Pressed sawdust for heating: advantages and disadvantages + comparison with traditional solid fuel
Pressed sawdust in the form of briquettes and pellets, which recently appeared on the Russian market, has long been used abroad for heating. Therefore, the production technology has been developed and their positive and negative qualities are known.
For modern, economical stoves and long-burning boilers, the use of this type of fuel is often the best option. But is it worth abandoning traditional solid fuel in favor of compressed fuel? And is sawdust really that good?
We will consider these issues in our article, paying attention to the pros and cons of this type of fuel, its main characteristics in comparison with traditional ones. We will also provide recommendations for use and an example of practical calculation of the required volume of compressed fuel for heating a house.
The content of the article:
The nuances of making and using briquettes
The idea of using sawdust and wood shavings for heating is not new. This type of fuel, along with wood and coal, is often used for combustion in furnaces.
The shape and subtleties of manufacturing pressed fuel
The chemical structure of sawdust and shavings is identical to the tree species from which they were obtained. Typically, birch and conifers such as pine, spruce, larch, fir and cedar are used in woodworking.Less commonly, you can find waste from ash, oak and other “expensive” species.
Loose combustible material has a number of disadvantages:
- Dirt. Scattered sawdust and small wood debris quickly litter the area. Therefore, the area of their use as fuel is often limited to non-residential objects for which cleanliness is not important: fireplaces, greenhouses and various household premises.
- Suspend. When sawdust is stored, the smallest particles rise into the air. The dust they create is harmful to health, as it provokes the development of lung diseases. In addition, a high concentration of flammable substances is explosive and therefore the use of small wood waste without adequate ventilation (which leads to additional costs) is prohibited in industrial facilities.
- Rapid and uneven combustion. When burning sawdust or shavings, it is quite difficult to achieve the planned heat transfer, since it depends on the size of the material, as well as its humidity and tree species.
All these problems can be solved by compressing wood waste into briquettes.

Wood consists of 20-30% lignin, which holds fiber together. When high pressure is created using a press, this natural polymer is released, which quite firmly binds the sawdust placed in the form.
When using industrial equipment for the production of briquettes from sawdust or shavings, creating high pressure in the mold ensures the necessary density and hardness of the structure. When using less powerful homemade devices To give strength to products, binders such as clay or cheap wallpaper glue are added to wood waste.
Features of using sawdust in heating
The chemical composition of firewood and compressed wood waste is the same, but the physical structure is different. This largely determines the specificity of their combustion.
The porosity of briquettes makes them easy to ignite. This allows you to regulate the intensity of heat transfer. Pressed, like dried rotten wood (rotten), can slowly smolder without the risk of complete extinction.

To reduce heat generation when using briquettes, you need to reduce the supply of oxygen - close the inlet.
If necessary, increase the combustion intensity - open the firebox to fresh air. Pressed waste reacts to such changes much faster than firewood.
Comparison of "Eurowood" with conventional solid fuel
The cost of coal, firewood or pressed sawdust used for heating varies depending on the region. Therefore, there is no clear decision on the choice of one type of fuel or another. It is necessary to take into account the current price and conduct an analysis of comparative characteristics.
Specific calorific value of fuel
One of the main indicators of fuel efficiency is its specific calorific value (specific heat of combustion). This parameter determines how much mass fraction of a substance, when burned, will be required to release a certain amount of energy.
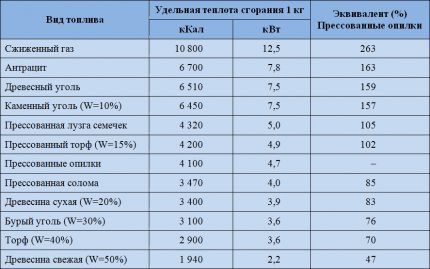
There is one nuance here: calorific value depends on mass, and firewood and sawdust briquettes are usually measured in cubes. When advertising compressed fuel, they often indicate that the energy output is almost twice as high as when burning wood, but they do not indicate the fact that the weight of dry briquettes per cubic meter is greater.
Let’s assume that the calorific value of freshly cut birch is about 2 kcal/kg, and that of briquettes is 4 kcal/kg. The weight of the folded firewood cube is about 570 kg/m3, and the weight of the same volume of pressed material is about 800 kg. Therefore, a cubic meter of raw chopped wood when burned will give about 1.14 mCal, and briquettes - about 3.2 mCal, that is, almost three times more.
The thermal efficiency of industrially produced briquettes can be compared with charcoal or coal, but the latter is much cheaper.
Storage and ease of use
One of the disadvantages of pressed raw materials is its high hygroscopicity. The intense ability to absorb moisture leads to a loss of rigidity between the bound particles and possible crumbling of the briquette. Therefore, unlike coal or firewood, sawdust must be stored in a dry place.
However, in winter, pressed fuel can be kept under an ordinary canopy, since at sub-zero temperatures the absolute air humidity is low. You just need to ensure there is no direct contact with snow.
Fuel briquettes can also be kept indoors. Industrially produced pressed raw materials practically do not produce waste, unlike the same firewood.

