Rotary well drilling: overview of drilling technology and necessary equipment
If a country house cannot be connected to a central water supply, you need to organize an autonomous system.Most owners prefer to build it on the basis of a well, the development of which uses various methods. We will look at rotary well drilling - a very promising, but so far little-known option.
The article we have proposed describes in detail the intricacies of rotary technology and the tools used. The advantages and disadvantages of this technique are analyzed, and ways of its implementation in practice are presented. Our advice will be useful to prudent owners of private plots who want to monitor the work of drillers.
The content of the article:
Definition of Rotary Drilling
First, let's look at what rotary well drilling actually is and what are its alternatives? Auger drilling is still recognized as one of the most common methods of constructing a water intake.
However screw technology does not allow passage of rocky bedrock. The screw drill used in auger drilling is not capable of destroying limestone. But it often happens that you need to drill into it, because... the overlying layers do not have a stable and sufficient flow rate for exploitation.
Therefore, rotary technology, previously used only in the mining industry, began to be introduced into the construction of private water intake structures. Its working element is a bit located in the downhole part of the well. Using a chisel, cohesive and non-cohesive soils are destroyed and bedrock is crushed.
The excavation of destroyed rock is carried out using a liquid that is supplied to the bottom through a working column or annular space. These are 2 different drilling methods, each of which will be discussed in detail below.
The diameter of the bit exceeds the diameter of the working string, which allows:
- reduce energy consumption for the entire drilling process (power is spent directly only on turning the bit with force in the bottom hole, and losses due to friction of the working string against the walls of the well are minimized);
- protect most of the elements of the working string from damage, as well as the walls of the drilled well from destruction;
- create wells of impressive diameter (for example, up to 70 cm) at extremely impressive depths.
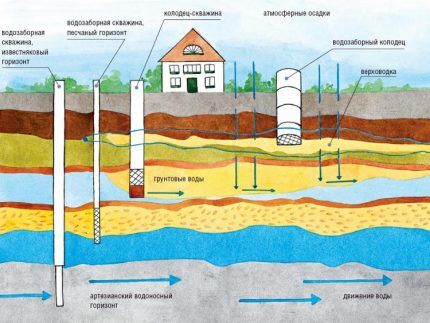
In this way you can form water-bearing wells, depth of 300 meters or more, i.e. drill water intake workings to supply water to dacha areas and villages.
So, the definition: drilling using the rotary principle is a method of developing a well in which the force on the bit in the bottom hole is transmitted from the rotary rotator through the work column. It is assembled from rods - narrow steel pipes that are connected sequentially to each other along a recess into the ground.
But in clearing the mine shaft and face of sludge, water supplied under pressure is used.Thanks to this solution, there is no need to constantly disassemble and reassemble the drill string to extract core, as in core drilling.
The fluid injected into the excavation immediately solves two important problems: it clears the way for the drilling rig to carry out further work and produces well cleaningnecessary to prepare the water intake for operation.
Advantages of rotary technology
What are the advantages of rotary drilling over possible alternatives? There are several of them.
FirstlyUsing a rotary bit, you can create large-diameter wells that can fully satisfy the water needs of several households at once.
It is no secret that drilling is not a cheap process: it requires specialized equipment, and experienced drillers must monitor and manage the process. After all, the activity associated with drilling wells is licensed. Hence its high price.

Uniting several households at once to finance one common well for adjacent plots is an economically profitable enterprise. But this requires a significant debit. In most cases, aquifers of Quaternary sediments (sands) cannot provide them.
Naturally, for collective operation, it is better to install the water intake on limestone. The groundwater extracted from it is characterized by greater water abundance and purity. The volume of precipitation does not have the slightest influence on the flow rate of wells on limestone. The same cannot be said about sand wells.
Secondly, convince by the relatively low energy costs. The working element in rotary drilling is the bit. But unlike the screw and core drilling, the drilling tool does not interact with the walls of the drilled hole
That is, only the bit is in direct contact with the ground, the height of which is negligible in relation to the height of the entire drill string. As a result, this method of forming wells is the fastest - up to 1000 linear meters per month!
Third, collective customers are attracted by the drilling depth. Only with the rotary method can a well be drilled deep into bedrock metamorphic and igneous rocks, from the cracks of which water can be pumped, the composition of which is most suitable for drinking purposes.
