Attic ventilation in a private house: rules and devices for organizing air exchange
Regular air exchange within the attic space and in the roofing system is necessary for the long-term service of the roof and the building as a whole.Properly organized attic ventilation in a private house ensures thermoregulation of the room. It will prevent the formation of mold and dampness.
In this article we will look at why we need flawless air exchange in the attic space. We will talk about what ventilation systems are required for complete removal of moisture and condensation. We will introduce you to the principles of operation of the ventilation system and the options for its design.
When performing the work yourself, use the given diagrams, ventilation calculations, as well as useful photos and videos with tips on arrangement ventilation systems.
The content of the article:
What functions does ventilation perform?
The process of air exchange in a room consists of regulating heat exchange processes and maintaining optimal environmental indicators - temperature, humidity level, speed of movement of air masses.
The engineering system, equipped in accordance with established technical requirements, ensures the free flow of air and its movement in space due to installed dormer windows, vents, aeration devices of various designs and other openings.

The functional purpose of the system is the regular supply of the required volume of air and its subsequent removal, which contributes to:
- reducing moisture in the room;
- providing the necessary microclimate;
- preventing the formation of condensation and the development of fungus;
- creating continuous air exchange;
- preventing deformation of rafters in the building.
The organization of ventilation should be carried out both in a warm and in an uninsulated attic. In the summer, the roof surface heats up to high temperatures, transferring most of the heat to the lower part of the house.

High humidity in autumn-winter period affects the microclimate of the attic. At the same time, the thermal insulation qualities of the structure will be significantly reduced, because the water contained in the insulation and materials will contribute to heat loss. Therefore, an air exchange system is equipped to remove excess moisture.
Due to the large temperature difference inside and outside the room, condensation forms, walls, floors, floor beams, rafters, mauerlat, and vertical posts become wet. All this leads to rotting of the wooden components of the roof and the appearance of dampness.

For effective ventilation of the room throughout the year, without loss of heat in the house, the following technical standards are provided: for every 500 m2 room required 1 m2 ventilation holes.
In addition, in order to prevent the formation of water droplets on the beams of the structure, insulation measures should be carried out - lay paro- and water protection.
Nuances of air exchange system equipment
In organizing roof ventilation, one or more organizational methods are used. Air exchange directly depends on the characteristics of the attic space, its area, shape, type of roof and building materials used.

The specificity of the roof ventilation device is that it is necessary to provide two directions indirectly connected with each other, these are:
- Ventilation of the roofing pie. It is needed to dry the system under the roof covering: insulation laid along the slopes, rafters, sheathing. Provided with vents and aerators.
- Removing excess moisture from the attic space. It is required to drain the attic or attic, creating a microclimate in it that is favorable for extending the service life of the structure and the stay of the owners. Provided ventilation gable windows, holes, hatches.
The roofing pie is ventilated by vents - longitudinal channels laid from the eaves overhang to the ridge ridge. Vents are formed during laying of the sheathing and counter-lattens on the rafter legs.
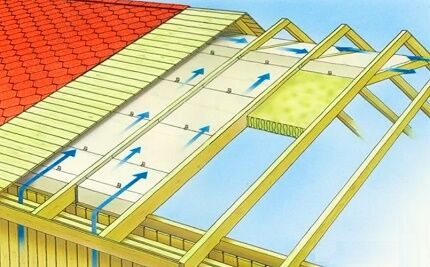
The distance created by this method allows the air flow to enter in the eaves area and exit in the ridge area, taking with it condensation and moisture settled under the roof.
For roofing from ondulin, bitumen, polymer-sand and natural tiles additionally use aerators that follow the shape of the roofing material. If they do not differ in color, they literally merge with the roof. The grille built into them allows air to move freely in the direction necessary for drying.

In the case of a roof with corrugated steel, metal tiles and corrugated sheets, when installing a ventilation system for the roofing pie, it becomes somewhat more complicated. Installation of the sheathing should be done with gaps, i.e. with additional transverse channels.
If the gap in the lathing is not initially observed, then side holes are drilled in the laths for the steel profiled roof. They are placed approximately 30 cm apart. As a result, the area of the air flow drying the insulation increases due to air movement not only upwards, but also sideways.
Air exchange in houses with a flat roof is characterized by the absence of gables in which attic windows can be installed. And although there is still an attic in well-designed flat and low-slope roofs, they are ventilated through ventilation holes.

The space in large hip roofs is ventilated through dormer ventilation windows, in small ones - through ventilation vents.
Despite the fact that the inclined ribs of the hips are arranged according to the ridge principle, they cannot provide sufficient outflow. To relieve and eliminate possible tension, aerators are installed.

