The operating principle of a double-circuit gas heating boiler and the features of its connection
All issues of organizing autonomous heat supply and hot water preparation are resolved by purchasing one boiler capable of servicing both systems.Without knowing the operating principle of a double-circuit gas heating boiler, it would be illogical not only to make a purchase, but also to operate the unit. Do you agree?
We will tell you about the operation scheme of the heating device, consider all its strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the basic operation of the equipment, you can easily take advantage of all its advantages. And if necessary, it will be possible to identify operational failures in a timely manner, understand and eliminate the causes of their origin.
The content of the article:
Boiler design for servicing two circuits
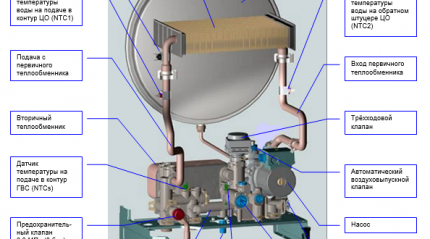
A double-circuit gas heat generator differs from a single-circuit analogue in that instead of one heat exchanger, it has two, which in technical terminology are called primary and secondary.
The first one, i.e. The primary heat exchanger is located directly in the flame combustion zone. Its task is to heat the coolant for the functioning of the heating network. The secondary heat exchanger is responsible for the operation of the hot water supply.

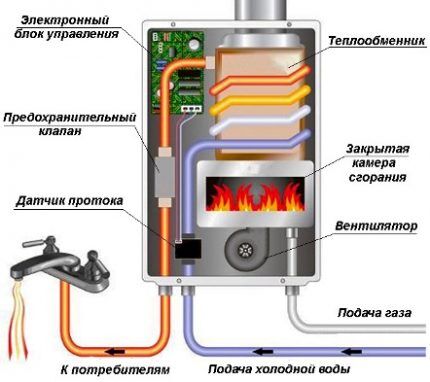
The design of any two-circuit unit includes the following standard elements:
- Combustion chamber with burner block;
- Heat exchangers;
- Equipment control and protection devices.
To understand the design features of double-circuit gas boilers, we will dwell in detail on each of its structural elements.
Types of gas burners for double-circuit boilers
The burner of a gas boiler is responsible for obtaining a sufficient amount of heat necessary for the functioning of the heating and hot water supply circuit. Thermal energy is obtained by burning fuel. Place the burner in the combustion chamber, into which air is pumped in addition to gas. It is needed for the combustion process.
Depending on the operating modes, burners can be classified into the following types:
- Single level burner. A unit with such a burner can operate in only two modes - “Stop” and “Start”. Such boilers, despite their low efficiency and reduced service life, are popular due to their simplicity of design and low cost.
- Two-level burner. A heater with such a burner can operate at full or half power. Its advantages are noticeable in the warm season, when there is no need to operate the device at full power to heat water that is not too cold.
- Modulating burner. A smart boiler system with a similar burner allows you to configure and regulate power. Such a boiler is characterized by a high service life and efficiency, but at the same time it costs an order of magnitude higher than units with single-level and two-level burners.
Burners are divided into open and closed designs. When the burner is open, the air required to burn the fuel comes directly from the room in which the boiler is located. To remove combustion products, a chimney is required, which must provide sufficient natural draft.
Atmospheric heating units are usually equipped with conventional metal pipe, turbine - coaxial chimney. Depending on the technical conditions of the room, the smoke duct is placed vertically or built at an angle. Corner options lead through the wall to the street or connect to a public chimney shaft.

