What methods are used during non-destructive testing - the main tasks
Pipelines are highways consisting of a large number of pipes connected to each other by welding. The latter can be carried out poorly, which will entail irreparable consequences - rupture of the weld. Therefore, before the pipeline is put into operation, non-destructive testing of pipelines is carried out.
The content of the article:
How important is quality control?
Pipe main structures are subject to serious loads, both from the inside and outside. Therefore, special attention is paid to quality control of welds.
Welding process associated with high temperatures that melt the metal of the pipes. It is at this time that their structure changes. If you do not follow the welding process technique, then after cooling, defects will form inside the seam. The welded metal becomes inhomogeneous.
Types of defects:
- External. Clearly visible on the seam surface. This category also includes those flaws that are located inside the metal at a depth of no more than 2 mm.
- Internal, they are also deep. Located deeper than 2 mm.
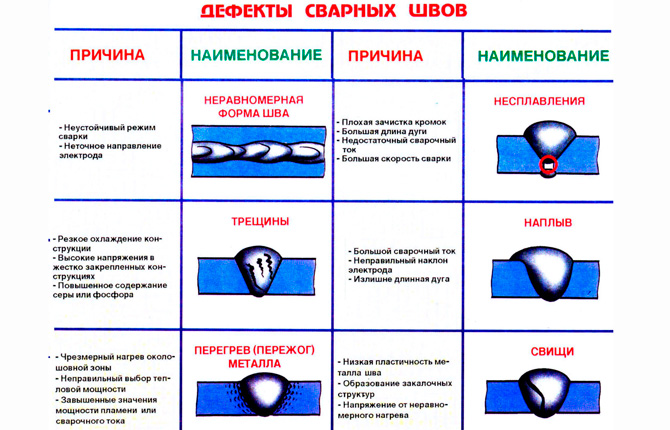
Defects in pipeline joints have different shapes and locations. Among them there are flaws with standard names and specific ones:
- Cracks. A defect that is several times longer than it is wide. This is the most dangerous moment in the weld, which often leads to its rupture. Cracks come in two categories. They can be located both inside the seam and outside.Through cracks are often encountered. They are the most dangerous.
- Pores are also shells. Spherical-shaped defects (the shape may be different, but always hollow), formed due to gases that are released during the welding process of metal. Belong to the inner group.
- Craters. These are practically pores that have formed on the surface of the pipeline weld (small depressions). The reason for their appearance is a break in the welding arc. The danger of craters is that where they appear, the thickness of the weld decreases. And this affects the strength of the joint.
- Undercuts. Formed at the boundary between the ends of the pipes and the weld. Due to this, the area of contact between the two metals is reduced. In such areas, internal stress increases, especially when the load on the pipeline increases.
- Surges. This is a layer of metal that is applied to the surface of the weld. It turns out that the upper and lower layers are practically not connected by anything. The connection cross-section is not the same as required by GOST.
- Lack of penetration. Internal type of defects. It is characterized by the fact that inside the pipeline connection there is metal that does not have the required characteristics. It was created under the influence of a lower temperature than required by GOST. Therefore, due to the loads in such an area, the stress of the metal quickly increases, which leads to deformation with subsequent rupture.
- The weld metal is porous. These are still the same pores or cavities, only small in size and distributed evenly throughout the entire volume of the welded joint (as a whole or in sections).
- Foreign particles inside the weld metal. The reason is poor work of the welder. Before starting welding work, all surfaces to be joined are thoroughly cleaned. Typically, metal brushes and degreasers are used for this.If preparation is not carried out, debris gets into the weld, reducing its strength.
- Burnout. This is when the welding technology is broken and the electrode arc passes through the metal of the joint. For the same reason, sagging forms on the other side.
To ensure that all these troubles do not affect the operation of the pipeline, control is carried out. Today, different methods are used, but they all fall into the non-destructive category. There are also destructive techniques, but they are used for laboratory research. Non-destructive in all other cases.
They are convenient because:
- there is no need to cut out the object under study and take it to the laboratory;
- all processes are carried out at the welding site;
- To carry out control, compact equipment of low weight is required.
There are strict requirements for non-destructive testing of pipelines. The diagnosis is performed by a trained specialist. At the same time, the rules and regulations of control are strictly adhered to.
What methods are used during non-destructive testing?
There are several types of non-destructive testing of pipelines, which use different materials, devices and technologies.
Basic:
- Visual and measuring control.
- Radiographic flaw detection.
- Using ultrasound.
- Magnetic flaw detection.
- Capillary method.
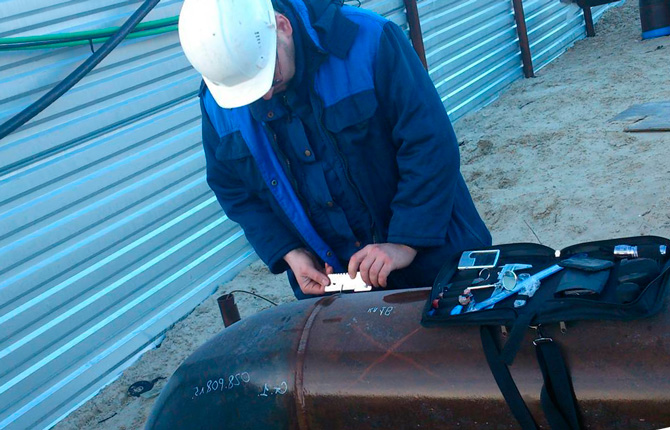
Visual-measuring
This type of pipeline inspection is based on inspection of pipe connections, both visually and using measuring instruments. Therefore, this technique detects only external defects.
This non-destructive method is inaccurate, although simple to perform. This type of control is mandatory. It is carried out before moving on to another non-destructive method.After all, having discovered a flaw on the surface, you don’t have to move on to another stage, which is more expensive to complete. Such a joint can be immediately rejected.
As for ease of implementation, a simple measuring device is usually used for this, for example, a caliper or ruler. Before measurements, the area with the flaw is cleaned with alcohol, acid or other solvent.
If, for example, the crack is small, use a magnifying glass to help. A prerequisite for carrying out this type of non-destructive testing is to determine the shape of the defect and its size.

