How to determine gas consumption: methods of measuring and calculating the fuel used
One way or another, you have faced the issue of saving and power of household appliances. Whether at the stage of the first repair or when replacing outdated equipment.It can be useful to calculate gas consumption or the need for it before purchasing a stove or boiler, choosing a gas meter, or its possible replacement. If you have questions about gas charges, if the search for new equipment is a matter of the next few weeks, an accurate method for determining gas consumption and formulas for calculation will make your life easier.
Gas prices are gradually rising, and appliances are becoming more powerful, so it doesn’t hurt to come up with your own strategy to optimize costs. Our article will help you with this. You cannot find out about the current level of gas consumption in your home from conversations with your neighbors; you need accurate information.
The content of the article:
Natural gas consumption at home
The owners of all apartments and houses and many enterprises need to calculate the volume of gas consumed. Data on the need for fuel resources is included in the designs of individual houses and their parts. To pay using actual numbers, use gas meters.
The level of consumption depends on the equipment, the thermal insulation of the building, and the time of year. In apartments without centralized heating and hot water supply, the load goes to the water heating boiler. The device consumes up to 3-8 times more gas than a stove.

The maximum consumption of the stove depends on the number of burners and the power of each of them:
- reduced — less than 0.6 kW;
- regular - about 1.7 kW;
- increased - more than 2.6 kW.
According to another classification, low power burners correspond to 0.21-1.05 kW, normal - 1.05-2.09, high - 2.09-3.14, and high - more than 3.14 kW.
A typical modern stove uses at least 40 liters of gas per hour when switched on. Typically, a stove consumes about 4 m³ per month per resident, and the consumer will see approximately the same figure if they use a meter. In terms of volume, much less compressed gas in cylinders is required. For a family of 3 people, a 50 liter container will last about 3 months.
In an apartment with a 4-burner stove and no water heater, you can install a counter marked G1.6. A device with standard size G2.5 is used if there is also a boiler. To measure gas flow, large gas meters are also installed, on G4, G6, G10 and G16. A meter with parameter G4 can handle the calculation of gas consumption by 2 stoves.
Water heaters are 1- and 2-circuit. For a boiler with 2 branches and a powerful gas stove, it makes sense to install 2 meters. One reason is that household gas meters do not cope well with large differences between the power of the equipment. A weak stove at minimum speed uses many times less fuel than a water heater at maximum.

Subscribers without meters pay for volume based on consumption per 1 inhabitant multiplied by their number, and consumption per 1 m² multiplied by the heated area. The standards are valid all year round - they contain an average indicator for different periods.
Norm for 1 person:
- Gas consumption for cooking and heating water using a stove in the presence of a centralized hot water supply (DHW) and central heating is about 10 m³/month per person.
- Using a stove alone without a boiler, centralized hot water supply and heating is approximately 11 m³/month per person.
- Using a stove and water heater without central heating and hot water supply is about 23 m³/month per person.
- Heating water with a water heater is about 13 m³/month per person.
In different regions, the exact flow parameters do not coincide. Individual heating using a water heater costs approximately 7 m³/m² for heated residential premises and about 26 m³/m² for technical ones.
The dependence in gas consumption was indicated in SNiP 2.04.08-87. The proportions and indicators are different there:
- stove, central hot water supply - 660 thousand kcal per person per year;
- there is a stove, no hot water supply - 1100 thousand kcal per person per year;
- there is a stove, a water heater and no hot water - 1900 thousand kcal per person per year.
Consumption according to the standards is influenced by the area, the number of residents, the level of amenities with household communications, the presence of livestock and its number.
The parameters are differentiated based on the year of construction (before 1985 and after), the use of energy-saving measures, including insulation of facades and other external walls.
More information about gas consumption standards per person can be found in this materiale.
Calculation of gas for heating, hot water supply, stove
The required amount of fuel for heating the premises is determined by the square footage or cubic capacity of the room. In the case of rooms 3 meters high or less, it is enough to determine the area. For 1 sq.a meter of such premises will require an average of 100 W.
In the southern regions of the country, the specific parameter per 1 m² is reduced to 80 W, in the far north it is increased to 200 W per m². The water heater is selected with a margin higher than the maximum load.
With the volumetric method of counting, from 30 to 40 W are allocated per cubic meter, with a decreasing number for the southern regions. All methods work well in winter, but the performance per 1 m² decreases as the difference between the outside and room temperatures drops from 40 degrees to 10.