Most often, only process water is extracted from water intake workings less than 30 m deep. Its composition is influenced by nearby reservoirs, rivers littered with garbage, precipitation, and simply technical fluids spilled on the ground. An auger and a core pipe will help to obtain only such a water intake.

In addition, rotary drilling allows you to go through the workings to full depth without switching to another drilling method. When developing a well with an auger, for example, if it is necessary to drill through a boulder, they switch to the percussion rope method.
To do this, remove the auger from the barrel and throw the chisel at the face until the boulder is broken. Then slaughter cleared with a bailer. It is also used if it is necessary to raise water-saturated sand to the surface, which simply cannot be retained in the core pipe.
Practice shows that wells drilled using the rotary method have a longer service life. Technologically, this is explained by the fact that after installing the casing that forms the walls of the well, the annulus is further strengthened.
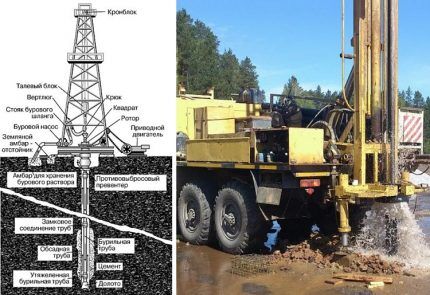
Equipment for well construction
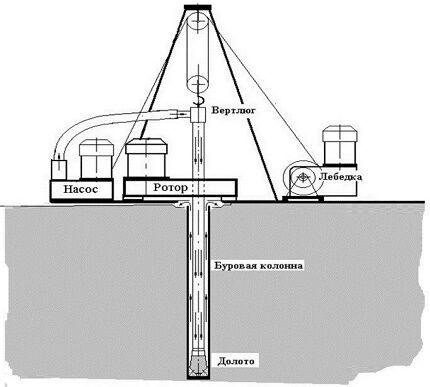
First, a vertical console is installed on the surface above the well for further fastening of the vertical links of the work string. The first link of this drill shaft is equipped with a working element - a bit, which can have different formats, depending on the drillability category of the rock.
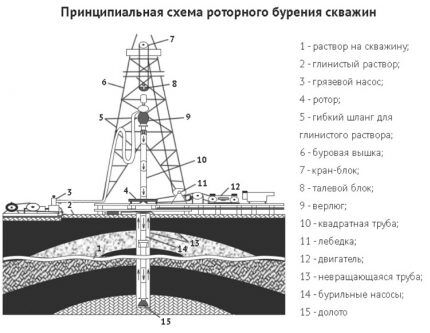
Drilling tool set
When the first link, the candle, is deepened, the next one, called the rod, is placed on it, and so on. The length of each such block of pipes can vary from 20 to 50 m. To simplify the formation of the working column, each rod is equipped with a conical thread with a lock.
As a result, a drilling tool is formed, which consists of:
- working bit;
- drive rod;
- columns of ordinary rods connected to each other by couplings.
The work string is held using a swivel, which is rotated by a rotor. Depending on how deep it is planned to drill, as well as the physical and mechanical properties of the soil, standard or weighted rods are used to form the leading link.
The drive rod is typically a weighted tube because it has an important technological mission. Through it, a washing solution flows into the face to the bit, the task of which is to wash out the crushed rock. And this, in turn, puts forward requirements for coupling connections, the task of which is to seal the connections between the links.
Do not forget that the liquid pressure directly depends on the height of the column being formed (and does not depend on the cross-section of the pipe). Moreover, even if water is used as a flushing solution, then every 10 meters the pressure will increase by 1 atmosphere.
For comparison, it is worth giving an example. The working pressure in the household pipeline network in the house is 10 atmospheres, and the strongest pipes are designed for a pressure of 20 atmospheres.
Only if the domestic systems are stationary and do not move, then a pressure equal to the weight of the drill string is applied to the drive rod. But it must still transmit rotational impulse and force to the bit.

The following requirements are imposed on couplings as structural elements of a drill string:
- must ensure the tightness of the rod connection and withstand fluid pressure of up to 100 atmospheres (for clearing the bottom with a pressure jet);
- must be resistant to wear so as not to become unusable due to friction against the walls of the well;
- must be able to transmit torque from the top of the workstring to the bottom and ultimately to the bit.
