Characteristics of 25 mm polypropylene pipe - application, how to install
Of the variety of polymer pipes for water, products made from polypropylene are especially in demand.The material is easy to process, easy to cut and solder. From the range of sizes 16-60 mm, a 25 mm polypropylene pipe is most often purchased. This is a universal size - suitable for both water and heating.
The content of the article:
How it works and where it is used
The popularity of 25 mm pipe blanks is explained by a successful combination of bore size, maximum water pressure and material cost. A polypropylene pipe with a transverse dimension of 2.5 cm is easy to hold with one hand when cutting workpieces or when welding with couplings or adapters.
Fittings for 25 mm polypropylene pipes are produced massive enough to provide a strong soldered seam, but the parts do not look oversized, so they do not spoil the appearance of the plumbing or heating system.
Advantages of using polypropylene pipes with an outer diameter of 25 mm:
- Large capacity for water consumption. It is enough to provide drinking water to a residential building or apartment for 120-150 m2.
- Small diameter. It’s easy to hide a 25 mm pipe in the wall under plaster or cover it with a decorative box.
- High strength of polypropylene pipe with optimal index value SDR.
Another positive factor is the low thermal conductivity coefficient.
It is equal to 0.15 W/(m*K). This is approximately at the level of dry cardboard. For comparison, for dry reinforced concrete and steel it is 1.55 W/(m*K) and 45.4 W/(m*K). The difference is several orders of magnitude. This means that a heating system based on 25 mm polypropylene pipes will not lose heat in intermediate sections.All energy is dissipated in places where radiators or batteries are installed.
This makes the 25 mm pipe blank truly universal - it can be used for any purpose, so customers purchase the material with a small reserve.
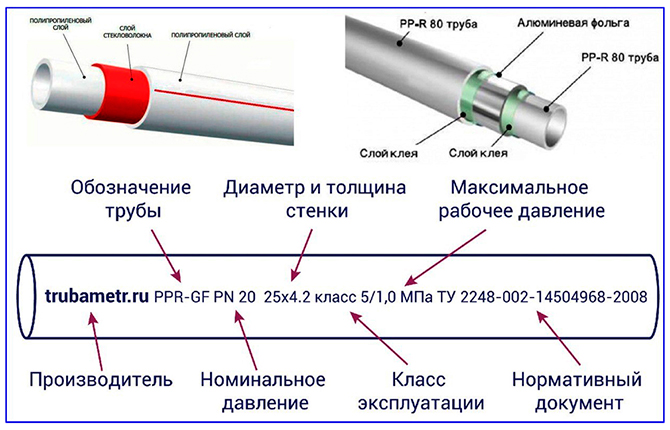
Before buying a polypropylene pipe, you need to pay attention to its markings. Pipe blanks with a diameter of 25 mm differ in characteristics, internal diameter, wall thickness and maximum water pressure.
In addition, in the marking of pipes, in the price offers of manufacturing companies and distributors, the dimensional characteristic of 25 mm is used. This value refers to the outer diameter of the polypropylene blank, although this is not entirely accurate.
In fact, the size of the workpiece is not 25 mm, but somewhat larger. For example, for a pipe designed for a working pressure of 20 bar, the initial diameter is 26.2 mm. After preliminary preparation before soldering, chamfering and calibration, the polypropylene pipe acquires the required 25 mm.
Characteristics of 25 mm pipe
General information about polypropylene pipelines is presented in GOST 32415-2013. Pipes measuring 25 mm are produced under different operating pressures. To indicate the load-bearing capacity of workpieces based on internal pressure, the indices SDR or PN are used. Pressure standards are determined last. They work both for 25 mm pipes and for other diameters.
According to GOST, standards are set in:
- 10 bar (PN10);
- 16 bar (PN16);
- 20 bar (PN20);
- 25 bar (PN25).
The SDR indicator characterizes the design of a polypropylene pipe. This is a numerical value obtained by dividing the pipe diameter (for this case - 25 mm) by the wall thickness.
Workpieces designed for different pressures will have different internal diameters (pipes).
| Outer diameter 25 mm | SDR=5 and PN25 | SDR=6 and PN20 | SDR=7.4 and PN16 |
| Wall thickness, mm | 5,1 | 4,2 | 3,5 |
| Inner diameter, mm | 14,8 | 16,6 | 18 |
Workpieces with an outer diameter of 25 mm, but with different PN and flow area, differ in internal volume. This is important and must be taken into account when designing heating systems.
