Solid state relay: types, practical application, connection diagrams
Classic starters and contactors are gradually becoming a thing of the past.Their place in automotive electronics, household appliances and industrial automation is occupied by solid-state relays - a semiconductor device that does not have any moving parts.
The devices have different designs and connection diagrams, which determine their scope of application. Before using the device, you need to understand its principle of operation, learn about the features of operation and connection of different types of relays. The answers to the above questions are described in detail in the presented article.
The content of the article:
Solid state relay device
Modern solid-state relays (SSRs) are modular semiconductor devices that act as power electrical switches.
The key operating units of these devices are represented by triacs, thyristors or transistors. SSRs have no moving parts, which makes them different from electromechanical relays.
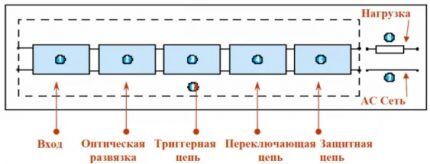
The internals of these devices can vary greatly depending on the type of load being regulated and the electrical circuit.
The simplest solid-state relays include the following components:
- input unit with fuses;
- trigger circuit;
- optical (galvanic) isolation;
- switching unit;
- protective circuits;
- load exit node.
The SSR input node is a primary circuit with a resistor connected in series. A fuse is built into this circuit as an option. The task of the input node is to receive a control signal and transmit a command to the switches switching the load.
With alternating current, galvanic isolation is used to separate the control and main circuits. The principle of operation of the relay largely depends on its design. The trigger circuit responsible for processing the input signal can be included in the optical isolation unit or located separately.
The protective unit prevents overloads and errors from occurring, because if the device breaks down, the connected equipment may also fail.
The main purpose of solid-state relays is to close/open an electrical network using a weak control signal. Unlike electromechanical analogues, they have a more compact shape and do not produce characteristic clicks during operation.
Operating principle of TTP
The operation of a solid state relay is quite simple. Most SSRs are designed to control automation in 20-480 V networks.
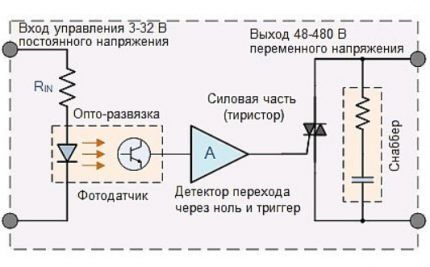
In the classic version, the device body includes two contacts of the switched circuit and two control wires. Their number may change as the number of connected phases increases. Depending on the presence of voltage in the control circuit, the main load is switched on or off by semiconductor elements.
A feature of solid-state relays is the presence of non-infinite resistance.If the contacts in electromechanical devices are completely disconnected, then in solid-state devices the absence of current in the circuit is ensured by the properties of semiconductor materials.
Therefore, at elevated voltages, small leakage currents may appear, which can negatively affect the operation of connected equipment.
Classification of solid state relays
The areas of application of relays are varied, therefore their design features can vary greatly, depending on the needs of a particular automatic circuit. SSRs are classified according to the number of connected phases, type of operating current, design features and type of control circuit.
By number of connected phases
Solid-state relays are used both in household appliances and in industrial automation with an operating voltage of 380 V.
Therefore, these semiconductor devices, depending on the number of phases, are divided into:
- single-phase;
- three-phase.
Single-phase SSRs allow you to work with currents of 10-100 or 100-500 A. They are controlled using an analog signal.
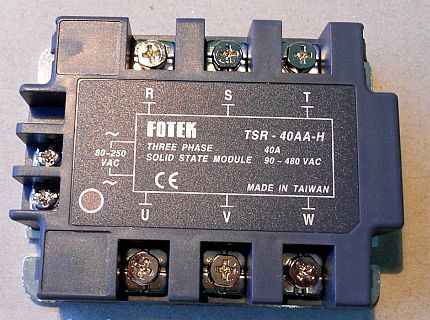
Three Phase Solid State Relays are capable of passing current in the range of 10-120 A. Their device assumes a reversible operating principle, which ensures the reliability of simultaneous regulation of several electrical circuits.
Often three-phase SSRs are used to ensure the operation of an asynchronous motor. Fast fuses must be included in its electrical control circuit due to high inrush currents.
By type of operating current
Solid state relays cannot be configured or reprogrammed, so they can only operate normally within a certain range of network electrical parameters.
Depending on the needs, SSRs can be controlled by electrical circuits with two types of current:
- permanent;
- variables.
Similarly, SSRs can be classified according to the type of active load voltage. Most relays in household appliances operate with variable parameters.

