Why gas cylinders explode: main reasons and preventive measures
Agree, the news that a gas cylinder exploded somewhere, which we, unfortunately, sometimes hear on TV or from friends, makes us think about our own safety. And there is no place for complacency that this will not happen to us in this situation.
The consequences that such an explosion and the fire caused by it lead to can be the most tragic, and not only for property, but also for the health and life of people nearby. We will help you understand why gas cylinders can explode and how, without sacrificing the convenience of their use, you can protect yourself from big troubles.
To do this, we conducted a study of the features of existing types of household gas vessels, analyzed the reasons why explosions occurred in a number of real cases, and studied the competent opinions of experienced users about this. The proposed article can be presented as a compilation of sets of rules, presented in an understandable form, that allow, in practice, the correct and safe use of gas in cylinders.
The content of the article:
Basic information about gas cylinders
The indispensability of gas cylinders in everyday life can be confidently confirmed by a significant part of the Russian population.

At the state level, Rostechnadzor has identified general problems with the use of gas vessels that you need to be aware of, as they are related to their safe use:
- outdated fleet - about 90% of all cylinders are not protected from overfilling during refueling;
- lack of clear government regulation in the field of circulation of cylinders on the market, which includes the presence of illegal refills;
- the need to improve and bring technical parameters to international standards.
Non-compliance with these requirements and recommendations of the European Commission imposes difficulties in ensuring the safety of gas cylinder products used in Russia and imported.
In addition to knowing the general problems, to make it easier to imagine the reasons leading to an explosion and the conditions that can contribute to this, it will be useful to know what cylinders exist, understand the device, and understand some of the nuances of the physics of explosion and combustion of the mixture used in them.
Types of gas vessels
Depending on the application, the filler used and the connection methods, gas vessels may differ both structurally and in the material from which the body is made.

The most popular are metal cylinders, both new and old vessels. The main reason for the increased demand for tanks of this type is their relatively low price and the large number of offers on the market, including due to tanks manufactured back in Soviet times.
But it is steel cylinders that are subject to the greatest risk of explosion and, following safety principles, require compliance with a number of conditions during their storage and operation. Therefore, we will dwell on them in more detail.
How is the balloon constructed?
The design of the gas vessel resembles an ordinary lighter, the container of which is also filled with a substance in two states of aggregation. Part of the reservoir is occupied by gas in the liquid phase, the remaining free space is filled with the same substance, but in gaseous (working) form. Through the shut-off device, the gas enters the appropriate equipment for ignition and use for its intended purpose.
The standard package of a gas cylinder includes:
- The gas vessel itself, or shell, is cylindrical in shape and with a minimum wall thickness of 2 mm.
- Balloon valve with locking element and handwheel.
- A ring support (shoe) that ensures a stable vertical position of the gas container.
- A casing that protects the valve from damage and contamination during transportation, storage and operation.
The cap is attached to a special threaded part - the ring of the neck of the cylinder.

