Choosing energy-saving lamps: a comparative review of 3 types of energy-efficient light bulbs
Saving energy is a large-scale task for which the latest technologies are used.Increasing electricity consumption forces users to use energy-saving lamps - innovative lighting technology has increased efficiency with reduced energy consumption.
The market offers a wide range of “housekeepers”, but it’s easy to get confused in such a variety, don’t you agree? We will help you make the right choice.
The article provides a detailed overview of three types of lamps with a description of their characteristics and application features, and identifies parameters that should definitely be taken into account when choosing energy-saving lamps.
The content of the article:
Classification of energy efficient lamps
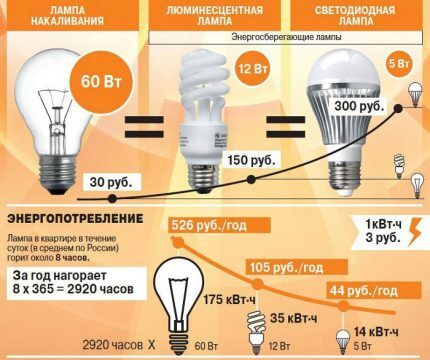
Determining the economic effect is possible by comparing two samples. Incandescent lamps, the most inefficient of modern light sources, were chosen as the object of analogy. This is what served as the basis for promoting the advertising slogan “energy-saving light bulbs.”
Electric lamps, which have high luminous output and low power consumption, are divided into three main types: LED, fluorescent and halogen.
Moreover, each category differs not only in design features, but also in the quality of savings:
- luminescent can save up to 80% of electricity;
- LED – 80-90%;
- halogen – 30-50%.
Economical performance in them is achieved due to high efficiency. Most of their power is aimed at reproducing light flow, and heat transfer and other costly processes are reduced to a minimum.
Fluorescent lighting technology has managed to gain the greatest popularity, which has found application not only in everyday life, but also in various spheres of life: offices, warehouses, etc. However, the cost of their disposal forces entrepreneurs to introduce a newer type - LED analogues.
Fluorescent gas discharge lamps
Fluorescent lamps used in everyday life are called compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). As a rule, they are made in the shape of an arcuate spiral and are traditionally equipped with a screw base. They can be screwed into a standard cartridge, instead of an uneconomical analogue.
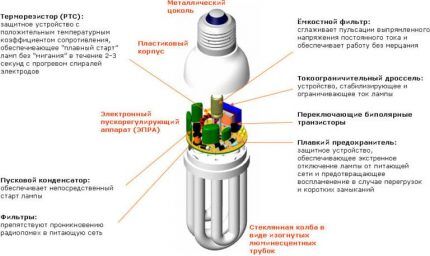
Main structural elements compact fluorescent lamps:
- gas discharge flask;
- choke;
- diode bridge;
- fuse;
- filter capacitor.
The glass flask is filled with an inert gas (argon or neon) mixed with mercury vapor. Mercury pressure is subject to the temperature of the CFL walls and at a standard operating temperature of 40°C will be in the range of 0.13-1.3 N/m2.
The inside of the lamp is coated with a layer of phosphor, which contains calcium halophosphate or antimony with manganese. By changing the ratio of so-called light activators, manufacturers were able to achieve different color parameters of the glow.
Tungsten spiral electrodes are also located here, connected via a ballast to the power supply. To increase emission, the contacts are treated with an oxide composition.
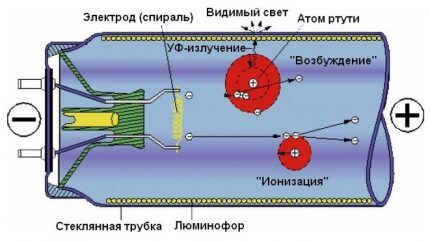
The technology used to reproduce light in them differs significantly from other analogues. Under the influence of an electric field applied to the contacts, the lamp produces a gas discharge.
It penetrates the inert environment of the flask, resulting in the formation of ultraviolet radiation. However, this spectrum is invisible to humans, so it is then absorbed by the phosphor, transforming it into a standard visible glow.
Gas discharge devices are presented both in open form and complete with a diffuser.
They are available with sockets of various modifications:
- E27 – standard socket;
- E14 – minion type;
- E40 – for a large seat;
- G23, 2G7, G53, 2D – decorative type of devices: spotlights, lighting, etc.
Depending on the quality of the constituent elements, the period of uninterrupted operation guaranteed by the manufacturer varies from 3,000 to 15,000 hours.
Installation is significantly simplified due to the placement of all elements in one inseparable housing, including the ballast.