The maximum gas consumption by the boiler is calculated using the formula V = Q/(q×efficiency/100), Where:
- V—fuel volume, m³;
- Q—power of the heating system and heat loss, kW;
- q—lowest specific calorific value of fuel, kW/m³ (average 9.2);
- Efficiency is the efficiency factor of a gas boiler, usually 96%.
Using the same, but modified formula, you can calculate the maximum consumption by the stove, including per unit of time.
When measuring the consumption of liquefied gas (LPG), the specific heat of combustion is substituted for the lowest specific calorie content. It differs for different mixtures, and for propane-butane it is 46 MJ per kg. The efficiency of a gas boiler when using LPG is reduced from 96 to 88%.
The amount of fuel for individual hot water supply is determined according to the needs of 1 person. The information is in the water consumption documentation, but you can make the calculation yourself. For a family of 4 people, 1 heating of 80 liters per day, from +10 to +75 °C, is enough.
The required power is determined by the formula Q = c×m×Δt, wherein:
- Q is the actual required power, in kW;
- c—heat capacity of water, 4,183 kJ/kg×°C;
- m—water consumption, kg;
- Δt is the difference between the initial and final temperatures, usually 65 °C.
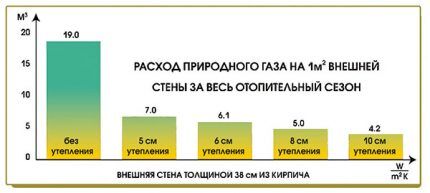
They save on fuel through systemic and external methods. Benefits are provided by condensing plates and indirect heating boilers with a timer. Automation will help with changing the temperature in the room from comfortable for a person to +10...+15 °C during absence. External savings options include home insulation and radiant floor heating.
You can save gas when using a stove using the following methods:
- “do not let out” the flame from under the bottom of the containers;
- cover kettles and pots with lids;
- for boiling, use only maximum heat;
- heat food in large portions.
Gas consumption is also determined before roofing work, in fusing burners. A 50-liter cylinder with a propane-air mixture will last for 10.8 hours, because the consumption will be approximately 2 kg/hour. For 1 m² of coverage you will need 0.2 kg in spring - autumn and 0.3-0.4 kg in winter.
We also suggest reading our other articles, where we talked in detail about how to correctly calculate gas consumption for heating a home:
Meters for measuring fuel consumption
The meter measures the amount of gas at different conditions of temperature and pressure and, using special equipment, brings the result to the indicator that will be under standard conditions (SU) - +20 °C and 101 kPa.
The volume of fuel for the control system is determined by the formula Vс = V×(p×Tс/pс×T×K), Where
- V is the volume of gas;
- p—density;
- T—thermodynamic temperature;
- K is the fuel compressibility coefficient.
Values with the letter “c” are indicators for standard conditions, without - for workers.
In everyday life, membrane, rotary and ultrasonic meters are used, in large enterprises - turbine and vortex meters - these are the most popular types of gas meters. In gas industry plants, volume is determined mainly by variable pressure changes in constrictions, often between 2 flange connections in close proximity. The meters differ in their operating features.

