How to choose bimetallic heating radiators: technical characteristics + analysis of all the pros and cons
The efficiency of the batteries determines the speed and quality of heating.The modern equipment market offers all kinds of solutions. One of the worthy options are bimetallic heating radiators that meet the main requirements of the heating network: strength, resistance to water hammer, high heat transfer and durability.
We will tell you how to choose the right heating device, in the manufacture of which two metals were used. Our article describes in detail the varieties popular among consumers. Their technical characteristics are given and leading manufacturers are listed.
The content of the article:
Structure of bimetallic radiators
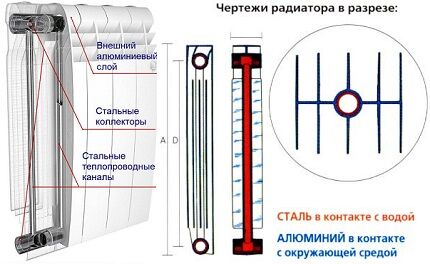
Externally, bimetallic models resemble ordinary ones aluminum radiators. The difference lies in the internal content. The design of composite products consists of two basic elements: an internal steel pipe and an external figure-ribbed body made of aluminum panels. Some radiators use copper instead of steel.
The coolant circulates through an internal steel or copper pipeline. Due to corrosion inertness, radiators do not rust and do not react with chemically active coolant.The external elements and the internal manifold are connected by spot welding or injection molding.
Based on their physical and operational properties, the batteries are suitable for installation in apartment buildings of any number of floors and for arranging a local heating system for cottage buildings.
Features of different heating convectors
You should understand the differences between different types of batteries made of two metals. Composite products are usually classified according to the following criteria: composition of the internal rod, external design and type of metal used.
Bimetallic and semi-bimetallic radiators
Users often confuse true bimetallic batteries with “half-breeds” - semi-bimetallic counterparts.
"Pure" bimetal
Aluminum is used to make the outer casing of the device. The convector core is 100% stainless steel or copper. During the production process, pipes placed in special molds are filled under pressure with aluminum - a sealed structure is formed.

A high-grade bimetal withstands the pressure of centralized and autonomous heating systems.
Semi-bimetallic batteries
The internal “skeleton” of the radiator is made of two metals: vertical guides – stainless steel, horizontal pipeline – aluminum. The reverse combination is also possible.
Such an alliance of metals is not able to ensure adequate reliability of central heating communications. The coolant may contain alkali, which, when interacting with aluminum, provokes corrosion. Over time, destructive processes “transition” to the steel components of the radiator.
In addition, the integrity of the product may be at risk due to thermal expansion of metals - leaks are possible at boundary temperatures.

It is better to avoid purchasing low-quality composites, especially when it comes to centralized heating.
Sectional and monolithic models
Among the variety of bimetallic heating batteries, there are two types of designs:
- sectional:
- monolithic.
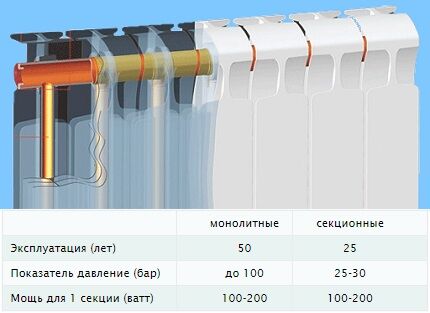
Models assembled from sections are attractive due to their variability of characteristics. They provide the opportunity to purchase a device with the exact heat transfer values required for heating rooms. Monolithic ones do not have such advantages.
Typesetting systems
Collapsible radiators, the panels of which are connected using nipples. Horizontal sections of pipes of individual sections have multi-directional threads for joining the fastening nipples and the sealing strip.

Disadvantages of sectional radiators:
- joints are weak points of collectors where leaks are likely;
- limited operating pressure – up to 20-30 bar.
Significant disadvantages also include partial ingress of coolant onto the aluminum “jacket” during leakage.
Monolithic devices
One-piece modifications do not have the listed disadvantages. The cast radiator is capable of withstanding pressure surges within 100 atmospheres.
For high-rise buildings (10 or more floors), experts recommend choosing solid radiators, since there will be significant pressure in the heating system.
Copper or steel core?
Most manufacturers offer hybrid batteries with a steel tube frame. The main reason is the affordability of the metal and good strength characteristics. The symbiosis of steel and aluminum made it possible to achieve vibration resistance heating system pressure, increase the level of heat transfer of the convector and reduce its inertia.