If we compare a fluorescent lamp with an incandescent lamp, we can note that the positive characteristics of the first significantly predominate:
- durability - due to the use electronic ballasts, characterized by resistance to mains voltage surges, the service life of the device increases significantly to 20,000 hours;
- heat transfer coefficient reduced, therefore they are allowed to be installed in any type of lamps without the risk of overheating;
- variability of color temperature spectrum, which are successfully used in room design.
Since the device uses standardized elements, provided that the gas cylinder remains sealed, it is possible to replace failed parts.
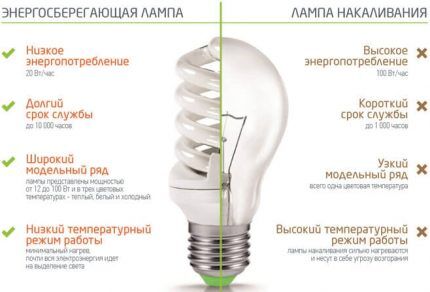
Thanks to leading developments, they are trying to minimize the disadvantages of ELLs, but at the moment they are still present:
- The service life of the LL is limited.
- The use of mercury vapor, which is harmful not only to humans, but also to the environment if the flask depressurizes.
- Due to the presence of the previous paragraph, it is required to take Product disposal measures. For large enterprises this is an additional expense item.
- Fragility of the glass case.
Uncontrolled supplies of low-quality products to markets and mass distribution of such products entail a loss of customer confidence. More than half of low-grade Chinese-made light bulbs do not comply with GOST.
Features of halogen lamps
This is an improved version of standard incandescent lamps, containing halogen pairs in its design. The filament body in these products is made of tungsten filaments located as close as possible to the device socket. To give them a spiral shape, they are twisted and fixed using electrodes and holders.

The operating algorithm of the device is as follows: tungsten atoms leave the hot wire and collide with halogen vapors in the flask and combine with them. But high temperature does not provide any other way for the development of the chemical process other than the decomposition of the compound - the tungsten atoms return to the wire helix again.
Today, methylene bromide or methyl is used as a halogen composition. However, work continues on the selection of effective volatile halogen compositions. Since all the elements are enclosed in a quartz flask, ultraviolet rays can pass through such a material, so measures are taken to block them.
In network products, the lamp is additionally placed in a glass shell. Partial filtration of harmful radiation is achieved by applying a special composition to the flask. These lamps are marked UV-Stop or UV-Block.

The service life of such light bulbs is determined by the moment the tungsten filaments are depleted. Thanks to the use of the halogen cycle, manufacturers achieve an increase in luminous efficiency while maintaining the same service life as incandescent lamps - 1000 hours.
Or they extend the operating period to 4000-5000 hours at the same light parameters.
The operation of such lamps is designed for low mains voltage - 6, 12 or 24 V, so they are used only in conjunction with transformer for halogen lamps.

The most powerful example - metal halide lamp directional light. This lighting option is suitable for rooms where there are objects with increased sensitivity to heat, due to which they deteriorate or collapse.
In most cases, they are used for illuminating shop windows. The intense white color of the glow with a color temperature of 3200 K successfully emphasizes the shiny elements and the color variety of the illuminated products.