Devices with constant control current are characterized by high reliability and use a voltage of 3-32 V for regulation. They can withstand a wide temperature range (-30..+70°C) without significant changes in characteristics.
AC regulated relays have a control voltage of 3-32 V or 70-280 V. They are characterized by low electromagnetic interference and high operating speed.
By design features
Solid-state relays are often installed in the general electrical panel of an apartment, so many models have a mounting block for mounting on a DIN rail.
In addition, there are special radiators located between the TSR and the supporting surface. They allow you to cool the device under high loads, maintaining its performance characteristics.
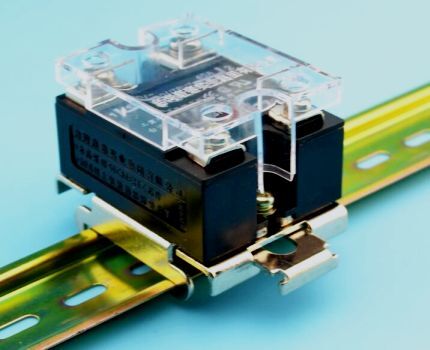
It is recommended to apply a layer of thermal paste between the relay and the radiator, which increases the contact area and increases heat transfer. There are also TTPs designed for fastening to the wall with ordinary screws.
By type of control scheme
The operating principle of an adjustable relay of equipment does not always require its instantaneous operation.
Therefore, manufacturers have developed several SSR control schemes that are used in various fields:
- Control "through zero". This type of solid-state relay control involves operation only at a voltage value of 0. It is used in devices with capacitive, resistive (heaters) and weak inductive (transformers) loads.
- Instant. Used when it is necessary to operate the relay sharply when a control signal is applied.
- Phase. It involves regulating the output voltage by changing the parameters of the control current. Used to smoothly change the degree of heating or lighting.
Solid state relays also differ in many other, less significant, parameters. Therefore, when purchasing a TSR, it is important to understand the operation scheme of the connected equipment in order to purchase the most appropriate control device for it.
A power reserve must be provided, because the relay has an operational life that is quickly consumed with frequent overloads.
Advantages and disadvantages of TTP
Solid state relays are not in vain replacing conventional starters and contactors from the market. These semiconductor devices have many advantages over their electromechanical counterparts, which force consumers to choose them.

These advantages include:
- Low power consumption (90% less).
- Compact dimensions allowing devices to be installed in limited spaces.
- High startup and shutdown speed
- Reduced operating noise, no clicks characteristic of an electromechanical relay.
- No maintenance is expected.
- Long service life thanks to a resource of hundreds of millions of operations.
- Thanks to the wide possibilities for modifying electronic components, TSRs have expanded areas of application.
- No electromagnetic interference during operation.
- Damage to contacts due to mechanical shock is eliminated.
- Lack of direct physical contact between control and switching circuits.
- Possibility of load regulation.
- The presence of automatic circuits in pulsed SSRs that protect against overloads.
- Possibility of use in explosive environments.
The indicated advantages of solid-state relays are not always enough for normal operation of the equipment. That is why they have not yet completely replaced electromechanical contactors.
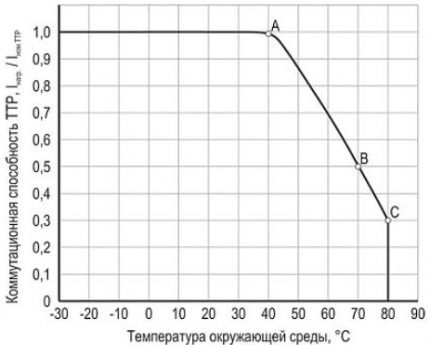
TTPs also have disadvantages that prevent them from being used in many cases.
The disadvantages include:
- Inability to operate most devices with voltages above 0.5 kV.
- High price.
- Sensitivity to high currents, especially in motor starting circuits.
- Restrictions on use in conditions of high humidity.
- Critical decrease in performance characteristics at temperatures below 30°C below zero and above 70°C above 70°C.
- The compact case leads to excessive heating of the device at consistently high loads, which requires the use of special passive or active cooling devices.
- Possibility of melting the device due to heat during a short circuit.
- Microcurrents in the closed state of the relay can be critical to the operation of the equipment. For example, fluorescent lamps connected to the network may flash periodically.
Thus, solid state relays have certain applications. In circuits of high-voltage industrial equipment, their use is sharply limited due to the imperfect physical properties of semiconductor materials.
However, in household appliances and the automotive industry, TTPs occupy a strong position due to their positive properties.
Possible connection diagrams
Connection diagrams for solid-state relays can be very diverse. Each electrical circuit is built based on the characteristics of the connected load. Additional fuses, controllers and regulating devices can be added to the circuit.

