Gas consumption from a gas holder for heating: how to calculate + tips for minimizing
It is well known that gas tanks are increasingly used for heating houses and cottages with permanent or long-term residence.It is also undisputed that a large share of the budget for heating a house is the cost of fuel. In our case it is liquefied gas.
Therefore, a prudent home owner must know how to correctly calculate the gas consumption from a gas tank for heating and be able to predict the intervals between refills. This is also relevant because gas delivery, as a transport service, has its own quite significant price.
We will help you in an accessible manner to independently calculate the consumption of liquefied gas for heating your home in gas supply systems with a gas holder. This knowledge is relevant when designing the construction of a new house and planning the reconstruction of an existing heat supply system. Correctly carried out calculations will allow you to control gas consumption and reduce gas costs.
The content of the article:
Factors affecting gas consumption
The gas holder has the form of a volumetric tank that is filled with liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). This is a mixture of two gases - propane and butane.
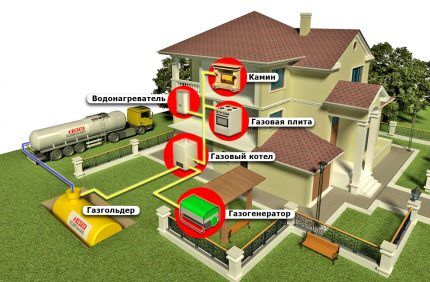
Storing gas in such tanks, with its further use for heating the house, may be due to the following factors:
- the inability to tie into the main gas pipe or the high cost of such a connection;
- constant and unresolved by gas services problems with gas pressure in the central pipeline.
For the normal functioning of most gas boilers gas pressure in the pipeline must be at least 35 mbar. This standard is often not maintained in main gas pipelines and ranges only from 8 to 22 mbar.
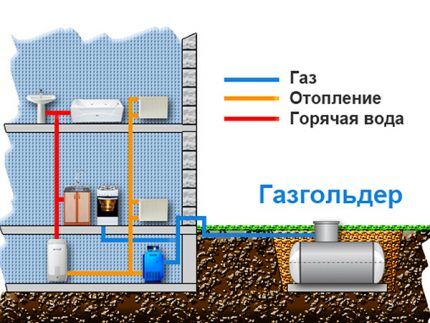
To determine the volume of liquefied gas in a tank, there are mechanical level gauges or more modern remote telemetry systems. Such equipment can be supplied complete with the tank or purchased separately. The average daily gas consumption can also be determined by the difference in readings gas meter, if available.
But a more accurate answer to the question of how much gas in a gas holder is enough to heat a home, what its consumption is and how to minimize costs for it, mathematical calculations will help. And this despite the fact that objectively such a calculation will be of an average nature.
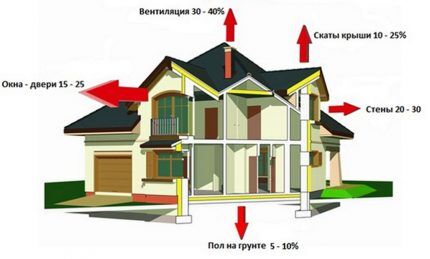
It should be taken into account that gas consumption is influenced by the following factors:
- climate of the region and wind rose;
- square footage of the house, number and degree of thermal insulation of windows and doors;
- material of walls, roof, foundation and the degree of their insulation;
- number of residents and mode of their stay (permanently or periodically);
- technical characteristics of the boiler, the use of additional gas appliances and auxiliary equipment;
- number of heating radiators, presence of heated floors.
These and other conditions make the calculation of fuel consumption from a gas tank a relative value, which is based on average accepted indicators.
Gas boiler power calculation
The main share of fuel consumption is heating. An important parameter of any house or apartment that affects the amount of gas spent on heating is the heat loss indicator. The task of heating is precisely to correctly compensate for these losses, creating conditions for comfortable living.
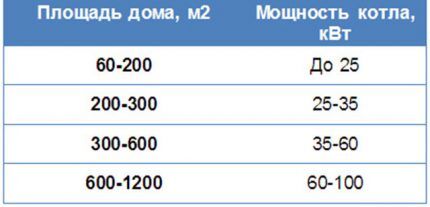
As a standard for calculations, we will take a house located in an area with an average climate, in satisfactory condition and insulated in accordance with technology. House area 80 m2.
The average values of heat loss and boiler power can be determined by the quadrature of the area.
The formula looks like:
Q = S × Рр /10, Where
Q—calculated heat losses (kW);
S - area of premises that are heated (m2);
Рр – specific power of a gas boiler (kW/m2) — power for every 10 m2.
Specific power for heating an area of 10 m2 has already been approximately established, taking into account amendments for regions with different climates. For our reference house, located, for example, in the Moscow region, Рр = 1.2 - 1.5 kW.
Taking into account the area of the house 80 m2, the optimal power of the heating system will have the following value:
Q = 80 × 1.2 / 10 = 9.6 kW.
Although simplified, this formula reflects the most accurate results.
Often, for convenience in carrying out calculations, unit is taken as the value of specific power. Based on this, the power of the heating system is taken at the rate of 10 kW per 100 m2 heating areas.
The second option, but accepted with a greater degree of error, is to calculate the cost of thermal energy for the heat loss of a building by cubic capacity - the volume of heated premises. Depending on the climate zone, 30 - 40 W are allocated for heating one cubic meter of a room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m.
Calculation of gas flow from a gas tank
Calculating the heating consumption of the mixture from the gas storage used in the home heating system has its own characteristics and differs from calculating the consumption main natural gas.
The predicted volume of gas consumption is calculated using the formula:
V = Q / (q × η), Where
V is the calculated volume of LPG, measured in m³/h;
Q—calculated heat losses;
q is the smallest specific value of the heat of combustion of the gas or its calorie content. For propane-butane this value is 46 MJ/kg or 12.8 kW/kg;
η – efficiency of the gas supply system, expressed in absolute value per unit (efficiency/100). Depending on the characteristics of the gas boiler, the efficiency can range from 86% - for the simplest ones, to 96% - for high-tech condensing units. Accordingly, the value of η can range from 0.86 to 0.96.
Let's assume that the heating system is planned to be equipped with a modern condensing boiler with an efficiency of 96%.
Substituting the values we accepted for calculation into the original formula, we obtain the following average volume of gas consumed for heating:
V = 9.6 / (12.8 × 0.96) = 9.6 /12.288 = 0.78 kg/h.
Since the LPG filling unit is usually considered to be a liter, it is necessary to express the volume of propane-butane in this unit of measurement. To calculate the number of liters in the mass of a liquefied hydrocarbon mixture, it is necessary to divide kilograms by density.
The physics of the transition of LPG from liquid to vapor (working) state is as follows: propane boils at minus 40 °C and above, butane - from 3 °C with a minus sign. Accordingly, a 50/50 mixture will begin to transition into the gaseous phase at a temperature of minus 20 °WITH.
For middle latitudes and a gas tank buried in the ground, such proportions are sufficient. But, in order to protect yourself from unnecessary hassle, it is optimal in winter conditions to use a mixture with at least 70% propane content - “winter gas”.
Taking the calculated density of LPG equal to 0.572 t/m3 - propane/butane mixture 70/30 at a temperature of - 20 ° C), it is easy to calculate the gas consumption in liters: 0.78 / 0.572 = 1.36 l/h.
Daily consumption with such gas selection in the house will be: 1.36 × 24 ≈ 32.6 l, during the month - 32.6 × 30 = 978 l. Since the obtained value was calculated for the coldest period, adjusted for weather conditions, it can be divided in half: 978/2 = 489 liters, on average per month.

