Do-it-yourself geothermal heat pump for heating a house: device, design, self-assembly
You can organize heating and hot water supply for a private home in different ways, for example, by connecting to the central gas supply communications or switching heating systems to electricity consumption. Do you agree?
Or you can assemble a geothermal heat pump with your own hands and effectively use the heat of the earth to create comfortable living conditions. Of course, this is a rather labor-intensive process, but for those who are at least a little versed in technology, it will not be difficult.
In our article we will talk about the principles of operation and types of geothermal installations. We will tell you how to build a heat pump yourself from scrap materials. In addition, in the article you will find expert advice on choosing geoaggregates. And the posted videos will reveal the secrets of installation and operating principles of geothermal pumps.
The content of the article:
How does a geothermal unit work?
The operating algorithm of a geothermal heat pump is based on the transfer of heat from a source with a low thermal energy potential to the coolant. The earth here plays the role of a radiator in the summer and is an active source of heat in the winter season.
The difference in ground temperatures helps improve the overall efficiency of the system and helps reduce actual operating costs.

In practice, the current coolant enters a pipeline located in the ground and is heated there by several degrees. Then the composition goes into a heat exchange unit (or evaporator) and transfers the accumulated thermal energy to the internal system circuit.

The refrigerant operating in the external circuit is heated in the evaporator, converted into gas and sent to the compressor. There it contracts under the influence of high pressure and becomes even hotter.
The hot gas passes into the condensation device and transfers thermal energy to the working coolant of the internal system responsible for heating the house. At the end of the process, the refrigerant, having lost its heat, returns to its starting point in a liquid state.
What are the types of geothermal installations?
Geothermal heat pumps differ from each other in the type of coolant on the internal and external contours of the structure. The energy of the device is obtained from soil, water (groundwater or an open natural reservoir) or air.
Inside the residential premises, the thermal resource is used for heating rooms, heating water and air conditioning.Depending on the combination of elements and functions used, systems are classified into types: “land-water”, “water-water” and “air-water”.
Option 1. Assembly using earth-water technology
An earth-to-water pump is one of the most effective alternative heating options for residential premises. The principle of its operation comes down to the selection of thermal energy from the ground using probes or collectors and its transfer to the home water heating system.

A special installation helps to implement the technology, consisting of a geothermal heat exchanger located below the depth of actual soil freezing, and directly a heat pump that functions like a refrigerator, only in reverse (reverse Carnot cycle).
How the device works
The “ground-water” installation, which heats residential premises using renewable heat produced by the soil, operates according to the following algorithm:
- The working fluid (brine or antifreeze), moving along the geothermal circuit, takes the temperature of the soil and is transferred through a pump to a heat exchanger - evaporator. There it gives off the collected heat to freon, and itself, having become 2-5°C colder, returns to its starting point.
- Freon enriched with thermal energy evaporates and, having assumed a gaseous state, enters the compressor unit. There, the gas temperature rises due to compression and condensation forms.
- Thermal energy is transferred to the coolant in the home heating system, and the freon again takes on liquid form. Its pressure drops after passing through the expansion valve of the system and the refrigerant returns back to the evaporator to gain another portion of the resource.
As a result of this procedure, the volume of thermal energy taken from the soil and transferred to the heating system of a residential building is more than 4 times greater than the amount of electricity spent to ensure the correct operation of the compressor unit, circulation pump and control unit.

An additional bonus is that the system has the ability to work in the opposite direction, that is, for cooling. True, the loss of efficiency reaches 20%, but this is considered justified, given the high heating capacity of the equipment.
Options for placing ground-water systems
To create the external contour of the earth-water system, high-strength polymer pipes with good performance characteristics are used. They are placed horizontally, laid on the bottom of the pit in a manner reminiscent of the arrangement of communications for “warm floor” complexes.

When installing, an area of 25-50 square meters is used. m for each individual kilowatt of installed pump power. The depth of the pit is chosen below the freezing line, and the exact dimensions and pitch of pipe laying are determined by additional calculations.

The territories where communications of geotremal earth-water systems are arranged are no longer used for agricultural needs. They can be used to create a beautiful grass lawn or a flower bed with flowering annuals.
Vertical installation is much more problematic and entails the use of professional equipment. At the site, using a drilling rig, a well is drilled to a depth of 20 to 150 m, a special geothermal probe is lowered into it and connected to a pump that supplies working fluid to the home heating system.