It is extremely important that the couplings are of the proper quality. If at least one of them does not withstand the load and the working string is torn, then it will be extremely difficult to get its lower part together with the bit. In terms of capital costs, it is sometimes easier to drill a new well nearby than to remove a detached drive rod.
Use of water during drilling
The liquid that is supplied to the face is most often ordinary water. Sometimes, in order to stabilize a wellbore passing through loose, incoherent rocks (sand, crushed stone, gravel and pebble deposits), a solution with drilling additives is fed into the well. This is necessary, because casing is not installed at the first stages of excavation.
Water enters the excavation either under pressure inside the drive rod (and then pumping occurs through annular space), or by gravity down through annular space, and removal already occurs through the working column with a pump-out pump.
These are 2 different rotary drilling technologies, the features of which will be discussed below.
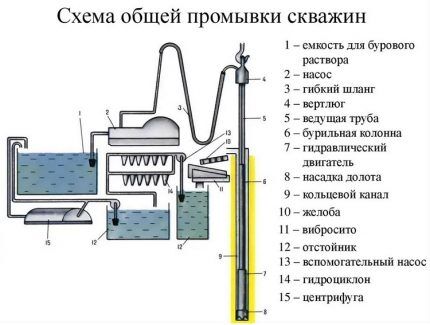
However, no matter what method is used, the fluid used in drilling everywhere needs to be purified (for further use).
For this, the following set of equipment is used:
- Drilling mud storage barn. (If you plan to drill a shallow well, within a few dozen you can build it directly in the ground, and ordinary water is used as a flushing fluid). The barn acts as a battery for the flushing fluid.
- Vibrating sieve. The flushing solution lifted from the well carries particles of crushed rock that need to be removed. The most effective method is mechanical, using a vibrating sieve.
- Sump. After large rock particles are removed, the liquid enters a settling tank to remove suspended particles that precipitate. When using water as a flushing liquid, a sump tank is also sometimes built directly in the ground. In addition, it is used to separate liquid substances and separate sediments. hydrocyclone.
- Mud pump. It is this that ensures the circulation of the washing solution.
- Gutter system. They are needed for the movement of water from the point of formation of the excavation to the place of its purification.
In total, to develop a well using rotary technology, the following mechanisms and equipment are needed:
- Tower or console for assembling a drill string from rods and disassembling it upon completion of drilling, as well as a traveling system.
- Engine, ensuring rotation of the rotor.
- Liquid Equipment. Mechanisms and devices for ensuring circulation of the washing liquid and its cleaning (pump; vibrating sieve; settling tanks and/or hydrocyclone; storage barn for washing liquid; system of pipes and gutters).
For rotary drilling of shallow wells, the entire listed set of equipment is very compact (for example, the console boom is foldable). This ensures ease of placement of drilling equipment in any place convenient for drilling operations and subsequent operation.
Two rotary drilling options
Depending on the method of supplying the drilling fluid to the bottom, there are 2 types of rotary drilling technology:
- with direct feed;
- with reverse feed.
It should be noted that the liquid supplied to the face is intended not only for washing and removing crushed rock. It also cools the bit, which becomes very hot from friction. In the case of direct liquid supply, the pump creates its excess pressure.
Water enters the bottom hole through the technological holes in the bit, “picks up” the crushed rock and then flows by gravity through the well (that is, through annular space in relation to the leading rod) enters the surface, where it enters the cleaning complex (vibrating sieve, hydrocyclone).
The reverse feed technology implies that the flushing fluid flows to the bottom by gravity, descending through the well, but the solution with crushed material flows back to the surface through the drive rod pipe. In this case, the mud pump creates negative pressure in it.
Despite the apparent simplicity of both technologies, there are many more nuances here than might seem at first glance. Therefore, it seems appropriate to dwell on each of these drilling technologies in more detail.
Drilling with direct supply of flushing fluid
This technology is also sometimes called “direct water flow”. It is advisable to use it in sandy, gravel, crushed stone soils. It is also used if the depth of the aquifer does not exceed 30 m. It is here that additives are added to the liquid, which increase its density and stability of the trunk.
Rotary drilling is characterized by a gradual reduction in the diameter of the well being drilled. In other words, the largest diameter well is drilled first, then it settles down pipe, and the annular space between the outer surface of the pipe and the well wall is filled with cement mortar through technological holes.
