Pulse relay for lighting control: how it works, types, markings and connections
To meet modern lighting requirements for apartments, offices and enterprises, complex electrification systems are used. When designing them, a number of equipment is used to solve individual problems, which is constantly being improved.
Thus, a pulse relay for controlling lighting from several places began to be used relatively recently. It is gradually replacing standard circuits with pass-through switches.
The content of the article:
Where can a pulse relay be used?
The introduction of this device into household use is explained by simple convenience. After all, it allows you to control lighting from at least two points.
In an apartment, this could be a bedroom, where the switch is on at the entrance and the switch off is next to the bed. In offices there are long corridors, flights of stairs and large conference rooms.

The task of three-position control can be handled by pass-through and cross switches. This scheme is still widely used. But it also has obvious shortcomings.
Firstly, this is a rather complex system to install, in which electricity passes through the main circuit breaker, the distribution box, the switches themselves and then to the lighting lamps.When installing it, errors often occur. If more than three control places are needed, the scheme becomes more complicated.
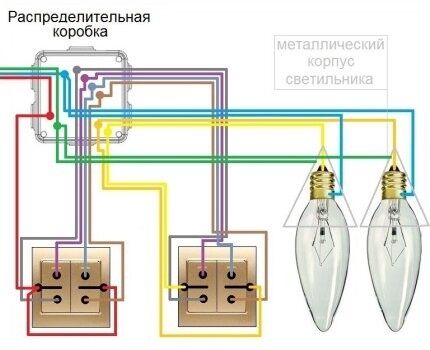
Secondly, all wires have the same cross-section, since they use the same voltage, which affects the overall costs. They also include the price of pass-through switches, several times higher than the cost of conventional ones.
But the need to use a pulse relay is not only for reasons of comfort. It is also used for signaling and protection.
For example, at an industrial enterprise to start production processes that require high electrical power, this device allows you to protect the operator. Since it operates from low voltage currents or is completely controlled remotely.
Device and principle of operation
In the general sense of the word, a relay is an electrical mechanism that closes or breaks an electrical circuit based on certain electrical or other parameters that affect it.
Its non-switching design was invented back in 1831 by J. Henry. And two years later they began to use S. Morse to ensure the functioning of the telegraph.
Two main groups can be distinguished: electromechanical and electronic. In the first type of device, the work is carried out by a mechanism, and in the second, a printed circuit board with a microcontroller is responsible for everything. It is convenient to consider its operation using the example of an electromechanical relay, which is a pulse relay.
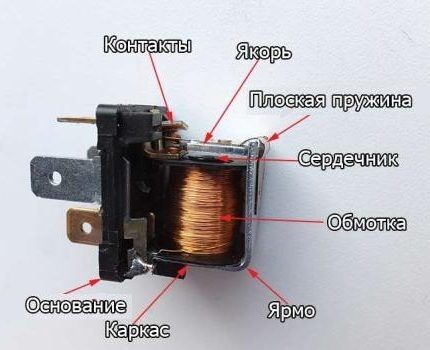
Structurally, it can be represented as follows:
- Coil - This is a copper wire wound on a base made of non-magnetic material. It can be insulated with fabric or coated with varnish that does not allow electricity to pass through.
- Core, containing iron and activated by the passage of electric current through the turns of the coil.
- Movable anchor - this is a plate that is attached to the armature and affects the closing contacts.
- Contact system – directly switch the state of the circuit.
The operation of a relay is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic force. It appears in the ferromagnetic core of the coil when current is passed through it. The coil in this case is a retractor device.
The core in it is connected to a movable armature, which activates the power contacts, carrying out switching. They can be of normally open/normally closed type. Sometimes a contact block may contain both open and closed types of connection.
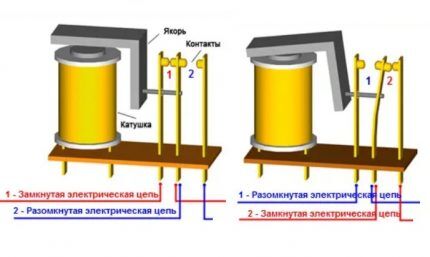
An additional resistor can be connected to the coil, which increases the accuracy of operation, as well as a semiconductor diode, which limits the overvoltage on the winding. In addition, the design may contain a capacitor installed parallel to the contacts to reduce sparking.
