How to calculate the power of a gas heating boiler: formulas and calculation example
Before designing a heating system or installing heating equipment, it is important to select a gas boiler capable of generating the required amount of heat for the room. Therefore, it is important to choose a device of such power that its performance is as high as possible and its resource is long.
We will tell you how to calculate the power of a gas boiler with high accuracy and taking into account certain parameters. The article we have presented describes in detail all types of heat losses through openings and building structures, and provides formulas for calculating them. A specific example introduces the features of calculations.
The content of the article:
Typical mistakes when choosing a boiler
Correct calculation of the power of a gas boiler will not only save on consumables, but will also increase the efficiency of the device. Equipment whose heat output exceeds the actual heat requirements will work ineffectively when, as an insufficiently powerful device, it cannot heat the room properly.
There is modern automated equipment that independently regulates the gas supply, which eliminates unnecessary costs. But if such a boiler performs its work to the limit of its capabilities, then its service life is reduced.
As a result, the efficiency of the equipment decreases, parts wear out faster, and condensation forms. Therefore, there is a need to calculate optimal power.
There is an opinion that the power of the boiler depends solely on the surface area of the room, and for any home the optimal calculation would be 100 W per 1 sq.m. Therefore, in order to select the boiler power, for example, for a house of 100 sq. m, you will need equipment generating 100*10=10000 W or 10 kW.
Such calculations are fundamentally incorrect due to the advent of new finishing materials and improved insulation materials, which reduce the need to purchase high-power equipment.

Calculate power gas boiler heating can be done in two ways - manually or using a special Valtec program, which is designed for professional high-precision calculations.
The required power of the equipment directly depends on the heat loss of the room. Once you know the heat loss rate, you can calculate the power of a gas boiler or any other heating device.
What is room heat loss?
Any room has certain heat losses. Heat comes out of walls, windows, floors, doors, ceilings, so the task of a gas boiler is to compensate for the amount of heat coming out and provide a certain temperature in the room. This requires a certain thermal power.

The following factors influence heat loss at home.
- Location of the house. Each city has its own climatic characteristics.When calculating heat loss, it is necessary to take into account the critical negative temperature characteristic of the region, as well as the average temperature and duration of the heating season (for accurate calculations using the program).
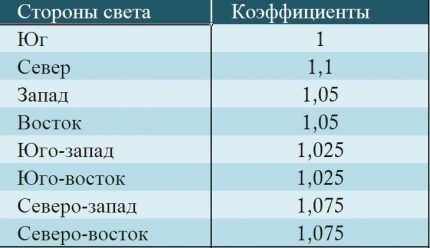
- The location of the walls relative to the cardinal directions. It is known that the wind rose is located in the north side, so the heat loss of a wall located in this area will be the greatest. In winter, cold wind blows with great force from the western, northern and eastern sides, so the heat loss of these walls will be higher.
- The area of the heated room. The amount of heat lost depends on the size of the room, the area of walls, ceilings, windows, doors.
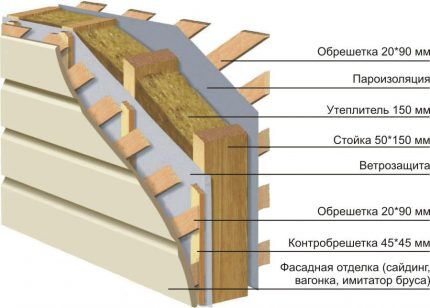
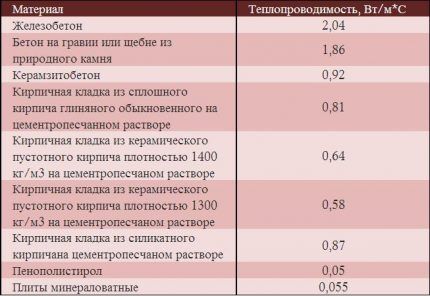
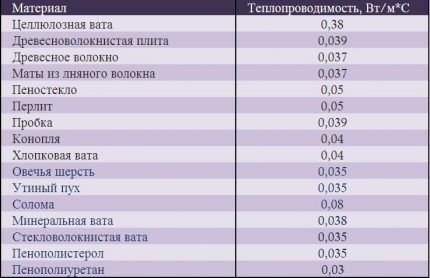
- Thermal engineering of building structures. Any material has its own coefficient of thermal resistance and heat transfer coefficient - the ability to pass a certain amount of heat through itself. To find them out, you need to use tabular data and also apply certain formulas. Information about the composition of walls, ceilings, floors, and their thickness can be found in the technical plan of housing.