Then drilling continues with a smaller bit. Then casing again, and the new section has an even smaller diameter, etc. The less often you need to be “distracted” by cementing a well, the greater the drilling productivity, which ultimately translates into the total cost of the process and the well as a whole.
In addition, too frequent casing ultimately leads to the fact that the effective diameter of the well (the diameter that opens the aquifer) is greatly reduced. So, “direct water flow” is characterized by the fact that the well with this method of its formation can not be planted up to 100 meters.
The main pressure of the flushing fluid is created by the pump inside the drive rod, and annular The liquid with elements of crushed rock fills the space by gravity, without destroying the well wall with excess pressure.
However, this drilling method also has disadvantages. In particular, too long uncased This area leads to the introduction of fine clay particles into the aquifers, which can significantly reduce and slow down the flow of water into the workings from the aquifer.
These particles here play the role of peculiar plugs of pores and microchannels in rock through which water seeps.Therefore, the casing procedure performed during the drilling process is necessary to maintain the further productivity of the well as a whole.
Drilling with reverse flow of flushing fluid
With this method of fluid control, the barrel and bottom are cleaned best. The pump here does not press the liquid into the bottom, but, on the contrary, sucks it back, and this leads to the fact that the speed of formation of a well with a bit increases by an order of magnitude and even several times more in comparison with direct flushing.
The well itself is not subject to contamination by clay inclusions with the flow of the supplied flushing fluid. After all, the pump sucks up everything that may be contained in it. By the way, there is no practical sense in additional additives here, so clean water is used as the same flushing liquid.
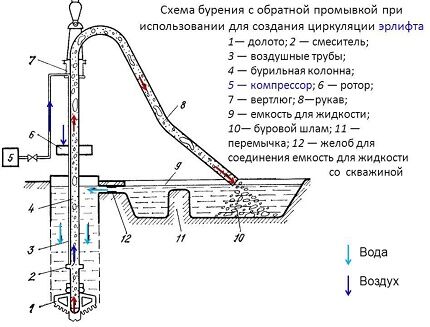
So, let’s summarize the advantages of reverse flow drilling:
- the drilling speed increases (compared to a direct watercourse) up to 15 times;
- the aquifer is not clogged with clay particles and silty grains of sand from the lower, yet open-ended well levels;
- thanks to the high-quality opening of the aquifer, the well does not need to be additionally prepared for operation, you can immediately install the internal casing with a filter and start pumping;
- Simple (and therefore cheap) water is used as a working fluid.
However, this method also has a significant drawback.It requires the use of expensive equipment, which ultimately leads to a significant increase in the cost of the entire drilling process as a whole.
Therefore, “reverse water flow” drilling is carried out only in cases where the well is designed for operation by several households at once. But if the well is designed for individual use, then it is much more reasonable to use rotary drilling technology with direct water flow.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. A visual demonstration of the rotary drilling process step by step:
Video #2. Analysis of rotary technology and principles of well construction:
Video #3. Water circulation during rotary drilling:
The situation with the presence and depth of aquifers can vary greatly from place to place (and in some places there are none at all, like on the island of Madeira).
When designing a well and choosing the optimal rotary drilling method, you should use existing maps of explored aquifers. This will help you save significant money and time.
Tell us about your experience in developing wells using rotary technology. Share technological nuances that will be useful to site visitors. Please leave comments in the block form below, post photos and ask questions about the topic of the article.




You write correctly that the rotary method of drilling a well is quite expensive. This raises the question: is it possible to go through soft layers with something cheaper, for example, an auger, and use the rotor only starting with limestone? Do such manipulations make sense or will it not be possible to save money?
If you are looking for an inexpensive method, I advise you to consider hydrodrilling water wells. A proven method, almost every homeowner will be able to get the necessary equipment. Here's what you'll need for this:
— collapsible metal frame;
— water pump (provides pressure in the system);
— hoses for water supply;
— drill (exploration or flap);
— motor for transmitting force to the drill;
- winch;
— related drilling tools;
— drill rods forming columns;
- Control block;
- swivel for sliding fastening of parts.
In this way you can drill wells up to 30 meters without much experience. For depths below this mark, appropriate practical knowledge is already required.
Drilling into limestone is best done using the percussion-rope method.