How a refrigerator works: structure and operating principle of the main types of refrigerators
A clear understanding of the device and the processes occurring inside the refrigeration unit helps to extend the service life of the equipment. It is not difficult to understand the principle of operation of a refrigerator.In any model, it consists in the formation of a cold environment by absorbing heat in the interior of the object and its subsequent removal outside the device.
You will learn everything about how refrigerators with different operating principles work from the article we presented. We will talk about the features of the device and the operating rules associated with it. Our advice will help protect refrigeration machines from premature breakdowns, and save you from the need for repairs.
The content of the article:
Operating principle of the main types of refrigerators
Refrigeration equipment is used in many fields of activity. You cannot do without it in everyday life and it is impossible to imagine the full-fledged work of production workshops at enterprises, trading floors, and public catering establishments.
Depending on the intended purpose and area of application, there are several main types of devices: absorption, vortex, thermoelectric and compressor.
The compressor type is the most common, so we will look at it in more detail in the next section. Now let's outline the main differences between all 4 designs.
Functioning of absorption technology
In the system of absorption-type installations, two substances circulate - the refrigerant and the absorbent. The functions of the refrigerant are usually performed by ammonia, less often - acetylene, methanol, freon, or lithium bromide solution.
The absorbent is a liquid that has sufficient absorption capacity. This can be sulfuric acid, water, etc.
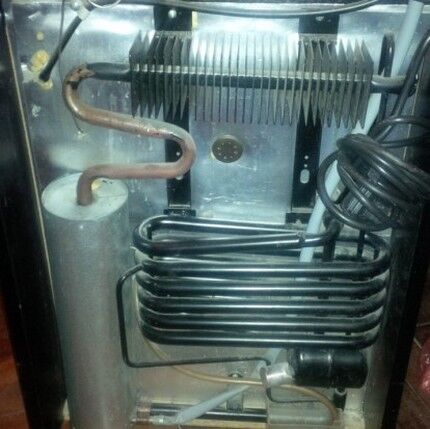

The elements of the system are connected by tubes, with the help of which a single closed circuit is formed. Cooling of the chambers occurs due to thermal energy.
The process is carried out as follows:
- the refrigerant dissolved in the liquid penetrates the evaporator;
- ammonia vapor boiling at 33 degrees is released from the concentrated solution, cooling the object;
- the substance passes into the absorber, where it is again absorbed by the absorbent;
- the pump pumps the solution into a generator heated by a specific heat source;
- the substance boils and the ammonia vapor released goes into the condenser;
- the refrigerant cools and turns into liquid;
- the working fluid passes through the control valve, is compressed and sent to the evaporator.
As a result, ammonia circulating in a closed circuit takes heat from the cooled chamber and enters the evaporator. And it releases it to the external environment while in the capacitor. The loops play continuously.
Since the unit cannot be turned off, it is not very economical and has increased energy consumption. If such equipment fails, it will most likely not be possible to repair it.

There are no bulky moving or rubbing elements in the design of the devices, so they have a low noise level. The devices are relevant for buildings whose electrical network is subject to constant peak loads, and places where there is no constant power supply.
The principle of absorption is implemented in industrial refrigeration units, small refrigerators for cars and office premises. Sometimes it is found in certain household models that run on natural gas.
Operating principle of thermoelectric models
Reducing the temperature in the chamber of a thermoelectric refrigerator is achieved using a special system that pumps out heat according to the Peltier effect. It involves the absorption of heat in the area where two different conductors are connected when an electric current passes through it.
The design of refrigerators consists of cube-shaped thermoelectric elements made of metals. They are combined by one electrical circuit. As current moves from one element to another, heat also moves.
The aluminum plate absorbs it from the internal compartment and then transfers it to the cubic working parts, which in turn redirect it to the stabilizer. There, thanks to a fan, it is thrown out. This is the principle that portable mini refrigerators and bags with a cooling effect.

This equipment is used in camping, in the field of arrangement of cars, yachts and motor boats, and is often installed in cottages and other places where it is possible to provide the device with a 12 V power supply.
Thermoelectric products have a special emergency mechanism that turns them off in the event of overheating of working parts or failure of the ventilation system.
The advantages of this method of operation include high reliability and a fairly low noise level during operation of the devices. Disadvantages include high cost and sensitivity to external temperatures.
Features of equipment on vortex coolers
Devices in this category have a compressor. It compresses the air, which further expands in the installed vortex cooler units. The object cools due to the sudden expansion of compressed air.
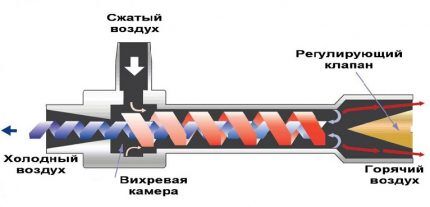
The vortex cooler method was not widely used, but was limited to test samples only. This is due to high air consumption, very noisy operation and relatively low cooling capacity. Sometimes devices are used in industrial enterprises.
Overview of compressor technology
Compressor refrigerators are the most common type of equipment in everyday life. They are found in almost every home - they do not consume too much energy and are safe to use. The most successful models from reliable manufacturers have served their owners for more than 10 years. Let's look at their structure and the principles by which they work.
Features of the internal structure
A classic household refrigerator is a vertically oriented cabinet equipped with one or two doors. Its body is made of rigid sheet steel with a thickness of about 0.6 mm or durable plastic, which reduces the weight of the supporting structure.
For high-quality sealing of the product, a paste with a high content of vinyl chloride resin is used. The surface is primed and covered with high-quality enamel from spray guns. In the production of internal metal compartments, the so-called stamping method is used; plastic cabinets are made using the vacuum molding method.