Turbine boilers are equipped with closed combustion chambers into which air cannot flow spontaneously. They are safer and more reliable in operation, but more expensive and more difficult to operate. Boilers with closed burners, in addition to a smoke exhaust, require a channel through which the oxygen required for combustion is supplied to the chamber.
That’s why they equip turbine boilers coaxial pipes, because in addition to removing smoke, they also draw in fresh air flow from the street. It happens that for normal operation, two coaxial chimneys are connected to a closed combustion chamber. In addition, the entire structure is supplemented with an air supply pipe.
All similar boiler models are equipped with fans that provide smoke movement, multi-level protection systems, and automation. The listed devices and systems require electricity to operate. Their disadvantage is their energy dependence, which increases operating costs.
Types of heat exchangers for gas units
If a burner burns fuel to produce heat, the heat exchanger provides this heat for further transfer to water. As already mentioned, the double-circuit design contains primary and secondary heat exchangers.
The primary heat exchanger is located directly above the burner and is a finned tube bent in the shape of a snake. Under the influence of the flame, the water in the heat exchanger heats up and moves through a three-way valve further into the distribution heating system.
The secondary heat exchanger is a system of wavy plates, which are assembled into a single block with two pairs of holes. Each pair of holes has its own functions.
Water from the water supply flows through one of the pairs, and the coolant flows through the second, entering the heating circuit. A similar system of plate and tubular heat exchangers is called dual.
There are heating devices that use a bithermic heat exchanger of complex configuration instead of a dual system. This heat exchanger is made of copper; it consists of a pair of tubes located one inside the other. Coolant flows through the outer tube, and water flows through the inner tube to ensure the operation of the hot water supply.

Boilers with a bithermal heat exchanger are more difficult to operate, since both heat exchangers are represented by a single unit, which makes it difficult to descale. But such heating devices are in demand, as they are characterized by small overall dimensions and high water heating speed.
Automation or boiler control unit
The boiler automation is responsible for safe and stable operation.It monitors the water temperature in the DHW components and maintains the temperature of the coolant in the heating lines. Gas boiler automation prevents the heating device from operating in hazardous situations.
The unit interrupts operation or does not turn on in the following cases:
- Reduced pressure in the gas system;
- Lack of traction;
- Absence or critical overheating of coolant.
The control unit, which controls the operation of protection and process automation devices, is represented by a set of switches, microcircuits, or a combination thereof. In addition to ensuring safety and temperature control, it monitors the operation of the circulation pump and fan.
Modern gas boilers are distinguished by the presence of intelligent controls, the software of which contains various operating modes.
Operating principle and specifics
Many owners of gas equipment do not even think about how a double-circuit gas boiler actually works. They mistakenly believe that heating of water and the heating circuit occurs simultaneously. In reality, things don't look so rosy.
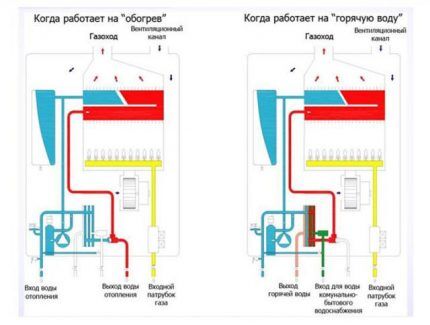
In normal mode, the boiler constantly operates only to heat the coolant circulating in the system. In this case, the switching frequency and intensity of the flame are controlled by a temperature sensor. The burner is started simultaneously circulation pump, if the operation of the heating system is not based on the natural circulation of the coolant.
Essentially, when the coolant temperature reaches a predetermined value, the sensor sends a signal to reduce burner activity. Until the temperature drops to the set value, the boiler will be in passive mode. Then again a command is received from the automatic sensor to activate the fuel supply valve.
Scheme of operation of a double-circuit boiler
The presence of a hot water supply system slightly complicates the operation of a double-circuit gas boiler. Heated by burner coolant, moving along the heat exchanger, ensures heating of the plate heat exchanger through which water from the water supply system moves.
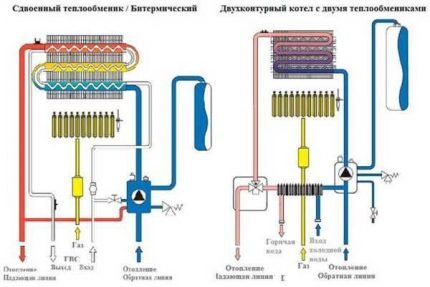
Simultaneous use of a dual-circuit model in heating and hot water supply mode is impossible. When the hot water tap is activated, the three-way thermostatic valve stops the circulation of coolant through the heating lines. The boiler switches to the mode of moving water along a circuit with a plate heat exchanger, which heats water for domestic needs.
If there is a significant consumption of hot water, the operation of the heating-oriented boiler may be paralyzed for a long time. The problem can be solved in two ways - to provide for the installation of a more powerful heating device or to include it in the arrangement scheme indirect heating boiler.
If the hot water system is actively used, it is possible to install a double-circuit boiler with a built-in boiler.In this case, fuel consumption increases slightly due to the fact that during the pause between operating cycles of the heating system, the burner energy is used to maintain the water temperature in additional gas water heater.
A certain supply of hot water in the built-in boiler allows you to use the DHW system without turning off the heating circuit. As a result, both systems operate alternately, without overheating the liquid and extending the life of the heat exchanger.
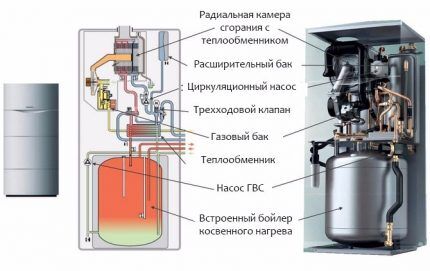
The built-in standard boiler allows you to get hot water at the desired temperature at any time, the supply of which is provided automatically. While a flow-through DHW system takes several minutes to heat the water to the required temperature.
Types of gas boilers with two circuits
The operating features of gas equipment are largely determined by the design version of the heating device. Modern boilers are available in two form factors - floor-mounted and wall-mounted.
When choosing a design option, you need to focus on the size of the heated area and the activity of using the hot water system. You need to understand that wall-mounted boilers are more compact, but at the same time they have much less power.