Pressed wood requires a minimal amount of ignition material to start burning. Here sawdust, like peat, has no competition.
Application in long-burning boilers
Nowadays they enjoy well-deserved popularity, especially among cottage owners. long burning boilers. They are economical, have high efficiency and are easy to operate. Their only significant disadvantage is the cost of the equipment and the costs of its installation.
Many advanced boiler models are equipped with an automated fuel loading system. For its operation, it is necessary to use a combustible material of uniform shape. For this purpose, pellets are made from sawdust and shavings.

The use of this type of fuel in such boilers allows maintaining the required temperature without human intervention. This allows cottage owners to be away for a long period (up to several days) without the risk of the home cooling to unacceptable levels.
Pros and cons of compressed fuel
Based on the comparative analysis of traditional fuel with compressed fuel discussed above, we can briefly highlight the main advantages and disadvantages of the latter.
So, among the advantages we should highlight:
- ease of use and quick ignition;
- ease of storage and absence of debris such as coal and firewood;
- the ability to use long-burning boilers;
- affordable price.
As for the price, it is really low if there are furniture factories and others working with wood in your area. In this case, it makes sense to spend money on an expensive pellet boiler and use the compressed fuel to heat your home in the future.

Among the disadvantages of sawdust in pressed form are the following:
- you need to allocate a lot of space for storing pellets or briquettes;
- it is necessary to ensure protection of fuel from water ingress;
- high cost for boilers operating on pellets in automatic mode.
Another disadvantage is the need to calculate how much compressed fuel will need to be purchased. At first glance, this task seems difficult if you have never heated with sawdust. But, if you understand the peculiarities of calculations, you can easily calculate fuel consumption. And we looked at how to do this correctly in the next section of our article.
An example of calculating the required volume
Knowing the specific heat of combustion and the efficiency of a furnace or boiler, you can approximately calculate the required mass of fuel for a certain period.
Pressed briquettes are sold either by weight or volume. In the second case, there are some nuances related to the shape of the products. To calculate the required amount of fuel, you need to determine the mass of one cubic meter.

To do this, you need to perform the following sequence of actions:
- It is necessary to know the density of the pressed raw materials (q(g/cm3)).
- It is necessary to calculate the fill factor (k) pressed raw materials of cube volume.
- The mass of one cubic meter (m(kg)) can be calculated using the formula: m = k * q * 103.
Let's give an example of solving a practical problem.
Let’s assume that according to calculations, for heating a cottage in winter it is necessary to receive 6 kcal/h.There are briquettes with a square cross-section with a side of 10 cm and a round technological hole with a diameter of 5 cm. The density of pressed wood waste is 0.95 g/cm3. Calorific value – 4 kcal/kg. Boiler efficiency is 80%. It is necessary to calculate the required purchase volume.
Let's find the cross-section of one briquette (together with the hole) using the formula for calculating the area of a square:
10 * 10 = 100 cm2.
Let's calculate the cross-section of the hole using the formula for the area of a circle:
π * 5 * 5 / 4 = 19.6 cm2.
Let's find the cross-sectional area occupied by sawdust:
100 – 19.6 = 80.4 cm2.
Let's calculate the fill factor:
k = 80.4 / 100 = 0.8.
Let's find the mass of one cubic meter:
m = 0.8 * 0.95 * 1000 = 760 kg.
Let's find the calorific value of one cubic meter taking into account the boiler efficiency:
760 * 4 * 80 / 100 = 2432 kcal.
Let's calculate the required energy for heating for the entire winter period (6 months):
6 * 24 * 30 * 6 = 25920 kcal.
Let's find the required number of cubic meters of briquetted fuel:
25920 / 2432 = 10.7 m3.
If briquettes are sold by weight, then solving the problem is greatly simplified. To determine the sufficient mass of fuel, you just need to divide the required energy by the calorific value of the raw material:
25920 / 4 = 6480 kg.
Some practical tips for use
The chemical composition of industrially produced briquettes is identical to wood.
If pressing was carried out on self-made equipment, then it is problematic to achieve the release of lignin in a volume sufficient to bind sawdust.