- Window and door openings. Size, modification of door and double-glazed windows. The larger the area of window and door openings, the higher the heat loss. It is important to take into account the characteristics of installed doors and double-glazed windows when making calculations.
- Ventilation accounting. Ventilation always exists in the house, regardless of the presence of artificial hood. The room is ventilated through open windows; air movement is created when the entrance doors are closed and opened, people move from room to room, which helps warm air leave the room and circulate it.
Knowing the above parameters, you can not only calculate heat loss at home and determine the power of the boiler, but also identify places that need additional insulation.
Formulas for calculating heat loss
These formulas can be used to calculate heat loss not only in a private house, but also in an apartment. Before starting calculations, it is necessary to draw a floor plan, note the location of the walls relative to the cardinal directions, designate windows, doorways, and also calculate the dimensions of each wall, window and doorway.
When calculating heat loss, two formulas are used - using the first, the value of the thermal resistance of enclosing structures is determined, and using the second, heat loss is determined.
To determine thermal resistance, use the expression:
R = B/K
Here:
- R – the value of thermal resistance of enclosing structures, measured in (m2*K)/W.
- K – thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which the enclosing structure is made, measured in W/(m*K).
- IN – thickness of the material, recorded in meters.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is a tabular parameter, thickness B is taken from the technical plan of the house.
The basic formula for calculating heat loss is also used:
Q = L × S × dT/R
In the expression:
- Q – heat loss, measured in W.
- S – area of enclosing structures (walls, floors, ceilings).
- dT – the difference between the desired indoor and outdoor temperatures is measured and recorded in C.
- R – value of thermal resistance of the structure, m2•C/W, which is found using the formula above.
- L – coefficient depending on the orientation of the walls relative to the cardinal points.
Having the necessary information at hand, you can manually calculate the heat loss of a particular building.
Example of heat loss calculation
As an example, let’s calculate the heat loss of a house with the given characteristics.
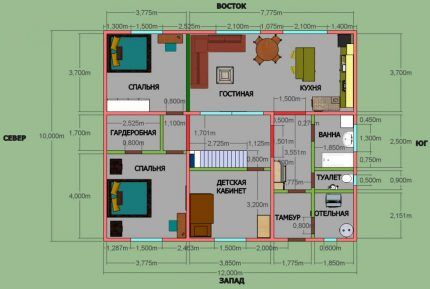
Based on the plan, the width of the structure is 10 m, the length is 12 m, the ceiling height is 2.7 m, the walls are oriented to the north, south, east and west. There are 3 windows built into the western wall, two of them have dimensions of 1.5x1.7 m, one - 0.6x0.3 m.
In the southern wall there are built-in doors with dimensions of 1.3x2 m, there is also a small window 0.5x0.3 m. On the east side there are two windows 2.1x1.5 m and one 1.5x1.7 m.
The walls consist of three layers:
- wall cladding with fiberboard (isoplast) outside and inside - 1.2 cm each, coefficient - 0.05.
- glass wool located between the walls, its thickness is 10 cm and the coefficient is 0.043.
The thermal resistance of each wall is calculated separately, because The location of the structure relative to the cardinal points, the number and area of openings are taken into account. The results of calculations on the walls are summarized.
The floor is multi-layered, made using the same technology throughout the entire area, and includes:
- cut and tongue-and-groove board, its thickness is 3.2 cm, thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.15.
- a layer of dry chipboard leveling with a thickness of 10 cm and a coefficient of 0.15.
- insulation – mineral wool 5 cm thick, coefficient 0.039.