Its use allows you to reduce, stabilize and maintain the pressure of the mixture in the values set for a specific gas consumer.This adapter can be easily installed on any type of cylinder.
Gas mixture for household cylinders
The filler for the cylinders is hydrocarbon gas - a mixture of propane and butane, which is pumped into the vessel under pressure up to 15 MPa.
The ratio of these hydrocarbons determines the seasonality of use of the mixture or a specific region. The fact is that, with relatively identical basic properties, propane and butane have a significant difference in evaporation temperatures: butane - 0.5 °C, propane - 43 °C (with a minus sign).
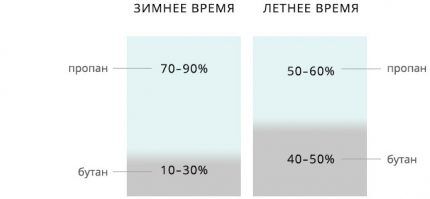
Knowledge of the principle of mixing hydrocarbons used in gas tanks is essential not only in the ability to reduce the cost of fuel (butane is cheaper than propane), but also in reducing, due to the less intense evaporation of butane, the risk of high pressure formation with a significant increase in ambient temperature. A sharp increase in pressure in the tank can cause its depressurization and, accordingly, an explosion or fire.
Preconditions for an explosion
Despite the increasing requirements for the safe handling of cylinders and their quality, every year in Russia more than 200 people become fatal victims of cylinder gas explosions, and many more are injured.
Having summarized the information from manufacturers of gas containers, we present the pressure ranges at which destruction of the flasks is possible:
| Gas cylinder volume | Pressure at which an explosion is possible, MPa | Pressure at which an explosion is possible, atm |
| 5 l | 15-16 | 120-160 |
| 27 l | 7,5-13 | 75-130 |
| 50 l | 7,5-12 | 75-120 |
As the strength of the flask walls decreases, the critical pressure value leading to its depressurization decreases to 5.3 MPa.
Gas explosion or combustion
You need to understand that an explosion and a cylinder ignition are not exactly the same thing. For example, the answer to the question whether a household gas cylinder that has received a shrapnel or bullet hole can explode is impossible to answer with a clear “yes.”

A mixture of propane-butane and oxygen in the air outside the cylinder or drawn inside explodes after the pressure inside the flask is equal to atmospheric pressure.
What causes gas cylinders to explode or burn?
Cylinder in a fire zone
The explosion hazard of a container caught in a combustion zone with a gas mixture in it under pressure is very high. According to GOST, the maximum safe temperature for a hydrocarbon cylinder is 45 °C. It is clear that in the source of the fire it significantly exceeds the permissible limit.
The physics of the process is as follows. At high heating temperatures, the mixture in the vessel boils and, accordingly, the pressure in it increases. In addition, uneven heating of the shell surface weakens its initial strength and leads to destruction of the walls.

Rapidly evaporating and igniting, the hydrocarbon ejected from the cylinder in a liquid and vapor state has an additional thermal effect in the fire zone on everything around it.
Having understood why gas cylinders explode during a fire in houses, you should also know how they can behave when heated.
There can be two options for rupturing the flask:
- According to “hydraulic” mechanics.
- Severe twisting and formation of a large crack on the bottom and shell.
In the first case, the liquid phase with an increase in temperature to 60 ° C will fill the volume of the vessel to the norm of 85% at a pressure of 1.5 - 2.5 MPa. Destruction of the shell will occur with a further increase in the temperature in the room to 70 – 75 °C.
The second option occurs when there is no liquid phase in the vessel, if, for example, evaporation of the liquefied mixture occurred due to depressurization of the shut-off device at elevated temperatures in fire conditions.
In any scenario, fragments of a ruptured cylinder can fly away at high speed in different directions, creating a threat of injury to people and damage to property.
Excessive filling of the gas cylinder
Often when filling containers with liquefied gas, they are overfilled. This happens due to negligence or deliberately, wanting to save on the utilization rate of the tank.

There should be part of the free volume left in the container - a cushion for the vapor phase of hydrocarbons. The safe volume of such a cushion is at least 15% of the total volume of the tank.In its absence, the pressure in the flask increases by 0.7 MPa with an increase in the temperature of the mixture by every degree, which is unacceptable according to safety standards and can lead to overstressing of the shell and its rupture.
The amount of gas pumped into the vessel is strictly regulated in terms of pressure and mass, and should not exceed 0.425 kg per 1 liter of container volume.
Even at the temperature of +45 °C prescribed by GOST, an overfilled flask poses a great danger of the possibility of longitudinal rupture along the weld.
We also recommend reading our other article, where we talked in detail about the rules gas cylinder refills.
Heating or cooling the walls of the vessel
The propane-butane mixture, having a large expansion coefficient, greatly increases in volume even with a slight increase in its temperature.