In the area we took as an example (Moscow region), this period averages 214 days.
Gas consumption for heating during the year when calculated will be: 32.6/2 × 214 ≈ 3488 liters.
Selecting the optimal gas tank for consumption
A gas tank is expensive equipment that is purchased and installed for more than one year. Not only the efficiency of the home heating system largely depends on its correct choice. Heating costs may indirectly depend on the type and type of liquefied gas storage facility.
Comparison of above-ground and underground gas tanks
An above-ground gas holder is a cheaper option for autonomous gasification. Such tanks are usually smaller in volume and their installation does not require expensive excavation work.
But, when using above-ground gas tanks for heating needs in winter, it is necessary to take into account that the evaporation of the propane-butane mixture during this period will be reduced and problems with gas pressure are possible.

It is possible, of course, to reduce the temperature threshold for the transition of LPG into the gaseous phase of fuel due to a higher content of propane in the mixture. But this will entail additional costs, since such gas is more expensive than butane.
Underground gas tanks are the most popular storage facilities for LPG.

The depth of immersion of the container should be such that the layer of soil above it is at least 0.6 m. This will protect the storage from freezing and mechanical damage.
Vertical or horizontal gas holder
There are two types of recessed gas tanks in shape:
- Vertical.
- Horizontal.
These containers differ from each other not only in design, but also functionally - in the surface area of the liquefied mixture, called the “evaporation mirror”.
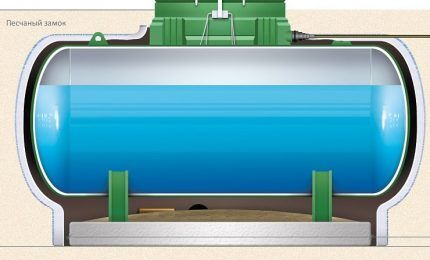
Vertical storage facilities are more often used in autonomous gas systems of small houses or cottages, if their full heating is not required in winter.

Features of a mobile gas tank trailer
Solving the problem of heating and creating comfortable living conditions in winter at dachas with temporary residence, objects under construction, where gas storage equipment is impractical or technically impossible, allows mobile gas tank.
This is a trailer-mounted tank with a capacity of 500-600 liters. How long such a gas tank with a capacity of 600 liters will last can be predicted by taking the average standard used - 30-40 liters of liquefied gas per 1 square meter of room.