The following will present the most simple and common SSR connection diagrams:
- normally open;
- with associated contour;
- normally closed;
- three-phase;
- reversible.
Normally open (open) circuit - a relay in which the load is energized in the presence of a control signal. That is, the connected equipment is turned off when inputs 3 and 4 are de-energized.
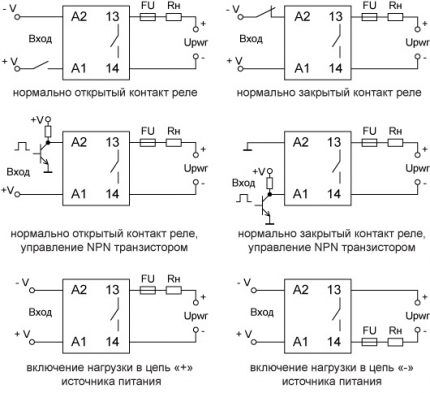
Normally closed circuit — means a relay in which the load is energized in the absence of a control signal. That is, the connected equipment is in working condition when inputs 3 and 4 are de-energized.
There is a connection diagram for a solid-state relay in which the control and load voltages are the same. This method can be used simultaneously to work in DC and AC networks.
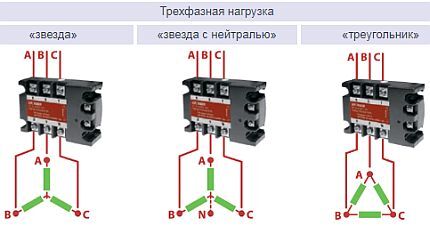
Three-phase relays are connected according to slightly different principles. The contacts can be connected in “Star”, “Triangle” or “Star and Neutral” configurations.
Reversing solid state relays used in electric motors in the appropriate mode. They are manufactured in a three-phase version and include two control circuits.

It is necessary to assemble electrical circuits with SSR only after preliminary drawing them on paper, because incorrectly connected devices may fail due to a short circuit.
Practical application of devices
The scope of use of solid-state relays is quite extensive. Due to their high reliability and lack of need for regular maintenance, they are often installed in hard-to-reach places on equipment.

The main areas of application of TTP are:
- thermoregulation system using heating elements;
- maintaining stable temperatures in technological processes;
- control of transformers;
- lighting adjustment;
- circuits of motion sensors, lighting, photo sensors for street lighting and so on.;
- electric motor control;
- uninterruptible power supplies.
With the increasing automation of household appliances, solid-state relays are becoming increasingly common, and developing semiconductor technologies are constantly opening up new areas of their application.
If desired, you can assemble the solid-state relay yourself. Detailed instructions are provided in this article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The presented videos will help you better understand the operation of solid-state relays and become familiar with how to connect them.
Practical demonstration of the operation of a simple solid-state relay:
Analysis of the types and features of solid-state relays:
Testing the operation and degree of heating of the SSR:
Almost anyone can install an electrical circuit consisting of a solid-state relay and a sensor.
However, planning a working circuit requires basic knowledge of electrical engineering because incorrect connections may result in electric shock or short circuit. But as a result of the right actions, you can get a lot of useful devices in everyday life.
Do you have anything to add, or do you have any questions about connecting and using solid-state relays? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience of using such devices. The contact form is located in the lower block.




And if I have constant voltage drops in my apartment, what should I do? Approximately 180-250 V, what to do and where to go?
In fact, this is a fairly common problem for many areas in cities throughout the post-Soviet space.Since you have an apartment, the problem is relevant not only for you, but perhaps for the entire entrance, house or even area. Therefore, it is best to submit a collective application to eliminate the problem with voltage surges.
Representatives of the company with which you have a contract for the supply of electricity should deal with this problem. Also, for the future, I advise you to use stabilizers and voltage relays, in conjunction, and not separately. The former are effective at low voltage, and the latter at high voltage.