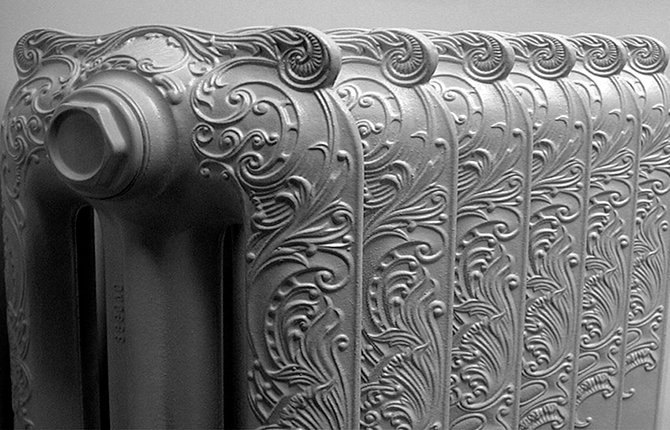
Cast iron sectional radiators
Even 20-25 years ago cast iron batteries were the most widespread, serving in heating systems of apartment buildings for 40-50 years. But at the first opportunity they changed owners to more modern aluminum sections. Old Soviet cast iron batteries looked unpresentable, especially after many years of painting with enamel paint.
Cast iron battery options
On the heating equipment market you can find three options for cast iron heating sections:
- An old design, cast using Soviet technology into earthen molds. Because of this, the surface of cast iron is rough and rough to the touch.
- Modern shape with smooth contours. Sections, as a rule, are manufactured using modern casting technologies in ceramic or steel molds. Painted with beautiful heat-resistant enamel.
- Imported models made in China, Turkey, and EU countries. They differ from domestic ones in the configuration of the radiator housing, the cross-section of the channels inside the section, thinner wall thickness and more elegant appearance.
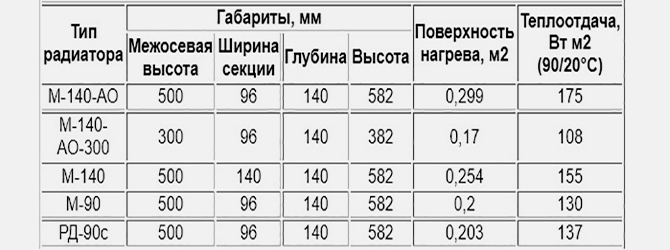
Heating radiators cast using Soviet technology, as a rule, have markings starting with the letters “MS”, “M”, “RD”. Next come one or two numerical values indicating the depth or maximum dimensions of the battery in the transverse direction.
For example, M-140 means that installing a cast iron radiator under a window sill will require at least 140 mm of free space in depth. The marking of sectional batteries “MS” may additionally indicate the center-to-center distance or size between the axes of the upper and lower pipes.
They go on sale partially assembled.Radiators are not painted, only covered with a red or brown primer. This makes it more convenient to store - sectional sets can be stacked on top of each other without the risk of scratching the decorative coating.
Chinese sectional radiators are offered assembled for 5 or 7 registers. Some models are already painted with hot-drying enamel, but you can also find simply sets of registers with a primed surface.
Sectional radiators made in Turkey or the European Union are supplied in the form of separate registers, painted and prepared for assembly, or already assembled and fully functioning batteries that simply need to be connected to the pipes.
It is better to choose already painted sectional batteries. Typically, for heating radiators, powder paints with additives are used that slow down the aging of the decorative layer under constant heating conditions.
The quality and density of the powder coating is an order of magnitude better than the most expensive pentaphthalic or polyurethane enamel. The layer of powder on a cast iron radiator is much smaller than that of enamel. This means that the heat transfer will be higher than that of a sectional battery painted with a brush, and in addition, the buyer will be spared the need to periodically update the paint layer.
Advantages and disadvantages of cast iron registers
The reputation of sectional cast iron batteries was spoiled by the low quality of Soviet cast iron radiators. This is due to primitive, outdated casting technology.
In general, the sectional radiator made of cast iron turned out to be cheap. Due to the large number of defects and cavities, in order to achieve tightness, the walls of the sections had to be made thick (at least 8 mm). As a result, the battery turned out to be inexpensive, but heavy and not very reliable.Therefore, when purchasing, you need to carefully inspect each section, otherwise there is a risk of getting a leaking heating system.
