Metal halide lamps: types, design, pros and cons + selection rules
Despite the development of LED technology, metal halide lamps (MHLs) continue to hold their market niche due to their unique characteristics. Their internal structure can vary greatly depending on the intended application. It is worth familiarizing yourself with the characteristic design types. Do you agree?
We will help you understand the operating principles and features of the MGL device. The article we propose presents design varieties and indicates the scope of application. Those wishing to purchase such a light bulb will find valuable recommendations for choosing from us.
The content of the article:
How do metal halide lamps work?
MGLs have a complex internal structure. Externally, it is a glass cylinder with a base, although some models look like a pear-shaped incandescent lamp.
Inside the shell there is another working capsule made of glass or transparent ceramics, as well as conductive elements and resistors.
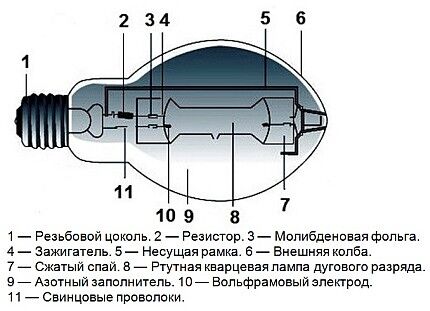
The outer flask is usually filled with nitrogen, and the inner flask is filled with inert gas under pressure, a small amount of mercury and additives of metal halides. This design determines the name of the product.
Sodium or scandium iodide is mainly used as metal halides.They serve to correct the light spectrum and influence the scope of application of metal halide lamps. When switched off, the mercury and additives are in a solid deposited state on the glass walls.
The MGL will not turn on on its own when connected to the electrical network. For this purpose, starting and adjustment devices (ballasts) are used, which provide the necessary starting current and voltage until the effect of thermionic emission appears in the inner flask.
Mechanism of light emission
The inclusion of MGL occurs in stages. First, due to the starting current, which is 10-20 times higher than the operating current, a minimal electrical discharge occurs in the inner flask in an inert gas environment.
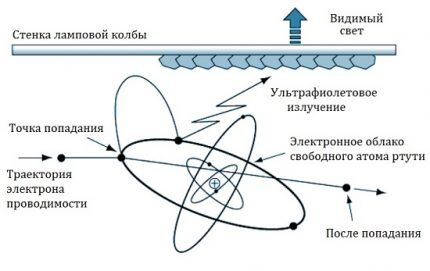
After this, within 3-6 minutes, the mercury and metal halides are heated, which, evaporating, pass into the ionized phase. The current at this time is approximately 2 times higher than the operating current. Ions increase the conductivity of the air mixture and ensure that the lamp gradually reaches its nominal luminosity.
Due to the double-flask device, a consistently high temperature is maintained in the working capsule, which prevents the deposition of metal vapors on the walls. After turning off, the MGL must cool down and metal vapors must settle on the walls of the inner flask. Only after this will it be possible to start the lamp again.
This limitation is a significant disadvantage, so metal halide lamps are not used for domestic purposes, where it is necessary to frequently turn the lighting on/off.The condensation processes in MGL are also affected by gravity, so many models require a clearly defined location in space.
The principle of operation of discharge lamps is not simple, but it allows you to achieve the correct spectrum and powerful luminous flux. In addition, the use of ballasts makes it possible to stabilize the characteristics of the emitted light when power grid parameters fluctuate.
Structural types of MGL
Metal halide lamps are used to illuminate both corridors and rooms, as well as large open industrial areas. Therefore, their power varies from 10 to 2000 W.
Lamps with high electricity consumption are usually connected to a 380 V network and are used only in industrial facilities. The most popular models have a low power of 35-250 W.

There are no uniform international standards for labeling MGLs, but in most cases the letter M stands for “metal halide”, and H informs about the mercury content in the lamp.
Domestic manufacturers can use their own abbreviation: D – arc; I – iodide, P – mercury. After indicating the model, there is usually a designation of the type and diameter of the base.
Metal halide lamps have different designs.
Below are the classification options for these products, depending on their technical parameters:
- By type of orientation: vertical (BUD), horizontal (BH), universal (U).
- By flask size: BT - bulbous-tubular, R - reflective, E or ED - ellipsoidal, ET - ellipsoidal-tubular, T - tubular, PAR - parabolic.
- By color of radiation: white, yellow, purple, green and others.
- By design type: baseless - with flexible down conductors, single-base, double-base.
The external design of a metal halide lamp has little effect on its efficiency, because the direct emitting element is located in a protected inner bulb. It is this that determines the characteristics of the emitted light.
Technical features of lamps
The technical characteristics of MGL are quite varied. They depend on the materials used in production and the electrical parameters of the metal halide lamps. These devices have distinct advantages and disadvantages that you should know about when purchasing.
General operating parameters
Metal halide lamps are not picky about external temperature and continuity of operation. They can burn for weeks at sub-zero temperatures without experiencing overload.