Advantages of copper core batteries:
- there is no likelihood of corrosion;
- a copper pipeline withstands any water hammer - the best option for use in domestic centralized heating systems;
- high efficiency of the device - the heat transfer of copper exceeds that of steel.
Copper-aluminum radiators have a service life of more than 50 years. The disadvantage of copper modifications is the high price.
Technical and operational characteristics
All basic parameters of the radiator are indicated in the passport of the heating device.
In order not to make a mistake with your choice, you need to understand the meaning of the following characteristics:
- heat transfer;
- operating pressure and temperature;
- center distance;
- dimensions;
- capacity, section weight.
Thermal power. The parameter indicates the amount of heat transferred from the battery to the atmosphere of the room at a given temperature coolant (+70°C). The indicator is measured in W.

Based on the thermal power of one section, the required battery performance for the entire room is calculated.
Work environment indicators. The maximum coolant pressure depends on the thickness of the steel core. The choice of strength is at the discretion of the manufacturer. The parameter value ranges from 15 to 35 bar and is determined based on the operating conditions of the battery.
An important characteristic is the limiting temperature of the coolant. All high-grade bimetals can withstand +90°C. Some manufacturers claim higher thermal resistance.
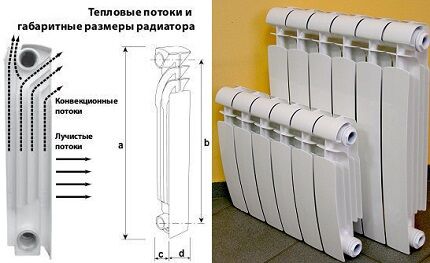
Radiator dimensions. Dimensional characteristics include the following parameters:
- Center distance – “distance” between the axes of horizontal collectors. The standard size is 20-80 cm. Vertically oriented models with increased interaxial distance are used if the room layout is not suitable for installing horizontal radiators.
- Geometric parameters determine the height, width, depth of the section.The total height of the radiator often exceeds the interaxial range by 6-8 cm. The traditional width of the fins of bimetallic models is 80 mm.
The depth of the section is 75-100 mm. Some manufacturers, in addition to external panels, add parallel fins to the design to increase heating efficiency due to convection flows.
Volume and mass. In bimetallic modifications, the coolant circulates through a core of round cross-section, in contrast to aluminum counterparts with a heat conductor of oval cross-section. The capacity of one bimetal section is less than the volume of an aluminum section with the same standard sizes.
For example, in convectors with an interaxial range of 500 mm, the coolant filling is about 0.2-0.38 l, with a core height of 350 mm - 0.15-0.25 l.
The weight of a standard bimetallic battery with dimensions of 580/80/80 mm (height/width/depth, respectively) and an axial distance of 50 cm is 1.8-2 kg. Less mass is one of the signs of a semi-bimetal.
Comparative analysis: bimetal and competitors
Before choosing a bimetallic or other radiator, it is advisable to compare its capabilities with its closest competitors. For composite convectors these are aluminum, cast iron, steel batteries.
The assessment should be carried out according to the main criteria:
- heat transfer;
- endurance to pressure changes;
- wear resistance;
- ease of installation;
- appearance;
- durability;
- price.
Heat release. In terms of heating efficiency, aluminum units are the leaders, bimetal takes an honorable second place. Steel and cast iron radiators lose noticeably.

