Brass threaded fittings - types of fastening and purpose
Brass threaded fittings - the most common type of pipe fastening, because the variety of offers is greater than that of connecting elements made of other metals. They can be used to connect workpieces made of different materials: steel, polypropylene, low-density polyethylene, metal-plastic, etc. But besides the advantages, do this fittings also have disadvantages? What are the nuances of installing it?
The content of the article:
What is brass - characteristics of the metal
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc in varying proportions. This composition makes the material highly plastic and high-tech. In terms of corrosion resistance, it is inferior to copper, so brass fittings are coated with chromium or nickel. To the advantages we must add low thermal and electrical conductivity.
Brass Specifications:
- electrical resistance – 0.07-0.09 Ohm/m, for steel 13-18;
- heat capacity – 0.377 J/kg K, this is at a temperature of +20 ℃;
- density – 3000-5500 kg/m³;
- Brass melts at a temperature of +900 ℃.
It is these indicators that make brass fittings competitive.
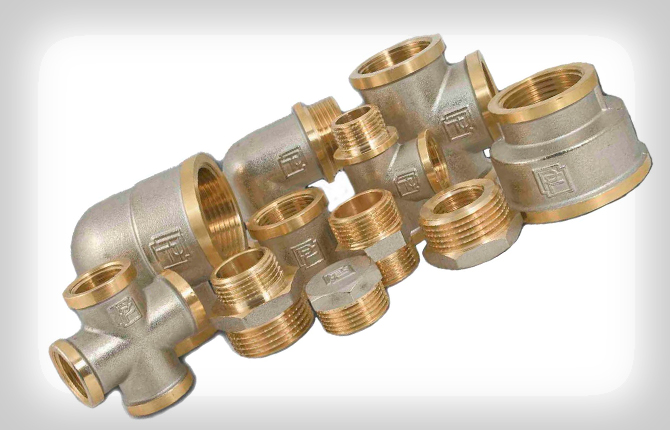
What do brass threaded fittings look like?
All fittings made from copper alloys are manufactured in accordance with GOST number 35585-2013. This applies to both threaded elements and crimp elements. Since pipes can be connected not only along one axis, the fittings can accordingly have different configurations.
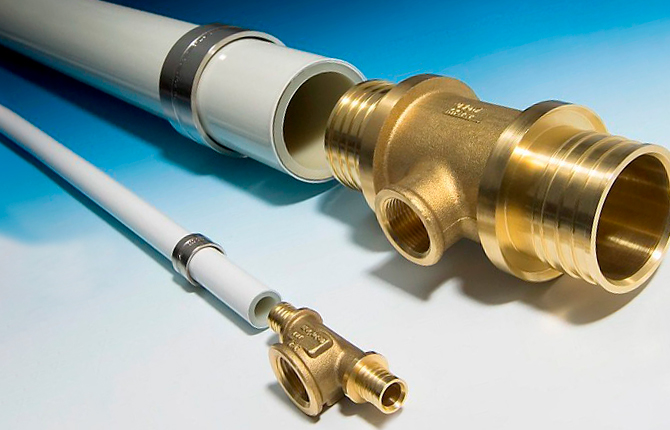
Often it is necessary to connect two circuits with different cross-sections of workpieces. Such elements are also made of brass. The main difference between threaded models is internal or external thread.There are no other distinctive features.
Why are brass threaded fittings needed?
Their main purpose is to connect pipe lines to each other. But among the threaded models there are those that are installed at the ends of pipeline circuits. For example, a plug or fitting through which plumbing equipment, measuring instruments, shut-off valves and other devices are connected to the pipe. With the help of the latter, the flow of the medium passing through the pipe circuit is regulated.
Types of brass threaded fittings for pipes made of HDPE and other materials
There are many varieties of brass fittings:
- Sgony, they are couplings. These are straight connecting elements with external or internal threads. Used to connect pipes located on the same axis. Their length is standard: 100, 150 and 200 mm. There are smaller ones called kegs.
- Bends, they are also corners. Pipe circuits located at an angle to each other are connected. Tilt angle – 45-120º.
- Tees. Using this element, three pipes are connected. One of them is located perpendicular to the other two. Typically this connecting element is mounted on the main pipeline from which the auxiliary circuit departs.
- Cross. Four pipes are connected, located at 90º angles to each other.
- American. This is a type of coupling that uses a union nut. Convenient design. The variety of forms is great.
- Stub. Used only if it is necessary to plug a pipe.
- Nipple. On one side there is a thread, on the other there is a pipe for the hose. It is used to connect the pipe and the measuring device.
- Futorka.In shape and design, it is a plug, only with a through hole in which an internal thread is cut. Used to connect devices to pipelines.
- Adapter. It is installed on pipelines in two cases. The first is when you need to connect two pipes of different diameters. It has two threads, either external or internal. The second is when you need to connect the pipeline to a device or shut-off valve. It has one external thread, the other internal.
Operating conditions are one of the main components of the long-term performance of brass threaded fittings. It's all about brass and its technical characteristics. You cannot install them in pipelines, through which media with temperatures above +2000 ℃ and pressure greater than 20 bar move, if there is no steam. If steam is present, then no more than 10 bar.
Brass is a heavy metal. Products made from it are also heavy. Some manufacturers skimp on wall thickness, which reduces quality. For example, a bend or coupling with a diameter of 20 mm cannot weigh less than 200 g. Thin walls are a reason not to purchase such an element.
Another important point regarding the protection of threaded brass fittings. The thickness of the chrome-plated layer should be in the range of 0.3-1.4 microns, nickel-plated - 12.6-15.3 microns. If the protective layer is thinner, the connection will not last long. If it is thicker, the layer will crack within a short time. In both cases, there is a high probability of metal corrosion.
Threaded brass fittings are very popular, so all hardware stores sell them.For example, Leroy-Merlin, Santehmir and others. When choosing, you need to pay attention not only to the design, but also to the thickness of the walls and the quality of the coating.
Brass threaded fittings. Fittings for connecting pipes. Review: video.
Have you ever bought brass threaded fittings? What did you pay attention to? Tell us in the comments. Save the article to bookmarks and share it on social networks.






There are no complaints about brass fittings. An excellent plumbing material - inexpensive, reliable and easy to use. Five plus is my rating.
Here, ease of use is the main sign of quality. Anyone, even a person who does not understand plumbing, can cope with connecting pipes.