Air exchange in the attic space of a gable roof is often organized by installing ventilation holes with grilles, as well as through ventilation or dormer windows. For natural air circulation, both openings and window openings should be located on both sides.
Features of the organization of the ventilation system
For proper operation of the system, the following recommendations should be followed:
- To allow free flow of air under the roof, it is necessary to leave special openings and gaps.
- Organize the air exchange system in such a way that air masses come from the bottom of the roofing pie and exit through the remote gap in the ridge ridge.
- Place a sufficient number of ventilated devices and openings, taking into account the area of the room, to ensure free movement of air in the attic.
- Ventilation ducts must be equipped with valves to be able to regulate the intensity of ventilation, as well as mosquito nets to prevent insects from entering.
Holes in the ridges under the roof overhang provide circulation due to the force of the wind and the thermal movement of masses circulating in the atmosphere naturally.
Products: location rules, calculations
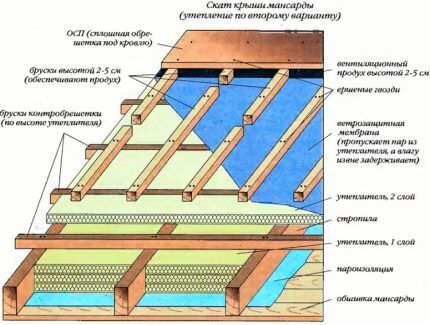
In a properly constructed roofing pie, air movement is directed from below through the vents, and then upward to the ridges with holes. A gap of 3-5 cm must be left along the ridge line, which is covered from above with a ridge strip, a row of ridge tiles, two mating boards and similar devices.
If the ridge is hermetically sealed, which prevents air from escaping, then ventilation holes are made in the gable just below the ridge girder. They do not replace the need to install gable and dormer window openings, because different ventilation problems are solved.
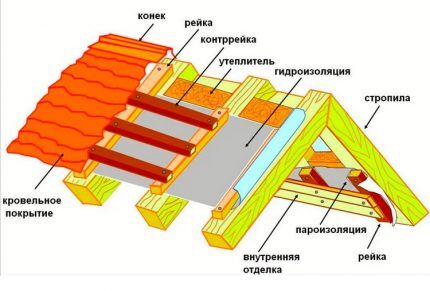
Regardless of the type of roofing, almost all roofing pies are supplied with air vents. They are installed both in insulated attic roofs and in cold structures without thermal insulation.
From below, along the eaves overhang, the entire pie along with these ventilation ducts is covered with a mosquito net, which at the same time protects from dust.

In addition to the vents laid in the roofing pie, there are also holes located in the upper part of the wall, along its line of interface with the slope.
Wall vents are divided into the following types:
- slotted, about 20 mm wide - located on both sides of the eaves, forming a gap between the wall and the roof;
- point, with a diameter of no more than 25 mm - have the form of holes on the surface, the size of which depends on the slope of the slopes.
It is important to observe the specified size of devices when arranging ventilation system. If there are smaller or larger openings, the efficiency of air flow will be reduced.

The width and number of holes may vary depending on the dimensions of the roof. For regular and proper ventilation without excessive heat loss from the room, the total area of the vents in the attic should be 0.2% of 100% of the room area. Also, we should not forget about the correctness of their location.
An example of calculating vents when installed in a roofing pie:
- for a 5-meter roof, the holes should be 8 mm;
- 6-meter - the width of the holes is no more than 10 mm;
- with a roof width of 7 to 8.5 m, the vents should be 12-14 mm;
- a roof 9-10 m wide is equipped with ventilation holes measuring 16 mm.
If the vents are located in the lower part and on the ridge, their width should be halved. It is not recommended to exceed the permissible area of the holes, as precipitation may enter them.

The vents in the upper part of the roof are intended for the exhaust outlet of flows. Their area should be 15% larger than the supply air ducts.For this, aerators or special grilles are used - more innovative devices that provide the required temperature difference and pressure level when air moves.
Rules for installing attic windows
When equipping the attic with dormer or ventilation windows, you will still need to additionally prepare vents and vents. This option is considered highly effective, since moisture not removed from the roofing pie will prevent adequate ventilation of the premises.
To improve circulation and reduce air stagnation, the dimensions of attic ventilation devices in a private house should be 600x800 mm.

