How and with what to insulate a ventilation pipe: rules and regulations for air duct insulation
Ventilation refers to communications, the installation of which is planned at the stage of creating a private house construction project. This is justified by basic sanitary and hygienic requirements.Without proper air exchange, comfortable living is simply impossible.
We will tell you how to insulate a ventilation pipe to ensure its normal operation in winter. From the article we present you will learn which thermal insulation materials meet modern requirements. You will understand how to choose the best option for insulation.
Interested DIYers will find brief instructions on how to install a thermal insulation barrier. Those who decide to insulate the hood themselves will receive information proven in practice. Compliance with our recommendations is a guarantee of a successful result.
The content of the article:
Purpose of thermal insulation of air ducts
The installation of ventilation ducts and air ducts is subject to technical rules that dictate the choice of pipes, their placement, connection methods and mandatory thermal insulation if communications pass through unheated areas.
Ventilation pipes run throughout the entire space of the house: they start in the basement, which is often used as a technical or utility room, and end above the roof.
Not all rooms of the house are heated. Often the temperature in the basement and attic is low, which causes problems, the main ones being heat loss and condensation.
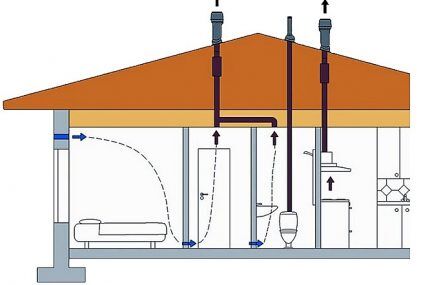
The rules for arranging ventilation are set out in SNiP 41-01-2003. There you can also find information about heating and air conditioning in general.
Thermal insulation of household ventilation air ducts performs 4 functions:
Each of these functions is very important. For example, condensation can cause big problems for home owners. Moisture that forms on the outer walls of pipes causes corrosion of the metal and in a short period of time can lead to the complete replacement of some ventilation sections. Mold forms on the walls of the attic, destroying the wood and creating an unpleasant odor.
Internal condensation is no less dangerous.Moisture seeps through the walls of pipes into living spaces and also causes negative consequences: it increases the overall level of humidity, causes deformation of wooden furniture and decoration, the appearance of fungus and mold, and poor health among residents.
Both the decrease in temperature in the bedrooms and extraneous noises that interfere with sleep are all the result of chilled ventilation pipes. If you are familiar with the problems listed above, then you can cope with them yourself by insulating the air ducts. First you need to choose the right thermal insulation material.
Requirements for material characteristics
In order for the insulation to serve for a long time, not to become damp before its time, not to become moldy, and to perform all the tasks assigned to it, it must have the following qualities.
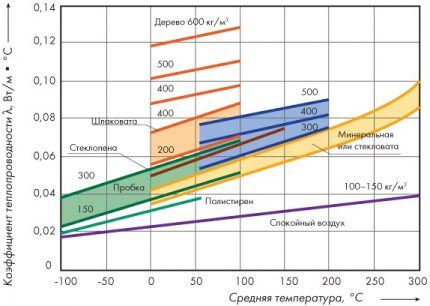
One of the most important characteristics is coefficient of thermal conductivity, expressed in W/m•°C. The degree of cooling of the air in the pipes depends on it. Manufacturers, taking into account different installation conditions, produce thermal insulation materials of various thicknesses and densities.
The second important parameter is vapor permeability. If the air ducts are prone to condensation, it first penetrates into the insulation and increases its moisture content, which increases thermal conductivity.

Next characteristic – acoustic efficiency. Air moves inside the ducts, causing vibration and noise. A running fan also creates sound waves. They are transmitted through the air and through the rigid structure of the air duct into the surrounding space and create discomfort for the residents of the house.
To reduce the noise level as much as possible, you need to think through the design features of the air ducts, make them straight, with a minimum number of turns. Noise can be significantly reduced by using sound-absorbing insulation.
Don't lose sight of quality like resistance to biological influences. The less suitable the material is for the formation of mold colonies and the proliferation of various microorganisms, the longer it will last, and along with it the structure of other building materials - for example, wood or concrete - will be preserved.