Let us assume that the floor does not have hatches into the basement or similar openings that impair the heating engineering. Consequently, the calculation is made for the area of all premises using a single formula.
Ceilings are made of:
- wooden panels 4 cm with a coefficient of 0.15.
- mineral wool is 15 cm, its coefficient is 0.039.
- steam and waterproofing layer.
Let's assume that the ceiling also does not have access to the attic above the living or utility room.
The house is located in the Bryansk region, in the city of Bryansk, where the critical negative temperature is -26 degrees. It has been experimentally established that the temperature of the earth is +8 degrees. Desired room temperature + 22 degrees.
Calculation of heat losses of walls
To find the total thermal resistance of a wall, you first need to calculate the thermal resistance of each layer.
The glass wool layer has a thickness of 10 cm. This value must be converted into meters, that is:
B = 10 × 0.01 = 0.1
We got the value B=0.1. Thermal conductivity coefficient of thermal insulation is 0.043. We substitute the data into the thermal resistance formula and get:
Rglass=0.1/0.043=2.32
Using a similar example, let’s calculate the heat resistance of the isoplyte:
Risopl=0.012/0.05=0.24
The total thermal resistance of the wall will be equal to the sum of the thermal resistance of each layer, given that we have two layers of fiberboard.
R=Rglass+2×Risopl=2.32+2×0.24=2.8
By determining the total thermal resistance of the wall, you can find the heat losses. For each wall they are calculated separately. Let's calculate Q for the north wall.
Based on the plan, the northern wall has no window openings, its length is 10 m, height is 2.7 m. Then the area of the wall S is calculated by the formula:
Snorth wall=10×2.7=27
Let's calculate the dT parameter. It is known that the critical ambient temperature for Bryansk is -26 degrees, and the desired room temperature is +22 degrees. Then
dT=22-(-26)=48
For the north side, the additional coefficient L=1.1 is taken into account.
Having made preliminary calculations, you can use the formula to calculate heat loss:
Qnorth wall=27×48×1.1/2.8=509 (W)
Let's calculate heat loss for the western wall. Based on the data, there are 3 windows built into it, two of them have dimensions of 1.5x1.7 m and one - 0.6x0.3 m. Let's calculate the area.
Sspare walls1=12×2.7=32.4.
It is necessary to exclude the area of windows from the total area of the western wall, because their heat loss will be different. To do this you need to calculate the area.
Swindow1=1.5×1.7=2.55
Swindow2=0.6×0.4=0.24
To calculate heat loss, we will use the area of the wall without taking into account the area of the windows, that is:
Sspare walls=32.4-2.55×2-0.24=25.6
For the western side, the additional coefficient is 1.05. We substitute the obtained data into the basic formula for calculating heat loss.
Qspare walls=25.6×1.05×48/2.8=461.
We make similar calculations for the eastern side. There are 3 windows here, one has dimensions of 1.5x1.7 m, the other two – 2.1x1.5 m. We calculate their area.
Swindow3=1.5×1.7=2.55
Swindow4=2.1×1.5=3.15
The area of the eastern wall is:
Seastern walls1=12×2.7=32.4
From the total wall area we subtract the window area values:
Seastern walls=32.4-2.55-2×3.15=23.55
The additional coefficient for the eastern wall is -1.05. Based on the data, we calculate the heat losses of the eastern wall.
Qeastern walls=1.05×23.55×48/2.8=424
On the southern wall there is a door with parameters of 1.3x2 m and a window of 0.5x0.3 m. We calculate their area.
Swindow5=0.5×0.3=0.15
Sdoor=1.3×2=2.6
The area of the southern wall will be equal to:
Ssouthern walls1=10×2.7=27
We determine the area of the wall without taking into account windows and doors.
Ssouthern walls=27-2.6-0.15=24.25
We calculate the heat loss of the southern wall taking into account the coefficient L=1.
Qsouthern walls=1×24.25×48/2.80=416
Having determined the heat loss of each wall, you can find their total heat loss using the formula:
Qwalls=Qsouthern walls+Qeastern walls+Qspare walls+Qnorth wall
Substituting the values, we get:
Qwalls=509+461+424+416=1810 W
As a result, the heat loss from the walls amounted to 1810 W per hour.