Resistance to water hammer. The most durable are bimetallic units, capable of withstanding up to 40 atmospheres (sectional models). The maximum operating pressure on an aluminum heating system is 6 bar, a steel one is 10-12 bar, and a cast iron one is 6-9 bar.
It is the bimetal that can withstand numerous water hammer shocks from a centralized heating system. This property is a key argument in favor of composite radiators for apartment buildings.
Chemical inertness. According to this criterion, positions were distributed as follows:
- Cast iron. The material is indifferent to adverse environments. Cast iron radiators can be used for decades, transporting an “alkaline”, “acidic” environment.
- Steel and bimetal. The steel core itself withstands the effects of aggressive components. The weak point of a steel pipeline is its interaction with oxygen, contact with which leads to the formation of rust.
- Aluminum. The metal reacts with various impurities in water.
Aluminum walls are especially susceptible to acidic environments - the pH of the coolant must be within 8. Otherwise, corrosion will actively develop.
Easy to install. In terms of installation, aluminum and bimetallic products are easier. Cast iron radiators are more difficult to install due to their impressive weight.

We can conclude.The purchase of a bimetallic radiator is definitely justified for assembling a heating network in a multi-storey building, where there are risks of pressure surges and contamination of the coolant. In a private house, with stable operation of the boiler and filtration of incoming water, it can be used in heating device affordable aluminum batteries.
What should you consider when choosing a radiator?
To achieve the proper thermal effect, it is necessary to calculate the total power of the battery. Bimetallic equipment is not a cheap purchase, so you should take care of its durability. The conscientious execution of the radiator is guaranteed by trusted manufacturers.
Capability assessment - thermal calculation
Having decided on the appropriate technical characteristics and dimensions of bimetallic radiators, it is necessary to calculate the required number of sections.

The section's heat transfer rate is taken from the radiator's passport, and the total power must be calculated.
Calculation by area
The normalized value of thermal power per 1 sq.m of living space for the average climate zone, subject to standard ceilings (250-270 cm):
- the presence of one window and a wall with access to the street - 100 W;
- there is a window in the room, two walls adjacent to the street - 120 W;
- several windows and “external” walls – 130 W.
Example. The section power is 170 W, the total area of the heated room is 15 sq.m. Additional conditions: window – 1, external wall – 1, ceiling height – 270 cm.
N=(15*100)/170 = 8.82.
Rounding is done upward. This means that to heat the room it is necessary to use 9 sections of 170 W each.
Calculation by volume
SNiP separately regulates the amount of thermal power per 1 cubic meter of space in the amount of 41 W. Knowing the volume of the heated room, it is easy to calculate the heat transfer of the entire battery.
Example. Heating the room with the previous parameters. For the purity of the experiment, we leave the power of the section unchanged - 170 W.
N=(15*2.7*41)/170= 9.76.
It is necessary to install a radiator into 10 sections. The second calculation is considered more accurate. When calculating, attention should be paid to sources of heat loss indoors.

How to avoid fakes: radiator inspection
In addition to analyzing passport data, it would be useful to conduct a visual assessment of the product. Some manufacturers, in pursuit of customers, tend to “embellish” their products by introducing incorrect data into the documentation.
First of all, pay attention to the thickness of the core and aluminum “jacket”, overall dimensions, weight and quality of components.
Steel core. The minimum thickness of the steel tube is 3 mm. With smaller standard sizes, the declared strength of the product - resistance to water hammer and the development of corrosion processes.

The result of a low-quality steel core is the formation of through holes and the creation of emergency situations in the heating network.
Radiator fins. Aluminum panels must be checked for strength - they should not bend from the efforts of the fingers of one hand. The minimum thickness of the panels is 1 mm.
It is better to choose models with profiled channels between the ribs. The formed confuser increases the speed of air flow, increasing the intensity of convective heat transfer.