Internal volume of polypropylene pipe 25 mm:
- for PN16, one linear meter of workpiece contains 0.254 liters of water;
- for PN20 – 0.237 l of water;
- for PN25 – 0.171 l of water.
Information about the volume will help determine the total capacity of the heating system and make calculations based on the performance of the pump and boiler.
The PN value indicated in the passport for a polypropylene blank characterizes the maximum pressure at room temperature. For a standard PPR or PPR-C polypropylene pipe, the temperature limit is 70 OC, but at a pressure of 8 bar.
At 60 OA 25 mm blank made of PPR100 polypropylene, class PN20, will withstand a maximum of 13 bar. If it is necessary to ensure maximum values of pressure and temperature, then you need to use workpieces of the “PP-FIBER” or “PP-ALUX” class with a reinforcing layer.
We pay attention to the material and scope of application
Two types of polypropylene are used for plumbing and heating systems:
- Random copolymer. The pipe marking may indicate PPR, PP-R is the usual one, or PPR-C is the heat-stabilized version.
- PPS – polypropylene. It is characterized by high ductility and the ability to operate at low temperatures down to -20 ℃.
The remaining brands - PPH, PPB are used for non-pressure systems, including ventilation and drainage, and for sewage.
PPR pipe with an outer diameter of 2.5 cm is used primarily for water supply systems. It is used to make wiring inside a house or apartment, additional branches for extensions and auxiliary needs (boiler room).
If you are replacing an old steel water supply system, then a blank made of polypropylene class PN20 and SDR6 in cross-section will be equivalent to sections with a diameter of ½’’. In theory, ¾” sections of pipeline can be replaced with a PPR pipe with SDR10-11, provided that the system will be operated at a temperature of no more than 40 ℃.
You can also use the “25” pipe for heating. For example, to heat a room using an individual system based on a gas boiler with a circulation pump. The pressure in the heating circuit does not exceed 1.5-1.7 bar, the outlet temperature is 60-70 ℃. For such conditions, you can use PPR pipes with PN20, SDR6 or PN25, SDR5.
| Inner diameter 25mm | Water flow speed in the heating main, m/s | ||||
| Thermal power W (volume of water per minute) | 0,2 | 0,3 | 0,4 | 0,5 | 0,6 |
| 7983(343) | 11975(515) | 15967(687) | 19959(858) | 23950(1030) | |
In the first case, at optimal coolant flow values of 0.3-0.4 m/s, the pump will pump 400-500 l/min of hot water, delivering 10-12 kW/h of heat to the radiators. In the second, the flow rate will drop to 230-300 l/min, the thermal power under equal conditions will drop to 5.5-7 kW/h.
PPR pipe can be used for residential hot water supply. The hot water temperature rarely exceeds 60-70 ℃, so it is quite possible to use polypropylene pipe blank with PN20 and SDR6. If, due to heating or hot water supply conditions, it is necessary to provide a water supply with a higher temperature and pressure, then instead of conventional PPR pipes for 25, models with a reinforcing sublayer are used.
Application is not limited to heating and water supply of private households. The main advantage of the 25th PPR pipe is its simple soldering technology and high joint strength.Therefore, from the remains of the material used for the manufacture of water pipes, channels are often made for laying wiring, and tubular frames of canopies, greenhouses, and greenhouses are assembled. Some craftsmen lay water mains for irrigation or collecting rainwater.
What types are produced?
For domestic water supply and heating, four types of polypropylene-based blanks are used:
- standard unreinforced based on random copolymer;
- polypropylene pipe, reinforced with glass fiber or glass fiber;
- reinforced with aluminum foil;
- with a reinforcing sublayer based on basalt fiber.
The first three types have long been known on the market. They have been used for many years in the manufacture of plumbing and heating systems. The option with basalt has relatively recently appeared on the water supply systems market.
In all cases, the workpiece is made on the basis of PPR polypropylene. The design consists of three layers. External and internal - polypropylene. The internal reinforcement can be made of thin aluminum foil glued to the internal sublayer, or in the form of a composition of polypropylene and mineral fiber, glass or basalt.