Chinese sectional radiators also suffer from casting defects. Cast iron batteries made in Turkey or the European Union are noticeably lighter, the geometry of the sections is highly accurate, but in general they are much more expensive.
Sectional radiators made using modern technologies are considered one of the best solutions for an apartment or private household. In contact with hot water, cast iron has higher corrosion resistance and is not afraid of overheating or washing the sectional space with chemical reagents.
Two disadvantages can be noted:
- Cast iron does not withstand thermal and mechanical shocks well, therefore, if during the repair of the heating system you need to disassemble a sectional radiator, it is better to contact a specialist.
- During operation, cast iron parts - threaded bushings and nuts - tightly stick to each other. Therefore, if during the assembly of a sectional radiator you “fall short” of any of them, then subsequently it will be difficult to eliminate the weak spot.
The heat transfer of sectional radiators made of cast iron is lower than that of aluminum; the massive cast-iron structure takes longer to heat up, although it dissipates heat into the air more efficiently. Cast iron batteries are recommended for use in central heating systems.
Aluminum sectional radiators
Structurally, aluminum sections are no different from cast iron. The same system of vertical channels inside the body and two pairs of holes for sectional nipples. The only thing is that the shape of the case is different. Instead of the rounded contours characteristic of cast iron batteries, sectional radiators made of aluminum inherent flat radiating surfaces.
The result is a more compact design with a shallower body depth. But thanks to the developed system of thin fins and bridges, the total surface area of an aluminum radiator will be larger than that of a cast iron one.
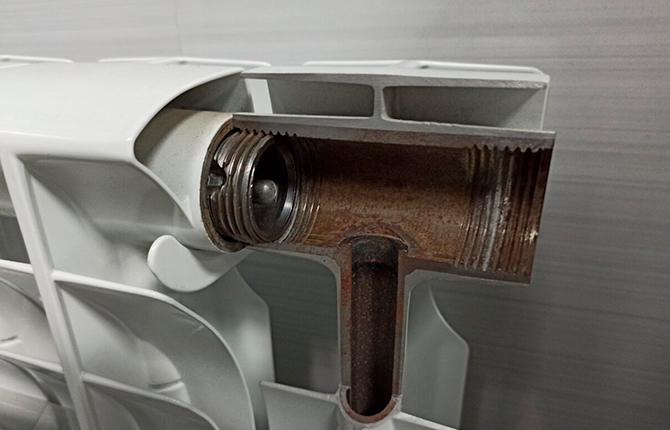
Batteries are assembled using threaded bushings. Each section has a threaded nipple insert inside. A special feature of the part is that the thread direction on opposite holes is different. As a result, if you take two sections and try to wrap the connecting sleeve inside the insert, then due to the opposite direction of the thread, the sections will be pulled together. The only thing you need to do is remember to put in the gasket and seal.
The parts of the sectional radiator are made by hot pressing in a steel die. Therefore, the quality of stamping and the geometry of the section are high. Which is important, since the wall thickness on the internal channels is only a few millimeters.
One of the advantages of aluminum sectional radiators, which few people pay attention to, is the smooth surface of the fins and heat-transferring planes of the body. As a result, the air flow flows around the radiator plates at a higher speed, so the heat dissipation of the battery improves. But if you paint an aluminum radiator at home, the efficiency of the sectional heating battery will decrease several times.
Aluminum radiators are recommended for use in individual systems, regardless of the type of boiler. It is not recommended to connect aluminum sections to centralized heating due to the large amount of contaminants in the water. In addition, most boiler houses regularly flush pipes with acidic reagents, which destroys the walls of the channels.
Aluminum oxidizes to oxide, flakes fall out inside the channels of the sectional radiator, which completely block the flow of water. It is difficult to clean the battery; you have to turn off the heating, disassemble it into sections and remove the plugs mechanically.
The durability and durability of a sectional radiator largely depends on the quality of the aluminum. The best material is from Polish and German manufacturers.
Bimetallic sectional radiators
They tried to solve the problem of severe corrosion of aluminum in hot water by protecting the internal surfaces of the flow channels with steel 0.8-4 mm thick. Bimetal sectional radiator differs from a composite one in that thin-walled steel tubes are placed in an aluminum body, forming the flow part. Water or any other coolant does not come into direct contact with aluminum. The cost and complexity of manufacturing bimetallic radiators has increased significantly.
