What diameter of metal-plastic pipes to choose - size table
The advent of technology for joining metal and plastic has given rise to a whole series of materials for water pipes and pressure lines. One of these new products was a pipe with two base layers - aluminum and polyethylene. The diameter of the metal-plastic pipe decreased somewhat, which at first confused even experienced craftsmen. It seemed that the strength of the thin wall was clearly not enough to withstand the water pressure of the standard 5-10 At.
The content of the article:
Production technology
Even a preliminary acquaintance with the structure of a metal-plastic “sandwich” suggests that the production of such products is not an easy task. There have been attempts to solder polymer and metal in one metal-plastic pipe before, but most often the experiments ended in failure.
Due to weak adhesion and different thermal expansion coefficients, the metal-plastic sandwich delaminated, regardless of the diameter and wall thickness of the workpiece.
Modern technology suggests not soldering, but gluing a layer of metal and polymer using an adhesive mass - an adhesive. What this gives is no peeling.
It doesn’t matter what diameter metal-plastic pipes are, everyone pipelines under strong heat or mechanical stress, the aluminum layer can even slip relative to the inner layer of polyethylene.The adhesive provides a strong connection without delamination with uniform pressure distribution over the inner surface of the metal-plastic pipe.
Metal-plastic pipes are manufactured according to the following scheme:
- A metal layer blank is formed from aluminum foil by winding it onto a mandrel. The machine does this. The width of the tape and the welding method depend on the diameter of the metal-plastic pipe.
- Adhesive with melted polyethylene is supplied inside the wound tape. This makes it possible to make the blank of the future metal-plastic pipe more rigid.
- Aluminum tape is welded into a pipe, and an outer layer of adhesive and protective polymer is laid.
- The metal-plastic pipe is cooled and wound into a coil. As the drum fills, it is cut off with a ring knife.
As a result, the output is a metal-plastic pipe, which can be bend even with your hands at any angle, and the passage section will not lose the original diameter and shape of the passage. But still, to bend workpieces, regardless of their diameter, a special device is used, otherwise a smooth bend will not work.
What are the benefits of using aluminum foil?
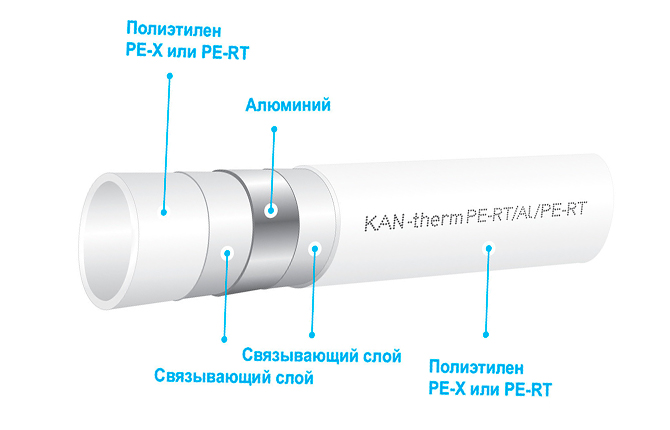
The inner layer consists of polyethylene. The material is safe and resistant to acids, but it has one drawback. Even in a relatively cold state, under the influence of the expanding pressure of water, a thin-walled polyethylene pipe without external reinforcement will expand.
The cross-section can be stabilized by external reinforcement, preferably aluminum. To do this, a layer of aluminum foil is formed.At the same time, the presence of a metal sublayer makes the walls as rigid as possible, which allows you to embed fittings and couplings without the use of glue or soldering.
The thickness of the aluminum sublayer for metal-plastic pipes of different brands ranges from 0.33-0.7 mm. Ideally, the larger the diameter, the thicker the layer of aluminum foil should be. In addition, the quality of the metal-plastic water supply depends on how the tape is welded.
