Gas discharge lamps: types, design, how to choose the best ones
Do you want to purchase gas discharge lamps to create a special atmosphere in your room? Or are you looking for bulbs to stimulate plant growth in your greenhouse? Equipping with economical light sources will not only make the interior more attractive and help in plant growing, but will also save energy. Isn't that right?
We will help you understand the range of gas-discharge lighting fixtures. The article discusses their features, characteristics and scope of application of high and low pressure light bulbs. Illustrations and videos have been selected to help you find the best option for energy-saving lamps.
The content of the article:
Design and characteristics of discharge lamps
All the main parts of the lamp are enclosed in a glass bulb. This is where the discharge of electrical particles occurs. Inside there may be sodium or mercury vapor, or any of the inert gases.
Options such as argon, xenon, neon, and krypton are used as gas filling. Products filled with vaporous mercury are more popular.
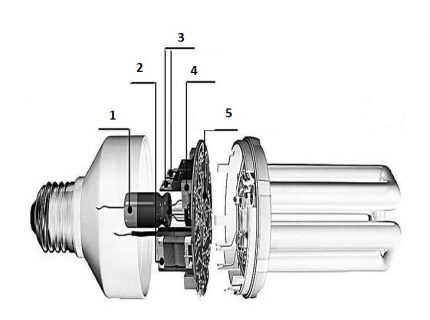
The capacitor is responsible for operation without blinking. The transistor has a positive temperature coefficient, which ensures instantaneous start-up of the GRL without flickering. The work of the internal structure begins after the generation of an electric field takes place in the gas-discharge tube.
During the process, free electrons appear in the gas. Colliding with metal atoms, they ionize it. When individual of them transition, excess energy appears, generating sources of luminescence - photons. The electrode, which is the source of the glow, is located in the center of the GRL. The entire system is united by a base.
The lamp can emit different shades of light that a person can see - from ultraviolet to infrared. To make this possible, the inside of the flask is coated with a luminescent solution.
Areas of application of GRL
Gas discharge lamps are in demand in a variety of fields. Most often they can be found on city streets, in production workshops, shops, offices, train stations, and large shopping centers. They are also used to illuminate advertising billboards and building facades.
GRLs are also used in car headlights. Most often these are lamps with high luminous efficiency - neon models. Some car headlights are filled with metal halide salts, xenon.
The first gas-discharge lighting devices for vehicles were designated D1R, D1S. Next - D2R And D2S, Where S indicates a floodlight optical design, and R - reflex. GR light bulbs are also used for photography.
During photography, these lamps allow you to control the light output. They are compact, bright and economical. The negative point is the inability to visually control the light and shadows that the light source itself creates.
In the agricultural sector, GRLs are used to irradiate animals and plants, and to sterilize and disinfect products.For this purpose, lamps must have wavelengths in the appropriate range.
The concentration of radiation power in this case is also of great importance. For this reason, powerful products are the most suitable.
Types of gas discharge lamps
GRLs are divided into types according to the type of glow, such a parameter as pressure, in relation to the purpose of use. All of them form a specific luminous flux. Based on this feature, they are divided into:
- fluorescent devices;
- gas-light varieties;
- induction options.
In the first of them, the light source is atoms, molecules, or combinations thereof, excited by a discharge in a gaseous medium.
Secondly, phosphors, the gas discharge activates the photoluminescent layer covering the flask, as a result, the lighting device begins to emit light. Lamps of the third type operate due to the glow of electrodes heated by a gas discharge.

Depending on filling arc discharge devices divided into mercury, sodium, xenon, metal halide lamps and others. Based on the pressure inside the flask, their further separation occurs.
Starting from a pressure value of 3x104 and up to 106 They are classified as high pressure lamps. Devices fall into the low category with a parameter value from 0.15 to 104 Pa. More than 106 Pa - extra high.
Type #1 - high pressure lamps
RLVDs differ in that the contents of the flask are subject to high pressure. They are characterized by the presence of a significant luminous flux combined with low energy consumption. These are usually mercury samples, so they are most often used for street lighting.
Such discharge lamps have solid light output and operate efficiently in bad weather conditions, but they do not tolerate low temperatures well.
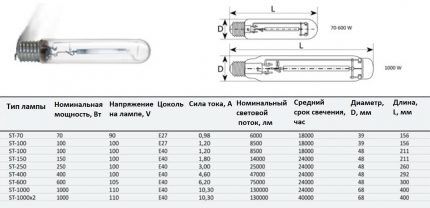
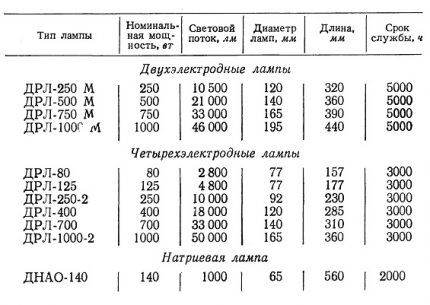
There are several basic categories of high pressure lamps: DRT And DRL (mercury arc), DRI - the same as DRL, but with iodides and a number of modifications created on their basis. This series also includes arc sodium (DNAT) And DKsT — arc xenon.