The most compact design is for capsule models. Their manufacturing process is based on low-pressure technology, so they can be used in open-type luminaires.There are only two modifications available - with longitudinal or transverse placement of the tungsten filament.
The main advantage over all glass analogues is the use of a quartz flask. The design is characterized by increased strength to mechanical stress and a high degree of thermal strength.
Thanks to this, it is possible to fill the lamp with xenon under high pressure, which ensures high brightness and light output.

Additionally, we note the following advantages:
- time-stable light flux;
- compact dimensions;
- operate without a transformer, with the exception of low-voltage networks in high-voltage networks of 220-240 V;
- wide angle of light dispersion, without sharp restrictions into a narrow beam;
- throughout the entire service life, brightness is not lost;
- it is possible to adjust the light intensity;
- high level of safety - low-voltage models can be used in rooms with high humidity and in lamps without protective glass.
In addition to the positive aspects, halogen lamps also have negative characteristics, which include excessive heating of the bulb. In some models the temperature reaches 500°C. For this reason, the installation of lighting equipment must be carried out at a certain distance from objects - other light sources and the ceiling.
Halogen products are also susceptible to voltage surges, which is a significant disadvantage.
Linear type models deserve the most criticism: they cannot be used for a long time in a vertical or inclined position. As a result, the halogen substances and gas are separated and the device ceases to function.
Separately, it is worth noting that you should not touch the lamp with your hands, because... stains remain on it. It is screwed in, having previously been wrapped in a piece of rags, or gloves are put on.
For more information on choosing halogen lamps, see this article.
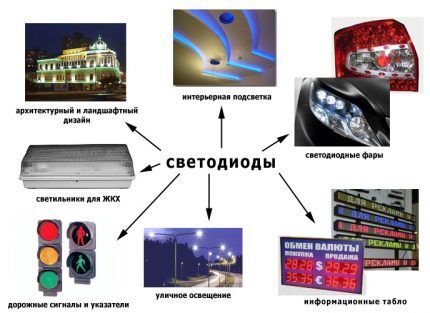
LED lamps
Due to low energy consumption, LED crystals were initially used exclusively for indicating various processes in radio-electronic devices. But over time, they began to be improved, using super-bright LED elements, which make it possible to use them in lighting schemes in almost all areas of activity.
The design of such light sources consists of several elements - a driver, LEDs and a getinax strip. The parts are enclosed in a housing shaped like a “corn”, an elongated flask or a spot type.
All of them are made of polycarbonate. This design made it possible to eliminate the main problem - the likelihood of mechanical damage.
Due to the fact that the device already has a ballast, the lamp is connected directly to the power supply without ballasts.