Sounding pipes extending from drilled wells enter the collection well. From it to the heat pump there are 2 main lines (resource supply and return), equipped with an insulating coating. The diameter of the line depends on the total volume of the system and the room that needs to be heated. Sometimes the parameters reach 160 mm.
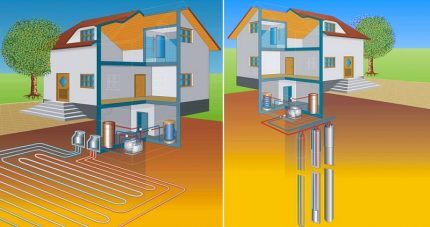
Due to the fact that at depth the soil temperature is always higher and more stable due to the influence of the earth's core, the vertical method of laying the heating system is recognized as the most effective. It demonstrates a high level of efficiency and operates reliably for many years without failures or breakdowns.
Option #2. Features of water-to-water heat pumps
A water-to-water geothermal system uses the thermal energy of a water resource in its operation. This is possible because at great depths the temperature of the water, as well as the soil, remains quite high and maintains stable constant values all year round.

There is no fundamental structural difference between the ground-to-water and water-to-water heat pumps. But the least financial and labor costs are required for a complex built on an open reservoir.Large-scale drilling activities are not required for installation.
The pipe material with the coolant is simply equipped with a weight, immersed in water and connected to the home heating system through connecting lines.
However, this option is only possible if the land plot is closely adjacent to the water and all communication parts of the system are under the control of the owners. If there is no access to open water, groundwater potential is used.
True, this entails serious excavation work and the construction of complex structures, for example, an additional well designed to discharge water passing through the heat exchange unit.

Usually water-to-water installations installed where it is not possible to connect central communications or use other types of coolants.
Experts say that alternative heating of this type is extremely effective in modern buildings that have minimal heat loss.

If the house is well insulated, protected from drafts, dampness and penetration of frosty air, or built using modern thermal insulation technologies, the cost of the heating system is significantly reduced due to the opportunity to purchase pumping equipment of much lower power.
Option #3. Arrangement of air-water systems
The air-to-water heat pump uses the most accessible, unlimited and renewable natural energy resource - air. The equipment operates through fans and evaporators combined into a single complex.
It is most effective at temperatures down to -15°C. With more aggressive performance, it loses a significant part of the power.

The unit is extremely convenient in that it does not require the owners of a private home to have special equipment for installation and complex installation work.
Does not require excavation of land, drilling of wells and other labor-intensive activities. Easy to install and does not take up much space. It can function correctly when placed on the roof of a living space.

The main advantages of the equipment include almost silent operation and the possibility of reusing heat released from the heated room in the form of exhaust air, water, gas, smoke, etc.
The owners carry out maintenance of the system themselves:
- clean fan blades and protective grilles on the evaporation unit from dust, small debris and leaves;
- lubricate the compressor special composition specified in the manufacturer’s instructions;
- change the oil in power units (fan, compressor) with a certain frequency;
- check the integrity of the power cable power supply and copper piping through which the refrigerant circulates through the system.
In addition to these actions, manufacturers of pumping equipment strongly advise customers to monitor the condition of thermal sensors that reflect the operation of the control unit.
They must be wiped, carefully removing dust and oil stains from the surface. This will extend the "life" fromair-to-air systems and will make the operating process simpler and more comfortable.
How to make a unit with your own hands?
Regardless of which resource option (earth, water or air) is chosen for heating, a pump will be needed for the system to function correctly.
This device consists of the following elements:
- compressor unit (intermediate element of the complex);
- evaporator, transferring low-potential energy to the coolant;
- throttle valve, through which the refrigerant finds its way back to the evaporator;
- capacitor, where freon releases thermal energy and is cooled to its original temperature.
You can purchase a complete system from the manufacturer, but this will cost a decent amount.When there is no free money at hand, it is worth making a heat pump with your own hands from the parts at your disposal and, if necessary, purchasing the missing spare parts.

When the decision to make your own heat pump is made, you must definitely check the condition of the electrical wiring and electric meter in the house.
If these elements are worn out and old, it is necessary to inspect all areas, identify possible faults and eliminate them before starting work. Then the system will work flawlessly immediately after startup and will not bother the owners with short circuits, fires in wiring, or knocked out plugs.
Method #1. Assembly from the refrigerator
To assemble the heat pump with your own hands, remove the coil located at the back from the old refrigerator. This part is used as a capacitor and is placed in a highly durable container that is resistant to aggressive temperatures. A properly working compressor is attached to it, and a simple plastic barrel is used as an evaporator.

The prepared elements are connected to each other, and then the created unit is connected to the heating system through polymer pipes and the operation of the equipment begins.
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a heat pump from a refrigerator are described in this article.
Method #2. Heat pump from air conditioner
In order to make a heat pump, the air conditioner is modified and some main components are redesigned. First, the outdoor and indoor units are swapped.
The evaporator, which is responsible for transferring low-grade heat, is not additionally installed, since it is located in the internal block of the unit, and the condenser transmitting thermal energy is located in the external block. Both air and water are suitable as coolants.
If this installation option is not convenient, the condenser is installed in a separate tank designed for correct heat exchange between the heating resource and the coolant.
The system itself is equipped with a four-way valve. For this work, a specialist with professional skills and experience in conducting events of this kind is usually invited.