The main parameters that characterize MGL are:
- color rendering index (CRI);
- work resource;
- power;
- light flow;
- type of base;
- Colorful temperature;
- ratio of luminous flux to electrical power;
- working temperature.
The color rendering index is considered an important characteristic of MGL. CRI characterizes the presence of different wavelengths in the emitted spectrum and the uniformity of their intensity.
This indicator is measured as a percentage of similarity to natural daylight. Modern MGLs have a color rendering index of 85-95%, and most household LED devices have a color rendering index of 70-85%.
Some lamps deliberately distort color rendition to give the light the necessary properties. For example, sodium MGLs used for plant growth have a CRI of only 50-60%. The efficiency of the lamp does not decrease because of this, it simply emits most of the energy in a given wavelength range.
To give light a yellow tint, sodium halides are used, green - thallium, and blue - indium. When it comes to performance, metal halide luminaires keep up with LED lamps. This figure for both devices in the mid-price range is 100-120 lm/W.
The color temperature of MGL can range from 2500-20000 °K. When the voltage in the network drops, it changes upward and the light becomes colder. If the value of 240 V is exceeded for a long time, the lamp may simply explode due to overheating of the gas-air mixture in the inner flask.

An important quality of MGL is the stability of the luminous flux throughout the entire period of operation, which is 6-15 thousand hours. If the efficiency of LEDs after 10,000 hours of operation drops by about 50%, then for metal halide lamps it drops by only 2-20%.
The remaining parameters depend on the specific luminaire model and are not specific.
Advantages of metal halide lamps
The modern market for discharge lighting devices is slowly shrinking due to the onset of LED lighting. But the unique properties of MGL will be in demand by consumers for at least several decades.
The main advantages of these lamps are:
- Excellent energy efficiency.For every watt of energy consumed, the lamp produces more than 100 lumens of light.
- High level of color rendering index.
- Refined production technology that minimizes damage to the internal elements of the lamp.
- Wide power range.
- Long service life.
- Resistance to high temperatures due to the absence of electronic components inside the lamp.
Metal halide devices compete primarily with LED and fluorescent lamps. All three technologies are actively developing, so further improvements can be expected from MGL.
Negative aspects of the device
The absence of metal halide lamps in the domestic sphere indicates that they have not only positive, but also negative qualities.

The main disadvantages of MGL are:
- The cost is several times higher than similar LED devices.
- Lack of brightness control.
- Requires cooling for 5-10 minutes before restarting.
- The presence of external ballasts, which require additional space for installation.
- Gradual increase color temperature during long-term use.
- Explosion hazard due to power surges.
- Sensitivity to spatial location.
- Absolutely irreparable.
- The need for special disposal due to the content of toxic substances.
- Time required to reach the calculated luminous flux after switching on.
Thus, they have even more disadvantages than advantages. This narrows the scope of application of MGL to industrial and public buildings and sites where continuous and high-quality lighting is required.
Scope of application of lamps
Using metal halides at home is not only economically irrational, but also dangerous due to the mercury content they contain. The flask may burst and the room will be filled with toxic fumes.
Due to unsafety, the use of metal halide lamps is mainly in demand only for non-residential spaces:
- Filming studios, photo studios.
- Car lights.
- Architectural structures.
- Public buildings, shopping center.
- Industrial workshops.
- Objects under construction.
- Street lighting.
- Sports objects.
- Park areas.
- Greenhouse complexes, greenhouses.
- Night lighting of country houses.
Most people are not faced with purchasing MGLs also because these devices are rarely sold in small hardware stores. They are purchased mainly by enterprises and entrepreneurs from specialized companies.
How to choose a metal halide lamp?
Specificity of areas of application discharge lamps forces you to carefully select their characteristics. The product, of course, can always be exchanged, but it is better to immediately purchase a suitable model.
The main recommendations when purchasing metal halides are as follows:
- Carefully read the labels on the packaging, which may indicate restrictions on the use of MGL in certain circumstances.
- The declared operating position of the product must correspond to the position of the luminaire for which it is intended. Vertically oriented models have the smallest resource.
- The diameter of the base must fit the lamp socket.
- The starter housing must be made of metal with a sufficient number of ventilation holes. Indeed, depending on the model, the ballast consumes 10-20% of the lamp power.
- The starter is designed for a certain voltage and current, so these factors must be taken into account when replacing the lamp.
- In some cases, the rapid ignition of the MGL is critically important, so the time it takes to reach the nominal luminosity must be read in the instructions in advance.
If you purchase a metal halide lamp to replace a broken one, you can take the broken model with you to the store as an example.
MGLs are expensive, so it is important to keep all receipts and invoices when purchasing so that you can later use your warranty rights.
Information will help you compare metal halide devices with halogen light bulbs next articlededicated to the analysis of the characteristics of the G4 model.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Overview of the characteristics of metal halide lamps:
Video #2. Checking the operation of a metal halide spotlight:
Video #3. Connecting a metal halide lamp:
Metal halide luminaires continue to be used in many areas, despite a number of design disadvantages. The diverse spectrum of radiation allows you to select them for various needs of economic activity. Therefore, MGLs will remain competitive in the industrial lighting niche for a long time.
Please write comments in the block below, ask questions, post photos on the topic of the article. Share your own guidelines for choosing a metal halide light bulb. Tell us why you chose this particular device.