The first development is the DRT model. In the marking, D stands for arc, the symbol P stands for mercury, and the fact that this model is tubular is indicated by the letter T in the marking. Visually, this is a straight tube made of quartz glass. On both sides there are tungsten electrodes. It is used in irradiation installations. Inside there is some mercury and argon.

The lamp is connected to the network in series with throttle using a resonant circuit. The luminous flux of a DRT lamp consists of 18% ultraviolet radiation and 15% infrared radiation. The same percentage is visible light. The rest is losses (52%). The main application is as a reliable source of ultraviolet radiation.
To illuminate places where the quality of color output is not very important, DRL (mercury arc) lighting devices are used. There is practically no ultraviolet radiation here. Infrared is 14%, visible is 17%. Heat losses account for 69%.
The design features of DRL lamps allow them to be ignited from 220 V without the use of a high-voltage pulsed ignition device.Due to the fact that the circuit contains a choke and a capacitor, fluctuations in the light flux are reduced and the power factor increases.
When the lamp is connected in series with the inductor, a glow discharge occurs between the additional electrodes and the main adjacent ones. The discharge gap is ionized and as a result a discharge appears between the main tungsten electrodes. The operation of the ignition electrodes stops.
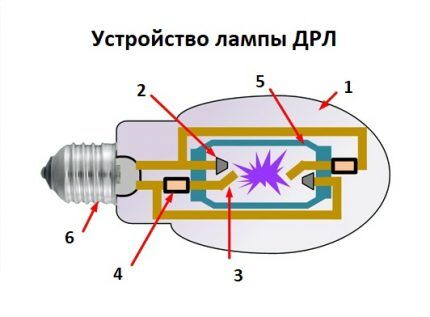
DRL burners generally have four electrodes - two working, two igniting. Their interior is filled with inert gases with a certain amount of mercury added to their mixture.
DRI metal halide lamps also belong to the category of high-pressure devices. Their color efficiency and color rendering quality are higher than the previous ones. The type of emission spectrum is influenced by the composition of the additives. The shape of the bulb, the absence of additional electrodes and phosphor coating are the main differences between DRI lamps and DRL lamps.
The circuit by which the DRL is connected to the network contains an IZU - a pulsed ignition device. The lamp tubes contain components belonging to the halogen group. They improve the quality of the visible spectrum.
As it warms up, both the mercury and the additives evaporate, thereby changing the resistance of the lamp, the luminous flux emitting the spectrum. DRIZ and DRISH were created on the basis of devices of this type. The first of the lamps is used in dusty, damp rooms, as well as in dry ones. The second is covered by color television footage.
The most effective are HPS sodium lamps. This is due to the length of the emitted waves - 589 - 589.5 nm. High pressure sodium devices operate at a value of this parameter of about 10 kPa.
For the discharge tubes of such lamps, a special material is used - light-transmitting ceramics. Silicate glass is unsuitable for this purpose, because sodium vapor is very dangerous for him. The working vapors of sodium introduced into the flask have a pressure of 4 to 14 kPa. They are characterized by low ionization and excitation potentials.
To compensate for the loss of sodium that inevitably occurs during the combustion process, a certain excess of it is necessary. This gives rise to a proportional dependence of the pressure indicators of mercury, sodium and cold point temperature. In the latter, condensation of excess amalgam occurs.
When the lamp burns, evaporation products settle on its ends, which leads to darkening of the ends of the bulb. The process is accompanied by an increase in the temperature of the cathode and an increase in the pressure of sodium and mercury. As a result, the potential and voltage of the lamp increases. When installing sodium lamps, ballasts from DRL and DRI are unsuitable.
Type #2 - low pressure lamps
In the internal cavity of such devices there is gas under pressure lower than the external one. They are divided into LL and CFL and are used not only for lighting retail outlets, but also for home improvement. Fluorescent lamps in this series are the most popular.
The conversion of electrical energy into light occurs in two stages.The current between the electrodes provokes radiation in mercury vapor. The main component of the radiant energy appearing in this case is short-wave UV radiation. Visible light is close to 2%. Next, the arc radiation in the phosphor is transformed into light.
The markings of fluorescent lamps contain both letters and numbers. The first symbol is the characteristic of the radiation spectrum and design features, the second is the power in watts.
Decoding letters:
- LD — fluorescent daylight;
- LB — white light;
- LHB - also white, but cold;
- LTBS - warm white.
Some lighting devices have improved the spectral composition of the radiation in order to obtain more advanced light transmission. Their markings contain the symbol “C" Fluorescent lamps provide rooms with uniform, soft light.

The LL emission surface is quite large, so it is difficult to control the spatial dispersion of light. In non-standard conditions, in particular, when there is a lot of dust, reflector lamps are used. In this case, the internal area of the bulb is not completely covered by the diffuse reflective layer, but only two-thirds of it.