Radiographic flaw detection
One of the most accurate methods of non-destructive testing of a pipeline, which allows you to identify even minor flaws in the weld. At the same time, their exact location is determined.
The technique is based on conventional x-rays. A small installation is used that scans the metal connections of pipeline elements and displays them on X-ray film.
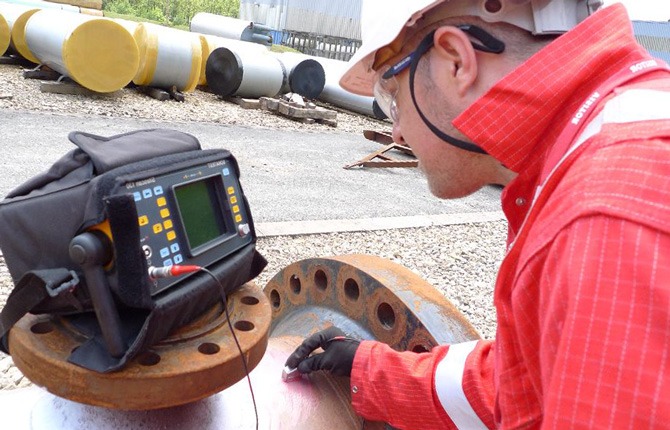
Ultrasonic non-destructive testing
The technology is based on acoustic changes inside the metal. If it is homogeneous, then the sound will pass without changing its characteristics and direction. When a defect is encountered along the way, changes will appear and they will be reflected on the receiver. The main parameter of change is the speed of sound.
The essence of the non-destructive technique:
- ultrasound, which has an ultra-high vibration frequency, is released from the amplifier;
- it passes through the weld;
- if it collides, for example, with a crack or shell, then it will be reflected from their inner surface (cavity), change direction and return to the receiver.
The greater the angle of refraction, the larger the crack or other defect.

Magnetic non-destructive testing
There is such a term as magnetic permeability. This is when magnetic waves pass through metal over a certain period of time. If this indicator decreases, then inside the material an obstacle was encountered on the way of the waves, which they began to bend around. Therefore, their speed dropped and their travel time increased.
To carry out this non-destructive testing of pipeline welded joints, special equipment is used. With its help, electromagnetic waves are passed through metal. Powder is first poured onto the surface or a suspension with iron inside is poured. The mineral collects around the defective area.
There is another option called magnetography. Here, instead of powder or suspension, magnetic film is used. All the imperfections of the metal are displayed on it. After the control procedures, the film is placed in a flaw detector, from where the information is read. It can be sound or in the form of images.
Penetrant non-destructive testing
This technology makes it possible to detect weld defects in a pipeline system using special liquids called penetrants. Their main property is to penetrate materials even if they have capillary changes.
These liquids include:
- kerosene;
- turpentine;
- benzene;
- transformer oil, etc.
If the penetrant has passed through the metal of the pipe joint, it means there is a flaw in it. If it doesn't pass, then everything is fine.
Non-destructive testing process:
- chalk or kaolin in liquid form is applied to the welded joint of the pipeline;
- after the applied layer has dried, the dry part is removed;
- Kerosene is applied on top of the remaining layer;
- after half an hour you need to check the reverse side of the joint;
- if kerosene leaks are found there, then the seam is defective; if not, the connection is reliable.
Today, substances are added to penetrants that help to more clearly identify metal imperfections. Mainly two:
- red pigment;
- luminescent substance.
The first is used when control is carried out during the day with natural lighting of the area. The second night, for which ultraviolet lamps are used.

Non-destructive testing of a pipeline that is not subjected to heavy loads, can be carried out in simpler ways: hydraulic or pneumatic. To do this, water or air is forced into the line under pressure, respectively.
In the first case, non-destructive testing is carried out by identifying leaks from the opposite side of the connection, that is, from the outside of the pipes. In the second, foam is additionally used, which is applied to the weld. If it starts to bubble, there is a defect.
Non-destructive pipeline inspection methods have made it easier to verify the integrity and quality of pipe connections. The use of flaw detection, especially with regard to X-rays and ultrasound, has brought the probability of detecting welding defects almost closer to 100%. Moreover, such control allows you to find out where the defect is located, how many there are, what size and shape.
What do you think, is it necessary to use more complex methods of non-destructive testing of pipelines or can we get by by supplying water/air to the system? Write in the comments. Share the article on social networks and save it to your bookmarks.
You will also learn more about how welds are inspected in the video.
Sources:
- https://iseptick.ru/truby-i-fitingi/nerazrushayushhij-kontrol-truboprovodov-i-svarnyx-soedinenij-metody-kontrolya.html
- https://elsvarkin.ru/texnologiya/kontrol/soedinenij-truboprovoda
- https://spark-welding.ru/montazh-i-remont/metody-nerazrushayushchego-kontrolya-truboprovodov.html