In this case, a binder such as clay or cheap wallpaper glue is added to the raw material. This fuel is characterized by high ash content.It should not be used in stoves with winding chimneys, as they are much more likely to be cleanthan when heating with conventional wood and coal.
The bark also has a high ash content. If it was used in the manufacture of compressed fuel, then this can be detected by inclusions of a darker color than the bulk of the shavings or sawdust.
In addition to “Euro firewood” made from sawdust, there are pressed briquettes made from other combustible materials on sale:
- dust from hard and brown coal;
- sunflower seed husks;
- straw;
- peat.
They have different calorific value and ash content. Manufacturers usually provide these data, but it must be understood that they are often obtained under “ideal” conditions.
Very often, firewood is used as a means to create the temperature at which the coal combustion process will begin. Pressed waste burns longer than wood, but less intensely, so their use in conjunction with coal is not justified.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Testing the burning duration of a fuel briquette on a barbecue:
Pressed wood material has a number of properties that allow it to compete with firewood and coal, especially when used in modern, economical boilers.
The choice in favor of one type of fuel or another depends on the current price on the market, as well as on the advantages and disadvantages that each option has.
Do you doubt whether it is worth buying European firewood instead of regular solid fuel? Ask our experts questions indicating the points that concern you - we and other visitors to our site who use compressed fuel for heating their home will try to clarify the controversial issues as much as possible.
If you use sawdust to heat your cottage, please write your opinion on this in the comments block. Tell us how this type of fuel met your expectations, was its purchase profitable for you and your family specifically?




This is an option for the rich. For those who do not want to dirty the house and pretend to be European. Although it is pressed, it is only suitable for lighting the stove. They'll burn out in a flash, how warm it is there! Sawdust is already expensive. Our sawmill over there sells a small bag of uncompressed ones for 40 rubles! Many people take it, but not for the stove. You can throw it under cattle, insulate the ceiling if you don’t have money for something more expensive, and dig in fertilizer for the winter. And for the house it is better to chop birch trees, having agreed with the forester. They burn for a long time.
You are too categorical in your judgments. Different regions have different fuel prices. Of course, nothing compares to gas, but if you can’t connect to it, then pellets are a completely normal option. And it takes a lot of time to chop firewood for proper heating. But besides work, you also need to devote time to your family and to your loved one.
Sergey, you clearly have no information and are writing nonsense... I have a country house of 150 sq.m., 2 floors. Last year I bought coal, selected nuts, a bag of 250 rubles (25-30 kg). 1-1.5 bags were enough for a day, depending on the frost (I live in Siberia).
This year I decided to try RUF fuel briquettes, there are 12 briquettes in a package, I think 1 kg each, at a price of 108 rubles - a package in Leroy. It's -7 outside, one log is enough for lighting, 6 briquettes are needed (I've taken note of the time). The boiler was set at 60 degrees, the temperature reached within 20 minutes.I closed the damper and switched to smoldering mode, threw in the rest of 6 more briquettes, it took about 8 hours. At home +29 +30 (I had to open the windows).
We heat the house once a day even in winter; a long-burning TT boiler is installed. I think that in a simple oven it is not reasonable - it will burn out in one fell swoop. Need an adjustable damper system...
So which + I extracted:
1. Good efficiency.
2. Clean and free of coal soot.
3. You don’t have to pay 40 thousand rubles right away, I drive past Leroy every day, 10 packs - 1080 rubles, this is about a week.
4. And it doesn’t take up much space.
Let's look at the winter, the frosts... these are still experiments, but I would not say that heating with coal is cheaper, at least for us...