A couple of years ago, the option with a reinforcing sublayer of aluminum was considered the optimal solution for soldering heating systems. Typically these are PN25 class models with a total wall thickness of 0.42 cm. Relatively reliable and inexpensive. The pipe has only one drawback - the need to strip the outer layer of polypropylene down to the foil before soldering.
Glass fiber reinforced blanks, with a diameter of 25, usually have a wall thickness of 0.42 cm, and are designed for a maximum pressure of 20 bar. The inner reinforcing layer contains up to 30% fiberglass.Withstands heat up to 90℃.
Pipes reinforced with basalt fiber differ from glass-filled ones in three ways:
- polypropylene blanks with basalt are more expensive than glass-fibre ones;
- 30% less wall thickness;
- 20% higher rigidity and tensile strength.
The reliability of the basalt sublayer is higher and less sensitive to thermal shocks and deformations. Models based on basalt fiber reinforcement are rapidly becoming cheaper and replacing aluminum and fiber.
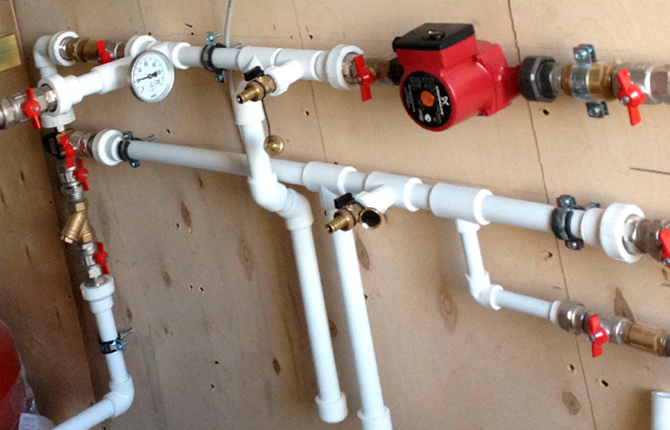
How to install
The most convenient option is to install a polypropylene pipe on clips or clamps. Clip fasteners are convenient due to their simple installation and low price for fasteners. For example, single clips for 25mm polypropylene pipes of good quality cost between $0.01 and $0.015 each.
Clips are used primarily as sliding supports. Thanks to this, the polypropylene pipe can move inside the support when heated and thermal expansion.
Attaches to the wall using a dowel and a plastic plug. The clip fastening system is such that its position can be adjusted in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the pipeline.
Clamps differ from clips in that the polypropylene pipe is enclosed by one or two metal brackets. Clamp fasteners are often a stationary, non-slip support. Therefore, they can be used to mount pipes on the wall and even on the ceiling surface. The cost of a clamp for a 25 mm pipe is no more than $0.5 per piece.
The number of clips used to secure polypropylene pipes can be unlimited, regardless of whether it is cold water or a heating circuit. There are limitations to clamps.For a section of 6 m there should be no more than two stationary supports, the rest are made according to a sliding scheme.
In addition to clamps and clips, polypropylene pipes can be laid in the walls of the room or under a concrete screed, but always in a heat-insulating cover. For wall installation, a groove is cut into the masonry, the dimensions of which must be at least twice the diameter. For a 25 mm pipe, a 50x50 mm groove is cut.
If polypropylene pipes are poured into concrete, then a thermal expansion compensator must be inserted into the gap in the line, otherwise cracks may form during the shrinkage or heating of the pipeline.
Polypropylene pipe 25 mm is considered the most versatile of all possible sizes. Its throughput is enough to connect an entire heating branch of 7-8 radiators. A standard flow rate of 250-300 l/m will provide reliable water supply for two to three families at the same time.
Polypropylene pipes: types, fittings, components. Master class on soldering pipes: video.
Tell us about your experience of choosing the appropriate diameter in the comments - why was preference given to this particular size and according to what criteria? Bookmark the article so that useful information is always available.





The pipe is excellent. Neither more nor less, 25 mm is just right. I soldered the water supply at home, and at the same time made all sorts of trinkets from the leftovers, just for fun.
The good thing is that a 25 mm pipe is soldered quickly, without effort. The bad news is that you even need to know how to use a soldering iron, otherwise you can ruin the entire water supply with one defective joint. Covers are the right thing to do, but few people install them.