Bimetal can be complete or incomplete:
- In the first case, aluminum does not come into contact with water even along the threads, in the places where the nipples are screwed in. In this way, it was possible to solve the problem of leaks at the joints of sections, especially if the radiator was operated for a long time on highly alkaline water.
- In the second - the ends and places for sealing gaskets, the surface of the thread remains unprotected. Aluminum is covered with steel only in the flow channels.
As a result, bimetallic sectional radiators can be operated on alkaline water with a high pH value of 10-12. Aluminum ones are allowed for use at pH 6-8.
If it makes sense to buy bimetal
It would seem that sectional radiators with steel channels and an aluminum body are a more advanced design compared to conventional aluminum batteries.This is true, but bimetal costs 1.5-2 times more than aluminum. At the same time, its heat transfer is worse, since the thermal conductivity of steel is 45 W/m*K, and that of aluminum is 220 W/m*K. The presence of steel only worsens the efficiency of a sectional radiator.
Bimetal is recommended for use in centralized heating networks, in conditions where it is not possible to control water quality. In other cases, installing aluminum may be more effective.
Many manufacturers of bimetal heating radiators use lower quality metal, and most often silumin - a cheap alloy of aluminum and silicon. Whereas pure aluminum sections receive metal after additional cleaning to remove impurities.
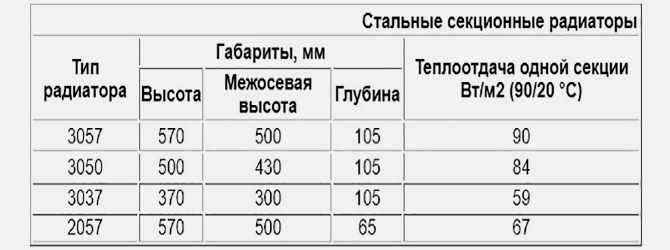
Steel sectional radiators
Heating sections made of steel are no less common in everyday life. Usually on the market the consumer is faced with cheaper and more accessible steel heating panels. This radiator is a package of several flat sections welded from thin sheet steel. All panels are approximately the same size, differing only in the number of sections in the package. There can be from one to three pieces, welded into a non-separable structure.
Essentially, this is one heating battery assembled in a factory. It is impossible to change the number of heating surfaces, which is very inconvenient.
Real sectional steel radiators are assembled from sections welded from steel pipes in such a way that the number of elements can be unlimited.
Structurally, such a section is a package of two or three vertical pipes connected to each other by stamped manifolds made of thin sheet steel. The shape and size of the pipes in a sectional radiator are determined by the developer or designer.
The only drawback of the design is that there are a lot of welds, which reduces the reliability of the battery.
The cost of a sectional radiator is higher than batteries based on standard steel panels. But the heat transfer efficiency is much higher due to the open design and good air flow around the heating surfaces.
Sectional radiator dimensions
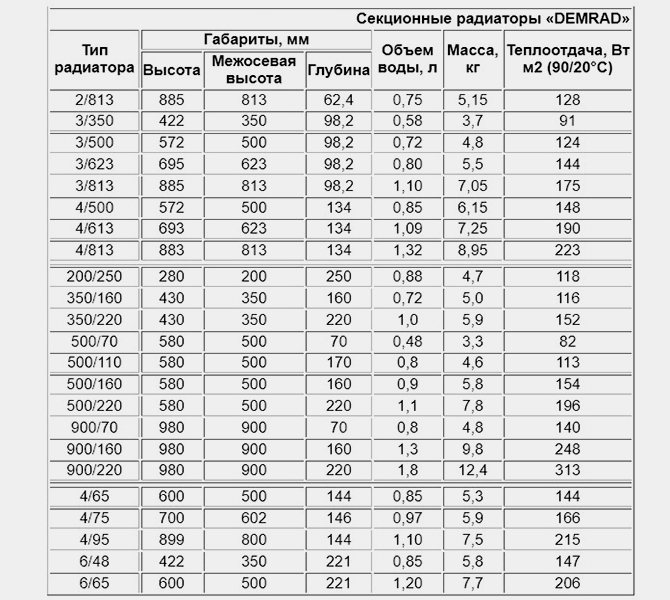
Domestic-made cast iron batteries, as a rule, are produced in a standard center distance of 500 mm. Sectional radiators differ only in the width and depth of the housing and the amount of heat transfer.