Installation steps for attic windows:
- Wooden frames are attached to the rafters using racks.
- Next, the roofing covering is laid.
- The openings are finished with clapboard or other material.
- After this, the window frame is installed in the prepared opening.
- Having fixed the frame, it is necessary to eliminate all gaps between the roof and the window using polyurethane foam.
- The last thing you should do is insert the glass unit.
You can do the work of installing attic windows yourself according to the instructions or use the services of specialists.
When installing a window, you must adhere to some recommendations:
- should not be placed close to the ridge;
- Additionally, they can be equipped with a grille;
- between windows gaps should not exceed 1 m;
- the devices must be positioned in this way: the lower border of the window should not be lower than 1 m from the ceiling level, the upper border should not be more than 1.9 m.
Their design can be varied.Basically, builders select the shape of the ventilation device depending on the type of building and architectural design.
Tips for arranging a utility system
To determine the level of complexity of work when installing the system, we will consider the ventilation features of an insulated residential and unequipped cold attic space. Let's figure out what the differences are in organizing air exchange with different types of room insulation and temperature conditions.
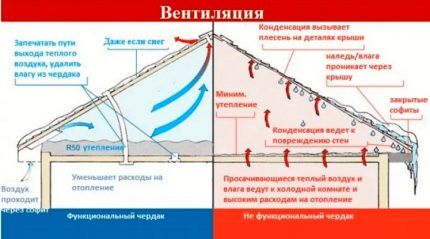
Air exchange helps extend the service life of the roof, rafter frame, equipped and unfurnished rooms under the slopes. The system also prevents snow accumulation, roof icing, and moisture formation.
Ventilation of non-residential attic space
A cold attic, not equipped for living, is a space under the roof without insulation and finishing of the walls and floor, which serves as a technical floor. However, it also needs to be equipped with a ventilation system.
It is optimal to deal with this issue at the stage of project development and construction. Rafters and gratings should be left partially open to allow air flow to circulate.
To organize the movement of air, various devices are used. For inflow - soffits with small holes that cover the overhangs from below right up to the wall of the house. The special design prevents debris and insects from entering the room, but allows air masses to flow freely.

The panels are produced in several modifications. The most common types of products:
- solid – used for installation on gazebos, verandas, terraces;
- perforated in the center - placed on the fronts, eaves of roofs;
- fully perforated - designed for roofs covered with bitumen shingles.
When covering a roof with slate, ondulin, without the use of insulation materials, natural air exchange will occur. Therefore, there is no need to organize a special ventilation system.

Gable roofs are most often equipped ventilation ducts, which are placed in the fronts. If there are small gaps on the overhangs, air circulation will occur correctly.
If the lining fits tightly to the eaves overhangs, you will need to make several holes, in accordance with the standards for organizing ventilation, or install special grilles with mesh with a pitch of 80 cm along the entire overhang.
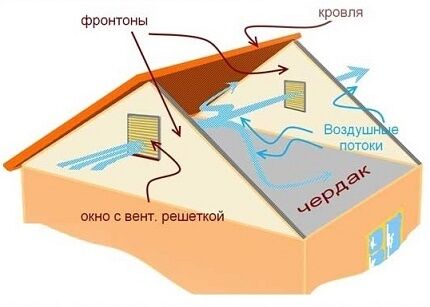
When arranging an air exchange system, it is necessary to take into account the design features and shape. For a certain type of roof, various ventilation elements are used.
For the efficient operation of an engineering system, devices are needed not only for inflow, but also elements that will remove exhaust air masses. In practice, various options are used - deflectors, making the ridge ventilated, leaving a gap around the perimeter of the roof, others.
Warm attic: is air exchange necessary?
The attic space is an integral part of the house, which can be used as additional space for permanent residence. However, this will require not only insulating it, but also properly organizing the ventilation system.
For the attic, everything is designed and arranged as they usually do in an organization ventilation of a two-story house. You should think through the design in detail and select the necessary air exchange elements, taking into account the area of the attic.

Let's consider the basic ventilation equipment schemes for various types of roofing:
- From sheet material, flexible tiles - a ventilated area is arranged by sewing a lath onto a continuous sheathing of plywood or OSB boards.
- From metal tiles – it is recommended to use lathing along the rafters.
- From slate, ondulina – no need for air to flow in and out freely counter-lattice. The material is attached to the sheathing, which will form a distance for the free entry of air flow at the eaves and exit through the ridge.
In modern homes, aerators are installed to remove waste air. The devices prevent the occurrence of condensation and also prevent precipitation from entering the room.
The living area should be ventilated no worse than other rooms. Air masses enter through attic windows and additional valves, and exit through overhead ventilation devices.
To properly ventilate a residential attic floor, use the following scheme:
- place pipes with a deflector on the roof;
- ventilation grilles are installed in the gables;
- located in the upper part of the roof or outer wall thermally insulated ventilation duct.
To install air exchange elements on the roof, you must use only durable products that are resistant to gusts of wind and precipitation.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Popular methods of installing ventilation to remove condensate:
Organization of room ventilation by making ventilation holes in the pediment:
Tips for arranging an air exchange system within an attic under a cold roof:
Installing attic ventilation in a private house is a mandatory procedure. It is important to pre-calculate the number of required holes and devices for air circulation. Since the low efficiency of the system worsens the microclimate in the premises, there is a risk of destruction of the roof structures and the service life of the building is reduced.
Please write comments in the block form below, ask questions on the topic, post photographs. Share useful information that site visitors should know. It is possible that your recommendations will help cope with the problem of dampness and condensation in the attic.