Diaphragm flowmeters produce minimal error in calculations and consume little electricity. The devices provide readings over a wide range, but with a low maximum pressure - up to 0.5 bar. In everyday life, the meter performs best, since the calibration interval reaches up to 10 years with high reliability of the device. The design does not respond well to mechanical gas contamination and is generally very bulky.
Rotary, or rotary, the models do not depend on the electrical network, they are suitable for small industrial facilities, but they are less convenient. With a small installation area and high precision under conditions of sudden pressure changes, they make noise and more often fail. They are “afraid” of pneumatic shocks and pollution.
Ultrasonic meters They are small in size and vary significantly in the complexity of their structure. Acoustic gas meters are valued for their reliability and ease of installation. Some devices contain non-volatile memory. Meters for standard sizes G1.6 and G2.5 are relatively expensive.
Turbine devices used to measure the amount of household and aggressive gases, multicomponent compositions. Meters have become widespread at gas pipelines and chemical plants. Turbine devices record large quantities of gas at pressures up to 10 MPa and vary significantly in size and operating pressure. These are universal instruments for measuring natural gas flow in industry.
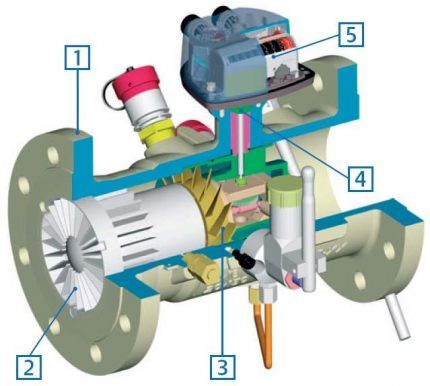
Vortex measure the volume of natural or inert gases. In terms of measurement range they have an advantage over other models. They detect the slightest movements in the gas mixture and determine large quantities of gas per diameter. The efficiency of a vortex flow meter is directly proportional to the fuel flow rate.
Measurement methods used in gas flow meters
Fuel consumption is calculated direct And indirect methods.
In the case of direct gas, gas fills the measuring chambers and leaves them. The volume passed correlates with the filling-emptying cycles. Counting in membrane, rotary and drum counters works according to the described principle.
Gas meters with an indirect measurement method work with speed indicators and a known cross-sectional area. The counting method can be mechanical or other, related to the characteristics of the counter. In mechanics, turbines, impellers, and balancing elements are used.
The indirect method of calculation has other methods:
- vortex detection;
- measuring the pressure difference on the constriction device;
- calculation of heat transfer from a heated body;
- measurement of velocity pressure;
- counting based on ultrasonic movement.
The correctness of indirect methods depends on the correspondence of the speed in direction and cross-section. Flow preparation means help: turbulators, condensers and flow straighteners. The devices come separately or as elements of meters.
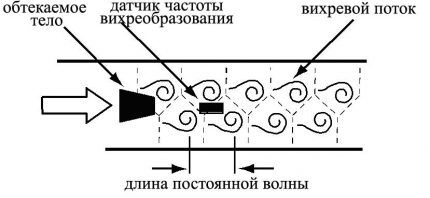
The devices can determine the difference in speed across the cross section simultaneously with the speed of gas movement and thus reduce the error. The latter often occurs due to fuel stagnation near the walls. Read more about direct and indirect methods for determining gas consumption Further.
How is gas pressure determined?
Pressure is measured directly using pressure gauges or by adding the values of atmospheric (Pb) and excess pressure (Pi). Pb is measured at the location of the Pi converter, if the latter is in a closed space and there is pressure or vacuum in it.

The pressure tapping hole for vertical and horizontal pipes is placed radially. On a transverse pipeline it is located in the upper half of the section.
In flow meters without the specified hole, sampling is carried out in front of the meter, at a distance of 1 to 3 pipeline diameters, with a reference point from the gas meter inlet flange.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Estimated gas consumption by the boiler at a certain power:
High gas consumption when using gas-cylinder equipment for a car:
Simple ways to reduce fuel consumption in your apartment/house:
Time has shown that it is better to have one or more meters in your apartment. Only with large volumes of consumption and high prices for gas meters does it become profitable to pay according to the standards. In domestic conditions, flow meters with rotors and membranes and smart counting are used to measure gas flow.
For commercial purposes, turbine, vortex and levitation are used. For the most accurate measurements, drum models are installed in laboratories. It’s not enough to have a gas meter; sometimes you need to count it yourself. The estimated amount of gas for current and planned needs should be determined using formulas or together with an invited specialist.
Write comments on the topic of the article. Tell us if you had to determine gas consumption yourself, and if so, for what purpose did you do it? Ask questions in the form located below the article.