Calculation of thermal losses of windows
There are 7 windows in the house, three of them have dimensions of 1.5x1.7 m, two - 2.1x1.5 m, one - 0.6x0.3 m and one more - 0.5x0.3 m.
The windows with dimensions of 1.5×1.7 m are a two-chamber PVC profile with I-glass. From the technical documentation you can find out that its R=0.53. Windows with dimensions of 2.1x1.5 m, two-chamber with argon and I-glass, have a thermal resistance of R=0.75, windows 0.6x0.3 m and 0.5x0.3 - R=0.53.
The window area was calculated above.
Swindow1=1.5×1.7=2.55
Swindow2=0.6×0.4=0.24
Swindow3=2.1×1.5=3.15
Swindow4=0.5×0.3=0.15
It is also important to consider the orientation of windows relative to the cardinal directions.
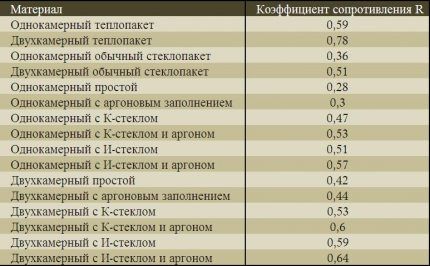
Let's calculate the heat losses of western windows, taking into account the coefficient L=1.05. On the side there are 2 windows with dimensions of 1.5×1.7 m and one with dimensions of 0.6×0.3 m.
Qwindow1=2.55×1.05×48/0.53=243
Qwindow2=0.24×1.05×48/0.53=23
In total, the total losses of the western windows are
Qlock windows=243×2+23=509
On the south side there is a window 0.5×0.3, its R=0.53. Let's calculate its heat loss taking into account coefficient 1.
Qsouth windows=0.15*48×1/0.53=14
On the eastern sides there are 2 windows with dimensions 2.1×1.5 and one window 1.5×1.7. Let's calculate heat losses taking into account the coefficient L=1.05.
Qwindow1=2.55×1.05×48/0.53=243
Qwindow3=3.15×1.05×48/075=212
Let's sum up the heat losses of the eastern windows.
Qeast windows=243+212×2=667.
The total heat loss of windows will be equal to:
Qwindows=Qeast windows+Qsouth windows+Qlock windows=667+14+509=1190
In total, 1190 W of thermal energy comes out through the windows.
Determination of door heat loss
The house has one door, it is built into the southern wall, has dimensions of 1.3x2 m. Based on the passport data, the thermal conductivity of the door material is 0.14, its thickness is 0.05 m. Thanks to these indicators, the thermal resistance of the door can be calculated.
Rdoors=0.05/0.14=0.36
For calculations you need to calculate its area.
Sdoors=1.3×2=2.6
After calculating the thermal resistance and area, the heat loss can be found. The door is located on the south side, so we use an additional factor of 1.
Qdoors=2.6×48×1/0.36=347.
In total, 347 W of heat comes out through the door.
Calculation of floor thermal resistance
According to the technical documentation, the floor is multi-layered, made identically over the entire area, and has dimensions of 10x12 m. Let's calculate its area.
Sgender=10×12=210.
The floor consists of boards, chipboard and insulation.
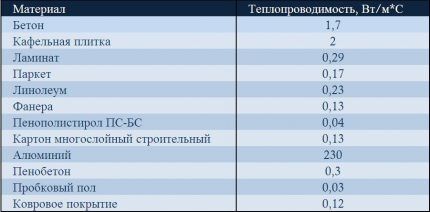
Thermal resistance must be calculated for each floor layer separately.
Rboards=0.032/0.15=0.21
Rchipboard=0.01/0.15= 0.07
Rinsulate=0.05/0.039=1.28
The total thermal resistance of the floor is:
Rgender=Rboards+Rchipboard+Rinsulate=0.21+0.07+1.28=1.56
Considering that in winter the temperature of the earth remains at +8 degrees, the temperature difference will be equal to:
dT=22-8=14
Using preliminary calculations, you can find the heat loss of a house through the floor.