It is better if the edges of the tape are butt welded together with a laser. Other welding methods often result in burnouts and undercooking. Also, a lot depends on the quality of aluminum; if you don’t save money and don’t buy cheap brands like HDPE, PE-HD, PERS, then you can avoid problems associated with the reinforcing layer of metal-plastic products.
The main layer of the metal-plastic pipe
The inner layer is made of PE-X or PE grade polyethylene mass. This is cross-linked polyethylene, one of the safest and most resistant types of polymers, second only to fluoroplastics. The material does not corrode, does not emit or accumulate toxic compounds, and is not destroyed under the influence of water and high temperatures. The inner layer of metal-plastic can withstand heating up to 110 ℃.
The polyethylene layer in the wall occupies more than 2/3 of the thickness, so whether water reaches the aluminum depends on the quality and density of the inner layer.
This is possible if the metal-plastic pipe was frozen with liquid inside. Due to the formation of ice, the cross-sectional diameter increases. At low temperatures, polyethylene becomes rigid, so the inner layer can become covered with microcracks.
This is not dangerous for cold water supply lines. Another thing is heating.In this case, a low-quality pipeline may develop pitting corrosion in areas of increased diameter. The inner layer of polyethylene protects aluminum from liquid and the formation of galvanic couples with brass and sometimes steel parts of taps and valves.
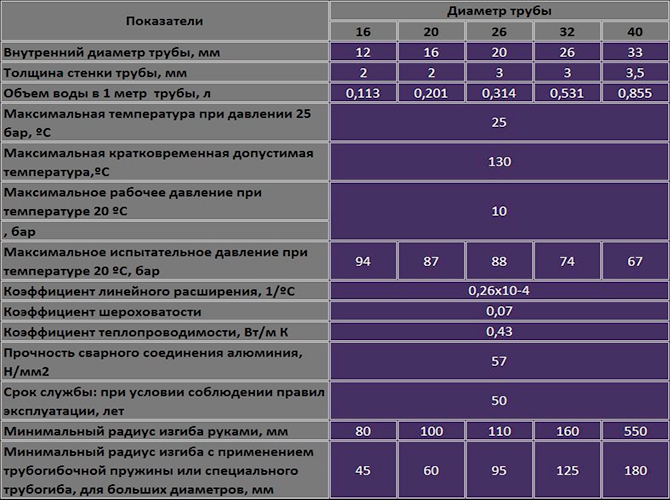
Diameter of metal-plastic pipes
Before choosing the appropriate cross-sectional size for the water supply line, it would be wise to figure out what diameter metal-plastic pipes are.
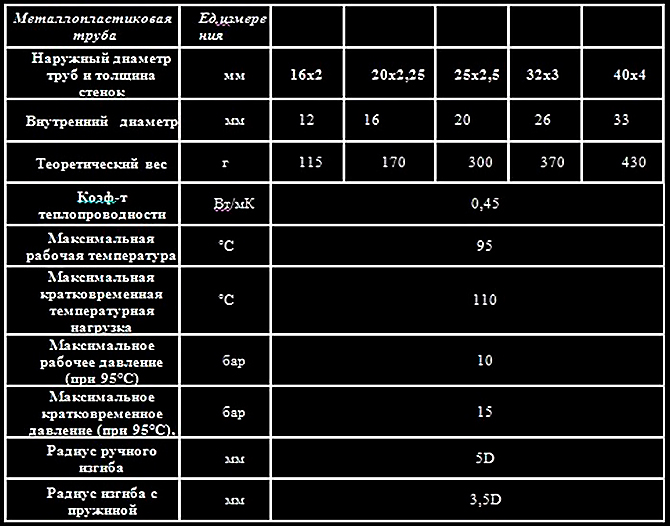
The line of pipe diameters is tied to the calculus, despite the fact that the dimensions of the internal and external diameters are indicated in the metric system. The diameter of the smallest pipe is 16 mm, the internal one is 12 mm or half an inch.
