Induction heating boilers: types, overview of advantages and disadvantages, how to choose a good model
In the household appliances market, the induction heating boiler remains a novelty, although the popularity of such an innovative solution is rapidly growing. Among electric boilers Induction models account for about 30%. How does this unit differ from its competitors with conventional heating elements or electrodes?
We will tell you everything about the principle of operation and the unique advantages of equipment whose operation is based on the use of induction. In our proposed article, its varieties are presented and described in detail. Our installation tips will help you easily install or upgrade the heating system of a cottage, store or warehouse.
The content of the article:
Features of design and operation
An induction boiler is capable of generating heat and heating rooms thanks to electromagnetic induction. This physical phenomenon was discovered by Faraday during his experiments with a cylindrical magnetic bar, around which copper wire was wound in the form of a spiral.
Induction unit design
A modern induction heating boiler also includes an inductor and a core. When an alternating electric current passes through a coil, an electromagnetic field is generated.
The field generates eddy electric currents that heat the core, the heat from which is transferred to the coolant. The amount of this heat is determined by the Joule-Lenz formula.
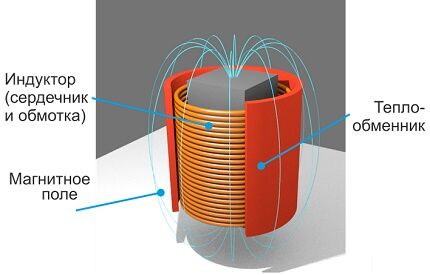
An induction heating boiler consists of two main parts.In one of them, consisting of a coil and a core, a magnetic field is formed. The second part is a heat exchanger with working fluid (coolant).
The coolant function is performed by ordinary water or a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. It is possible to use other liquids, the choice of which depends on the specific boiler model.
The heating system with induction boiler is always switched on closed circuit. The installation diagram also includes a membrane tank, which is necessary to receive excess water that occurs due to its thermal expansion. If such a tank is not included in the package, it must be purchased separately.
Specifics of use in heating circuits
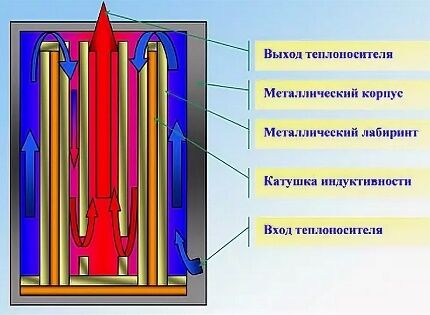
Induction boilers are designed to operate in a forced circulation system. Therefore, the connection diagram must include circulation pump, stimulating the movement of working fluid along the heating circuit.
This need is due to the relatively small volumes of heat exchangers – Due to rapid heating, the water in them boils faster than gravitational circulation occurs.

In multi-circuit systems, circulation pumps are installed on each circuit. If the house has a heated floor system, then the package must include a distribution manifold and an additional pump.
The boiler control system includes, in addition to the thermostat and temperature sensors, the so-called security group, which is designed to prevent overheating, excess pressure and the breaking point of parts.
The safety group usually includes a pressure gauge, air vents and safety valves. Surge protection is implemented using automatic components. Treating individual parts with a compound increases their protection. Thanks to the protection components, safe and uninterrupted operation of the boiler is ensured.

Household induction boilers, depending on the rated power, operate on a voltage of 220 V or 380 V at a current frequency of 50 Hz. To electric boiler connection to the grid, you will need to notify your local power company (electricity supplier) and obtain their approval.
The connection can be single- or three-phase. The wires used to connect the power supply must have the appropriate cross-section.
In an induction device, heating is controlled by cycling it on and off. This process is helped temperature sensors (thermocouple) included in the control system.
The user sets the optimal temperature mode and the boiler, after heating the coolant to a certain temperature, automatically turns off, and after cooling it turns on again.
Thanks to the continuous heating cycle of the coolant, a comfortable microclimate is maintained in heated rooms. In many models, data on temperature and other operating parameters are displayed, which makes it easier to control the operation of the equipment.

Types of induction boilers
All models of induction boilers operate on the same principle, but there are differences in their design. According to this criterion, they are conventionally divided into several types, which will be discussed further.
Casing boilers. The boiler casing has a cylindrical shape. The casing contains an inductor. There is a heat exchanger running both inside and outside the coil.
The working fluid entering the inlet pipe passes through the heat exchanger, heats up and enters the heating circuit through the upper pipe. Boilers casing type in Russia produces NPK «INERA" They are known in the market under the brand SAV.
Boilers with volumetric heat exchangers. This type of boiler is also called inductiveconductive. The unit has a metal body in the form of a cylinder.
The housing contains an induction coil with a ferromagnetic rod, which acts as a heat exchanger. Inductively-conductive boilers on the market are represented by the VIN series. Manufacturer – thermal equipment plant "Alternative Energy".
Boilers with a tubular heat exchanger. Classic induction boilers have a heat exchanger in the form of a set of pipes that go around an inductor coil. The first unit on the market was just such a unit.
Induction boilers with inverters. An induction boiler can be supplemented with an inverter, in which the direct electric current of the batteries is converted into high-frequency alternating current and only then supplied to the inductor.
This solution helps to obtain the necessary eddy currents to generate heat in the absence of mains power.

What do you need to know about installation?
The delivery set of electrical devices includes a technical passport with a detailed description of the characteristics and instructions that indicate the rules of installation and operation. The installation of boilers must be carried out in accordance with the attached manual.
If there are any shortcomings, for example, if the system does not have a pump for forced circulation, the boiler may be removed from warranty service. Therefore, manufacturers recommend engaging experienced plumbers or trained employees of the organization that sold the electrical equipment for installation.
An induction boiler can be built into an existing heating system as either the main one or a backup one when connected in parallel. As for the installation location, you should definitely adhere to the rules that are standard for all electric heating devices.
The heater must be located at least 80 cm from the ceiling and floor. The gap with the wall must be at least 30 cm. Like any powerful power equipment, the induction boiler must be grounded in accordance with GOST 12.2.007.0.