For a thermal insulation material, such a parameter as working temperature. It differs for different insulation materials, but the average range is from -35°C to +60°C.
And one more characteristic - sanitary and hygienic properties. Thermal insulation should not distribute toxic gases harmful to health.From this point of view, materials that contain components of natural origin are valued - for example, felt or mineral wool.
Review of the best modern insulation materials
The Russian market offers all kinds of thermal insulation materials, ranging from polystyrene foam and glass wool, which are used less and less, to sprayable solutions that are easy to apply.
Selection of materials for insulation of ventilation in the attic is built taking into account specific environmental conditions, installation nuances and financial capabilities.
Let's look at how you can insulate home exhaust hood pipes running in cold rooms. We offer four thermal insulation options that are suitable for independent use. Their characteristics meet the requirements and standards, and even a beginner in the construction business can handle the installation.
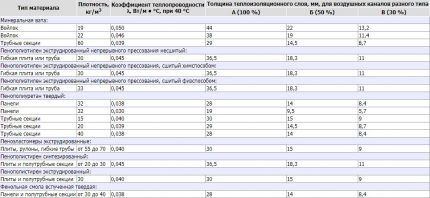
Option #1 – mineral wool
Mineral wool includes completely different categories of insulation made from glass, basalt, and slag fibers. Glass wool is considered the least effective and cheapest material, which, despite many advantages, has no fewer disadvantages.

But, unfortunately, this budget option may contain harmful phenol-formaldehyde resins, is extremely hygroscopic, requires vapor barrier, and after 3-4 years the thermal insulation function is lost by about 50%.
Due to its shortcomings, glass wool is becoming a thing of the past, and its place has been taken by basalt or stone wool.It is presented in two installation solutions: in the form of mats (thinner rolls) and shells, often foil-coated.
The shell is more suitable for insulating small-diameter pipes; ventilation ducts in the attic are often wrapped in rolled mineral wool.

Advantages:
- non-flammable, fire-resistant material, operating temperature – up to +1000°C;
- thermal insulation coefficient – on average up to 0.038 W/m•°C;
- long service life;
- minimal deformation.
Flaws:
- inexpensive varieties may contain harmful binders;
- higher cost than glass wool.
The installation method for cylinders and roll products is different. The cylinders or shells consist of 2 parts, which are held together with a locking joint. To strengthen the fixation, the seams are taped with construction tape.

Basalt wool in the form of mats or rolls is mounted differently.
Operating procedure:
- Measure the section of pipe that requires insulation.
- Cut a piece of thermal insulation to suit the size.
- Wrap the pipe in mineral wool with an overlap, like a blanket. If the insulation is thin, you can wrap it in several layers.
- Secure the “blanket” with construction tape, wrapping the pipe in a spiral along its entire length. Instead of tape, you can use annealed wire.
For rectangular ventilation ducts, another method is used: mats or slabs are “set” on special glue.
Option #2 – polyethylene foam
This material is so good that many manufacturers have started producing it. Insulation can be found under the brands “Izolon”, “Penolon”, “Tepofol”. Foamed polyethylene is somewhat reminiscent of foam rubber, but differs in large cells and technical characteristics.
You can find various varieties, including foil-coated, covered with a layer of aluminum foil. Its advantages are maximum protection from moisture and heat retention.