The operation of the device can be more clearly represented by dividing it into several blocks:
- performing – this is a contact group that closes/opens an electrical circuit;
- intermediate – the coil, core and moving armature activate the executing unit;
- manager – in this relay converts an electrical signal into a magnetic field.
Since a single electrical impulse is required to switch the position of the contacts, we can conclude that these devices consume voltage only at the moment of switching. This significantly saves energy, unlike conventional pass-through switches.
The second type of pulse relay is the electronic type. The microcontroller is responsible for its operation. The intermediate block here is a coil or semiconductor switch. The use of elements such as programmable logic controllers in the circuit makes it possible to supplement the relay, for example, with a timer.
Types, labeling and benefits
The main types of pulse relays are electromechanical and electronic. Electromechanical ones, in turn, are classified according to their operating principle.
Types of pulse devices
This means that switching of power contacts can be carried out by forces other than the force of the magnet.
They are divided into:
- electromagnetic;
- induction;
- magnetoelectric;
- electrodynamic.
Electromagnetic devices in automation systems are used more often than others. They are quite reliable due to a simple method of operation based on the action of electromagnetic forces in a ferromagnetic core, provided that there is current in the coil.
Impact on contacts electromagnetic relays is carried out by a frame, which is attracted by the core in one position, and returned to the second by a spring.

Induction ones have a principle of operation based on the contact of alternating currents with induced magnetic fluxes with the fluxes themselves. This interaction creates a torque that moves a copper disk located between two electromagnets. Rotating, it closes and opens contacts.
The operation of magnetoelectric devices is carried out due to the interaction of the current in the rotating frame with the magnetic field created by a permanent magnet. The closing/breaking of contacts is controlled by its rotation.
These relays are very sensitive relative to their type. However, they are not widely used due to the response time of 0.1-0.2 s, which is considered long.
Electrodynamic relays operate due to the force generated between moving and fixed current coils. The method of closing contacts is the same as in a magnetoelectric device. The only difference is that induction in the working gap is created electromagnetically.
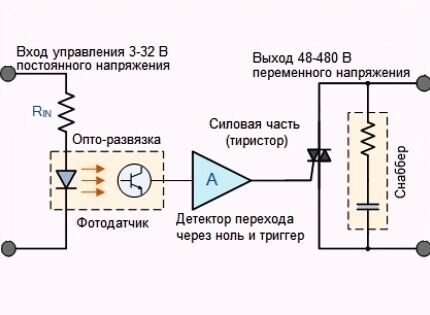
Electronic models are almost identical in design to electromechanical ones. They have the same blocks: executing, intermediate and control. The only difference is the latter. Switching is controlled by a semiconductor diode as part of a microcontroller on a printed circuit board.

This type of relay is equipped with additional modules.For example, a timer allows you to run a lighting control program after a specified period of time. This is convenient for saving energy when there is no need to operate the equipment. If necessary, you can turn off the light by pressing the button twice.
Advantages and disadvantages of the main types of relays
Unlike semiconductor switches, electromechanical switches have the following advantages:
- Relatively low cost due to inexpensive components.
- A small amount of heat is generated at the switched contacts due to the low voltage drop.
- The presence of powerful insulation of 5 kV between the coil and the contact group.
- Not subject to the harmful effects of overvoltage pulses, interference from lightning, or switching processes of powerful electrical installations.
- Control of lines with a load of up to 0.4 kV with a small device volume.
When a circuit is closed with a current of 10 A in a small volume relay, less than 0.5 W is distributed across the coil. While on electronic analogues this figure can be more than 15 W. Thanks to this, there is no problem of cooling and harm to the atmosphere.
Their disadvantages include:
- Wear and problems when switching inductive loads and high voltages with direct current.
- Turning the circuit on and off is accompanied by the generation of radio interference. This requires installing shielding or increasing the distance to the equipment subject to interference.
- Relatively long response time.
Another disadvantage is the presence of continuous mechanical and electrical wear during switching. These include oxidation of contacts and their damage from spark discharges, deformation of spring blocks.

Unlike electromechanical relays, electronic relays control the intermediate unit via a microcontroller.
The advantages and disadvantages of electronics can be analyzed using the example of devices from the F&F company relative to the ABB brand, which produces mechanics.