Advantages of induction heating boilers
Induction boilers have many absolute and comparative advantages, including the following:
- highest efficiency among all electric boilers;
- constancy of energy characteristics;
- minimum requirements for coolant;
- increased reliability;
- record long service life;
- ability to work autonomously;
- simple installation without ventilation system;
- automatic control system;
- there is no need for fuel delivery and storage:
- heating the coolant to 95 degrees;
- high level of security.
The device converts electrical energy into thermal energy with an efficiency of 98-99%. It takes 7-10 minutes to heat the coolant. A simple design in which there are no moving mechanical parts, steel alloys used as manufacturing materials make induction boilers record-breakingly durable.
Only damage can disable such equipment. electrical insulation. But as the practice of operating transformers, which in their design are in many ways similar to induction boilers, shows, they can really last for many decades.
According to manufacturers, units operating due to the effect of electromagnetic induction provide uninterrupted heating of rooms for 100 thousand hours, that is, 30 heating seasons. At the same time, their power does not decrease over time, which cannot be said about electrode and conventional heating elements boilers.
The same reasons that determine the durability and increased reliability of induction heaters also reduce operating costs. The induction boiler does not require regular maintenance and repair, which saves money.
Compared to many other fuels, using electricity to heat homes remains the most cost-effective. Especially it concerns non-gasified settlements.
The design of the certified induction boiler prevents short circuits. Manufacturers claim that any model is of the highest class electrical safety. An induction boiler should not be confused with a microwave oven, since it uses a different frequency of electric current to operate.
Heating of the coolant in an induction boiler occurs evenly – The temperature difference in the system is no more than 30°C. That is, there are no local overheats that could lead to fire, which makes such units fireproof.
Thanks to the magnetization of the coolant, fine vibration, invisible to others, and turbulent turbulence, virtually no mineral deposits form in induction boilers, which has a beneficial effect on efficiency. Let us remember that a thick layer of scale slows down the speed and efficiency of heating the coolant.

If you follow the operating rules specified in the instructions, then after installation and setting the temperature regime you will not have to think about the boiler throughout the entire heating season. Unlike solid fuel "brothers", induction appliances do not require regular loading of firewood and coal and removal of ash. No pipe cleaning is required, which distinguishes them from other types electric boilers.
The boiler itself and its additional equipment take up little space and can be installed in a small room. The control system components allow the use of induction boilers in conjunction with other climate control equipment.

Disadvantages of induction models
There are no ideal technical solutions yet. Even the most advanced equipment has its drawbacks, and an induction heating boiler is no exception.
It is characterized by:
- high price;
- heavy weight;
- noise.
In the manufacture of induction boilers, expensive materials are used, including ferromagnets that react to a magnetic field.
In order for the boiler to perform its function, engineers must accurately calculate the diameter of the coil wire, the number of its turns, the size of the core and other parameters. Then all these calculations must be implemented in the finished product.
Thus, the production of induction devices is a labor-intensive and metal-intensive process, which leads to high production costs. At the same time, this drawback is offset by a long service life and minimal operating costs.
The compact dimensions of the boiler are combined with its significant weight, which is explained by the large number of steel parts. Some models weigh 40 kg. The induction boiler makes a slight noise during operation, but this drawback is easily eliminated by sound-absorbing gaskets that are recommended to be installed during installation.
Equipment selection rules
When choosing an induction boiler model, the main criteria are its power and the characteristics of the heated room. They assume that for heating 10 sq. m. with a ceiling height of up to 3 meters, 1 kW is required.
Thus, it is enough to divide the area of the heated room by 10 and as a result the required rated power will be obtained electric boiler. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m. you will need an induction heater of 10 kW.

In order not to overpay for unnecessary power and not to freeze if there is a lack of it, it is necessary to evaluate the specific characteristics of a house or other object, including wall materials, window area, presence of thermal insulation, etc., and based on these data choose heating equipment.
It doesn’t hurt to ask the seller about the power factor, that is, the ratio of active and total power of the selected model. This indicator is called cosine phi (Сos φ) and is measured in volt-amperes. It helps to determine what share of consumed electricity is spent directly on heating the coolant, and what share is spent on generating a magnetic field.
Power factor values range from 0 to 1. Well-designed induction boilers Сos φ is 0.97-0.98 kVA, which is considered an excellent indicator, since almost all the electricity consumed is spent on heating the working fluid.
A variety of models allows you to choose an option for use as a main or backup heat source. Powerful boilers operating on a voltage of 380 V are capable of independently heating large houses, commercial and industrial facilities.
Effective for use in the country house or garage induction boiler you can make it with your own hands. The following article will provide a detailed guide to assembling a useful homemade product.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video will clearly demonstrate the operating principle of the induction unit:
Expert opinion on the safety of using an induction boiler:
Video presentations of induction boilers from ZSTM (Siberian Technological Engineering Plant):
Induction heating boilers have many advantages and competitive advantages with minor or easily eliminated disadvantages. How beneficial this option is for heating a particular house can only be decided by weighing the pros and cons.
An indisputable fact remains the constant growth in demand for such equipment, and this trend is likely to continue in the future.
Would you like to talk about your own experience in choosing, installing, and operating an induction boiler? You have useful information on a topic that is worth sharing with site visitors. Please write comments, post photos, ask questions in the block form below.