The danger of increasing the pressure of the mixture on the walls of the flask also exists in a cylinder installed next to a heat source.
In addition to heating, a number of dangers are also fraught with the negative effects of negative temperatures. The first is an increase in the fragility of the metal. And secondly, you must remember forever that under no circumstances should you bring a vessel that has been exposed to the cold for a long time into a warm room. A sharp increase in the temperature of the hydrocarbon mixture is unsafe.
Impacts and falls of cylinders
Damage and ignition of a container with gas can be caused by sudden mechanical impacts on its walls, especially when the reservoir is in conditions of low or, conversely, extremely high temperatures.
When using a cylinder in abnormally cold conditions, the mechanical properties of the metal change - the impact strength of the steel decreases.

In the second case, increasing the temperature and heating the gas contained in the flask, as was said, sharply increases its pressure, which, with additional shock impacts on the vessel, can rupture it.
Foreign impurities in gas
The danger of explosion lurks when water and hydrogen sulfide enter a vessel with liquid gas. Their high content in the tank contributes to the appearance of delaminations and bulges on the inner metal surface of the shell.
Such vascular defects occur when there is 0.3% or more hydrogen sulfide in propane, and can be observed after only two years of using the cylinder.
Weld defect
Less common, but encountered, are problems associated with depressurization of gas vessels in the heat-affected zone.
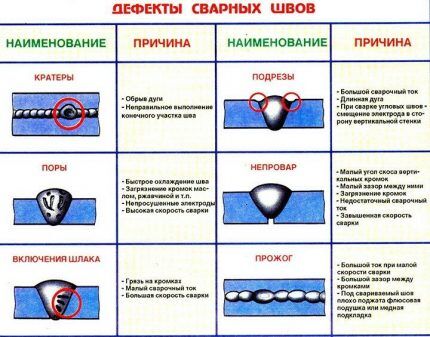
The overall integrity of the shell may be preserved when a defective weld ruptures.
Scenarios for the consequences of a cylinder explosion
The above reasons for the explosion or fire of gas vessels can, in various ways, provoke the following dangerous scenarios.
Cylinder rupture and flame emission
Explosion of a cylinder and ignition of propane-butane are dangerous due to the following factors:
- a column of strong flame, quickly increasing the area of the fire;
- high temperature of fire at the source of the explosion;
- toxicity of combustion products.
Damage can also occur from suffocation, due to a significant decrease in oxygen with a sharp concentration of harmful gases.

Typically, a vessel ruptures along its side.
Secondary damaging effects from the explosion
Secondary, but no less serious, damaging consequences of a cylinder explosion are:
- valve separation;
- impact of a compression wave or shock wave;
- damage from fragments of shell elements.
Fragments from the cylinder and its detached elements can fly very far, causing damage within a radius of up to 250 m, and rise to a height of thirty meters.
Danger of gas leakage
The danger of propane leaking from a damaged container is that an explosive concentration of a mixture of hydrocarbon and oxygen is created in the room very quickly and in large volumes - much faster than with leaks of liquid flammable substances.
A strong leak of the mixture from a flask or faulty shut-off valve can be detected by smell or hearing - the sound is similar to what we hear when a balloon is quickly deflated.