In the third option, the air conditioner is completely disassembled into its component parts, and then a pump is assembled from them according to the traditional generally accepted scheme: evaporator, compressor, condenser. The finished device is connected to the equipment heating the house and started to be used.
The site has a series of articles on making heat pumps with your own hands, we recommend that you read:
- How to make a heat pump for heating a house with your own hands: operating principle and assembly diagrams
- How to make an air-to-water heat pump: device diagrams and self-assembly
Tips for choosing a system
Installation of ground-to-water equipment is more expensive than all other options, because it requires deep excavation when the equipment is located vertically or a large free area when laying communications horizontally.
These parameters limit the use of the system and significantly reduce its attractiveness.
Installing a water-to-water pump also has some limitations. If there is an accessible body of water nearby, you can place the system in it. The lack of open water will entail drilling wells and drainage wells, which is also not cheap.
An air-to-water pump does not pose any installation problems, and can operate correctly even in apartment buildings, but in severe winters with low temperatures, its efficiency decreases and a parallel energy source is required to support it.
However, arrangement of geothermal heating As a result, it pays off its costs and begins to produce a free resource, allowing owners to live in the most convenient, pleasant and comfortable conditions, without spending a lot of money on utilities.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video clearly shows how a heating system based on air-to-water geothermal heating equipment is installed in a large house made of a gas silicate block. Some interesting nuances regarding the installation of equipment are revealed and real figures for utility bills for the month are announced.
How land-water equipment works.A detailed description from a specialist in the installation of geothermal thermal boilers, recommendations and useful tips for home craftsmen from a professional in his field.
A real user of the equipment shares his impressions of the geothermal heat pump.
A professional mechanic tells how to make a heat pump at home using a powerful compressor and tubular heat exchange parts. Detailed instructions in step-by-step mode.
A geothermal pump for heating a private household is a successful way to create comfortable living conditions even where centralized communication systems and more conventional sources of energy resources are not available.
The choice of system depends on the territorial location of the property and the financial capabilities of the owners.
Do you have experience making a geothermal heat pump? Please share information with our readers and suggest your assembly option. You can leave comments and attach photos of your homemade products in the form below.




Our people are not yet ready for geothermal thermal energy source. It seems to me that all sorts of installations associated with similar methods of generating energy are being used in Europe, where people have long learned to save money. But we are far from this. Such technologies, unfortunately, are too labor-intensive; it is much easier to connect to a gas pipeline. And even more so try to do it yourself. No, this is not for us yet. At least learn how to use solar panels.
But I disagree with the previous comment.What does it mean: “our people are not ready for such an energy source”? If no one tries to use it, then we will never be ready for anything. These things don't happen by themselves. Personally, I am going to set up a water-air system and I am confident of success. I have a good understanding of the topic and am not afraid to try something new.
I fundamentally disagree with the first comment. Alexander, apparently, does not think that in Russia beyond the Urals it will be problematic to connect to a gas pipeline, because all gas pipelines lead to that same Europe, where they have long learned to save money. Considering the annual rise in prices for coal and firewood, it’s time to seriously think about installing a heat pump.
Alexey, in Europe we also learned because governments there actively support energy-saving technologies. For example, interest-free loans for the purchase of such equipment. Well, propaganda is ubiquitous, in the positive sense of the word.
There is no need to point fingers at Europe. How much does gas cost there? How much does it cost there? energy? How much does coal cost there? And one more thing... what is their monthly income in rubles? This is where everything stems from.
Here is an example of the city of Uglich. The cost of a kW of thermal energy: birch firewood - 2.28 rubles, natural gas - 0.63 rubles, liquefied gas - 2.02 rubles, grade D coal - 1.11 rubles, light pellets - 1.72 rubles. geothermal heat pump (when delivering 1 kW of electric energy - 4.5 kW of heat) - 1.51 rubles. And taking into account the cost of work and the heat pump... the costs will not be recouped even after 10 years. And a 15-year guarantee is not needed... think for yourself, will these companies (supplier or contractor) still exist in 5-10-15 years? In our economy, this guarantee is more like zilch.
My point is that you can give guarantees for 100 years :) There is only one conclusion. Bring natural gas to your home. Well, while you wait (sometimes this process is not quick), then install an automatic coal boiler.
Please tell me, is it possible to install a horizontal heat pump circuit directly under the house? If not, why not?
Thank you.
Seryozha, it’s not worth it, in the case of a slab foundation, you will freeze your own house, refer to the SNP for calculating heat loss through the floor, look at the zones, and then again delve into the principle of transferring thermal energy from the heat pump. Give it back where you got it...it's like that