100% of the internal surface is covered with phosphor. The part of the bulb that does not have a reflective coating transmits a luminous flux much greater than the tube of a conventional lamp of the same volume - about 75%. You can recognize such lamps by their markings - they include the letter “P”.
In some cases, the main characteristic of LL is Colorful temperature TC.It is equated to the temperature of a black body producing the same color. According to their outlines, LLs can be linear, U-shaped, W-shaped, or circular. The designation of such lamps includes the corresponding letter.
The most popular devices have a power of 15 - 80 W. With a light output of 45 – 80 lm/W, LL combustion lasts at least 10,000 hours. The quality of LL work is greatly influenced by the environment. The operating temperature for them is considered to be from 18 to 25⁰.
With deviations, both the luminous flux and the efficiency of light output and the ignition voltage decrease. At low temperatures, the chance of ignition approaches zero.
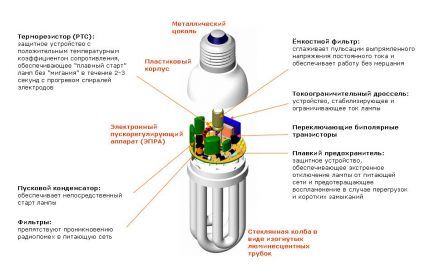
Low-pressure lamps also include compact fluorescent lamps - CFLs.
Their design is similar to conventional LLs:
- High voltage passes between the electrodes.
- Mercury vapor ignites.
- An ultraviolet glow appears.
The phosphor inside the tube makes ultraviolet rays invisible to human vision. Only visible glow becomes available. The compact design of the device became possible after changing the composition of the phosphor. CFLs, like conventional FLs, have different powers, but the performance of the former is much lower.
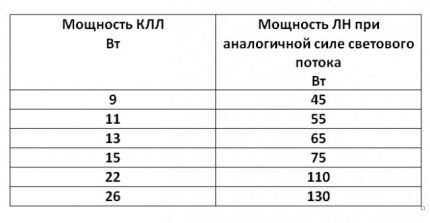
Color temperature is measured in Kelvin. A value of 2700 – 3300 K indicates a warm yellow color. 4200 – 5400 – regular white, 6000 – 6500 – cold white with blue, 25000 – lilac.Color adjustment is carried out by changing the components of the phosphor.
The color rendering index characterizes such a parameter as the identity of the naturalness of color with a standard that is as close as possible to the sun. Absolutely black - 0 Ra, the largest value - 100 Ra. CFL lighting fixtures range from 60 to 98 Ra.
Sodium lamps belonging to the low-pressure group have a high temperature of the maximum cold point - 470 K. A lower one will not be able to maintain the required level of sodium vapor concentration.
The resonant radiation of sodium reaches its peak at a temperature of 540 - 560 K. This value is comparable to the sodium evaporation pressure of 0.5 - 1.2 Pa. The luminous efficiency of lamps in this category is the highest compared to other general-purpose lighting devices.
Positive and negative aspects of GRL
GRLs are found both in professional equipment and in instruments intended for scientific research.
The main advantages of lighting devices of this type are usually called the following characteristics:
- High luminous efficiency. This indicator is not greatly reduced even by thick glass.
- Practicality, expressed in durability, which allows them to be used for street lighting.
- Resistance in difficult climatic conditions. Before the first drop in temperature, they are used with ordinary lampshades, and in winter - with special lanterns and headlights.
- Affordable price.
There are not many disadvantages to these lamps. An unpleasant feature is the rather high level of pulsation of the light flux. The second significant drawback is the complexity of inclusion.For stable combustion and normal operation, they simply need a ballast that limits the voltage to the limits required by the devices.
The third disadvantage is the dependence of combustion parameters on the achieved temperature, which indirectly affects the pressure of the working steam in the flask.
Therefore, most gas-discharge devices achieve standard combustion characteristics after a certain period of time after switching on. Their emitting spectrum is limited, so the color rendition of both high-voltage and low-voltage lamps is imperfect.
The devices can only operate under alternating current conditions. They are activated using a ballast throttle. It takes some time to warm up. Due to the content of mercury vapor, they are not entirely safe.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Information about GL. What is it, how it works, pros and cons in the following video:
Video #2. Popular information about fluorescent lamps:
Despite the emergence of more and more advanced lighting devices, gas-discharge lamps do not lose their relevance. In some areas they are simply irreplaceable. Over time, GRLs will certainly find new areas of application.
Tell us about how you chose a gas-discharge light bulb for installation in a country street or home lamp. Share what was the decisive purchasing factor for you personally. Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions and post photos on the topic of the article.




In our holiday village we have a problem with voltage - at times it drops to 160V. Will gas discharge lamps function normally in this case? I'm going to illuminate the area itself and part of the road.
Good afternoon, Maxim. Before planning lighting, concern the chairman of the holiday village with finding the cause of the voltage drop. The symptoms you cited are typical for phase imbalances. Here, an additional influence will be exerted by the grounding of the transformer zero and the presence of repeated groundings at the supports.
After normal operation of the network is restored, ask the chairman whether you can increase the lighting power in the area. I think your load is limited.