If there is a gas leak, then it is necessary to cover the leakage area with a wet rag, carefully take the vessel outside and call the gas workers.
Since 2016, technical regulations have provided for the mandatory installation of gas alarms in new houses. For previously built housing, this standard is advisory in nature, but the benefits of this device, especially in houses that use bottled gas, are undoubted.
The fact is that the density of the hydrocarbon mixture is greater than the density of air. If the sealing of the flask, shut-off equipment or connecting hose is broken, gas begins to accumulate at the bottom, and its odor may not be immediately detectable. This is why a propane mixture released into the air from a damaged gas cylinder often explodes in houses from any spark without being noticed.
Basics of safe cylinder handling
Before installing the cylinder and connecting it to gas appliances the first thing to do is to make sure that there is no damage, rust on the body and that the valve is in good working order.
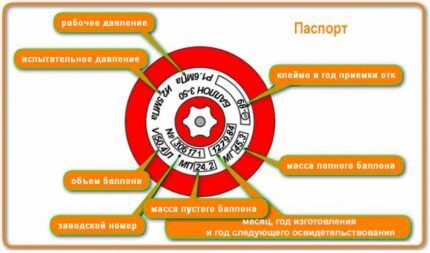
The main technical requirements that must be observed when operating cylinders include:
- All cylinders, with the exception of one (five-liter for connecting to a gas stove) must be installed in outbuildings outside buildings and at a distance no closer than 5 m from the entrance to them.
- Avoid storing cylinders in living rooms, basements and attics.
- Do not place cylinders closer than 1 m from heating devices and 5 m from open fire.
Obvious, but often forgotten safety measures when using vessels with gas include and must be strictly followed:
- Do not bring a lit match or lighter to the cylinder to check for gas leaks.
- Strictly exclude the use of open flames to heat the gearbox or valve. For these purposes, only hot water can be used.
- If gas is detected in the room, do not turn on any electrical appliances, including lights, or turn them off. The temperature of a spark in a socket or switch can reach up to a thousand degrees.
- Do not try to repair shut-off valves and other structural elements of the cylinder yourself.
In addition, you must strictly follow the time frame for using the cylinders prescribed by the manufacturer. Vessels manufactured before December 2014 can be used for 40 years.
In the absence of information about the permitted period of use of gas cylinders produced after this date and without accompanying documentation, Rostechnadzor recommends taking 20 years as the shelf life of the cylinder.

A safe alternative to steel gas cylinders are more modern polymer-composite vessels - Eurocylinders. Their flasks are protected by a plastic casing and do not accumulate static electricity. The explosion safety of composite cylinders is ensured by equipping them with new generation safety devices - a fusible link and a check valve for releasing high pressure.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The reasons for explosions of gas cylinders using examples of real facts, and what can and cannot be done when using them:
How to properly use gas cylinders at home, and what requirements they must meet:
With all the existing risk factors that accompany the operation of gas equipment, there is no reason to succumb to fear and refuse the convenience of using them in everyday life.
Theoretical knowledge of the causes and conditions accompanying the explosion of household gas cylinders is intended to help overcome such fear. And compliance with the given set of standards for their safe use will serve as reliable insurance against the serious consequences of a gas explosion and fire.
If you have valuable information that can complement our material, please share it with other site visitors - leave your comments in the block below. There you can ask questions about the topic of the article.




Unfortunately, not everyone understands the increased danger of gas. Although it would seem that something is constantly exploding somewhere, people are dying and getting injured. Maybe they were right in the USSR, where it was impossible to recharge the cylinder yourself, you could only exchange it at the station?
To be honest, I think this approach is very correct and safe. No self-filling, just exchange for another cylinder. The bottom line is that cylinders are subject to wear and corrosion, and over the years, microcracks appear inside the gas cylinder itself. It is the latter that pose the greatest danger. When refueling yourself, it is impossible to detect such defects. In addition, many gas stations have the sin of trying to fill as much as possible in order to sell more fuel, and this already puts excess pressure on the walls of the gas cylinder.
Personally, I can name the three most important reasons that lead to explosions:
1. Violation of the rules for storing gas cylinders;
2. Wear of the cylinder (inspection must be carried out every two years);
3. Sudden temperature changes (related to the first point, but I’ll highlight it separately).
If you follow safety regulations, the gas will be no more dangerous than an electric stove.
If they are changed only at stations, then this is even worse, because they are not checked so carefully at the stations, there may be a dangerous chemical substance inside, which is light in weight, then they will refill them and place the cylinders not far from each other. There are many nuances here.
The Taganka seller has no information about using a butane stove to operate on methane (main gas). Can Domotec MS 6604 be used for methane?
Let them find the person responsible for the gas station, tell everyone and show them what not to do. Although this needs to be done regularly. And not show the same political programs every day.