Dimensions and weight. By individual order it is possible to produce radiators with a section width of less than 80 mm. However, store-bought models with inappropriate parameters are most likely fake.
To reduce costs, some manufacturers significantly reduce the width of the internal ribs, “masking” them behind standard-sized front panels. This measure worsens the heat transfer of a bimetallic radiator.
Battery components. It is almost impossible to check the quality of gaskets and nipples on site. Rely on the manufacturer's name and warranty period. Reliable companies guarantee up to 15-20 years of trouble-free operation.
Rating of popular manufacturers
The review includes high-quality foreign heating systems and domestic products adapted to the changing conditions of heating networks.
In practice, the company’s products have proven themselves well:
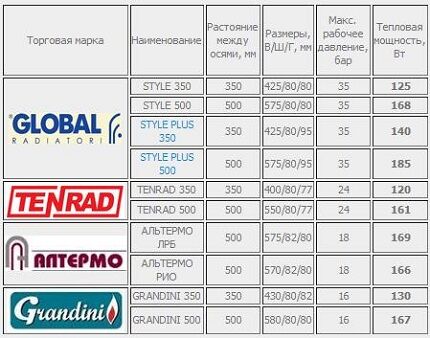
- Global Style (Italy);
- Sira (Italy);
- Rifar (Russia);
- Tenrad (Germany).
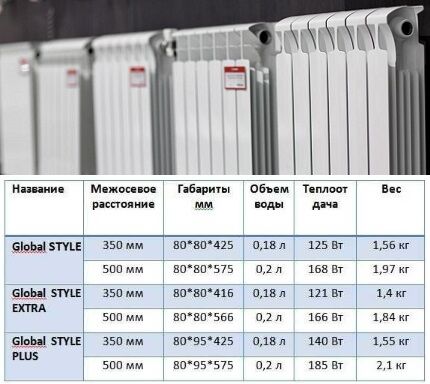
Place #1 - Global
This is a generally recognized leader in the production of heating radiators.
The company produces three series of bimetallic batteries:
- Style – basic characteristics;
- Style Extra – compact dimensions;
- Style Plus – maximum heat transfer.
The sections are connected by paronite gaskets, ensuring the tightness of the joints. Efficient heat transfer between metals is achieved through injection molding of an aluminum “jacket”.
Place #2 - Sira
The Italian manufacturer positions its products as premium products. The devices have gained popularity among consumers due to their durability and attractive design. The manufacturer provides a 20-year guarantee for a series of full-fledged bimetallic radiators Sira Ali Metal.

Place #3 – Rifar
A domestic manufacturer has developed a wide range of bimetallic radiators:
- Base – models with center distances of 200/350/500 mm, warranty from Rifar – 10 years;
- Forza – reinforced external coating, resistant to scratches and mechanical damage;
- Alp – shallow depth (75 mm);
- Monolit is a one-piece radiator.
Monolit series batteries are characterized by the highest performance indicator at high coolant pressure.

Location #4 – Tenrad
German quality bimetal is suitable for centralized and independent heating networks. Suitable for use in gravity, elevator and pump systems with one- and two-pipe wiring.
Distinctive features:
- the thickness of the vertical tubes is 1.8 mm, the thickness of the collector walls is 3.6 mm;
- three-row fins;
- the side panels are located at a slope, which creates a diffuser effect for convective flow.
Two-layer enamel coating made of high-quality paints and varnishes - when heated, the device does not emit harmful fumes.

Will familiarize you with the rules for calculating the power and number of radiators for a heating device next article, which is worth reading before purchasing devices.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video review clearly demonstrates the design features of composite radiators and the basic requirements that a high-quality device must meet:
Full bimetallic radiators combine the positive characteristics of both materials. The batteries are distinguished by high thermal power, resistance to water hammer and excellent decorative properties. Their purchase is a justified investment provided that you purchase a certified product.
Tell us about how you chose a bimetallic heating device for your own apartment or country house. Share what argument was decisive in your choice? Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions, post thematic photographs.




We have a three-section cast iron radiator in our kitchen. He has already outlived his usefulness, to be honest. Therefore, when choosing something instead, I came to the conclusion that for such water quality as ours, in no case do you need aluminum batteries, unless, of course, you plan to change them in 5 years. Therefore, I decided for myself to take bimetallic Tenrad, They are both adequate in cost and in terms of service life.I don’t want the cast iron ones back, although now they make them very beautiful, with an antique look.
I am very glad that bimetallic radiators have replaced bulky cast-iron batteries. And all this talk that only cast iron can heat, hold and save is an extremely outdated judgment. When in our apartments there were drafts from the double, sealed windows, and there was no high-quality insulation, then yes.
Now in terms of price-quality ratio there is no better than bimetal. Both installation and later disposal of these batteries is not difficult. The main thing is not to save money and choose a reliable manufacturer; we install batteries for decades - you can spend money.