For imported batteries, for example, the popular Turkish company DEMRAD, the center distance ranges from 200 mm to 813 mm.
The choice of depth for Turkish sections is greater, the quality of cast iron is better, although the price is higher.
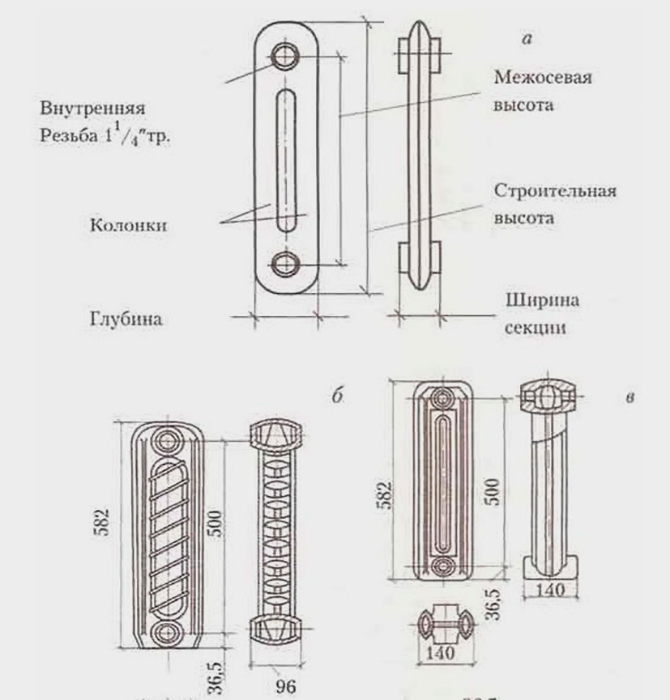
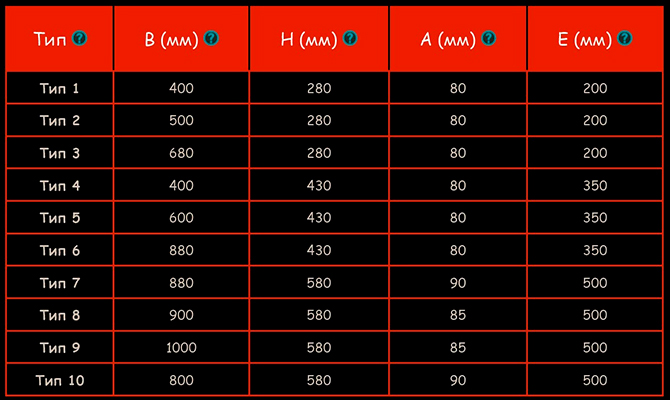
Recommended sizes for bimetallic radiators.
In this case:
- B – optimal length of a sectional battery;
- E – internipple distance;
- A – depth;
- H – body height.
When choosing a specific model, pay attention to parameters such as wall thickness, maximum pressure, heat dissipation and warranty service life. The parameters given differ for different manufacturers.
The marking, as a rule, does not indicate the size of the heating radiator, but a single section indicating the dimensions in the format HEIGHTS, DEPTHS, WIDTH.
Steel sections are inferior in thermal power to bimetallic models of similar sizes.
Calculation of heating radiators by area
The traditional way to calculate the heating power for an enclosed space is to multiply the area of the room by the coefficient K = 100 W/m2. This diagram is recommended for calculating the size and power of sectional radiators for apartments inside multi-storey buildings or for the interior rooms of a private house. Under one condition - the room must be located inside the building, and accordingly, have no external main walls.
In other cases, especially for corner apartments or private houses, such a method for calculating heating power turns out to be not entirely correct.
Calculation of the required power of a heating system for a home
Private housing construction differs in the quality of thermal insulation and the amount of heat loss through the windows. In order not to make a thermal engineering calculation of heating taking into account the thermal conductivity of walls, leakage through window openings and ventilation, you can calculate the power of the system based on the required heat flow into a room of a given volume.