It should be understood that the operation of a mobile gas tank as a ground-based tank in winter or in northern regions will require insulation and forced heating of the tank. For this reason, a trailed gas tank is not a completely acceptable heating option.
How to choose a gas tank by volume
Of the typical underground gas tanks, tanks with volumes of 2700 liters and 4850 liters are optimally suitable for country houses and cottages.
When choosing the standard size of a gas storage facility, the following factors must be taken into account:
- If you live permanently in a house with autonomous heating, it is advisable to refill the tank twice a year. This is due to different concentrations of butane and propane in mixtures intended for use in summer and winter.
- The tank should be filled with liquefied phase by 85%. The remaining free volume in the storage is a vapor cushion for hydrocarbons in the evaporation phase.
Therefore, when calculating how much gas can be enough in a gas holder with a capacity of 2700 liters or in a gas storage facility of other sizes, it is necessary to take into account that the rated total volume of a gas holder and its filling volume are not the same thing.
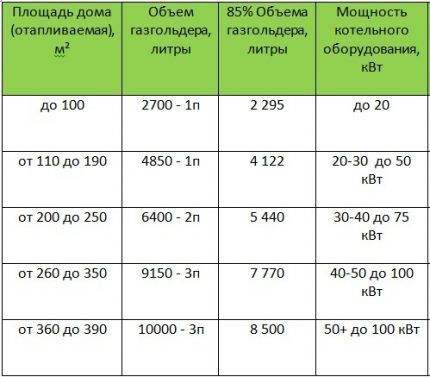
Our calculation of the average values of liquefied gas withdrawal from a gas tank and generally accepted standards allow us to determine the frequency of refilling gas tanks. With an average annual consumption of 30 liters of gas per 1 m2 heated area, refilling liquefied gas with a volume of 2295 l in a tank of 2700 l for a house 100 m2 will be enough for 9 months.
Using the same method, but for a house 150 m2, we calculate how long LPG will last in a heating system from a 4850 liter gas tank. During the year, 4500 liters are consumed, so a filling volume of 4122 liters is enough to heat the house for 10 months.
From the calculations it is clear that refueling will have to be done twice a year. And this is economically justified due to the use “summer” and “winter” LPG.
Tips for saving gas
You can reduce gas consumption from a gas tank by performing the following energy-saving measures:
- insulation of walls, roofs, attics, basement floors;
- replacing old window units with modern double-glazed windows with frost-free profiles;
- optimal setting of boiler parameters;
- installation of an energy-efficient condensing-type gas boiler for heating;
- usage collector heating system, which has a higher efficiency and the ability to regulate the coolant supply on each heating device;
- equipping heating radiators with thermostats.
A good gas saving effect is achieved through the installation of controllers that automate the process of heat supply control.

Moreover, modern controllers are, as a rule, smart devices with which you can remotely control the boiler from a mobile phone.
An inexpensive alternative to such remote-controlled devices are programmable or daily thermostats, which also allow you to save energy.
A modern solution for saving gas from an autonomous storage facility is smart home system.
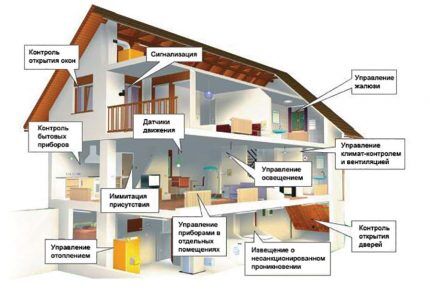
The climate control function in the house can be installed separately or integrated into a general set of “utilities”.
Such technologies make it possible to economically use gas for heating throughout the day in individual rooms. You can configure the system to operate in heating mode when there are no residents and turn on full heating remotely before arriving home.
The main problem with implementing a “smart home” climate control system is the relatively high cost of the issue and the need for design before installation of the heating system.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
An interesting method for calculating gas consumption for heating and tips for reducing gas costs:
Expert advice on economically feasible choice of gas tank volume:
9 tips for reducing gas consumption used to heat your home:
It is necessary to understand that all the calculations that we propose to use when using gas from a gas tank are rather arbitrary. Even a specialist cannot determine and predict exactly how much liquefied gas will be consumed over a specific period.
But the presented methodology, based on the practice of operating autonomous gas systems, displays reliable average gas consumption values.
These calculations and the useful tips provided will make it possible to correctly select the optimal gas tank and plan the frequency of its refills.
If you have experience using gas holders for heating, please share it with our readers. Tell us about the intricacies of using such equipment. Write your comments, ask questions - the contact block is located below.




As far as I understand, a gas tank is an option for those who do not have a pipe nearby? In some ways is it superior to gas from the main line, or is it a plus in autonomy?
There is only one advantage from a gas tank: it will provide gas if there is no main pipe nearby. Well, or they won’t build the gas pipeline according to our moronic laws (as in my case).