Heating elements for heating: types, principle of operation, rules for selecting equipment
Electric heating elements have not changed their design for decades and remain in demand in heating equipment.The shape of these devices and construction materials change, but the principle of operation and efficiency remain unchanged. For a competent selection, information about the differences and characteristics will be useful. Do you agree?
You will learn what heating elements for heating are and how they work. We have described in detail the types of heating elements and provided indisputable arguments for an informed choice of the optimal type. Taking into account our recommendations, you will purchase the required device without errors.
The content of the article:
Purpose of heating heating elements
Electric heating elements have gained popularity due to their versatility and high efficiency. All the electricity they consume is used for its intended purpose - heating the surrounding space.
The main heating devices where heating elements are used are:
- Portable and stationary oil electric heaters.
- Water heating radiators.
- Bathroom heated towel rails.
- Electric fireplaces.
- Electric convectors.
- Electric boilers.
The specified equipment can be used as a main or additional heating source.It is inexpensive, easy to install and does not require special skills to operate.

Internal structure of electric heaters
It is convenient to consider the device using the example of a tubular model. An electric heater is a ceramic or metal tube filled with a thermal conductor with a spiral located inside. In the place where the tube is fixed to the flange there are insulating bushings that make it impossible for the conductive spiral to contact the heating element body.
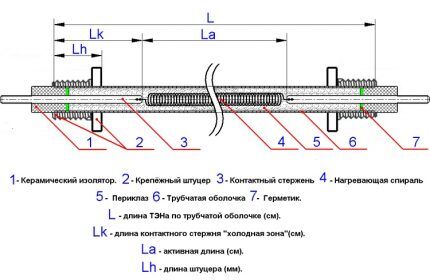
The electric heater is mounted primarily with a flange connection, which allows the internal environment of the heating device to be sealed from the external space. The disadvantage of this design is the impossibility of replacing the spiral if it burns out internally.
Operating principle of heating elements
The heating element works according to the following principle. When connected to the network, the internal spiral is heated and energy is transferred to the thermal conductor and the outer shell. The heat is then transferred to the surrounding fluid, air or solid material.
When heating a heating element immersed in oil or water, convection currents are created around the tube, which mix the coolant and contribute to its uniform heating.
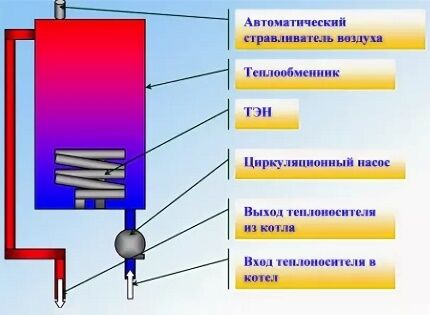
In liquid-free heating devices, the heating temperature is usually limited so as not to damage surrounding parts or cause a fire.
To speed up heat transfer, they often use a fan, which circulates air both inside the device and in the room surrounding it.
Types of heating elements for heating devices
The simplicity of manufacturing heating elements does not always translate into convenience for users. Many manufacturers produce electric heaters with a specific shape and mounting. If they break, they are quite difficult to buy in a store. Therefore, to make the right choice, it is necessary to study all possible design options.
Tubular models for domestic heating
The tubular design of electric heaters is the most common in mobile oil heaters, portable and wall-mounted electric radiators. Heat transfer in them can occur using: convection, infrared radiation or thermal conductivity.

The shape and length of the tube in such devices can be any and is dictated only by design features. For example, heating element mycatremic heater is a coil located behind the mineral plate. When heated, the plate emits infrared heat.
Its most common characteristics are:
- diameter – 5-18 mm;
- length – 200-6000 mm;
- shell material – steel, stainless steel, ceramics, copper;
- power – 0.3-2.5 kW.
Heating elements with a power of more than 2.5 kW are not used in household heating devices, because apartment wiring simply cannot withstand the greater load.
Finned version of electric heaters
Finned devices are a modification of a tubular heating element. Their feature is the presence of many thin steel plates located along the entire length of the device. This design dramatically increases the area of contact with the environment, ensuring a high heating rate.