A simple technique is used:
- For uninsulated cinder block buildings and buildings with single brick walls, the heat flow per hour must be at least 70 kcal/m3.
- For insulated rooms – at least 50 kcal/m3.
To determine the power in watts, it is enough to use the conversion factor KP=1.163 W/m3*kcal. To calculate the heat release of a heating system, multiply the volume of the room by the conversion factor and the amount of inflow. For example, for a bedroom with an area of 3x3 m, with a ceiling of 2.5 m, the volume of internal space will be 23 m3.
Multiply 70x23x1.163 = 1872 Wh. The power of the heating battery must be at least 1900 W/h.
What to consider when calculating the power of sectional heaters
The resulting value will provide the required level of comfort only with electric heating. Sectional batteries connected to hot water pipes are somewhat different from an electric heater.
In the standard version, the water sectional battery heater consists of 5-10 sections connected to each other by nipples through sealing gaskets. Each manufacturing company indicates in the passport for the section the thermal power at a certain temperature (usually 70 ℃ or 95 ℃). If all sections were heated to the same temperature, then the power of the heating battery could be calculated by multiplying the passport data of one by their number.
But heat transfer from different sections may differ. Hot water with a temperature of 70-90 ℃ is supplied to the entrance to the sectional housing of the battery-heater, and the output flow is already 50-60 ℃.
In order to determine the real thermal power, it is necessary to calculate the average temperature of the case. For example, (70+50)/2=60 ℃. Next, take the power of the radiator section from the passport, for example, 180 W at 90 ℃. We recalculate the power reduction factor in the proportion 60/90 = 0.67. All that remains is to multiply by the rated power 180*0.67=120.6 W.
Knowing the heat dissipation of one section (120.6 W), you can calculate the power of the entire sectional radiator by multiplying it by their number. Only after this the required number of radiators for heating a particular room is calculated.
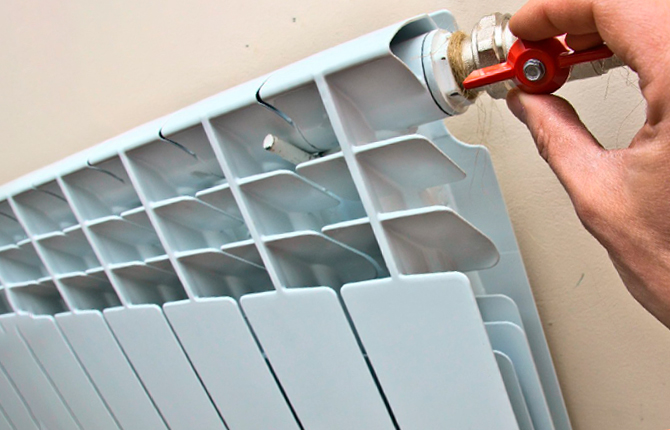
How to correctly connect sectional radiators
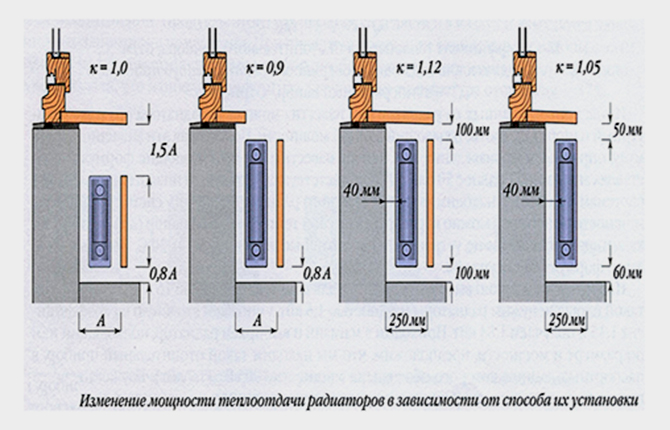
The first thing that needs to be maintained when connecting to a heating system is the distance from the radiator to the walls, floor, and window sill. Depending on the location of the housing, the heat transfer power may increase or decrease.