Depending on the brand and thickness, the material has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.031-0.051 W/m•°C, operating temperature - from -65°C to +100°C, water absorption up to 1%, service life - 10 years.
Advantages:
- strength and wear resistance;
- elasticity, ease of installation;
- resistance to chemical and biological influences;
- light weight;
- possibility of reuse.
Flaws:
- flammability class – 2G, melting occurs at temperatures above +100°C;
- high degree of smoke generation - D3;
- environmentally harmful, decomposes in natural conditions for 200 years.
We recommend using cross-linked polyethylene, which differs from non-cross-linked polyethylene in having superior technical characteristics. According to European requirements, the use of non-crosslinked (gas-foamed) varieties is prohibited.
Installation of insulation is carried out according to the instructions and is practically no different from the installation of other roll materials.
Option #3 – polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam
Many people are familiar with polystyrene foam - it is still used in packaging of household appliances to prevent damage during transportation. This is a polymer foam mass, very light due to the large amount of gas in the cells.

Expanded polystyrene is extruded polystyrene, the production of which uses the same raw materials as for the production of polystyrene foam. It has improved characteristics and is more expensive. The difference between these two materials can be seen in the table:
| Styrofoam | Expanded polystyrene | |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m•°С | 0,032-0,050 | 0,028-0,034 |
| Water absorption, %/day | 4/30 | 4/30 |
| Bending strength, kgf/m² | 0,07-0,20 | 0,40-1,00 |
| Operating temperature, °C | -50 … +75 | -50 … +75 |
| Service life, years | 25 | 50 |
Expanded polystyrene retains heat better and lasts longer; moreover, it is used to produce convenient covers for round pipes.
Advantages:
- light weight;
- resistance to biological effects;
- low cost.
Flaws:
- flammability class - G3/G4;
- smoke harmful to health;
- Possibility of insulating only round pipes.
When installing shells from extruded polystyrene foam you need to know some of the “strange things” of the material, especially when using glue. Foam plastic melts from ordinary adhesive solutions, so for additional fixation you need to purchase special glue. An alternative is to use adhesive tape or polymer mounting tape.
Option #4 – spray polyurethane foam
If previously sprayed products for insulating pipelines and other structures were used only in industry, now they are actively used in private housing construction, for example, for thermal insulation of air ducts.

Thermal conductivity of the material is 0.019-0.04 W/m•°C, flammability is G1, service life is about 20 years. The operating temperature limits are wide – -160° … +150°С.
Advantages:
- maximum adherence of the insulation to the air ducts;
- absence of seams and “cold bridges”;
- thermal insulation of structures of even the most complex configuration;
- high application speed.
Flaws:
- high price;
- skills required to operate a spray gun;
- During installation, protection is required - special clothing, goggles, and a respirator.
No special preparation of pipe material is required. Insulation in the form of foam can be applied both to individual pipes in advance, before their installation, and to the finished structure.

Operating procedure:
- Wear protective clothing, a protective mask and goggles.
- Attach the holder to the cylinder and insert the nozzle.
- Rotate the nozzle to the desired position for horizontal/vertical application of insulation.
- Apply foam to open sections of the pipeline using up/down, left/right, etc. movements.
- Check to see if there are any “bald patches” left.
As a result of proper spraying, a dense, durable layer of polymer should appear on the surface of the pipes.
In addition to the listed materials, foamed synthetic rubber and PIR boards are used for insulation of ventilation ducts. They also buy insulated pipes - but this happens less frequently and is mostly practiced at industrial facilities.
Let us add that modern materials for thermal insulation of air ducts are safe and completely ready for use. But it still doesn’t hurt to make sure that the product is certified and meets safety requirements.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Experience insulating plastic pipes in the attic:
Application of sprayed insulation "Polinor":
How to install Izolon self-adhesive insulation:
Now you know how you can independently insulate the ventilation in a private house and what materials meet all standards. But do not forget that the correct choice of material will not solve all problems: you need to install the thermal insulation correctly and without errors.
Before work, we recommend making sure that the ventilation system is operating at full capacity, is not dirty, and does not require repair or alteration. If troubles occur due to errors in pipe installation, no amount of insulation will help.
Do you have information on the topic of the article that is worth sharing with site visitors? Do you have technological subtleties in your arsenal that only you know? Please write comments in the block below, ask questions and post photographs.



