Intermediate relay: how it works, markings and types, nuances of adjustment and connection
Most electrical circuits are designed and used in low-current systems.The main purpose of this kind of circuit is the transformation of incoming signals according to the established algorithm of actions.
For galvanic isolation of circuits of low voltage and higher voltage ratings, an intermediate relay is used. Due to their small size and reliability, these devices are widely used in various fields.
The content of the article:
Purpose and functions of the device
This type of switch is an auxiliary object in the electrical circuit. The versatility of the samples allows them to be used in automated, protective and control circuits.
It is used in cases where there is a need for synchronous closing or opening of several autonomous electrical circuits, in other words, multiplication of current-carrying channels.
The contactor can also be used as a regulator of a more powerful relay, thanks to which a high-voltage circuit is switched.
Let's take, for example, the following situation: there is a need to supply current to the inductor of the switch, where the maximum instantaneous value of the electrical conductive force when turned on is 63 A.However, it is not possible to perform such a task using one electromagnetic device.
Therefore, it is initially necessary to supply power to the core coil of the separating device, which uses its own connections, and turn on a contactor with a higher power, which will be entrusted with the task of switching a higher power of electricity.
The part can also be used to create an artificial delay in the action of a protection relay or, as they say, to form a time delay.
Structural structure of the device
Electromagnetic devices are connected to an electrical circuit that controls or regulates products that are connected to the power unit for conversion. Starting can be carried out under the influence of various factors: power supply, light energy, hydrostatic or gas pressure.
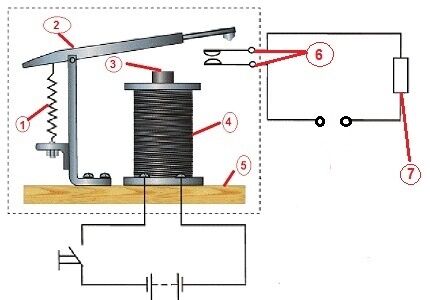
According to the standards, the simplest contact device is coordinated by three main sections: the sensing, intermediate and executive. Each of them is represented by an individual mechanism responsible for certain actions in the switching system.
The primary, so-called sensitive element reacts to the incoming parameter and transforms it into a physical quantity required for the operation of the contactor.
Such a sensing mechanism is embodied in an electromagnetic coil with a core - designated number 4 in the diagram. Depending on the network, either alternating or direct voltage can be connected to it.
The intermediate link begins a comparative analysis of the transformed value with the underlying sample. As soon as the set value is reached, the node transmits the signal from the sensitive mechanism to the actuator. This section consists of counter springs (1) and dampers.

In the production part, by means of switching lines (6) located on the housing above the block, the influence on the slave line is reproduced and the contacts are closed.
Operating principle of the contactor
The operating algorithm of this type of relay involves the use of electrodynamic forces created in a ferromagnet during the passage of electricity through the spiral of turns of the insulated wire of the coil.

The initial location of the L-shaped plate (anchor) is fixed by a spring. By supplying current to the magnet, the armature, with the commutating contact located on it, overcomes the spring forces and is drawn towards the magnetized field.
When moving, the shank located on the contact plane catches the lower contact circuit, moving it down. If the supply of electricity to the coil stops, the spring pulls the yoke back and the device returns to its original form.
Let's look at an example of how an electromagnetic-type relay works in a car.
If it is connected to a three-phase asynchronous motor, the following actions will be reproduced:
- Start – activation of the alarm.
- Starter activation.
- The closing of the last pair of contacts results in the start of the engine mechanism.
In addition, it is the relay that is responsible for turning off the engine when the reverse breaks. This eliminates the problem of sudden engine stops.

It is also important to know that an electromagnetic relay can be equipped with several groups of control contacts. The number of the latter depends entirely on the purpose of the specific device model.
Types of intermediate switches
Intermediate type contactors relieve the load on the main actuators. Otherwise, arc extinguishing conditions will become more stringent, which will make production, for example, of such powerful sources as thermal power plants unprofitable.
Inclusion methods used
The classification of electromagnetic switches is carried out according to the main features and characteristics, namely:
- according to the method of inclusion;
- design features - number and type of windings, as well as the number, condition and power of contact lines;
- operating principle;
- according to the time of operation and return to the initial position.
Based on their purpose, contactors are manufactured with voltage or current windings, or two types at the same time. There are two unified methods for connecting them.