Finned models are used mainly in heaters for air heating. They provide a quick increase in room temperature, especially with a built-in fan.
Block designs of heating elements
The block version consists of several tubular heaters combined on the basis of a single mounting.

This design is used by a combination of two factors:
- The need for increased device power and high heating rate of the working environment.
- The impossibility of rapid transfer of thermal energy from the spiral to the environment due to the small area of the outer shell.
In fact, in a block heating element, the load on each heating tube is reduced and the heat transfer rate is increased. Such devices are included in domestic heating boilers and industrial electric heating installations.
The power of block models can be 5-10 kW, so when placing them in an apartment, it is necessary to extend an additional electrical cable into the room.
Cartridge-type devices
Cartridge heating elements have the form of a tube with one free end, which is due to the peculiarity of their installation. The outer shell is usually made of polished steel to provide maximum contact with the surrounding material. Such tubes are tightly inserted into the corresponding hole in the heating device.

Fixation of cartridge models is carried out mainly using a flange connection. They are usually used in industry to heat the working parts of extruders.
There are other structural types of heating elements, but they are used mainly in industrial production and do not affect the topic under consideration.
Additional functions of electric heaters
Above we discussed the simplest designs of devices that do not have any built-in adjustment mechanisms.

But electric water heaters can be equipped with simple automation that provides the device with additional functions.
These include:
- Thermoregulation. Heating elements with a built-in thermostat for heating have a temperature sensor that is triggered when the working environment is heated to a certain level. The electric heater is adjusted from the outside of the flange.
- Antifreeze. This function is provided by a simplified thermostat, which operates only when the temperature drops to 0-2°C.It prevents water from freezing in heating pipes, consuming a minimum of electricity.
- Turbo heating, which provides forced heating of the working environment during the initial start-up of the equipment. It must be remembered that the electrical wiring of the room must withstand a short-term increase in power.
There are not many devices that support additional functions, because the operation of heating devices as a whole is often regulated using a separate automation unit.
How to choose a heating element for heating equipment?
Choosing Heating element for replacement in a water heater or in a radiator, you need to pay attention to its power, design, tube length and the presence of additional features. Therefore, before purchasing, you need to find out as much as possible about all its characteristics.
Calculation of device power
The high power of a heating element is not always a positive quality.
When choosing, it is important to consider several factors that are related to the level of energy consumption:
- maximum heat transfer power of the heating device as a whole;
- electrical wiring options;
- room volume.
You cannot buy a device with a power that is more than 75% of the maximum heat transfer level of heating equipment.
For example, there is a radiator with 10 sections, each of which releases 150 W of heat to the air, a total of 1.5 kW. When installing an electric heater with a power of 2 kW into it, the surface of the battery will not be able to quickly release all the energy generated. As a result, the heating element will constantly turn off due to overheating.

In apartments with worn-out wiring, the constant load on the outlet should not exceed 1.5-2 kW, otherwise it may catch fire and lead to dire consequences. Therefore, before purchasing a heating element, you need to check the condition of the wiring and, if necessary, dismantle the old one and lay a new electrical network.
When the issue with electrical equipment and equipment capabilities has been resolved, you can begin to calculate the required power to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room.
In well-insulated houses and apartments, a level of 40 W/m will be sufficient3. And if there are cracks in the windows, the heating power should be increased to 60-80 W/m3. You can buy a specific model only after taking into account all the energy factors described above.
Consideration of design features
Most heating elements have an alloy steel shell, which provides strength and resistance to corrosion. Copper devices are used primarily in water heaters, although there are no restrictions on their use in homemade radiators.