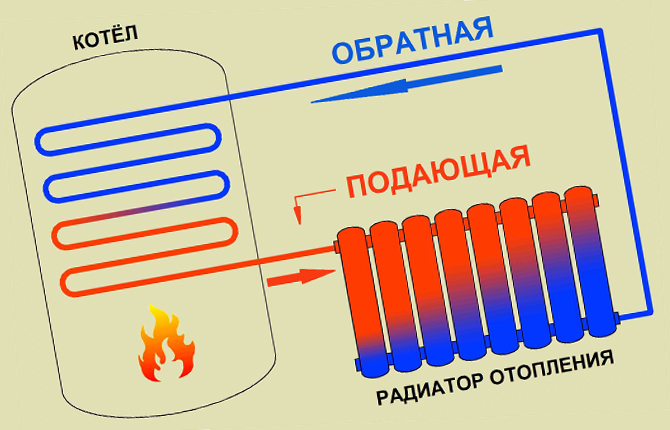
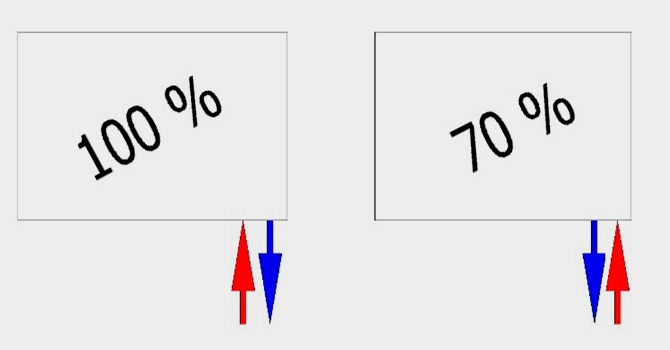
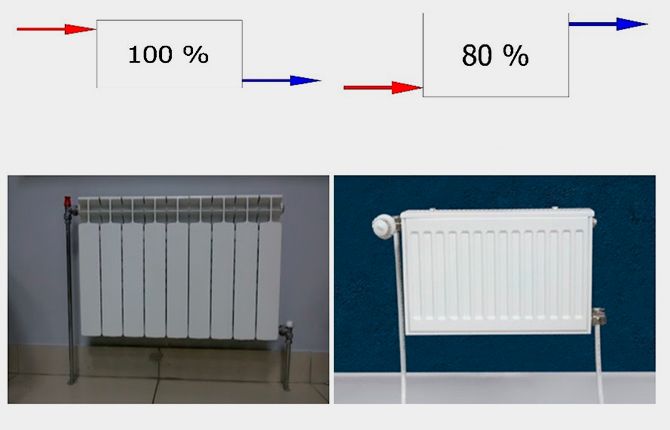
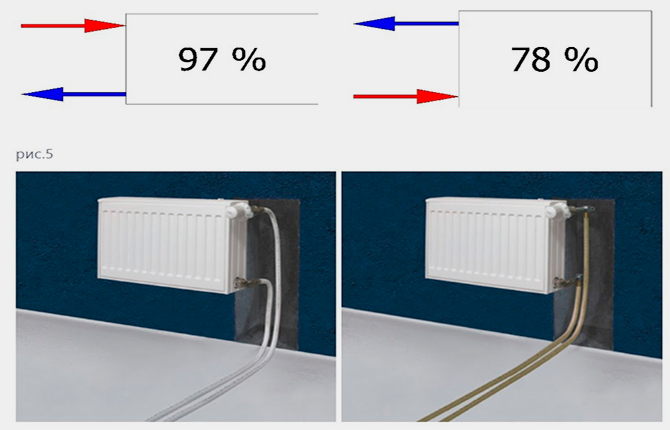
Next, select the location for connecting the pipes on the radiator body. An incorrect supply of hot and cool water usually leads to a decrease in heating efficiency.
If the supply is made to the bottom, then the “hot” fitting should be located on the side of the body.
When connecting pipes to the lower side fitting on the same line, efficiency is reduced by 10% or more.
If the hot pipe is connected diagonally to the outlet, the heat dissipation may drop or remain the same.
A one-way connection almost always leads to losses in the heating system.
Sectional heating radiators today are the best thing that has been invented for water heating of a room. The ability to more or less accurately select power, simple repairs - replacing a section more than compensates for the increased price of the battery.
Share your experience in installing and operating sectional heaters. What do you remember most, positive or negative? Write in the comments. Save the article in your bookmarks so as not to lose the necessary information.