A layer of thermal insulation must be laid between the inner and outer walls of the product, which protects the chamber from heat trying to penetrate from the environment and prevents the loss of the cold generated inside. Mineral or glass felt, polystyrene foam, and polyurethane foam are well suited for these purposes.
The internal space is traditionally divided into two functional areas: refrigeration and freezing.
According to the shape of the layout, they are distinguished:
- one-;
- two-;
- multi-chamber devices.
Separately allocated Side-by-Side units, including two, three or four cameras.
Single-chamber units are equipped with one door. In the upper part of the equipment there is a freezer compartment with its own door with a folding or opening mechanism, in the lower part there is a refrigeration compartment with height-adjustable shelves.
Lighting equipment with an LED or a regular incandescent lamp is installed in the chambers in order to see what is actually in the refrigerator.

In two-chamber units, the internal cabinets are insulated and each separated by its own door. The location of departments in them can be European or Asian. The first option assumes a lower layout of the freezer, the second - an upper one.
Components of the structure
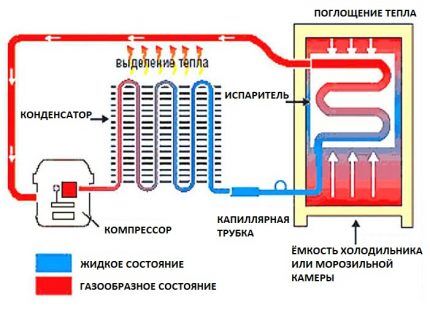
Compressor-type refrigeration units do not produce cold. They cool an object by absorbing internal heat and transferring it out.
The cold formation procedure involves the following components:
- refrigerant;
- capacitor;
- evaporative radiator;
- compressor apparatus;
- thermostatic valve.
The refrigerant used to fill the refrigerator system is played by various brands of freon - mixtures of gases with a high level of fluidity and rather low boiling/evaporation temperatures. The mixture moves in a closed loop, transferring heat through different parts of the cycle.

Compressor - the central part of the design of any refrigerator. This is an inverter or linear unit that provokes forced circulation of gas in the system, increasing pressure. Simply put, refrigerator compressor compresses freon vapors and forces them to move in the desired direction.
The equipment can be equipped with one or two compressors. Vibrations arising during operation are absorbed by external or internal suspension. In models with a pair of compressors, a separate device is responsible for each chamber.
The classification of compressors provides two subtypes:
- Dynamic. Forces the refrigerant to move due to the force of movement of the blades of a centrifugal or axial fan. It has a simple structure, but due to low efficiency and rapid wear under the influence of torque, it is rarely used in household equipment.
- Volume. It compresses the working fluid using a special mechanical device that is driven by an electric motor. It can be piston or rotary. Mostly, these are the compressors installed in refrigerators.
Piston apparatus presented in the form of an electric motor with a vertical shaft, enclosed in a solid metal casing. When the start relay connects power, it activates the crankshaft and the piston attached to it begins to move.
A system of opening and closing valves is connected to the work. As a result, freon vapor is drawn out of the evaporator and pumped into the condenser.

In rotary mechanisms, the required pressure is maintained by two rotors moving towards each other. Freon enters the upper pocket located at the beginning of the shafts, is compressed and exits through the lower hole of a small diameter.To reduce friction, oil is introduced into the space between the shafts.
Capacitors are made in the form of a coil grid, which is mounted on the rear or side wall of the equipment.
They have different designs, but are always responsible for the same task: cooling hot gas vapors to set temperatures by condensing the substance and dissipating heat in the room. They can be panel or ribbed-tubular.