The narrow targeting of diodes allows them to be combined into small or large groups.
Depending on the intended installation location, lamps are divided into:
- automobile;
- industrial;
- phytolamps for plants (presented in linear type);
- street spotlights;
- household and office.
Devices linear type used in various conditions. For lighting in landscape design, it is advisable to choose devices with a high degree of protection - IP65, IP67.
They can be either tubular or more powerful, represented by spotlights. IP20 is suitable for rooms with a standard climate.
The review form factor has the greatest number of positive characteristics compared to all the sources described above:
- power supply from 220 V network without ballasts;
- lowest energy consumption of all types presented;
- does not require special disposal methods;
- does not emit heat;
- the dispersion angle reaches 230 degrees;
- no pulsating effect;
- high degree of light transmission up to 120 lm/W;
- service life 50,000-100,000 hours;
- unbreakable body material;
- resistance to temperature changes and other negative factors.
The only drawback of this modification is the high price category. However, it is more likely that future developments will help offset this disadvantage.
On our website there is a series of articles devoted to the choice of LED lamps, we recommend that you read:
- LED lamps for the home: which diode bulbs are better, review of LED lamp manufacturers
- Characteristics of LED lamps: color temperature, power, light and others
- Dimmable LED lamps: tips for choosing, review of the best manufacturers
Rules for choosing energy-saving lamps
Incandescent light bulbs have been in use for so long that when choosing an economical replacement, we focus solely on the power indicator. For greater understanding, many manufacturers indicate directly on the packaging the equivalent power in comparison with the luminous flux of a conventional vacuum lamp.
For clarity, it is worth pointing out that power and light flux are different indicators. The first value is measured in watts, the second in lumens. For example, a 40 W incandescent light bulb emits light of 470-500 lm, 60 W – 700-850 lm, 75 W – 900-1200 lm.
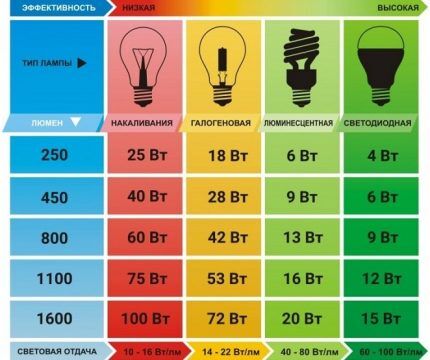
It is the ratio of these two factors - power and light flux - that allows us to judge the economical performance of the device. The total value is measured in lm/W.
Here is another example: standard lighting technology produces 10-15 lumens of light per 1 W of electricity consumed. For halogen - 15-20 lm/W, for fluorescent - 40-80 lm/W and for LED leaders - 60-90 lm/W.
However, this is not the only aspect that requires attention.
It is important to pay attention to the following characteristics:
- Colorful temperature. If you take lamps of identical power, but of different modifications, the color of their radiation may be different. This value is measured in kelvins. Choice color temperature can be done in the range of 2700-6500 K. The lower the value, the warmer (yellow) the light.
- Color rendering index. An indicator of correct color rendering is sunlight – CRI=100. Artificial lighting has not yet reached such parameters. Here you need to start from the optimal CRI = 80 or more.
- Operational life. Manufacturers indicate this value in hours. However, such labeling is not convenient for everyone. Let's imagine it in years: halogen - 2 years, fluorescent - 5 years, LED - up to 12 years.
- Chuck type. Form lamp base selected for a specific lamp model. The standard option, like an incandescent lamp, is E27.
When choosing the shape of the flask, only the aesthetic side plays a role here. However, it is worth considering that a lamp that is too large may not fit into the glass frame of the lamp.

To meet all expectations, it is worth paying attention to manufacturers whose products have already proven themselves positively: Philips, OSRAM, G.E., Ecola. These companies offer a warranty period of 2-3 years for their products.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video material on which light sources are the most economical:
Review and testing of Feron LED lamps:
Despite the fact that incandescent lamps can still be found in markets, energy-efficient analogues will soon completely displace them from the shelves. If you replace all the devices in the lamps with them, in just two years the money spent will be fully recouped. Next comes the complete savings.
Share with readers your experience of using energy-saving lamps. Tell us what lamps you chose and whether you are satisfied with your purchase.Please leave comments on the article, ask questions and participate in discussions. The contact form is located below.




I almost never used halogen lamps, I became more and more accustomed to the classic energy-saving versions of the standard socket - the 27th base of various powers of the white and blue spectrum of light. Fluorescent lamps, thanks to their variety of color spectrum, perfectly complement the interior of the room, emphasizing the unique style.
Despite the fact that LED light bulbs are quite durable, yesterday one of my bulbs burned out. About two years have passed since I installed it in the chandelier. And here's the problem: where to dispose of it? Can it be thrown into a regular trash bin or not? Does it contain dangerous substances? I handed over fluorescent lamps to special collection points, but what about these?
You can safely throw LED lamps in the trash. This is not a luminescent, there is nothing harmful in them. Inside there is only a driver (read electronic control board) and diodes on this very board. And as far as I know, the manufacturer of LED lamps gives a considerable guarantee on them. And they seem to be exchangeable in case of early failure. Naturally, no one here does this, but it’s worth a try.