The advantages of the first type of switches include:
- greater security;
- high switching speed;
- availability on the market;
- indicator alerts about the operating mode;
- advanced functionality;
- silent operation.
In addition, the indisputable advantage lies in several installation options - it is possible to install not only on the DIN rail of the panel, but also in socket box.
Disadvantages of F&F electronics compared to ABB mechanics:
- disruption of work due to power failures;
- overheating when switching high currents;
- “glitches” are possible for no apparent reason;
- switching off the device during a short-term power outage;
- high resistance in closed position;
- some relays only operate on DC current;
- The semiconductor circuit does not immediately allow current to flow back to its normal direction.
Despite these shortcomings, electronic switches are constantly evolving and, due to the greater potential of functionality relative to electromechanical ones, their predominant use is expected.
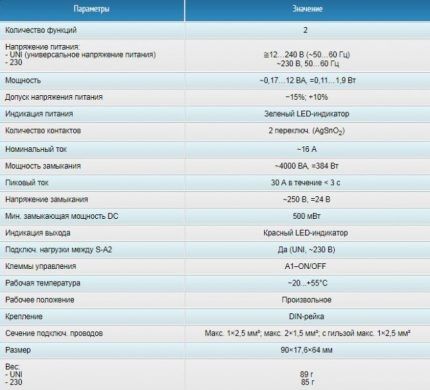
Main characterizing parameters
Depending on the purpose and area of application, relays can be classified according to several criteria:
- return factor – the ratio of the value of the armature output current to the retraction current;
- output current – its maximum value in the coil clamps when the armature exits;
- pull-in current – its minimum indicator in the coil clamps when the armature returns to its original position;
- setpoint – the level of the response value within the specified limits set in the relay;
- actuation value – the value of the input signal to which the device automatically responds;
- nominal valuesi – voltage, current and other quantities underlying the operation of the relay.
Electromagnetic devices can also be divided by response time. The longest delay for a time relay is more than 1 second, with the ability to configure this parameter. Then there are slow ones - 0.15 seconds, normal ones - 0.05 seconds, fast ones - 0.05 seconds. And the fastest inertia-free ones are less than 0.001 seconds.
Decoding product labeling
The contactor marking code can often be found in store catalogs and on the device itself. It gives a complete description of the design features, purpose and conditions of their use.
The composition of the designation can be seen on the electromagnetic intermediate relay REP-26. It is used in AC circuits up to 380 V and DC up to 220 V.
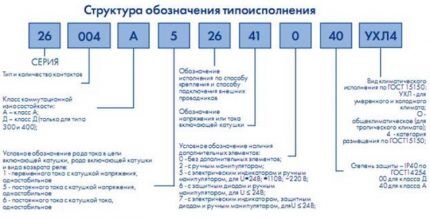
The product designation in the store may look like this: REP 26-004A526042-40UHL4.
REP 26 – ХХХ Х Х ХХ ХХ Х – 40ХХХ4. This type of notation can be parsed as follows:
- 26 – series number;
- XXX – type of contacts and their number;
- X – wear resistance class of switching;
- X – type of switching coil, type of relay return and type of current;
- XX – design according to the method of installation and connection of conductors;
- ХХ – coil current or voltage value;
- X – additional structural elements;
- 40 – protection level according to IP standard or GOST 14254;
- ХХХ4 – climatic zone of application in accordance with GOST 15150.
Climatic design can be: UHL - for cold and temperate climates or O - for tropical or general climate design.
According to special designation tables, the device in question is electromagnetic intermediate relay, with four switching contacts, switching resistance class A, using direct current. It has a socket mount with lamellas for soldering external conductors, a 24 V coil and a manual manipulator.
Several types of connection diagrams
There are several installation options, each of which has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
The designation of the RIO-1 relay contacts has the following meaning:
- N – neutral wire;
- Y1 – enable input;
- Y2 – shutdown input;
- Y – on/off input;
- 11-14 – switching contacts of the normally open type.
These designations are used on most relay models, but before connecting to the circuit you should additionally familiarize yourself with them in the product data sheet.
