Coagulants for pool water purification: how to choose + rules of application
Owners of suburban areas with swimming pools are well aware of the problem of gradual contamination of the water and walls of the structure.Despite its cyclical movement and regular passage through filters, cloudy sediment and a suspension hazardous to health almost inevitably appears.
To combat the loss of water quality, there are effective means that are worth familiarizing yourself with. Do you agree?
Using coagulants to purify pool water, you can quickly and efficiently get rid of these problems and threats. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with information covering the principle of action of substances, their varieties and the specifics of choosing the optimal composition.
The article describes in detail the process of using coagulants, provides recommendations for keeping a private reservoir clean, and provides folk methods for combating its cloudiness. The information presented is supported by photo collections and videos.
The content of the article:
How coagulants work
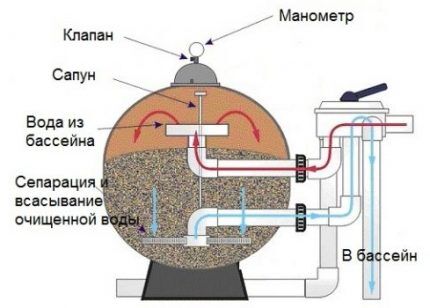
These substances have the property of combining microscopic particles of various pollutants, debris, heavy metals and biological particles into a bulk jelly-like mass with the subsequent transition of this emulsion into flakes.
In this form, a suspension that could seep through pool filters, is retained by the mesh and stops circulating in the water space of the pool.
Contaminants from the bottom and surface must be removed.The top film can be removed with an ordinary net.
When using automated container care products, sediment will be retained on the filter, from which it can be easily removed by regular washing. To do this, you can use a jet of water under pressure.
In addition to cleaning pool water, coagulants are actively used for wastewater treatment.
Varieties and selection rules
All commercially available products contain organic or inorganic binding active substances.
They are produced on the basis of sulfates, polyoxysulfates or chlorides of the following metals:
- Aluminum (aluminium) Al.
- Iron (ferrum) Fe.
- Titanium (titanium) Ti.
- Magnesium (magnesium) Mg.
Manufacturers indicate the composition in Latin, therefore, along with the name of the active substance, its Latin name will be duplicated. The composition of the drug can be found either on the back of its packaging or in the instructions.
Organic coagulating agents
The most popular coagulants are produced on the basis of aluminum polyoxychloride (polyaluminium chloride), its second name is hydrochloride. Aluminum polyoxychloride has a number of advantages over inorganic reagents.
The key ones include:
- High quality cleaning, which means that less reagent is required compared to sulfates.
- Low residual aluminum content in the water after the coagulation process, which reduces the frequency of water changes in the pool.
- The rate of floc formation is higher, which means the settling period is reduced.
- Reduced residual salt content, which allows you to change the water in the pool less often.
- Effect duration — a high degree of purification is maintained even at reduced ambient temperatures.
When released into the soil, this reagent does not disrupt the natural balance in the region.The process of dissolving in water is simplified, since the product does not require prolonged stirring.

When using this product, you do not need to use additional protective equipment. It is enough to use gloves to protect the skin of your hands from irritation. It is also recommended to use a respirator.
Inorganic compounds with a coagulating effect
The most popular inorganic compounds for coagulation are:
- Aluminum sulfate (aluminum sulfate).
- Ferrous sulfate (ferrous sulphate).
- Titanium dioxide (titanium dioxide).
Aluminum sulfate It is easy to use, as it is diluted in water without long-term settling. Its disadvantage is sensitivity to the predominance of acidic or alkaline components in water.
The tester values should not go beyond the neutral pH range of 6.5 - 7.5, otherwise the effectiveness of the coagulant is sharply reduced. The reagent is also sensitive to low temperatures and its use in the spring and autumn is excluded.

The disadvantage of its use is the increased (compared to hydrochloride) release of salts, which changes the pH level in the water.This necessitates its leveling, and also increases the frequency of changing the water in the pool, since in addition to salt, when using it in the water, the dose of aluminum is exceeded.
Ferrous sulfate allows you to get rid of the unpleasant odor of hydrogen sulfide, neutralize oily contaminants and get rid of high levels of heavy metals. In terms of these properties, the reagent is superior to aluminum-containing reagents.
It does not completely dissolve in water; a small part of the sediment remains, not exceeding 1% of the weight of the reagent.

Titanium dioxide has the highest cleaning percentage. This reagent has a pronounced bactericidal effect and can be used without additional chlorination.
Titanium dioxide has a number of advantages over iron and aluminum derivatives. It reduces settling time. In terms of this indicator, the reagent has no analogues.