There are also metal-plastic pipes with the following diameters:
- external - 26 mm, internal - 20 mm, this is ¾ inch;
- external - 32 mm, internal - 26 mm, this is an inch;
- external - 40 mm, internal - 33 mm, an inch and a quarter.
A small error occurred due to the roughness of the inner surface.
This diameter step was chosen for a reason. The system for calculating pipelines for water and heating uses calculations in inches. Therefore, the diameters of the produced metal-plastic pipes were also tied to the inch of water pipes. This turned out to be not enough. I had to introduce one intermediate size with an outer diameter of 20 mm and an inner diameter of 16 mm.
The outer shell of a metal-plastic pipe from most manufacturers is made of white or yellow polymer. In appearance, all options for metal-plastic pipes are the same, so when choosing, you need to pay attention to the markings on the outer surface.
Outer and inner diameter of the pipe and purpose of the product
For internal water supply in an apartment or house, blanks with an outer diameter of 16 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm are usually used. Accordingly, the internal diameter of the metal-plastic pipe will be 12 mm, or in inch terms - half an inch. This is enough to connect a toilet cistern, kitchen faucet, bathtub or shower.
At the entrance to the room, from the gate valve to counter, they mainly use metal-plastic with a diameter of 20 mm, with a wall thickness of 2.5 mm. If this is a private house with two floors, then water consumption will need to be calculated according to the number of consumers. Often, owners do not bother with calculations and install a metal-plastic pipe with an outer diameter of 40 mm and a wall thickness of 4 mm at the inlet.
The diameter table will help you make the right choice.
The question often arises about choosing the cross-section of the main line in the heating circuit. There are two ways to solve the problem.
In the first case, choose what diameter of the metal-plastic pipe is needed for heating by measuring the transverse size of the pipeline of the existing heating system. The area of the premises, new and with existing heating, must be equal. It is enough to measure the outer size of the pipe and use a reference book to determine its inner diameter. All that remains is to choose the brand of metal-plastic pipe, the diameter of which is larger or exactly corresponds to the value from the reference book.
The second option requires certain knowledge regarding heating systems. It is best to take the recommended value from the heating boiler data sheet. If such information is not available, then the diameter is calculated based on the volume of pumped hot water.
Basic properties of metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic lines are designed for use in domestic water supply, hot water or heating systems. Therefore, the characteristics of metal-plastic pipes may be inferior to the operational parameters of polypropylene and steel pipelines of a similar cross-section.
The estimated service life for pipes of all diameters is 50 years. This is twice as much as steel communications serve. The main advantage of metal-plastic remains the simple technology of bending the workpiece at an angle. If polypropylene or steel needs to be joined at corners with angles or couplings, then the metal-plastic pipe, depending on the diameter, can be bent simply by hand with a bending radius of 80-550 mm. Small diameters are bent using a spring at a radius of 45 mm. For 40 mm, the turning radius of the device is already at least 180 mm.
Permitted temperature and pressure values
Operating limits for maximum temperature and pressure practically correspond to the parameters established for polypropylene and steel pipelines for domestic heating and water supply.
Namely:
- The operating pressure in the pipeline should be no more than 10 At. In this case, the safety margin is such that the line at 20 OC is able to withstand a fivefold increase in water pressure.
- The maximum temperature is limited to 90 ℃ in heating systems, a short-term jump to 130 ℃ is allowed.
As for domestically produced metal-plastic pipes, according to SP 40-103-98, the limit is set to 75 ℃, and SP 41-102-98 raises the limit to 90 ℃. For imported materials, 95℃ is allowed.
At high temperatures and pressures, the inner layer of polyethylene does not experience any special problems - the plastic becomes denser, without the formation of tears or cracks. Pipelines, especially large ones, 32-40 mm, may lose their tightness due to silicone or rubber gaskets.