Choice wall-mounted double-circuit boiler may be justified if the heated area does not exceed 200 sq.m, and the total productivity of the hot water system does not exceed 14 l/min.
The small size of a wall-mounted boiler, although it seems like an advantage, actually hides many disadvantages. Compactness is achieved through the use of thinner heat exchanger tubes. In addition to the fact that they have a shorter service life, there is a possibility of clogging.
In floor-standing installations, more massive and reliable cast iron heat exchangers are used. This not only increases the reliability of the heating device, but also extends its service life.
Advantages and disadvantages of dual-circuit devices
The advantages of a double-circuit heating unit are as follows:
- Economical fuel consumption. The direction for comparison is to use a double-circuit boiler or a single-circuit boiler with indirect heating.
- Compact sizes. The overwhelming majority of double-circuit boilers are wall-mounted heating devices. They are easy to place both in utility rooms and in small kitchens.
- Versatility. There is no need to buy additional equipment and resolve issues with its compatibility with the boiler.
In one unit, a flow-through water heater, a heating device and a circulation pump have already been successfully combined into a single automated system.
Obviously, along with the advantages, there are also disadvantages:
- Impossibility of simultaneous operation of the heating and DHW circuit. In this regard, significant consumption of hot water can cause a decrease in the temperature in the house.
- Power limitations of wall-mounted models. Compact wall-mounted boilers, due to the minimum size of the burner, are not able to provide the required temperature conditions at maximum pressure. A similar disadvantage is observed when water intake points are located remotely.
- Sensitivity to water quality. The secondary plate heat exchanger is demanding on the quality of the water consumed. The presence of impurities causes the use of means to reduce its hardness and clean the coolant.
Another criterion for evaluating a double-circuit boiler is its cost. The price of a double-circuit heater is higher than the price of a single-circuit analogue.
However, if we consider the presence of a hot water system and ways to resolve the issue in the case of installing a single-circuit boiler, then if indirect heating is included in the boiler assembly scheme, the price of a double-circuit boiler will be lower.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The following video will introduce you to the design components and operating principle of gas heating equipment:
The author of the video will present the piping of a double-circuit gas boiler:
A detailed acquaintance with the features and operating principle of double-circuit gas units makes it possible to determine the advantages of their operation. Purchasing such heaters will help you save on the purchase of additional equipment necessary for organizing a hot water system.
If one of the circuits breaks down, the other can be used, and replacing the circuit will always cost less than repairing a separate heating installation. A double-circuit boiler can also be used in the warm season, operating it only in the mode of heating water for domestic needs, which is what is convenient and economical compared to purchasing separate units.
Tell us about how you chose a double-circuit gas boiler to equip your own home/apartment/dacha. What was the decisive criterion for you in your choice? Please share useful information on the topic, photographs in the block below, and ask questions.




How to find out: 1. Is it possible to operate a double-circuit gas boiler?
exclusively only in heating mode? And is this heating system open with an expander in the return?