Thermostatic valve needed in order to maintain the pressure of the working fluid at a certain level. Large units of the unit are connected to each other by a system of tubes forming a hermetically sealed closed ring.
Work cycle sequence
The optimal temperature for long-term storage of food in compression devices is created during operating cycles, carried out one after another.
They proceed as follows:
- when the device is connected to the electrical network, the compressor starts, compressing freon vapors, synchronously increasing their pressure and temperature;
- under the force of excess pressure, the hot working fluid, which is in a gaseous aggregate state, enters the condenser tank;
- moving along a long metal tube, the steam releases the accumulated heat into the external environment, smoothly cools to room temperature and turns into liquid;
- the liquid working fluid passes through a filter-drier that absorbs excess moisture;
- the refrigerant penetrates through a narrow capillary tube, at the exit of which its pressure decreases;
- the substance cools and transforms into a gas;
- the cooled steam reaches the evaporator and, passing through its channels, takes away heat from the internal compartments of the refrigeration unit;
- The temperature of the freon rises, and it is again sent to the compressor.
If we talk in simple words about how a compressor refrigerator works, the process looks like this: the compressor distills the refrigerant in a closed circle. Freon, in turn, changes its state of aggregation thanks to special devices, collects heat inside and transfers it outside.
After cooling to the required parameters, the thermostat stops the motor, opening the electrical circuit.
When the temperature in the chambers begins to rise, the contacts close again and the compressor motor is activated protective starting relay. That is why, during operation of the refrigerator, the hum of the motor constantly appears and then subsides again.
Recommendations for use and care
There is nothing complicated in operating the equipment: it operates automatically around the clock. The only thing that needs to be done when you first turn it on and periodically adjust it during operation is to set the optimal temperature regime in specific circumstances.
The desired temperature is set thermostat. In an electromechanical system, values are set by eye or taking into account the recommendations specified in the manufacturer's instructions.In this case, you should take into account the type and quantity of food stored in the refrigerator.
The control knob, as a rule, is a round mechanism with several divisions, or, in more modern and more expensive models, control can be carried out using a touch panel.

Each mark on such a handle corresponds to a certain temperature regime: the larger the division, the lower the temperature. The electronic unit allows you to set the temperature with maximum accuracy up to 1 degree using a rotary controller or buttons.
For example, set the freezer compartment to -14 degrees. All entered parameters will be displayed on the digital display.
To maximize the life of your home refrigerator, you should not only understand its structure, but also properly care for it. Lack of proper maintenance and improper operation can lead to rapid wear of important parts and poor functioning.
You can avoid undesirable consequences by adhering to a number of rules:
- Clean the condenser regularly from dirt, dust and cobwebs in models with an open metal grille on the rear wall. To do this, you need to use a regular slightly damp cloth or a vacuum cleaner with a small attachment.
- Install the equipment correctly. Make sure that the distance between the condenser and the wall of the room is at least 10 cm. This measure will help ensure unhindered circulation of air masses.
- Defrost in a timely manner, preventing the formation of an excessive layer of snow on the walls of the chambers. At the same time, to remove ice crusts, it is forbidden to use knives and other sharp objects, which can easily damage and disable the evaporator.
You also need to take into account that the refrigerator should not be placed next to heating devices or in places where direct contact with sunlight is possible. Excessive influence of external heat has a bad effect on the operation of the main components and the overall performance of the device.

If you plan to transport from place to place, it is best to transport the equipment in a truck with a high van, securing it in a strictly vertical position.
In this way, it is possible to prevent breakdowns and oil leakage from the compressor entering directly into the coolant circulation circuit.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. How the refrigeration unit works:
Video #2. Detailed explanation of the structure of compression refrigerators:
Video #3. Information about the operation of absorption machines:
While refrigeration equipment is working properly, consumers are rarely interested in its design. However, this knowledge should not be neglected. They are very valuable because they allow you to quickly determine the cause of the breakdown and locate the problem area, preventing serious malfunctions.
Please leave comments, post thematic photographs, and ask questions about the topic of the article in the block below. Tell us about how you figured out the structure of your own refrigerator.Share how you applied your knowledge about the design of a refrigeration machine in practice.




Everything is detailed, everything is understandable even for a woman. 🙂 The only question left is regarding no-frost refrigerators: why does ice not form inside them? As I understand it, moisture is being removed from the air, and there will simply be nothing left to make ice from. But apparently, it follows that the electricity consumption of no-frost refrigerators will be much higher than that of a conventional one. How big is this difference?
In fact, the difference is significant. A regular two-chamber refrigerator consumes about 230-250 kW per year, and with No Frost - up to 600 kW. But a lot also depends on the energy saving class.
That's right, there are some nuances of using technology that you don't always know. I used to really like putting hot water in the refrigerator to cool it faster or hot soup, now I know that I was simply ruining the equipment with my own hands. You should never do this. And to cool the water faster, just throw some ice in it from the freezer. For the same reason, you cannot put hot water, tea in the freezer.
I read it and had fun. Solid aphorisms, such as “The regulator knob is a round mechanism with several divisions.” It turns out that the handle is already classified as a mechanism. And in this spirit the entire technical part of the article.
Smiling is good :)
But seriously, we are talking about a temperature control mechanism that works when you turn the knob in one direction or another. I think you understood this yourself, it just seems like you wanted to find fault.Other things are written in a language that is as simplified as possible for the average person; we try not to complicate anything on purpose.