The first type of connection is serial. The device is connected in series in sections of the windings of other devices and operates from the current flowing along the contour of this circuit.
The next one is shunt. It is switched on at the nominal voltage of the operating current source.
Device design features
Features of the device suggest samples with one turn of the voltage or current winding (RP-23, RP-252), two (RP-11) and, rarely, three.
DC relays (RP-23) are manufactured for the following rated voltage values: 12, 24, 48, 110 and 220 V, alternating current (RP-24) - 127, 220 and 380 V.

Switches of types RP-23 and RP-24 are designed to operate on galvanic current and have 5 contact lines each, which can be used in different combinations. The differences between them are in their structure.
The second type of device is equipped with a built-in mechanical trip indicator. Their power consumption at base voltage is 6 W. The RP-25 and RP-26 series operate exclusively on alternating current and are designed in the same way as previous devices.
An additional element is a short-circuited turn on a core with a coil, designed to eliminate vibrations of the moving part of the mechanism. Their energy consumption is the same - 10 W.
Recently, CJSC CHEAZ (plant for the production of electrical devices in Cheboksary), instead of the above modifications, has been reorienting to modernized models. These are switches RP16-1 (galvanic current) and RP16-7 (alternating current), equipped with two breaking and four closing contact groups.

Two- and three-winding peripherals are typically used in several applications.
Let's consider what problems they solve and what type of device is required for this:
- If there is a need to activate the mode of operation on current and hold on voltage, for example, the RP-232 series with a single-turn operating winding.
- If it is necessary to operate the device from voltage and abstain from electricity, use RP-233 for two holding current turns.
In the same way, instead of the contactors described above, ChEAZ is introducing new models RP-16-2 - RP16-4 and RP17-1 - RP17-5.
Operating principle of switches
Contact devices are used in the communications and automation segment. Based on the principle of operation, they are divided into neutral and polarized (pulse) types.
The main difference between them is that in the first, the armature displacement is not subject to the polarity of the control signal, in the second, on the contrary, it has a direct dependence on the direction of movement of charged particles in the winding.
Neutral switches have the simplest device, consisting of two systems: contact and magnetic. The contact group has two fixed and one generalized movable contact. The magnetic assembly consists of an armature, an electromagnet and a yoke.
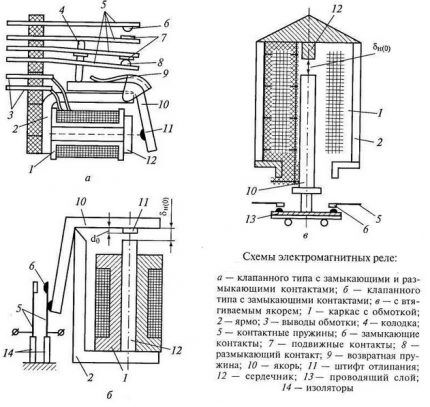
Additionally electromagnetic relays are divided according to the nature of the movement of the anchor: angular (float) and retractable. To reduce the resistive forces of the magnetic air channel between the movable plate and the core. The latter is equipped with a pole piece.
Such relay electrical circuits are used in control systems of industrial machines and machines. RES-6 is one of the representatives of low-current contactors of the neutral class. The device can be two-position or single-stable. Its rated operating voltage is 80-300 V, switching current is 0.1-3 A-V.
The impulse category is made up of the same systems. However, the magnetic section impulse relays additionally equipped with two rods with a winding, as well as a contact rod and a permanent magnet that creates a polarizing flux.
Thanks to this type of supply, the direction of the electromagnetic force acting on the armature changes based on the direction of the power flow in the coil.