Titanium dioxide is produced in Russia and abroad, so it can be found and purchased from suppliers.
The disadvantage of the reagent is its high cost. After using titanium dioxide, the water becomes drinkable, which is unnecessary for a swimming pool. It is worth choosing in favor of budget analogues based on aluminum.
When choosing a cleaning product, you need to pay attention to the integrity of the packaging. Some reagents are sensitive to oxygen and actively oxidize when interacting with it. This applies to iron-based coagulants.
Reagents in liquid form contain a ready-made solution, which simplifies the process of use, but their price is higher. It is more profitable to purchase the product in powder form.
It will last for more uses and is cheaper. This also applies to cartridges that are installed in the filter pump.
Comparison of coagulants with available means
If there are no filters or their low power, the problem of water blooming in the pool arises. The lack of necessary reagents forces the use of improvised substances.
The most popular means:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- potassium permanganate;
- brilliant green in alcohol.
They have a disinfecting effect. The effect of their use lasts temporarily and leads to consequences that need to be considered separately.

After using peroxide, flakes of dirty foam appear on the water surface. They are removed mechanically. Even after two days, the process of oxygen release will continue, which gives uncomfortable tactile sensations. When water with dissolved peroxide comes into contact with the skin, a slight tingling sensation will begin.
This aqueous solution should not be ingested or enter the respiratory system. This causes irritation of the mucous membranes. Peroxide allows water to cool more slowly as it increases its density. However, peroxide cannot replace complete cleaning with a coagulant.
Potassium permanganate diluted in water has a disinfecting property until its color changes from pale pink to light brown or green.

The composition of brilliant green includes alcohol and triphenylmethane dye. There is no exact data on how this coloring pigment affects a person when it enters the body. With prolonged contact of water in which the brilliant green is dissolved with the walls of the pool, the material changes color.

These reagents cannot serve as a full replacement for coagulants, since they do not bind fine suspensions. They can only disinfect water for a short period of time, while dangerous heavy metals and substances invisible to the eye do not disappear. They continue to be in the container.
Step-by-step instructions for use
Before cleaning with preparations, it is necessary to measure the acid-base balance. It must be done with a special device (pH tester) or litmus papers.
The optimal level is from 7.5 to 8.0. If the result obtained is less than the specified range, then it is necessary to add alkali, if more, then add acid.

After bringing the pH balance to neutral, you can begin disinfection. This is a necessary measure to prevent infection by infectious pathogens. For this purpose, chlorine-containing tablets are used, which, unlike liquid products, do not release antiseptic in doses during the dissolution process.
#1: Calculation of proportions depending on displacement
Before pouring the reagent, you need to calculate the displacement. To determine it, it is necessary to calculate the volume of the pool. To calculate, you need to measure the length, width and depth of the container. If the pool is round, then you need to measure the diameter and depth.
All measurements must be taken in meters.
- formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular container: length*width*depth;
- formula for calculating the volume of a round container: depth * 6.28 * radius squared.
The resulting values will be the displacement in liters. The dose of the substance is calculated based on this value. If the degree of water contamination can be visually determined to be severe, an increased dose may be needed; in this case, it is necessary to fill in 1.3 times that recommended by the manufacturer and can reach 25 ml per 1 m3.
Coagulant consumption can be reduced if flocculants are used as an addition. These substances are used specifically to form flakes and to make the mass heavier to facilitate filtration processes. They are added within two minutes after the coagulant is introduced.
#2: Preparing and pouring the solution
Manufacturers offer to purchase the reagent in three states:
- powder;
- liquid;
- briquetted.
The liquid reagent requires preliminary preparation. It must be diluted in water in a ratio of 1:5. Next, you need to turn off the filtration system. If this is not done, it will quickly become clogged with dirty flakes. The prepared solution must be poured into a watering can and spread evenly over the entire surface.
The use of a dispenser is suitable for weekly care, since the concentration of the substance in the water will be too low to clean heavy contaminants.
Coagulant briquettes are placed in special cartridges. They are installed in filtration pumps. When water passes through the briquette, it carries with it part of the reagent back into the pool.

If the reagent has a powdery consistency, then you must first prepare a concentrated solution. The mass fraction of aluminum sulfate should be 15%. To do this, the contents of the package must be dissolved in an amount of water equal to its weight. Dilution ratio 1:1.
To prepare a solution with a mass fraction of aluminum sulfate or polyoxychloride less than 15%, use the following formulas:
- K1 = K * D/D1 — to calculate the mass of the reagent in kilograms;
- V = K - K1 = K * (1 - D/D1) - to calculate the amount of water in liters.
Explanations for the formulas:
- K1 — mass of the reagent;
- K - required mass of solution;
- D — mass fraction (%) of aluminum sulfate (polyoxychloride) in solution;
- D1 — mass fraction (%) of aluminum sulfate (polyoxychloride) in the starting reagent.
The resulting solution must be poured into the pool. You can make the solution in advance; it can be stored unchanged for a year.
#3: Cleaning the surface and bottom after coagulation
After 10-12 hours after the start of coagulation, you need to clean the bottom and surface of the fallen sediment. For this purpose it is used water vacuum cleaner. This device has two hoses, one of which is connected to a tube.