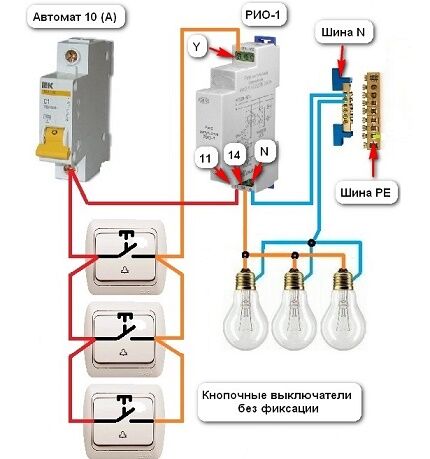
In this circuit, the power relay contacts use a current of 16 A. Protection of control circuits and lighting systems carried out by a 10 A circuit breaker.Therefore, the wires have a diameter of at least 1.5 mm2.
The connection of push-button switches is made in parallel. The red wire is the phase, it goes through all three push-button switches to power contact 11. The orange wire is the switching phase, it comes to input Y. Then it leaves terminal 14 and goes to the light bulbs. The neutral wire from the bus is connected to terminal N and to the lamps.
If the light was initially turned on, then when you press any switch the light will go out - a short-term switching of the phase wire to the Y terminal will occur and contacts 11-14 will open. The same thing will happen the next time you press any other switch. But pins 11-14 will change position and the light will turn on.
The advantage of the above circuit over pass-through and crossover switches is obvious. However, with a short circuit, detecting the damage will cause some difficulties, unlike the next option.
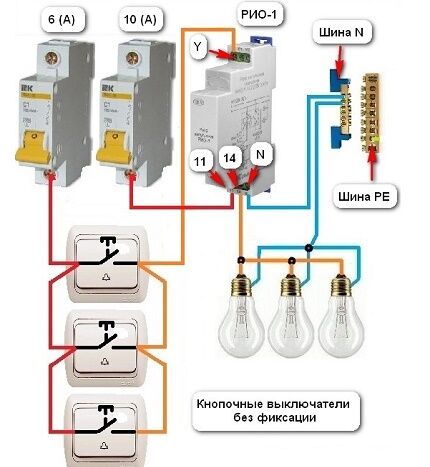
This is a less common connection option. It is the same as the previous one, but the control and lighting circuits have their own circuit breakers for 6 and 10 A, respectively. This makes it easier to identify faults.
If there is a need to control several lighting groups with a separate relay, then the circuit is slightly modified.
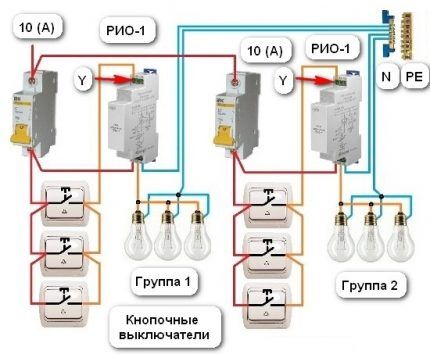
Another option for using impulse relays is a centrally controlled system.
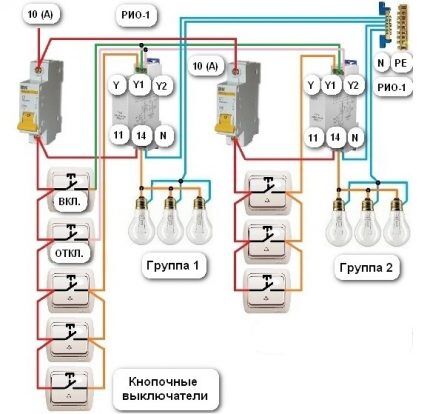
Two switches are added to this circuit to make and break the circuit. The first button can only turn on the lighting group. In this case, the phase from the “ON” switch will come to the Y1 terminals of each relay and contacts 11-14 will close.
The trip switch operates similarly to the first switch. But switching is carried out on the Y2 terminals of each switch and its contacts occupy the circuit-breaking position.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video material tells about the device, operation, application and history of the creation of this type of device:
The following story describes in detail the operating principle of solid-state or electronic relays:
The use of pulse relays is increasingly used in modern electrification systems. Increasing demands for functionality and flexibility in lighting control, material savings and safety create a continuous impetus for the improvement of contactors.
They are reduced in size, simplified in design, increasing reliability. And the use of fundamentally new technologies at the heart of the work allows them to be used in harsh conditions of dusty industries, vibration, magnetic fields and humidity.
Please write comments in the block below. Ask questions, share useful information on the topic of the article that will be useful to site visitors. Tell us about how you selected and installed the impulse switch.