IMSh1-0.3 contactors are widely used as a track relay mechanism in pulse protective (RP) galvanic current circuits. IMVSH-110 is used in alternating current circuits. Technically, it consists of a diode bridge that converts variable forces into a constant value.
Operation and return time
The actuation time of the intermediate mechanism (attraction t) is the period from the moment the operation command is received until the output parameters begin to increase. This value is completely dependent on the design features of the relay, its connection diagram and input signal.
Shutdown time (t release) – the interval from the signal to turn off until the output parameter reaches its minimum value.
The type of relay under consideration is subject to increased performance requirements.
Depending on the response time interval, devices are classified as follows:
- fast-acting – deceleration time for attraction and disconnection up to 0.03 s (for example, REP37-13, RP 17-4M);
- normal – 0.15–0.20 s (RE series);
- slow – 1.0-1.5 s (НММ4–250, НММ4–500);
- temporary – more than 1.5 s (RP18-2-RP18-5).
Such modifications are presented on the market by various manufacturers. Therefore, depending on the brand, the design of the relay may differ slightly. However, using the markings on the device, you can accurately determine the parameters of the product.
What does the marking tell you?
The marking of contactors contains a complete set of data on the purpose and design features, including information on climatic design.
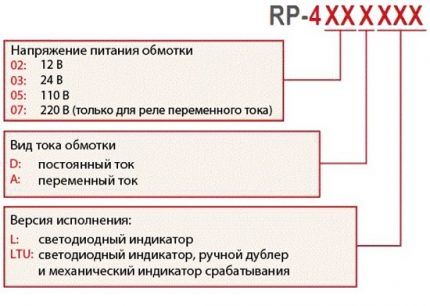
Let us consider in detail the structure of the symbol using the example of PE41(N) (*)(*)(*)(*)(*)/(*)(*)(*)(*)5:
- REP - electromagnetic intermediate relay.
- 37 (N) – development number.
- (*) - designation of the type of current in the circuit of the switching winding: 1 - direct current; 2 - alternating current.
- (*) — type of deceleration: 1 — decelerated when turned on; 2 - slow when turned off.
- (*) - value based on the number of windings;
- (*)(*) — numerical value of the normally open and closed contacts;
- (*)(*) - voltage or current of power winding: constant (D) and alternating (A);
- (*)(*) - designation of the electrical force of the holding windings;
- (*) - type and technology of connecting rear conductor lines: 1 – with lamellas for soldering; 2 – installation with screw fixation; 3 — fastening with terminals to the connector block.
- (*)5 - climatic design and placement category according to GOST: UH - moderately cold; B - all-climate.
When choosing the required model of a switching device, not only its electrical parameters are taken into account, but also the environment in which it will operate.
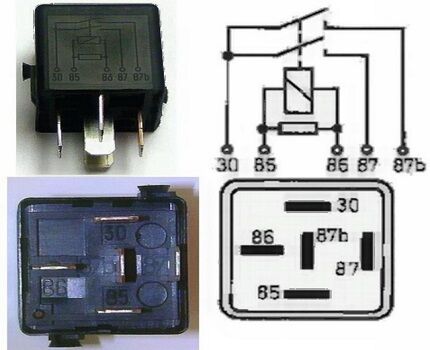
Despite the high quality of the switch, the main drawback lies in the contact system. It is assumed that a pure connected group can only exist under sealed vacuum conditions. If the main negative factor is exposed - contact with air - an oxide film begins to form on them.
Connection and adjustment nuances
After installing the intermediate mechanism, it must be connected to electrical circuit. For this, coil contacts will be used, as well as additional connecting elements. Typically, the device has several contact pairs: NO - normally open and normally closed (NC).
In the first position, it is assumed that the signal to the coil is completely deprived. Since there is no polarity, the internal connection of the contact group can be performed in a chaotic manner.
To connect the review mechanism, consider the schematic instructions. The expected voltage in the coil can be: 12, 24 or 220 V.
We will analyze the regulation of the electronic starter using the example of the most common model RP-23.
The process consists of the following steps:
- By checking the start and return voltage with the supply of a galvanic current source to the coil, we carry out gentle regulation.
- At the moment of attracting the armature, the moving unit of the system should have a joint stroke of 0.1-1.5 mm. We carry out the correction procedure by bending the shank onto an L-shaped plate.
- Between the active and inactive contacts, the gap level is set within the range of 1.5-2.5 mm. The deflection is adjusted by pressing the square of the fixed contacts and the upper stop of the moving system.
- At the final position of the armature (closure), the dip of the inactive contacts will be 0.3-0.4 mm.
- In the middle of the plane, the moving and fixed contacts must coincide. The adjustment is made by moving the plate and guide bracket.
The same method is used to reproduce the settings of the RP-25 relay, however, the gap between the coil with the core and the armature in the attracted state is eliminated.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The operating principle of electromagnetic relays, where they are used, and the main indicators of the reliability of devices are also considered. More details in the video:
Having selected the required device model, we proceed to its connection and configuration. The main nuances are described in the presented plot:
Technological developments in intermediate relay designs have always been aimed at reducing weight and dimensions, as well as increasing the degree of reliability and ease of installation of devices. As a result, small contactors began to be placed in a sealed casing filled with compressed oxygen or with the addition of helium.
Due to this, the internal elements have a longer service life, uninterruptedly executing all assigned commands.
Tell us about how you chose an intermediate disconnecting device for your home electrical network. Share your own selection criteria. Please write comments in the block below, post photos related to the topic of the article, and ask questions.