When calculating floor heat losses, we take into account the coefficient L=1.
Qgender=210×14×1/1.56=1885
The total floor heat loss is 1885 W.
Calculation of heat loss through the ceiling
When calculating the heat loss of the ceiling, a layer of mineral wool and wooden panels are taken into account. Steam and waterproofing are not involved in the thermal insulation process, so we do not take it into account. For calculations, we need to find the thermal resistance of wooden panels and a layer of mineral wool. We use their thermal conductivity coefficients and thickness.
Rvillage shield=0.04/0.15=0.27
Rmin.cotton wool=0.05/0.039=1.28
The total thermal resistance will be equal to the sum of Rvillage shield and Rmin.cotton wool.
Rroofs=0.27+1.28=1.55
The ceiling area is the same as the floor.
S ceiling = 120
Next, the heat losses of the ceiling are calculated, taking into account the coefficient L=1.
Qceiling=120×1×48/1.55=3717
A total of 3717 W goes through the ceiling.
To determine the total heat loss of a house, it is necessary to add up the heat loss of walls, windows, doors, ceiling and floor.
Qgenerally=1810+1190+347+1885+3717=8949 W
To heat a house with the specified parameters, you need a gas boiler that supports a power of 8949 W or about 10 kW.
Determination of heat loss taking into account infiltration
Infiltration is a natural process of heat exchange between the external environment, which occurs when people move around the house, when opening entrance doors and windows.
To calculate heat loss for ventilation you can use the formula:
Qinf=0.33×K×V×dT
In the expression:
- K - the calculated air exchange rate, for living rooms the coefficient is 0.3, for heated rooms - 0.8, for the kitchen and bathroom - 1.
- V - the volume of the room, calculated taking into account the height, length and width.
- dT - temperature difference between the environment and the residential building.
A similar formula can be used if ventilation is installed in the room.
The height of the room is 2.7 m, the width is 10 m, the length is 12 m. Knowing these data, you can find its volume.
V=2.7 × 10 × 12=324
The temperature difference will be equal
dT=48
We take 0.3 as the coefficient K. Then
Qinf=0.33×0.3×324×48=1540
Q must be added to the total calculated indicator Qinf. Eventually
Qgenerally=1540+8949=10489.
In total, taking into account infiltration, the heat loss of the house will be 10489 W or 10.49 kW.
Boiler power calculation
When calculating the boiler power, it is necessary to use a safety factor of 1.2. That is, the power will be equal to:
W = Q × k
Here:
- Q - heat loss of the building.
- k — safety factor.
In our example, we substitute Q = 9237 W and calculate the required boiler power.
W=10489×1.2=12587 W.
Taking into account the safety factor, the required boiler power to heat a house is 120 m2 equal to approximately 13 kW.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video instruction: how to calculate heat loss at home and boiler power using the Valtec program.
Competent calculation of heat loss and power of a gas boiler using formulas or software methods allows you to determine with high accuracy the necessary equipment parameters, which makes it possible to eliminate unreasonable fuel costs.
Please write comments in the block form below. Tell us how you calculated heat losses before purchasing heating equipment for your own dacha or country house. Ask questions, share information and photographs on the topic.




How did my father-in-law and I buy the boiler? We came to the store, the salesman asked the area of the house and showed us what to choose from. I told my father-in-law, take it with a reserve of power, but he is tight-fisted, and took it right on top.
And what do you think? The boiler puffs at maximum, does not turn off, and the house does not warm up above 19-20ºС. Now we will buy polystyrene foam and insulate the walls. And then he saves, I insist on 10 mm, and he says 5 mm is enough. And the roof too - the wind is blowing. Heat loss has a strong impact, that's a fact.
Skimping on heating your home = chattering your teeth in winter and spending even more on insulation. Fact. Therefore, you should always take a boiler whose power is at least slightly higher than that expected by the area of your home. Then the device will not work at the limit of its capabilities, and heat losses will be compensated. Although, of course, it is better to try to minimize them in order to save on electricity bills.