The surface of the water in a temporary structure built for the summer season is cleaned either with a vacuum cleaner or with mounted water intakes made in the form of skimmers. This is a special bowl that connects to the filter system and collects debris from the surface.
In stationary pools, this is a mechanism built into the system used to collect water from the surface for subsequent cleaning.

The skimmer bowl has a mesh that prevents the passage of large debris that can damage the filter system. As the bowl fills, you must empty it manually. Such a system is capable of completely cleaning the surface within an hour of active operation.
A practical but expensive solution to the problem of cleaning a pool is to purchase a robot vacuum cleaner. An overview of popular models is given in this article.
Tips for keeping your pool clean
To prevent the pool from clogging, it is necessary to regularly chlorinate with special tablets. After chlorination, cleaning with reagents is carried out every 2 weeks. After the reagents are used, the pool is cleaned with a water vacuum cleaner. After this, the filtration system is turned off and the filter is washed.
After 12 hours, the filtration system is turned on and the cloudy suspension is removed from the bottom and surface of the pool. During this period, it is necessary to clean the filter again. It must be cleaned by rearranging the hoses according to the pump model and turning on backwashing. Some of the old water from the pool is removed, and the quartz sand is washed in the filter.
After finishing the washing, you need to return the hoses to their original working condition and, if necessary, add fresh water to the pool.Since the decomposition of the coagulant in the water accumulates over time an excess amount of products of the reagent’s action, a complete replacement of the water in the swimming pool is necessary every two months.
The cleanliness of the pool largely depends on the efficiency of the filter unit and the quality of the water. Some craftsmen, in an effort to save money, do DIY filter.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Water purification using the coagulation method using the example of experience:
Removing cloudy sediment after coagulation:
Good reagents should be purchased from reliable manufacturers, be sure to pay attention to the mass fraction of the active substance. The higher the percentage of its content, the more effective and economical its use will be.
If the desired result is not achieved when using the drug, then it is necessary to increase the dose. If this does not help, it is better to drain the water from the pool, as the unknown composition may be harmful.
Do you have experience using coagulants to clean a pool, or maybe you know effective methods for removing contaminants? Or still have questions on the topic? Please share your opinion and leave comments.





It's really difficult to choose. I would like to know how safe the water is for the health of swimmers after purification with coagulants. I am especially worried about the health of children. So, if a lot of aluminum accumulates in the body, Alzheimer's disease may develop. Is titanium harmless? I prefer potassium permanganate or peroxide, maybe not as effective, but safe.
Titanium is not absorbed and does not accumulate in the human body, but is eliminated from it after a few hours.And think about it - well, okay here, in the USA the manufacturers of coagulants would have been sued long ago if it was dangerous to health.
I would happily use only brilliant green and potassium permanganate, but they do not clean completely, and they can also paint the tiles. You have to use hydrochloride - it is both more effective and less dangerous to the skin and mucous membranes than sulfates. I follow safety precautions and thoroughly clean the bottom after using reagents: so far, no one in my household has been poisoned by reagents and no one has allergies either.
We bought an inflatable pool for our grandchildren. The children are delighted and flop around there almost all day. But a problem arose - although the size of the pool is not the most gigantic, it is not possible to change the water in it every day. What is the best way to clean it in such a situation? Will the available means listed in the material be enough or will I have to buy all these sulfates and dioxides?
Hello. There are many products that can help you clean your water. For example, one of these - ordinary salt, calculated at 5 kg per 1 ton of water, brilliant green - 3 bottles per 10 cubic meters, 700 ml of hydrogen peroxide per 1 cubic meter (swim only 24 hours after cleaning), again, listed in the article means. But, of course, it would be best to change the water daily and clean the surface.
This is not the advice of an engineer, but of a classic C student who cannot decide what he wants to multiply when calculating the volume of a cylinder. For some reason, in the formula the perimeter was multiplied by the depth, when everyone knows that the area of a circle is πR^2, which must be multiplied by the height (depth) of the pool.
Yes, and by the way, the measure of volume is cubic liters (according to the SI system), multiplying by meters, you will not get liters.
It is worth adding to Vlad’s remark that aluminum polyoxychloride (Al2(OH)nCl6-n, where is the carbon here?) does not fit the definition of organic. However, articles with so many errors and misconceptions are a common occurrence for compilation materials.