Also, when choosing, it is necessary to take into account the direction of the thread of the plug, which can be right or left. Different models of electric heaters also differ in flange diameter. They can range in size from 0.5 to 1.25 inches.
Typically, a heating element from a good manufacturer comes with a brief instruction manual that describes its design parameters. Studying them will help you buy a device that will exactly fit your existing heating equipment.
Heating tube length
The length of the tube is one of the main characteristics that determine the efficiency of the device.
Its large length with equal power leads to an increase in the surface area of the electric heater and acceleration of heat exchange with the working environment. This has a positive effect on the durability of the heating element and the coolant circulation rate.

It is desirable that the tube runs along the entire length of the working area of the heating device, without reaching the opposite wall by 6-10 cm. This recommendation will allow you to quickly and evenly warm up the coolant.
Availability of additional functionality
It is not always necessary to overpay for the additional capabilities of heating elements. If the heating device is used as an auxiliary device and does not have its own built-in automation, then purchasing a model with a thermostat makes sense.
But if a radiator or electric convector has its own temperature sensors and temperature control mechanisms, additional functions will remain unclaimed.

Therefore, it is recommended to purchase expensive electric heaters with built-in automation only if there is a clear need for such equipment. If it is necessary to individually select the temperature background, it is better to buy thermostat in socket, which can be used periodically.
As for the manufacturers of heating elements, their choice is not important. The main suppliers are companies from Russia, Ukraine, Turkey and Italy.The quality of their products is approximately the same, so there is no point in overpaying for the brand.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Practical overview of heating elements of various types:
Video #2. Review of heating element with thermostat:
Video #3. Features of a block heating element used in electric heating boilers:
Buying a heating element for heating appliances is not an easy task. To do this, you need to clearly know the characteristics of the equipment into which the electric heater is built. Therefore, you need to choose a specific model only after a thorough analysis of its parameters.
Please write comments, ask questions, publish photographs related to the topic of the article in the block below. Tell us about how you selected a heating element to replace in an electric boiler or mobile heater. Share what was the decisive argument in your choice for you personally.




I have an idea to try electric heating instead of gas. I have my own boiler, so my hands are itching to experiment. I want to put a heating element on the last point. Bimetallic radiators, coolant – water.
This is still at the level of plans, because I can’t figure out whether it will be profitable for the money, or, taking into account the costs of the heating element and additional electronics, a waste of money?
Hello. I don’t know about your project, but in general, any electric is usually more expensive than gas, as Alexey correctly noted.
I have a 6 kW electric boiler installed in one house. In winter, we turn it on on regular days for 2. There are 24 hours in a day. Multiply by 2 = 48 kW x 30 days = 1440 kW x tariff 3.40 = 4896. If the winter is very frosty, the amount is doubled.
Gas in a second house of equal insulation and square footage costs me half as much. Add here the change of wiring and your costs for heating elements and so on.
As a reserve, yes, to replace gas - stupid, it will cost much more. I myself heat with solid fuel (coal) + electric, if I heat only with an electric heating element, the bill comes out to about 10k in the cold months (-20 -30 + wind) (day/night tariff 5.09/1.32 Khabarovsk). If you leave the heating elements only at night until the morning, it will reach 5k. I would love to connect the gas, but there is no pipe, and it’s inconvenient for us to carry cylinders.
Hello. I want to install 10-section bimetallic radiators in the garage. I want to connect two radiators into one. What power heater should I install?
Hello, my friend Ramin, I’m from Baku, I have a question for you. My house has 2 floors, each floor is 80 sq. m. On the floors there is underfloor heating, please tell me which heater according to my budget I should choose for underfloor heating. The water in the pipes totals about 170 liters. We almost never have sub-zero weather. Thank you.
Hello, please tell me, I have a 12 kW heating boiler from the Bastion company, the heating elements burn out, the first burned out after three weeks of use, I replaced it, the second burned out after 1.5 months, I bought the heating element specifically for this electric boiler, please tell me if a regular heating element will work for 12 kW inexpensive, example from a cheap 12 kW boiler, for my boiler the price of the heating element is 3000 rubles,
For a cheap 1000, I checked with a multimeter the Ohm power is the same, but from a cheap boiler the heater is a little shorter and the thickness of the heater itself is smaller