At temperatures of 90-95 ℃, silicone can become so soft that it will no longer seal the connection on the fitting or coupling. Therefore, it is important not only to choose high-quality metal-plastic, but also connecting elements and gaskets.
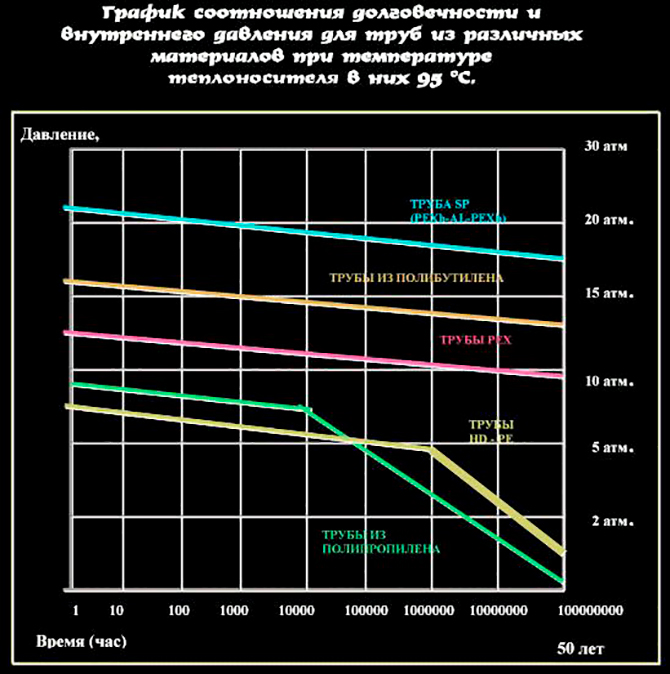
Temperature values
If the operating temperature does not exceed the recommended 95 ℃, then metal-plastic can last quite a long time. At the same time, the reliability of the connection, as can be seen from the graph - top row, decreases evenly.
Due to aluminum, metal-plastic has a high coefficient of thermal expansion - 0.26x10-4 1/m*S. This means that hot water pipes can sag under their own weight. If this happens periodically, cycle after cycle, then there is a risk that the joint on the fitting may leak moisture. It’s easy to get rid of this - you should install the lines on clips with small pitches and do not make the sections between connections too large.
There is one more temperature limitation: metal-plastic is afraid of low temperatures, mainly the aluminum layer suffers - the weld and gaskets at the joints may come apart. Therefore, in winter, water from the water supply at the dacha must be drained.
Metal-plastic pipes of all diameters have proven themselves as a simple and reliable tool for arranging water supply systems, heating systems, supplying all types of liquids in greenhouses, summer showers, irrigation and condensate drainage. Unfortunately, metal-plastic requires careful handling and high-quality connections, otherwise the pipes will leak and corrode.
Installation and connection of metal-plastic pipes: video.
Was the information received useful to you?
Which pipes do you prefer - metal-plastic, steel or polypropylene? Write in the comments. Save the article to bookmarks and share it on social networks.






Metal-plastic is not a bad idea, but there are a lot of outright defects. Five years ago I bought an apartment, the builders persuaded me to put metal-plastic on the water. I saw all this confusion of white tubes, I almost fainted, I argued with the foreman all day. As a result, half of the water supply started leaking in a week, the second one is as good as new, although one person did the watering. Look what these workers buy and supply for you.It’s better to buy German metal-plastic yourself, bring it into the house, install fittings - then it will stand, and all this talk about corrosion is nonsense.
A lot depends on the water; hard water with salts eats up the metal-plastic wall from the end in a couple of months, especially on a hot branch. It can be used for heating, it is better than metal or polypropylene.
Metal-plastic water supply is ideal for a summer residence. It can be disassembled and assembled in the spring without any problems. Just change the gaskets at the joints. The neighbors chuckled, then came to ask what and how. I made them a metal-plastic supply from the well to the house, also collapsible. So far, no leaks.